Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) ABCDE 题解 python
| # | Name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A |
standard input/output
1 s, 256 MB |
||
| B |
standard input/output
1 s, 256 MB |
||
| C |
standard input/output
1 s, 256 MB |
||
| D |
standard input/output
2 s, 256 MB |
||
| E |
standard input/output
2 s, 256 MB |
以后cf的题能用python写的我就python了,因为以后没正式比赛参加了,不必特地用C++。python写得快,也容易看得懂,我最近也比较需要练习这个。当然有的题C++写得少我还是用C++。
A. Infinite Sequence
题意:给出a,b,c,求是否a加若干个c能得到b,是就输出YES,否就输出NO
题解:
就特判各种情况,一般情况是看(b-a)%c==0
特殊情况,依次判断:
1.a==b,YES
2.c==0,NO
3.b-a与c不同号,NO
4.c小于零,则把b-a和c都变正数再判。
- def gank(a,b,c):
- d = b - a
- if(d==0):
- return True
- if(c==0):
- return False
- if((d<0 and c>0) or(c<0 and d>0)):
- return False
- if(c<0):
- d*=-1
- c*=-1
- if(d%c==0):
- return True
- else:
- return False
- a,b,c = map(int , raw_input().split(' '))
- if(gank(a,b,c)):
- print "YES"
- else:
- print "NO"
B. Restoring Painting
题意:有个3*3的九宫格,每个格子能填1~n中任意的数(n由输入给出)。要求其中任意2*2的格子中4个数的和与其他各个2*2格子都相等。
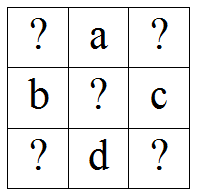
输入n,a,b,c,d,求剩下的数有多少种填法。(可能为0种)
题解:
固定中间的为1,则4种2*2格子的和,要是使得一个相邻的数比较大的角为1,另一个相邻数字比较小的角为n,格子和也没法相等的话,就不行,所以要找2*2格子的最小值和最大值,判断可行性。
比如有这种情况,最大那个角填1,最小那个角最少只能填x,则它们有(n-x+1)种情况(最小的那个角为x,为x+1,直到为n)。
中间那个数其实随便填,不影响,所以最后答案(n-x+1)*n
- def gank(n,A,b,c,d):
- a = [0]*4
- a[0] = A+b
- a[1] = A+c
- a[2] = b+d
- a[3] = c+d
- mi = 1e9
- ma = 0
- for i in range(4):
- ma = max(ma,a[i])
- mi = min(mi,a[i])
- if(1 + 1 + ma > 1+n+mi):
- return 0
- x = ma - mi + 1
- y = n - x + 1
- return y*n
- n,a,b,c,d = map(int , raw_input().split(' '))
- print gank(n,a,b,c,d)
C. Money Transfers
题意:
有一圈银行,瓦夏在各个银行存的钱为a[i](可能为负数,代表借了钱),sum(a[i])==0,瓦夏可以进行一种操作:把一个银行的若干钱转到相邻的银行。求最少多少次操作能把所有银行存款归零。
题解:
这题,难!过D的人都比过C的多,我是不会的,看的题解。
首先考虑,若有一个区间[L,R],使得其中的sum(a[i])==0,则这个区间可以单独转钱就能归零,用的操作数为R-L。如果一个银行为0,它可以单独当一个区间。最后,我们可以得到若干个相邻的区间,总操作数为(n - 区间数)。
所以问题转化为最大化这种区间数。
为了找到和为0的区间,我们算一波前缀和。
当有两个位置的前缀和相同,说明这两个之间的各个元素和为0!
