Oracle数据库启动和关闭
在介绍oracle数据库的启动和关闭前,先看一下Oracle的参数文件。
oracle参数文件
1.初始化参数文件
oracle的初始化参数文件分为spfilesid.ora、spfile.ora、initsid.ora,都在oracle database下。
pfile 和 spfile 可以相互生成:
SQL>create pfile from spfile //通过spfile文件中创建pfile文件
添加路径例:
SQL>create pfile='/oradata/oracle/app/oracle/product/12.1.0/dbhome_1/dbs/wind.ora' from spfile;
SQL>create spfile from pfile//通过pfile文件中创建spfile文件
添加路径例:
SQL>create spfile from pfile='/Data/oradata/pfile.ora'
注:使用 spfile 启动后不能在线生成 spfile,ORA-32002: 无法创建已由实例使用的 SPFILE
可以通过当前内存参数生成 pfile 和 spfile(11g 新特性):
SQL>create pfile from memory;
SQL>create spfile from memory;
当oracle启动时,初始化参数文件的加载顺序为:spfilesid.ora、spfile.ora、initsid.ora。
有了 spfile,pfile 一般留做备用,特殊情况也可以使用 pfile 启动,命令如下:
SQL> startup pfile=$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/inittimran.ora
注:如果使用 pfile 启动,设置 scope=spfile 将失败!但可以设置 scope=memory,要修改 pfile 文件,使用文本编辑工具。
怎样知道实例是 通过spfile 还是 pfile 启动的呢?
方法1:
SQL> show parameter spfile
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
spfile string /u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/dbs/spfileprod.ora
//如果 value 有值,说明数据库启动时读的是 spfile
方法2:
查看 v$spparameter(spfile 参数视图)中参数 memory_target 的 isspecified字段值。
如果是 TRUE 说明是 spfile 启动的。
SQL> select name,value,isspecified from v$spparameter where name like 'memory_target';
NAME VALUE ISSPECIFIED
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
memory_target 423624704 TRUE
2.管理文件
OMF用来将一些设置交给oracle系统来完成。
通过设置两个参数 DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST 和 DB_CREATE_ONLINE_LOG_DEST_N
create tablespace test;//出错,因为不知道表空间放在哪里
需要首先执行:
alter system set DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST='路径';
然后再执行:
create tablespace test;
这样才会成功 。
Oracle数据库启动和关闭
要了解Oracle数据库的启动和停止需要先了解“实例”(instance)和“数据库”(database)这两个名词的定义:
- 数据库(Database):物理操作系统文件或磁盘(disk)的集合。
- 实例(Instance):一组Oracle后台进程/线程以及一个共享内存区,这些内存由同一个计算机上运行的线程/进程所共享。
这两个词有时可以互换使用,不过二者的概念完全不同。实例和数据库之间的关系是:数据库可以由多个实例mount和open,而实例可以在任何时间点mount和open一个数据库。
Oracle System Identifier (SID)
SID是Oracle实例在服务器上的唯一名字,在UNIX和Linux机器上,Oracle用SID和Oracle home值来创建共享内存的键值,即SID和Oracle home指定一个实例,SID也是用来定位参数文件。
有了对以上概念的认识,下面来看Oracle数据库的启动和关闭过程。
1、Oracle实例和数据库的启动
启动Oracle数据库的方式有很多种,最简单的启动Oracle数据库的方式就是使用sqlplus执行startup命令。
先来看官方给的图:
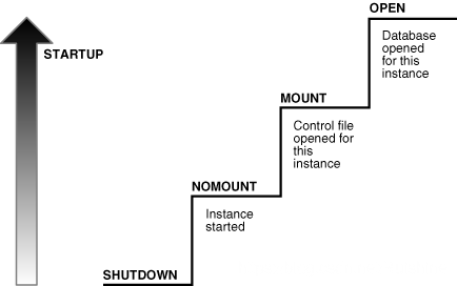
从上图可以看出库Oracle从shutdown状态到open状态经历以下阶段:
1)启动实例,不mount数据库
实例被启动,但还没关联数据库,对应的命令是startup nomount。
- Searches for a server parameter file in a platform-specific default location and, if not found, for a text initialization parameter file (specifying STARTUP with the SPFILE or PFILE parameters overrides the default behavior)
- Reads the parameter file to determine the values of initialization parameters
- Allocates the SGA based on the initialization parameter settings
- Starts the Oracle background processes
- Opens the alert log and trace files and writes all explicit parameter settings to the alert log in valid parameter syntax
该过程可以创建DB和控制文件。可以访问实例、后台进程、SGA,不能访问DB的结构信息(select * from v$database失败 )。
Reading the initialization file from $ORACLE_HOME/dbs in the following order:
从环境变量下dbs目录按如下顺序读取初始化文件:
-first spfileSID.ora
首先,读取spfile+实例名.ora
-if not found then, spfile.ora
若未发现文件则读取spfile.ora
-if not found then, initSID.ora
若未发现文件则读取init+实例名.ora
Specifying the PFILE parameter with STARTUP overrides the default behavior.
