图解Janusgraph系列-分布式id生成策略分析
JanusGraph - 分布式id的生成策略
大家好,我是洋仔,JanusGraph图解系列文章,实时更新~
本次更新时间:2020-9-1
文章为作者跟踪源码和查看官方文档整理,如有任何问题,请联系我或在评论区指出,感激不尽!
图数据库网上资源太少,评论区评论 or 私信我,邀你加入“图库交流微信群”,一起交流学习!
源码分析相关:
源码图库-一文搞定janusgraph图数据库的本地源码编译(janusgraph source code compile)
图解图库JanusGraph系列-一文知晓导入数据流程(待发布)
图解图库JanusGraph系列-简要分析查询读数据流程(待发布)
图解图库JanusGraph系列-一文知晓锁机制(本地锁+分布式锁)(待发布)
图解图库JanusGraph系列-一文知晓分布式id生成策略
图解图库JanusGraph系列-一文知晓图库存储分区策略(待发布)
存储结构相关:
图解图库JanusGraph系列-一文知晓图数据底层存储结构
其他:
图解图库JanusGraph系列-官方测试图:诸神之图分析(待发布)
源码分析相关可查看github(求star~~): https://github.com/YYDreamer/janusgraph
下述流程高清大图地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/5f471b2e7d9c086b9903b629
版本:JanusGraph-0.5.2
转载文章请保留以下声明:
作者:洋仔聊编程
微信公众号:匠心Java
正文
在介绍JanusGraph的分布式ID生成策略之前,我们来简单分析一下分布式ID应该满足哪些特征?
- 全局唯一:必须保证ID是分布式环境中全局性唯一的,这是基本要求
- 高性能:高可用低延时,ID生成响应快;否则可能会成为业务瓶颈
- 高可用:提供分布式id的生成的服务要保证高可用,不能随随便便就挂掉了,会对业务产生影响
- 趋势递增:主要看业务场景,类似于图存储中节点的唯一id就尽量保持趋势递增;但是如果类似于电商订单就尽量不要趋势递增,因为趋势递增会被恶意估算出当天的订单量和成交量,泄漏公司信息
- 接入方便:如果是中间件,要秉着拿来即用的设计原则,在系统设计和实现上要尽可能的简单
一:常用分布式id生成策略
当前常用的分布式id的生成策略主要分为以下四种:
- UUID
- 数据库+号段模式(优化:数据库+号段+双buffer)
- 基于Redis实现
- 雪花算法(SnowFlake)
还有一些其他的比如:基于数据库自增id、数据库多主模式等,这些在小并发的情况下可以使用,大并发的情况下就不太ok了
市面上有一些生成分布式id的开源组件,包括滴滴基于数据库+号段实现的TinyID 、百度基于SnowFlake的Uidgenerator、美团支持号段和SnowFlake的Leaf等
那么,在JanusGraph中分布式id的生成是采用的什么方式呢?
二:JanusGraph的分布式id策略
在JanusGraph中,分布式id的生成采用的是数据库+号段+双buffer优化的模式; 下面我们来具体分析一下:
分布式id生成使用的数据库就是JanusGraph当前使用的第三方存储后端,这里我们以使用的存储后端Hbase为例;
JanusGraph分布式id生成所需元数据存储位置:
在Hbase中有column family 列族的概念; JanusGraph在初始化Hbase表时默认创建了9大列族,用于存储不同的数据, 具体看《图解图库JanusGraph系列-一文知晓图数据底层存储结构》;
其中有一个列族janusgraph_ids简写为i这个列族,主要存储的就是JanusGraph分布式id生成所需要的元数据!
JanusGraph的分布式id的组成结构:
// 源码中有一句话体现
/* --- JanusGraphElement id bit format ---
* [ 0 | count | partition | ID padding (if any) ]
*/
主要分为4部分:0、count、partition、ID padding(每个类型是固定值);
其实这4部分的顺序在序列化为二进制数据时,顺序会有所改变;这里只是标明了id的组成部分!
上述部分的partition + count来保证分布式节点的唯一性;
- partition id:分区id值,JanusGraph默认分了32个逻辑分区;节点分到哪个分区采用的是
随机分配; - count:每个partition都有对应的一个count范围:0-2的55次幂;JanusGraph每次拉取一部分的范围作为节点的count取值;JanusGraph保证了针对相同的partition,不会重复获取同一个count值!