当很多个位置的前缀和相同,说明这些位置分成的各个区间,每个区间和为0。
我们就算一波各个前缀和出现的次数,出现次数最多的那个就是按照最碉的分区间法得到的最多区间数。
- def farm(n, a):
- dic = dict()
- re=0
- sum = 0
- for i in a:
- sum += i
- if not sum in dic:
- dic[sum]=0
- dic[sum]+=1
- re = max(re,dic[sum])
- return n - re
- n = input()
- a = map(int, raw_input().split(' '))
- ans = farm(n, a)
- print ans
D. Tree Construction
题意:给出一个各不相同的序列,插入二叉搜索树中,二叉搜索树不作平衡处理,直接强插,输出除了第一个点之外各个点的父亲的值。
题解:
直接强插,O(n^2),会爆。我不懂,我又看的题解会的。
这个朴素二叉搜索树的特性,是我要插x,那它肯定要成为之前插入过的数中比它小的中最大的数的右儿子 或者 比它大的数中最小的数的左儿子。
所以我们就找用别的平衡树找到这2个数在朴素树中的位置。然后根据性质,肯定只有一个地方能插,我们就插。(可恶,我不懂为什么,对这个树的性质理解不完全)
可以用C++的STL的set和map来当平衡树,我就用C++写了。
- //#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<map>
- #include<set>
- #include<stack>
- #include<queue>
- using namespace std;
- #define MZ(array) memset(array, 0, sizeof(array))
- #define MF1(array) memset(array, -1, sizeof(array))
- #define MINF(array) memset(array, 0x3f, sizeof(array))
- #define REP(i,n) for(i=0;i<(n);i++)
- #define FOR(i,x,n) for(i=(x);i<=(n);i++)
- #define FORD(i,x,y) for(i=(x);i>=(y);i--)
- #define RD(x) scanf("%d",&x)
- #define RD2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
- #define RD3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z)
- #define WN(x) printf("%d\n",x);
- #define RE freopen("D.in","r",stdin)
- #define WE freopen("huzhi.txt","w",stdout)
- #define MP make_pair
- #define PB push_back
- #define PF push_front
- #define PPF pop_front
- #define PPB pop_back
- template<class T>inline void OA(const T &a,const int &st,const int &ed) {
- if(ed>=st)cout<<a[st];
- int i;
- FOR(i,st+,ed)cout<<' '<<a[i];
- puts("");
- }
- typedef long long LL;
- typedef unsigned long long ULL;
- const double PI=acos(-1.0);
- const double EPS=1e-;
- const int MAXN=;
- const int MAXM=;
- struct Node {
- int value;
- Node *son[];
- Node() {}
- Node(int v) {
- value = v;
- son[]=son[]=NULL;
- }
- } root;
- typedef pair<int, Node*> PIN;
- set<PIN> s;
- int n;
- int a[MAXN];
- int ans[MAXN];
- void farm() {
- root = Node(a[]);
- s.clear();
- s.insert(MP(a[], &root));
- int i;
- FOR(i,,n-) {
- set<PIN>::iterator it = s.upper_bound(MP(a[i],(Node*)NULL));
- if(it!=s.end() and it->second->son[]==NULL) {
- (it->second)->son[] = new Node(a[i]);
- s.insert(MP(a[i], it->second->son[]));
- ans[i] = it->second->value;
- } else {
- set<PIN>::iterator it2 = it;
- if(it2!=s.begin())it2--;
- it2->second->son[] = new Node(a[i]);
- s.insert(MP(a[i], it2->second->son[]));
- ans[i] = it2->second->value;
- }
- }
- }
- int main() {
- int i;
- RD(n);
- REP(i,n)RD(a[i]);
- farm();
- OA(ans,,n-);
- return ;
- }
E. Trains and Statistic
题意:有一个一条直线的地铁线路。给出a数组,每个站点i只能买到去往[i+1, a[i]]内的票。设p(i,j)为从i到j所需要的最少票数,求对所有ij的p(i,j)的和。(1=<i<j<=n)
题解:
设f[x]为从站点x到它之后所有站点票数的和。
简单设想,f[x]的值对f[x-1] f[x-2]等等各个值的计算是有用的。
当从一个站点i到不了所有点时,会到它能到的点中a[i]最大的点x。这时就能用到f[x]。
- b[i] = x-i + b[x] + n - a[i]
其中自己能走i+1~x-1点,用x-i票。
x能到x+1~n,用b[x]票。
x能走的那些中,x+1 ~ a[i]是i自己能走的,把x走的当做自己走的,更远的要自己买票走到x,要n - a[i]张票。
综合起来就是上面那个公式。
x能走的肯定比a[i]远,因为a[a[i]]肯定要大于a[i]。
这样,我们要做的就是每次找出区间[i+1, a[i]]中a[x]最大的x。
这可以用各种RMQ方法。不能用单调区间O(1)求,因为这个区间不是纯粹向左移动的,左界是一个个往左,右界是会来回动的。
所以我们可以维护一个只进不出的单调下降队列,然后用二分找。
O(nlogn)
- from collections import deque
- def argmax(q,z):
- l = 0
- r = len(q) - 1
- while(l<=r):
- mid = (l+r)/2
- x = q[mid]['i']
- if(x<=z):
- r = mid - 1
- else:
- l = mid + 1
- return q[l]['i']
- def gank(n,A):
- a = [0]*(n+1)
- a[1:] = A
- b = [0]*(n+1)
- b[n-1] = 1
- q = deque()
- q.append({'i':n-1, 'a':a[n-1]})
- for i in range(n-2, 0, -1):
- if(a[i]>=n):
- b[i] = n-i
- else:
- x = argmax(q,a[i])
- b[i] = x-i + b[x] + n - a[i]
- while(len(q)>0 and q[-1]['a'] < a[i]):
- q.pop()
- q.append({'i':i, 'a':a[i]})
- return sum(b)
- n = int(raw_input())
- a = map(int , raw_input().split(' '))
- print gank(n,a)
Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) ABCDE 题解 python的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #460 (Div. 2) ABCDE题解
原文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/8397685.html 2018-02-01 $A$ 题意概括 你要买$m$斤水果,现在有$n$个超市让你选择. ...