指定pfile参数文件启动以替代默认启动方式
* Allocating the SGA
分配SGA
* Starting the background processes
启动后台进程
* Opening the alertSID.log file and the trace files
启动预警日志文件(记录实例生命周期内事件,如系统内部错误、数据块损坏、系统参数修改等)和追踪文件(记录SQL操作及时间消耗等)
The database must be named with the DB_NAME parameter either in the initialization Parameter file or in the STARTUP command.
数据库必须用初始参数文件或启动命令中的DB_NAME参数命名。
2)数据库被mount
实例被启动,打开数据库的控制文件关联一个数据库。数据库对用户还是close状态。对应的命令是alter database mount。
To mount the database, the instance obtains the names of the database control files specified in the CONTROL_FILES initialization parameter and opens the files. Oracle Database reads the control files to find the names of the data files and the online redo log files that it will attempt to access when opening the database.
In a mounted database, the database is closed and accessible only to database administrators. Administrators can keep the database closed while completing specific maintenance operations. However, the database is not available for normal operations.
关联实例与数据库,读取控制文件并获取数据文件和重做日志文件名称状态。可以访问DB的结果信息和内存信息。DB数据不能正常读写。
Mounting a database includes the following tasks:
装载数据库包括以下任务:
* Associating a database with a previously started instance
将先前启动的实例与数据库相关联
* Locating and opening the control files specified in the parameter file
从参数文件中找到控制文件位置并打开
* Reading the control files to obtain the names and status of the data files and online redo log files.However,no checks are performed to verify the existence of the data files and online redo log files at this time.
从控制文件中读取数据文件及重做日志文件名称与状态,但是,此时并不检查数据文件与重做日志文件的存在性。
3)数据库被open
实例被启动,关联的数据库被open。数据库中的数据可以被用户访问。对应的命令是alter database open。
Opens the online data files in tablespaces other than undo tablespaces
If a tablespace was offline when the database was previously shut down (see "Online and Offline Tablespaces"), then the tablespace and its corresponding data files will be offline when the database reopens.Acquires an undo tablespace
If multiple undo tablespaces exists, then the UNDO_TABLESPACE initialization parameter designates the undo tablespace to use. If this parameter is not set, then the first available undo tablespace is chosen.Opens the online redo log files
此阶段,DB数据可正常读写。
opening the database includes the following tasks:
打开数据库包含以下任务:
opening the online data log files
打开数据文件
opening the onling redo log files
打开重做日志文件
If any of the datafiles or noline redo log files are not present when you attempt to open the database ,the oracle server returns an error.
若在打开数据库时数据文件或重做日志文件任何一个不存在,则Oracle服务器返回一个错误。
During this final stage,the oracle server verfies that all the data files and online redo log files can be opened and checks the consistency of the database. If necessary,the SMON background process initiates instance recovery.