保证count在partition维度保持全局唯一性,就保证了生成的最终id的全局唯一性!!
则分布式id的唯一性保证,就在于count基于partition维度的唯一性!下面我们的分析也是着重在count的获取!
JanusGraph分布式id生成的主要逻辑流程如下图所示:(推荐结合源码分析观看!)
分析过程中有一个概念为
id block:指当前获取的号段范围
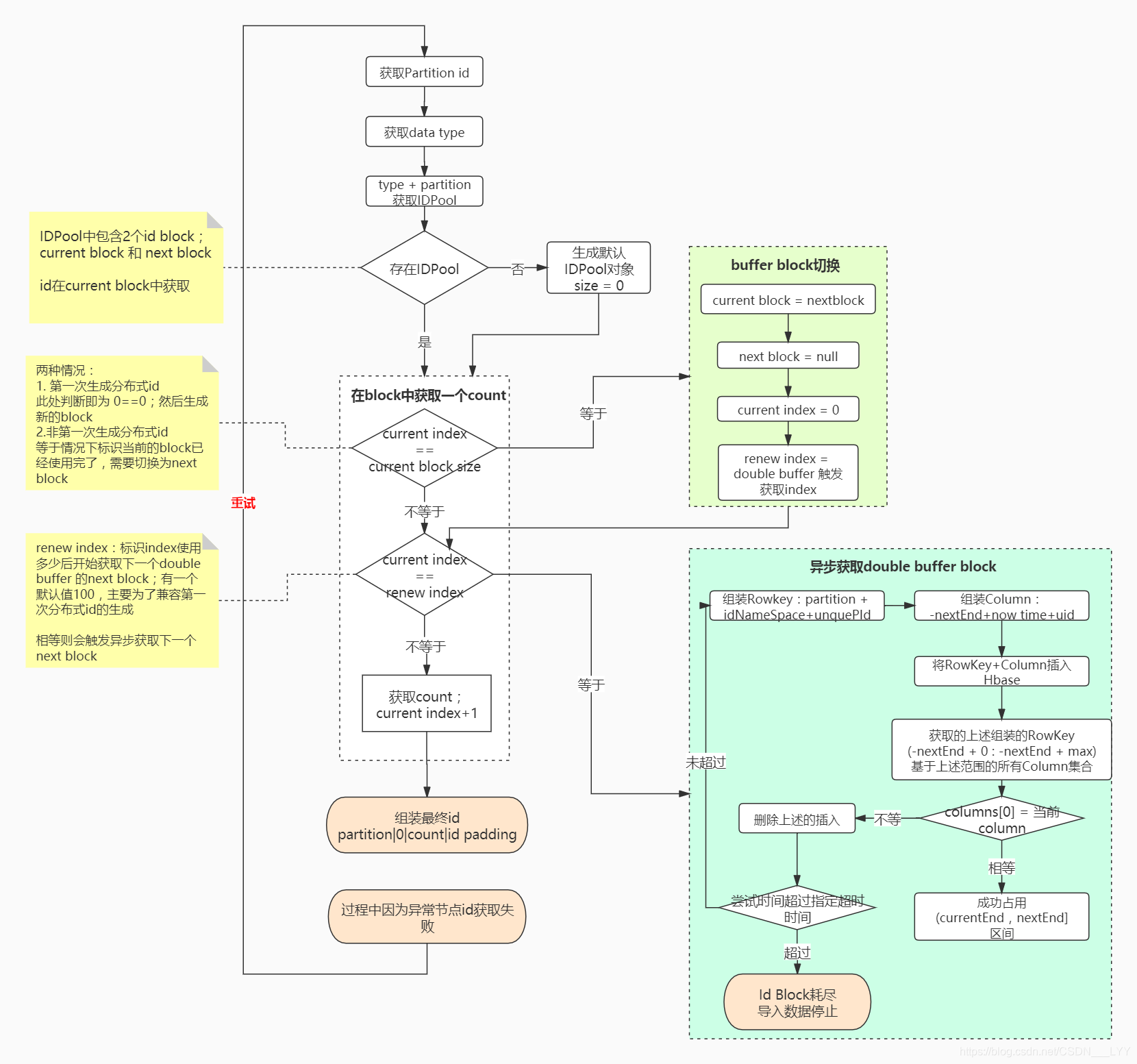
JanusGraph主要使用``PartitionIDPool 类来存储不同类型的StandardIDPool; 在StandardIDPool`中主要包含两个id Block:
- current block:当前生成id使用的block
- next block:double buffer中的另一个已经准备好的block
为什么要有两个block呢?
