elasticSearch6源码分析(8)RepositoriesModule模块
1.RepositoriesModule概述
Sets up classes for Snapshot/Restore
1.1 snapshot概述
A snapshot is a backup taken from a running Elasticsearch cluster. You can take a snapshot of individual indices or of the entire cluster and store it in a repository on a shared filesystem, and there are plugins that support remote repositories on S3, HDFS, Azure, Google Cloud Storage and more. Snapshots are taken incrementally. This means that when creating a snapshot of an index Elasticsearch will avoid copying any data that is already stored in the repository as part of an earlier snapshot of the same index. Therefore it can be efficient to take snapshots of your cluster quite frequently. Snapshots can be restored into a running cluster via the restore API. When restoring an index it is possible to alter the name of the restored index as well as some of its settings, allowing a great deal of flexibility in how the snapshot and restore functionality can be used.
1.2 repository
You must register a snapshot repository before you can perform snapshot and restore operations. We recommend creating a new snapshot repository for each major version. The valid repository settings depend on the repository type. If you register same snapshot repository with multiple clusters, only one cluster should have write access to the repository. All other clusters connected to that repository should set the repository to readonly mode.
实例:备份
PUT /_snapshot/my_backup
{
"type": "fs",
"settings": {
"location": "my_backup_location"
}
}
恢复
POST /_snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1/_restore
删除
DELETE /_snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1
监控
GET /_snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1/_status
2.配置类BlobStoreRepository
protected BlobStoreRepository(RepositoryMetaData metadata, Settings globalSettings, NamedXContentRegistry namedXContentRegistry) {
super(globalSettings);
this.metadata = metadata;
this.namedXContentRegistry = namedXContentRegistry;
snapshotRateLimiter = getRateLimiter(metadata.settings(), "max_snapshot_bytes_per_sec", new ByteSizeValue(40, ByteSizeUnit.MB));
restoreRateLimiter = getRateLimiter(metadata.settings(), "max_restore_bytes_per_sec", new ByteSizeValue(40, ByteSizeUnit.MB));
readOnly = metadata.settings().getAsBoolean("readonly", false);
indexShardSnapshotFormat = new ChecksumBlobStoreFormat<>(SNAPSHOT_CODEC, SNAPSHOT_NAME_FORMAT,
BlobStoreIndexShardSnapshot::fromXContent, namedXContentRegistry, isCompress());
indexShardSnapshotsFormat = new ChecksumBlobStoreFormat<>(SNAPSHOT_INDEX_CODEC, SNAPSHOT_INDEX_NAME_FORMAT,
BlobStoreIndexShardSnapshots::fromXContent, namedXContentRegistry, isCompress());
ByteSizeValue chunkSize = chunkSize();
if (chunkSize != null && chunkSize.getBytes() <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("the chunk size cannot be negative: [" + chunkSize + "]");
}
}
配置类的实现
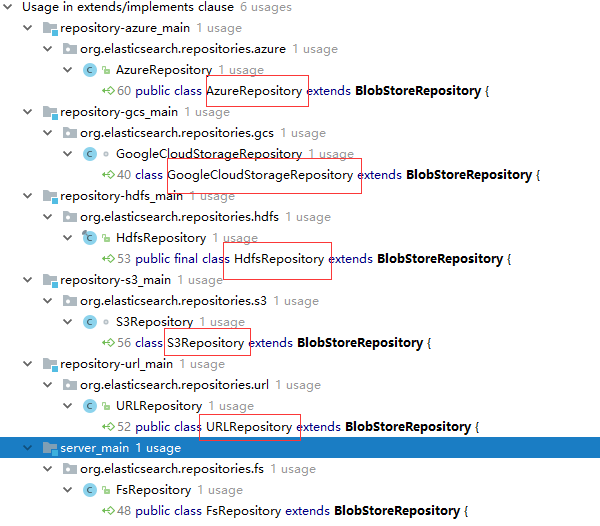
3.重点类
3.1 SnapshotsService
创建snapshot
/**
* Service responsible for creating snapshots
* <p>
* A typical snapshot creating process looks like this:
* <ul>
* <li>On the master node the {@link #createSnapshot(SnapshotRequest, CreateSnapshotListener)} is called and makes sure that no snapshots is currently running
* and registers the new snapshot in cluster state</li>
* <li>When cluster state is updated the {@link #beginSnapshot(ClusterState, SnapshotsInProgress.Entry, boolean, CreateSnapshotListener)} method
* kicks in and initializes the snapshot in the repository and then populates list of shards that needs to be snapshotted in cluster state</li>
* <li>Each data node is watching for these shards and when new shards scheduled for snapshotting appear in the cluster state, data nodes
* start processing them through {@link SnapshotShardsService#processIndexShardSnapshots(ClusterChangedEvent)} method</li>
* <li>Once shard snapshot is created data node updates state of the shard in the cluster state using the {@link SnapshotShardsService#sendSnapshotShardUpdate(Snapshot, ShardId, ShardSnapshotStatus)} method</li>
* <li>When last shard is completed master node in {@link SnapshotShardsService#innerUpdateSnapshotState} method marks the snapshot as completed</li>
* <li>After cluster state is updated, the {@link #endSnapshot(SnapshotsInProgress.Entry)} finalizes snapshot in the repository,
* notifies all {@link #snapshotCompletionListeners} that snapshot is completed, and finally calls {@link #removeSnapshotFromClusterState(Snapshot, SnapshotInfo, Exception)} to remove snapshot from cluster state</li>
* </ul>
*/
3.2 RestoreService
/**
* Service responsible for restoring snapshots
* <p>
* Restore operation is performed in several stages.