在最后阶段,Oracle数据库验证数据文件和重做日志文件可否打开并检验数据库的一致性,若不一致,SMON后台进程将启动实例恢复。
2、Oracle实例和数据库的关闭
通常关闭Oracle数据库使用sqlplus执行shutdown命令
再看官方给的图:
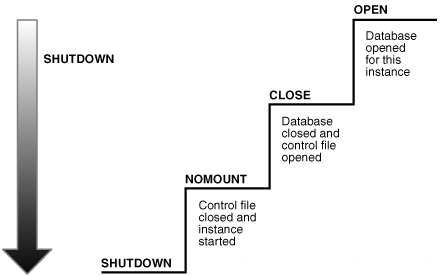
从上图中也可以看出从数据库open状态到shutdown状态也经历三个阶段:
1)数据库被关闭
数据库还是mount状态,但在线数据文件和日志文件被关闭了。
The database close operation is implicit in a database shutdown. The nature of the operation depends on whether the database shutdown is normal or abnormal.
When a database is closed as part of a SHUTDOWN with any option other than ABORT, Oracle Database writes data in the SGA to the data files and online redo log files. Next, the database closes online data files and online redo log files. Any offline data files of offline tablespaces have been closed already. When the database reopens, any tablespace that was offline remains offline.
At this stage, the database is closed and inaccessible for normal operations. The control files remain open after a database is closed.
If a SHUTDOWN ABORT or abnormal termination occurs, then the instance of an open database closes and shuts down the database instantaneously. Oracle Database does not write data in the buffers of the SGA to the data files and redo log files. The subsequent reopening of the database requires instance recovery, which Oracle Database performs automatically.
2)数据库被umount
实例是启动的,但不再通过控制文件关联数据库。
- After the database is closed, Oracle Database unmounts the database to disassociate it from the instance. After a database is unmounted, Oracle Database closes the control files of the database. At this point, the instance remains in memory.
3)实例被shutdown
- The final step in database shutdown is shutting down the instance. When the database instance is shut down, the SGA is removed from memory and the background processes are terminated.
数据库关闭的4种模式:ABORT、IMMEDIATE、TRANSACTIONAL、NORMAL。下面的表格介绍了各模式下数据库的行为。
| Database Behavior | ABORT | IMMEDIATE | TRANSACTIONAL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parmits new user connections | NO | NO | NO |
| Waits until current sessions end | NO | NO | NO |
| Waits until current transations end | NO | NO | Yes |
| Performs a checkpoint and closes open files | NO | Yes | Yes |
- SHUTDOWN ABORT
This mode is intended for emergency situations, such as when no other form of shutdown is successful. This mode of shutdown is the fastest. However, a subsequent open of this database may take substantially longer because instance recovery must be performed to make the data files consistent.
Note:
Because SHUTDOWN ABORT does not checkpoint the open data files, instance recovery is necessary before the database can reopen. The other shutdown modes do not require instance recovery before the database can reopen.
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE
This mode is typically the fastest next to SHUTDOWN ABORT. Oracle Database terminates any executing SQL statements and disconnects users. Active transactions are terminated and uncommitted changes are rolled back.SHUTDOWN TRANSACTIONAL
This mode prevents users from starting new transactions, but waits for all current transactions to complete before shutting down. This mode can take a significant amount of time depending on the nature of the current transactions.SHUTDOWN NORMAL
This is the default mode of shutdown. The database waits for all connected users to disconnect before shutting down.
