Codeforces 976C Nested Segments
题面:
C. Nested Segments
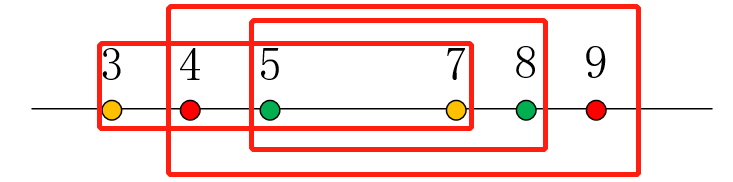
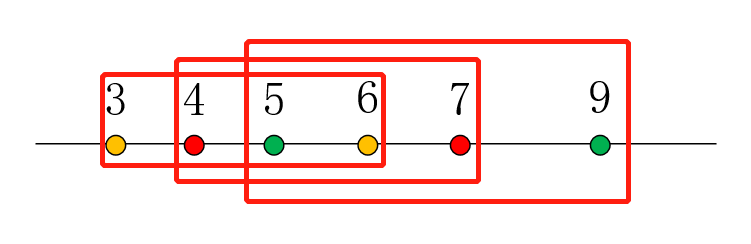
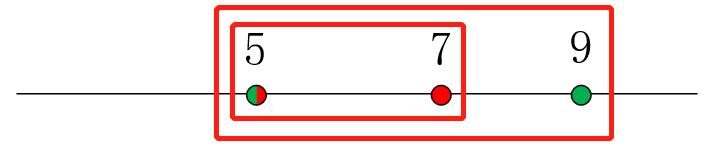
- (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (5, 1) — not even touching borders;
- (3, 2), (4, 2), (3, 5), (4, 5) — touch one border;
- (5, 2), (2, 5) — match exactly.
题目描述:
题目分析:



1 #include <cstdio>
2 #include <cstring>
3 #include <iostream>
4 #include <cmath>
5 #include <set>
6 #include <map>
7 #include <algorithm>
8 #include <utility>
9 using namespace std;
10 const int maxn = 3e5+5;
11 struct node{
12 int l, r; //左右端点
13 int num; //编号
14 };
15 node seg[maxn]; //存放区间
16
17 bool cmp(node a, node b){
18 return a.l < b.l; //使区间按左端点从小到大排序
19 }
20
21 int main(){
22 int n;
23 scanf("%d", &n);
24 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
25 scanf("%d%d", &seg[i].l, &seg[i].r);
26 seg[i].num = i;
27 }
28
29 sort(seg+1, seg+n+1, cmp);
30
31 int max_right = seg[0].r; //最大的右端点
32 int max_i = 0; //最大右端对应区间
33
34 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
35 if(seg[i].r > max_right){
36 if(seg[i].l == seg[i-1].l){
37 cout << seg[i-1].num << " ";
38 cout << seg[i].num << endl;
39 return 0;
40 }
41 else{
42 max_right = seg[i].r; //更新最大右端点
43 max_i = i; //记录位置
44 }
45 }
46 else {
47 cout << seg[i].num << " ";
48 cout << seg[max_i].num << endl;
49 return 0;
50 }
51 }
52 cout << "-1 -1\n";
53 return 0;
54 }
Codeforces 976C Nested Segments的更多相关文章
- [离散化+树状数组]CodeForces - 652D Nested Segments
Nested Segments time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
- codeforces 652D Nested Segments 离散化+树状数组
题意:给你若干个区间,询问每个区间包含几个其它区间 分析:区间范围比较大,然后离散化,按右端点排序,每次更新树状数组中的区间左端点,查询区间和 注:(都是套路) #include<cstdio& ...
- codeforces 652D . Nested Segments 线段树
题目链接 我们将线段按照右端点从小到大排序, 如果相同, 那么按照左端点从大到小排序. 然后对每一个l, 查询之前有多少个l比他大, 答案就是多少.因为之前的r都是比自己的r小的, 如果l还比自己大的 ...
- CodeForces 652D Nested Segments
离散化+树状数组 先对坐标离散化,把每条线段结尾所在点标1, 询问某条线段内有几条线段的时候,只需询问这段区间的和是多少,询问结束之后再把这条线段尾部所在点标为0 #include<cstdio ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 10 D. Nested Segments 离线树状数组 离散化
D. Nested Segments 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/652/problem/D Description You are given n ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 10 D. Nested Segments 【树状数组区间更新 + 离散化 + stl】
任意门:http://codeforces.com/contest/652/problem/D D. Nested Segments time limit per test 2 seconds mem ...
- D - Nested Segments CodeForces - 652D (离散化+树桩数组)
D - Nested Segments CodeForces - 652D You are given n segments on a line. There are no ends of some ...
- codeforces 652D D. Nested Segments(离散化+sort+树状数组)
题目链接: D. Nested Segments time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 10 D. Nested Segments
D. Nested Segments time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
随机推荐
- cin的用法
int val=0; cin>>val; 上述程序先定义了一个整型数据val,通过cin读取数据放在val中,如果输入的整型数据,则读取成功,返回的是>>左侧的对象,也就是is ...
- JavaScript常见笔试题分析
1.Javascript的typeof可能返回的结果有哪些? 答:共6种,具体为number ,boolean,string,undefined,function,object(对象或者null返 ...
- webpack4.0源码解析之打包后js文件分析
首先,init之后创建一个简单的webpack基本的配置,在src目录下创建两个js文件(一个主入口文件和一个非主入口文件)和一个html文件,package.json,webpack.config. ...
- Ubuntu16安装chrome
不免让您失望, 安装正常的chrome,Dependency is not satisfiable: libnss3 (>= 2:3.22)问题一直没能解决,故使用chromium次而代之. s ...
- 技术分享: CSS3 系列
技术分享: CSS3 系列 css 一键换肤 css 打印样式,媒体查询 css 禁用选择 css 性能优化 css 计算单位 css 3D 特效 refs xgqfrms 2012-2020 www ...
- webpack-cli bugs All In One
webpack-cli bugs All In One Error: Cannot find module 'webpack-cli/bin/config-yargs' webpack version ...
- HTML5 Template in Action
HTML5 Template in Action https://developer.mozilla.org/es/docs/Web/HTML/Elemento/template https://de ...
- free online markdown editor
free online markdown editor markdown https://blog.csdn.net/xgqfrms/article/details/50129317 In-brows ...
- Linux shell create file methods
Linux shell create file methods touch, cat, echo, EOF touch $ touch file.py $ touch file1.txt file2. ...
- 视屏剪辑软件 & free video editor
视屏剪辑软件 & free video editor purpose add animation keyframe to tutorials video vlog demos tutorial ...