* <p>
* First {@link #restoreSnapshot(RestoreRequest, org.elasticsearch.action.ActionListener)}
* method reads information about snapshot and metadata from repository. In update cluster state task it checks restore
* preconditions, restores global state if needed, creates {@link RestoreInProgress} record with list of shards that needs
* to be restored and adds this shard to the routing table using {@link RoutingTable.Builder#addAsRestore(IndexMetaData, SnapshotRecoverySource)}
* method.
* <p>
* Individual shards are getting restored as part of normal recovery process in
* {@link IndexShard#restoreFromRepository(Repository)} )}
* method, which detects that shard should be restored from snapshot rather than recovered from gateway by looking
* at the {@link ShardRouting#recoverySource()} property.
* <p>
* At the end of the successful restore process {@code RestoreService} calls {@link #cleanupRestoreState(ClusterChangedEvent)},
* which removes {@link RestoreInProgress} when all shards are completed. In case of
* restore failure a normal recovery fail-over process kicks in.
*/
elasticSearch6源码分析(8)RepositoriesModule模块的更多相关文章
- elasticSearch6源码分析(5)gateway模块
1.gateway概述 The local gateway module stores the cluster state and shard data across full cluster res ...
- elasticSearch6源码分析(4)indices模块
1.indices概述 The indices module controls index-related settings that are globally managed for all ind ...
- elasticSearch6源码分析(3)cluster模块
1. cluser概述 One of the main roles of the master is to decide which shards to allocate to which nodes ...
- 【转】Spark源码分析之-deploy模块
原文地址:http://jerryshao.me/architecture/2013/04/30/Spark%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90%E4%B9%8B- ...
- ADB 源码分析(一) ——ADB模块简述【转】
ADB源码分析(一)——ADB模块简述 1.Adb 源码路径(system/core/adb). 2.要想很快的了解一个模块的基本情况,最直接的就是查看该模块的Android.mk文件,下面就来看看a ...
- 使用react全家桶制作博客后台管理系统 网站PWA升级 移动端常见问题处理 循序渐进学.Net Core Web Api开发系列【4】:前端访问WebApi [Abp 源码分析]四、模块配置 [Abp 源码分析]三、依赖注入
使用react全家桶制作博客后台管理系统 前面的话 笔者在做一个完整的博客上线项目,包括前台.后台.后端接口和服务器配置.本文将详细介绍使用react全家桶制作的博客后台管理系统 概述 该项目是基 ...
- elasticsearch源码分析之search模块(server端)
elasticsearch源码分析之search模块(server端) 继续接着上一篇的来说啊,当client端将search的请求发送到某一个node之后,剩下的事情就是server端来处理了,具体 ...
- elasticsearch源码分析之search模块(client端)
elasticsearch源码分析之search模块(client端) 注意,我这里所说的都是通过rest api来做的搜索,所以对于接收到请求的节点,我姑且将之称之为client端,其主要的功能我们 ...
- (一) Mybatis源码分析-解析器模块
Mybatis源码分析-解析器模块 原创-转载请说明出处 1. 解析器模块的作用 对XPath进行封装,为mybatis-config.xml配置文件以及映射文件提供支持 为处理动态 SQL 语句中的 ...
随机推荐
- Http TCP/IP协议和socket之间的区别和联系
总结,TCP/IP是传输层协议,主要解决数据如何在网路中传输,socket是TCP/IP协议的具体实现,是对TCP/IP协议的封装和应用,属于程序员层面,HTTP是应用层协议,应用层协议很多,类似的像 ...
- 1.html基础
认识html 1.1 Hyper text markup language 超文本标记语言. 超文本:超链接.(实现页面跳转) Html结构标准 < ! doctype html> ...
- windows下安装ubuntu
在学习linux的过程中,ubuntu无疑是初学者的最佳选择. 下面来列举给Windows系统安装ubuntu双系统的三种方法. 一.虚拟机安装(不推荐) 使用工具:Vmware 如果不是因为迫不得已 ...
- strom ui Topology 可视化视图各个指标含义说明
In the visualization, spout components are represented as blue, while bolts are colored between gree ...
- bootstrap基础学习小记(二)排版、列表、代码风格、表格
排版——标题.副标题.段落(正文文本).强调内容.粗体.斜体.强调相关的类.文本对齐 <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta ...
- 记录一次错误处理 (xml序列化和反序列化相关)
XML序列化后,反序列化时出现错误 报错现象 System.InvalidOperationException: XML 文档(40, 11)中有错误. ---> System.Xml.XmlE ...
- devexpress gridview 添加按钮
#region 添加按钮事件 private RepositoryItemButtonEdit CreateRepositoryItemButtonEdit(Dictionary<object, ...
- 5. ASP.NET MVC 中的Areas【区域】是什么
[PS返回上一篇:-->4.ASP.NET MVC 5.0 视图之模型绑定] 从ASP.NET MVC 2.0开始,微软就提供了一个新特性:Areas[区域].Areas仅仅是用来将大型程序拆分 ...
- ConcurrentHashMap源码解析(3)
此文已由作者赵计刚授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. 4.get(Object key) 使用方法: map.get("hello"); 源代 ...
- .NET Core 从1.1升级到2.0记录(Cookie中间件踩坑)
.NET Core 2.0 新时代 万众瞩目的.NET Core 2.0终于发布了,原定于9.19的dotnetconf大会的发布时间大大提前了1个月,.NET Core 2.0/.NET Stand ...