shutdown或startup状态可执行的操作
shutdown参数
shutdown有四个参数:normal、transactional、immediate、abort,即:
shutdown [normal|transactional|immediate|abort]
前面三种比较安全,abort不推荐。不带参数默认为normal。
shutdown normal:
不断开现在连接用户,阻止任何用户建立新的连接,包括管理员在内。已经连接的用户能够继续他们当前的工作,如递交新的更新事务,直到此用户自行断开连接。这样需要等待的时间长,可以查出现连用户,再通知其自行断开。所有的用户都断开连接,数据库才进行关闭操作,即关闭数据库、卸载数据库、终止例程。在这种情况下关闭的数据库在重新启动后,不会出现问题。启动时不需要实例恢复。
shutdown transactional:
阻止任何用户建立新连接,等待所有当前连接用户的未递交的活动事务提交完毕,然后立即断开用户的连接。所有的用户都断开连接则立即关闭数据库,进行关闭数据库、卸载数据库、终止进程等操作。这种方式,用户有可能正在算账,做复杂报表!一次数据库操作做不完的,在刚做了一次数据库操作后,将被断开,这样对用户有一定影响,启动时不需要实例恢复。
shutdown immediate:
阻止任何用户新的连接,同时限制当前连接用户开始新的事务。如果已连接用户有未完成的事务,则数据库系统不会等待他们完成,而是直接把当前未递交的事务回退。数据库系统不再等待用户主动断开连接,当未递交的事务回退成功后,系统会直接关闭、卸载数据库,并终止数据库进程,启动时不需要实例恢复。
shutdown abort:
当数据库出现故障时,可能以上三种方式都无法正常关闭数据库,则使用这种方法。强制结束当前正在执行的SQL语句,任何未递交的事务都不被回退!这种方法基本上不会对控制文件或者参数文件造成破坏,这比强制关机要好一点(在无法正常关闭数据库的时候),启动时自动进行实例恢复。
startup参数
startup有7个参数:nomount、mount、open、pfile、force、restrict和recover,即:
startup [nomount|mount|open] pfile=... restrict recovery force
其中force是强制启动,而restrict是限制有特权的用户可以访问 。
startup nomount:
通过参数文件,分配sga,启动数据库后台进程,不打开控制文件和数据文件,不能访问数据库。
startup mount:
仅给dba进行管理操作,不允许数据库用户访问。仅当前实例的控制文件被打开,数据文件未打开,在这个模式下可以进行如下操作:重命名数据文件、添加取消或重命名重做日志文件、设置归档模式、设置闪回、执行完整的数据库恢复操作等。
startup open:
startup的默认参数就是open,打开数据库,允许数据库的访问,当前实例控制文件中所描述的所有文件都已经打开。
startup pfile=FILENAME:
以FILENAME为初始化文件启动数据库,不是采用默认初始化文件。
startup force:
中止当前数据库的运行,并开始重新正常的启动数据库。