- Codeforces Round #546 (Div. 2) ABCDE 题解
1136A: 题意:一本书有n个章节,每个章节的分别在li到ri页,小明读完书后将书折在第k页,问还有多少章节没有读 题解:控制k在li~ri的范围内后输出n-i即可 #include <set ...
- Codeforces Round #261 (Div. 2)[ABCDE]
Codeforces Round #261 (Div. 2)[ABCDE] ACM 题目地址:Codeforces Round #261 (Div. 2) A - Pashmak and Garden ...
- # Codeforces Round #529(Div.3)个人题解
Codeforces Round #529(Div.3)个人题解 前言: 闲来无事补了前天的cf,想着最近刷题有点点怠惰,就直接一场cf一场cf的刷算了,以后的题解也都会以每场的形式写出来 A. Re ...
- Codeforces Round #557 (Div. 1) 简要题解
Codeforces Round #557 (Div. 1) 简要题解 codeforces A. Hide and Seek 枚举起始位置\(a\),如果\(a\)未在序列中出现,则对答案有\(2\ ...
- Codeforces Round #540 (Div. 3) 部分题解
Codeforces Round #540 (Div. 3) 题目链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1118 题目太多啦,解释题意都花很多时间...还有事情要做,就选 ...
- Codeforces Round #538 (Div. 2) (A-E题解)
Codeforces Round #538 (Div. 2) 题目链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1114 A. Got Any Grapes? 题意: 有三个人, ...
- Codeforces Round #531 (Div. 3) ABCDEF题解
Codeforces Round #531 (Div. 3) 题目总链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1102 A. Integer Sequence Dividin ...
- Codeforces Round #527 (Div. 3) ABCDEF题解
Codeforces Round #527 (Div. 3) 题解 题目总链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1092 A. Uniform String 题意: 输入 ...
随机推荐
- 编译protobuf的jar文件
1.准备工作 需要到github上下载相应的文件,地址https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases protobuf有很多不同语言的版本,因为我们需要的是ja ...
- JS原型链
JS作为发展了多年了对象语言,支持继承,和完全面向对象语言不同的是,JS依赖原型链来实现对象的继承. 首先JS的对象分两大类,函数对象和普通对象,每个对象均内置__proto__属性,在不人为赋值__ ...
- linux基础知识3_根文件系统详解
文件系统: rootfs:根文件系统 /boot:系统启动相关的文件,如内核.initrd以及grub /dev:设备文件 块设备:随机访问 字符设备:线性访问,按字符为单位 设备号:主设备号(maj ...
- 深入java集合学习2-ArrayList的实现原理
ArrayList概述 类概述 ArrayList是List 接口的大小可变数组的实现.实现了所有可选列表操作,并允许包括 null 在内的所有元素. 每个 ArrayList 实例都有一个容量(ca ...
- [转]Asp.Net Core 简单的使用加密的Cookie保存用户状态
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Joes/p/6023820.html 在以前的Asp.Net中可以用 FormsAuthentication 类的一系列方法来使用加密的Coo ...
- python爬虫学习(11) —— 也写个AC自动机
0. 写在前面 本文记录了一个AC自动机的诞生! 之前看过有人用C++写过AC自动机,也有用C#写的,还有一个用nodejs写的.. C# 逆袭--自制日刷千题的AC自动机攻克HDU OJ HDU 自 ...
- AC日记——二叉堆练习3 codevs 3110
3110 二叉堆练习3 时间限制: 3 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 黄金 Gold 题解 题目描述 Description 给定N(N≤500,000)和N个整 ...
- Nutch搜索引擎(第1期)_ Nutch简介及安装
1.Nutch简介 Nutch是一个由Java实现的,开放源代码(open-source)的web搜索引擎.主要用于收集网页数据,然后对其进行分析,建立索引,以提供相应的接口来对其网页数据进行查询的一 ...
- Windows 下 zip 版的 MySQL 的安装
创建 配置文件 当 MySQL server 启动时,它会在按照下表列出位置的顺序寻找并读取配置文件: File Name Purpose %PROGRAMDATA%\MySQL\MySQL Ser ...
- 2-SAT
n个布尔变量,满足m个如 A为x或B为y的限制 建一个点拆成两个,分别表示选TRUE或FALSE 建立A的!x B的y 的连边 与 A的x B的!y 的连边 每次dfs. 若一个点在之前条件下无论 ...