startup restrict:
只允许具有restricted session权限的用户访问数据库,该模式下登陆者可做如下操作:执行数据库数据的导出或导入、执行数据装载操作用SQL*Loader、暂时阻止一般的用户使用数据、在某个移植过程和升级操作过程中restricted session登陆后可使用ALTER SYSTEM 语句来禁止RESTRICTED SESSION特性ALTER SYSTEM DISABLE RESTRICTED SESSION;如果是在非受限模式下打开的数据库,后来发现需要限制访问,此时可以使用带ENABLE RESTRICTED SESSION 子句的ALTER SYSTEM 语句来完成。
startup recover:
数据库启动,并开始介质恢复。
实例演示
下面通过实例演示Oracle数据库的启动和关闭过程,例子中Oracle版本为11.2.0.4.0
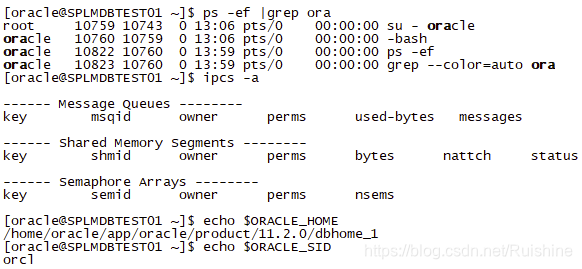
1、启动数据库
- 当前没有任何进程和共享内存,设置好ORACLE_SID和ORACLE_HOME环境变量
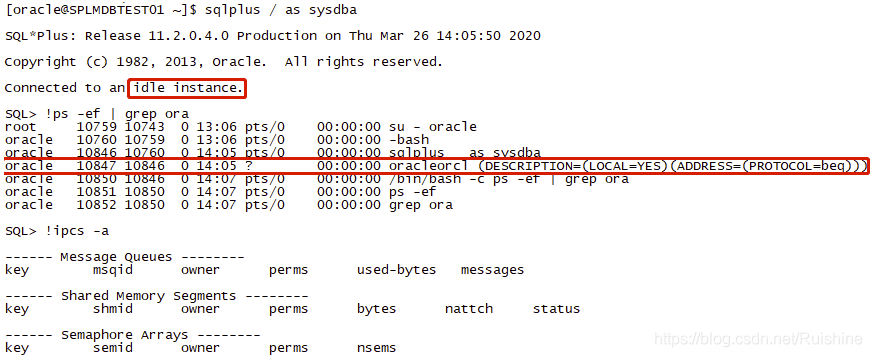
- 执行sqlplus / as sysdba连接到一个空实例,当前仍然没有共享内存,只增加了一个进程oracleorcl的进程
- 使用startup nomount启动数据库实例,该命令默认查找spfile参数文件启动实例,也可以使用startup nomount pfile='/dir/init.ora'指定参数文件启动,在内存中分配共享内存并创建后台进程。
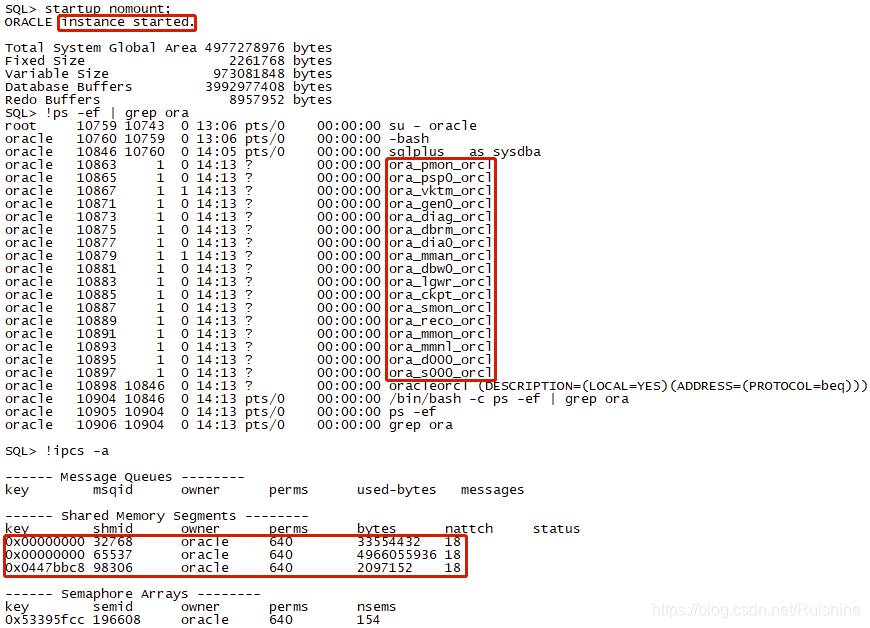
- 查看当前的实例状态,当前状态只能查少量的视图如v$instance,但大部分视图无法查询如v$database、v$datafile,会报错:ORA-01507: database not mounted
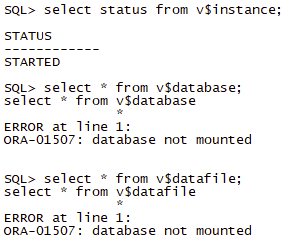
- 使用alter database mount命令mount数据库,这种状态只能查询部分视图,dba开头的大部分视图都不能查询会报错:ORA-01219: database not open: queries allowed on fixed tables/views only
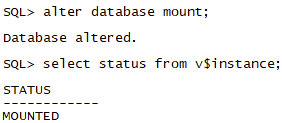
- 使用alter database open命令open数据库
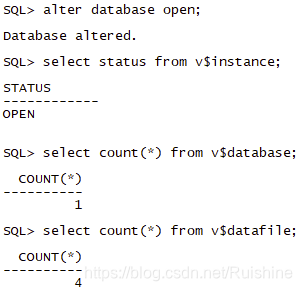
- 当前数据库被打开,可以对外提供服务。
此时pl/sql连接数据库仍然报错
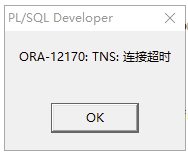
此时需检查防火墙和监听的状态。
防火墙
防火墙状态查看:
# filewall-cmd --state
若防火墙处于running状态,执行如下命令关闭防火墙:
# systemctl stop filewalld.service
监听
监听状态查看
$ lsnrctl status
启动监听服务
$ lsnrctl start
此时pl/sql可成功连接数据库了。
2、关闭数据库
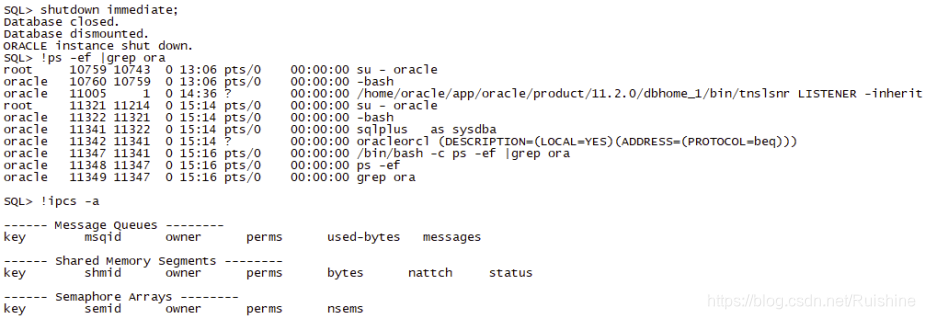
整个启动和关闭的过程都会记录在alert日志文件中。11g的alert日志目录是$ORACLE_BASE/......。
如:/home/oracle/app/oracle/diag/rdbms/orcl/orcl/alert
Oracle数据库状态查询
| 启动状态 | SQL语句 | 结果 |
| nomount | ||
|---|---|---|
| select status from v$instance; | STARTED | |
| select open_mode from v$database; | ERROR at line 1:ORA-01507: database not mounted | |
| mount | ||
| select status from v$instance; | MOUNTED | |
| select open_mode from v$database; | MOUNTED | |
| open | ||
| select status from v$instance; | OPEN | |
| select open_mode from v$database; | READ WRITE 或者 READ ONLY |
参考文章:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33843608
https://www.cnblogs.com/diyunpeng/p/8051741.html
Oracle数据库启动和关闭的更多相关文章
- Oracle 数据库启动与关闭 各种方式详解整理
概述 只有具备sysdba和sysoper系统特权的用户才能启动和关闭数据库. 在启动数据库之前应该启动监听程序,否则就不能利用命令方式来管理数据库,包括启动和关闭数据库. 虽然数据库正常运行,但如果 ...
- Oracle 数据库启动与关闭
只有具备sysdba和sysoper系统特权的用户才能启动和关闭数据库. 在启动数据库之前应该启动监听程序,否则就不能利用命令方式来管理数据库,包括启动和关闭数据库. 虽然数据库正常运行,但如果没有启 ...
- Linux 中 Oracle 数据库启动和关闭
有时候你需要重启Linux 上的 Oracle 数据库. 注意先启动数据库,然后在启动数据库监听. a.切换为 oracle 用户身份,也可以使用 su - 将 home 和 path 都切换到 or ...
- oracle数据库--启动和关闭
oracle--启动 oracle数据库的启动过程包含3个步骤:启动实例->加载数据库->打开数据库 分步骤启动过程可以对数据库进行不同的维护操作,对应我们不同的需求. 启动模式: 1.s ...
- oracle数据库启动和关闭方式
Oracle数据库是重量级的,其管理非常复杂,将其在Linux平台上的启动和关闭步骤整理一下. 安装完毕oracle以后,需要创建oracle系统用户,并在/home/oracle下面的.bash_p ...
- Oracle——数据库启动与关闭
本文内容 服务器环境 客户端环境 概述 启动数据库 关闭数据库 补充 参考资料 本文说明 Oracle 数据库的启动和关闭,内容虽然基础,但是在数据库很多操作中都需要,因此,基础而重要,必须深入理解. ...
- Linux下oracle数据库启动和关闭操作
第一步:登陆 root登陆之后切换到oracle用户上,输入 su oracle 第二步:连接 在oracle用户下,输入 sqlplus /nolog 第三步:使用管理员权限 输入 connect ...
- Oracle强制启动和关闭实例
要启动和关闭数据库,必须要以具有Oracle 管理员权限的用户登陆,通常也就是以具有SYSDBA权限的用户登陆.一般我们常用SYS用户以SYSDBA连接来启动和关闭数据库.下面介绍Oracle数据库几 ...
- Oracle的启动与关闭
启动数据库的前提条件: 环境变量定义好($ORACLE_HOME,$ORACLE_SID,$PATH) 能密码文件认证或OS认证(确保能登入sys) 有正确的参数文件(启动数据库需要查找参数文件,默认 ...
随机推荐
- Spring Cloud Alibaba基础教程-Nacos(二)
在Spring Cloud Alibaba基础教程-Nacos(一)当中学习了,如何从 nacos当中 通过Java的方式获取值,以及连接数据库,下面我们开始第二篇的学习 ,如果对你有帮助,方便下次寻 ...
- RabbiMQ重新安装会遇到的错误-SpiritMark
这里只做安装过程中遇到错误的介绍,不喜勿喷,如果对您有帮助右上角关注一下,是对我最大的肯定 重新安装的注意事项: 先卸载RabbitMQ,后卸载Erlang RabbitMQ卸载,选择uninstal ...
- Python机器学习课程:线性回归算法
本文的文字及图片来源于网络,仅供学习.交流使用,不具有任何商业用途,如有问题请及时联系我们以作处理 最基本的机器学习算法必须是具有单个变量的线性回归算法.如今,可用的高级机器学习算法,库和技术如此之多 ...
- EF Core扩展工具记录 批量操作 记录修改删除历史 动态linq
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.UnitOfWork Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore的插件,用于支持存储库,工作单元模式以及支持分布式事务 ...
- 谈谈hive中join下on和where
本文为博客园作者所写: 一寸HUI,个人博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zsql/ 很多人如果先接触mysql的执行顺序(from ->on ->join -&g ...
- Web自动化测试:xpath & CSS Selector定位
Xpath 和 CSS Selector简介 CSS Selector CSS Selector和Xpath都可以用来表示XML文档中的位置.CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)是 ...
- 使用Python实现搜索任意电影资源的磁力链接
对于喜欢电影的人来说各种电影资源必不可少,但每次自己搜索都比较麻烦,索性用python自己写一个自动搜索的脚本. 这里我只分享我的思路,具体如何实现参考代码,要想实现搜索功能先要抓包分析如何发送数据, ...
- 10天,从.Net转Java,并找到月薪2W的工作(二)
辞去.Net工作之后,第一天直接去星巴克学习. 研究如何入门Java,对比学习资料以及安装Ieda. 由于正版太贵,Mac又不容易破解.鼓捣半天,最后结果是,我决定用教育账号申请一年的免费IDEA. ...
- flowable 实现多实例-会签-动态配置人员 参考demo
会签 即多人执行当前任务 设置判断数 通过 例如:设置了是半数通过即可通过当前节点 如果当前是4人那就是2人即通过 如果是6人那就是三人即通过 如果是5人 即三人通过 看各位的判断值是如何书写 这个值 ...
- Spring Cloud Hystrix原理篇(十一)
一.Hystrix处理流程 Hystrix流程图如下: Hystrix整个工作流如下: 构造一个 HystrixCommand或HystrixObservableCommand对象,用于封装请求,并在 ...