主要是如果只有一个block的话,当我们在使用完当前的block时,需要阻塞等待区获取下一个block,这样便会导致分布式id生成较长时间的阻塞等待block的获取;
怎么优化上述问题呢? double buffer;
除了当前使用的block,我们再存储一个next block;当正在使用的block假设已经使用了50%,触发next block的异步获取,如上图的蓝色部分所示;
这样当current block使用完成后可以直接无延迟的切换到next block如上图中绿色部分所示;
在执行过程中可能会因为一些异常导致节点id获取失败,则会进行重试;重试次数默认为1000次;
private static final int MAX_PARTITION_RENEW_ATTEMPTS = 1000;
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < MAX_PARTITION_RENEW_ATTEMPTS; attempt++) {
// 获取id的过程
}
ps:上述所说的IDPool和block是基于当前
图实例维度共用的!
三:源码分析
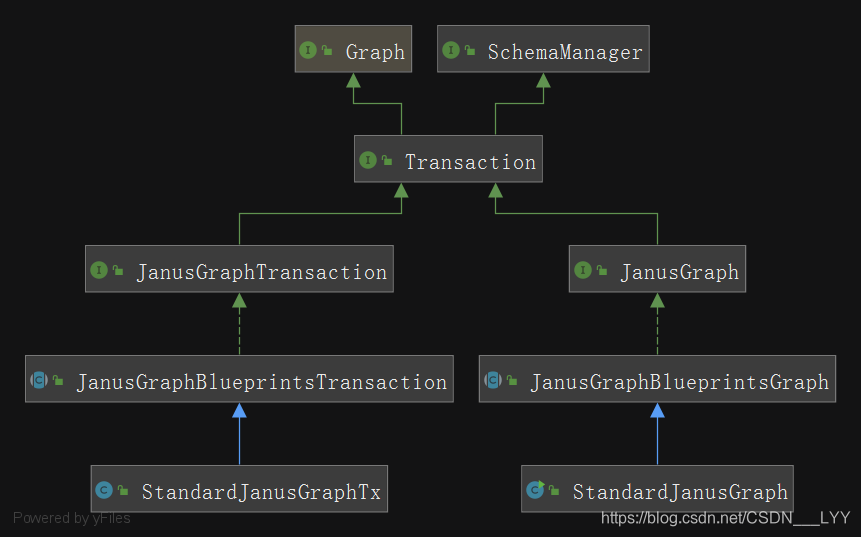
在JanusGraph的源码中,主要包含两大部分和其他的一些组件:
- Graph相关类:用于对节点、属性、边的操作
- Transaction相关类:用于在对数据或者Schema进行CURD时,进行事务处理
- 其他一些:分布式节点id生成类;序列化类;第三方索引操作类等等
Graph和Transaction相关类的类图如下所示:
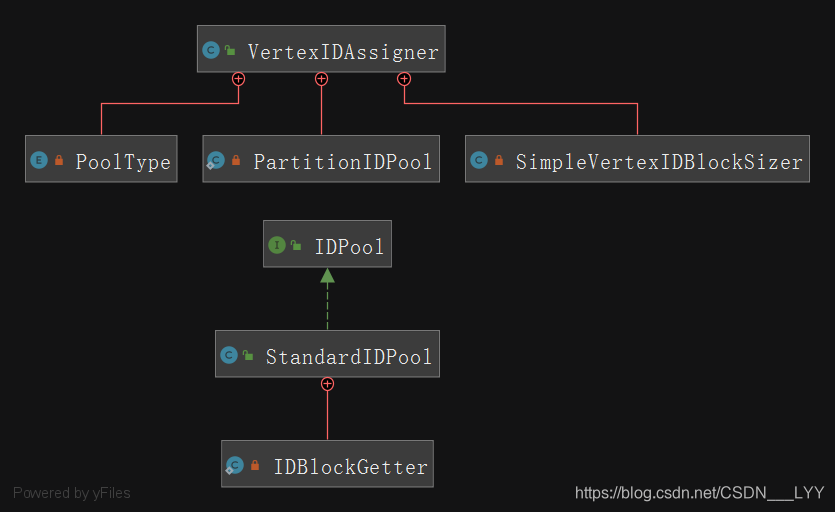
分布式id涉及到id生成的类图如下所示:
初始数据:
@Test
public void addVertexTest(){
List<Object> godProperties = new ArrayList<>();
godProperties.add(T.label);
godProperties.add("god");
godProperties.add("name");
godProperties.add("lyy");
godProperties.add("age");
godProperties.add(18);
JanusGraphVertex godVertex = graph.addVertex(godProperties.toArray());
assertNotNull(godVertex);
}
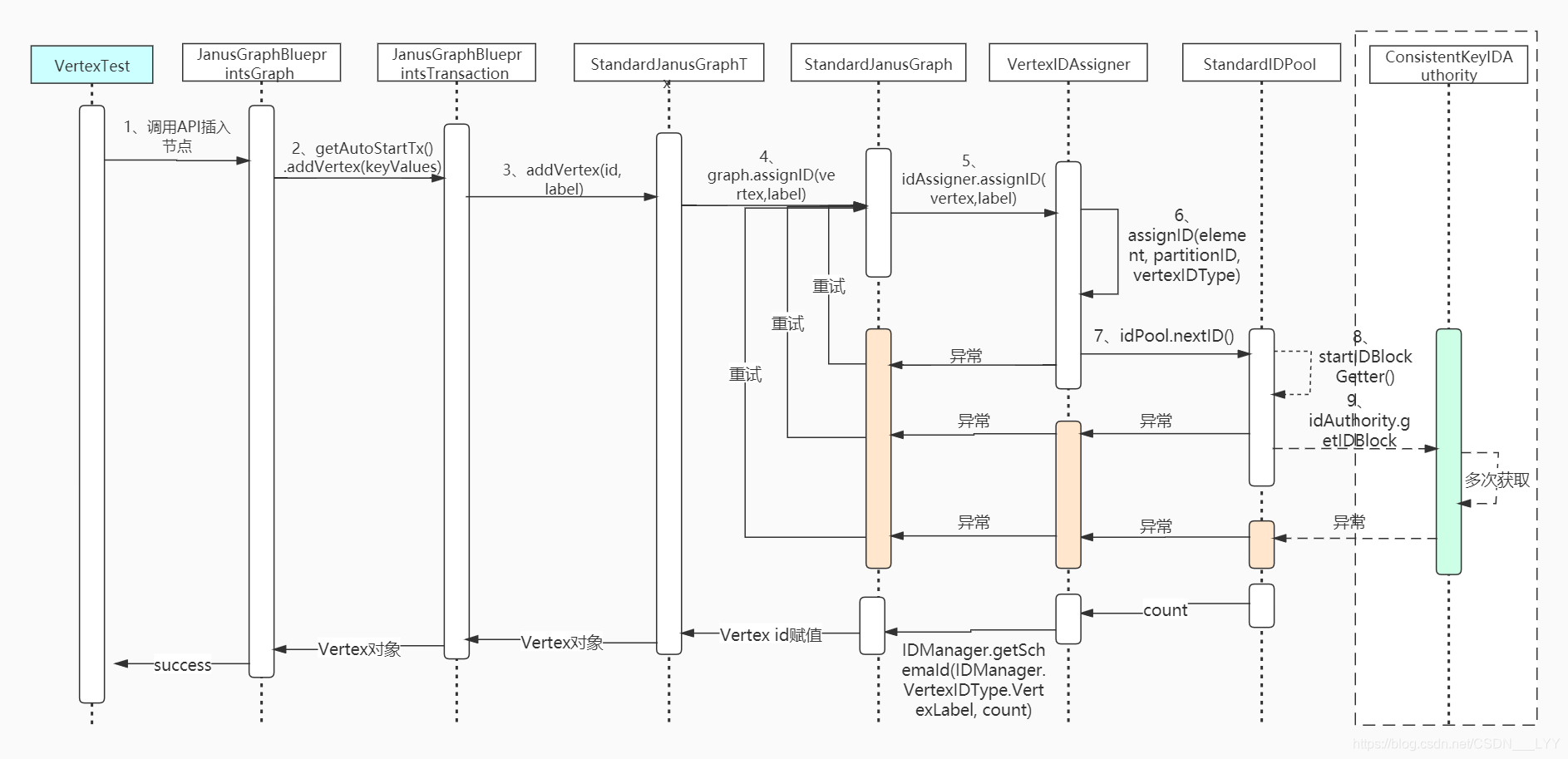
在诸神之图中添加一个name为lyy节点;看下执行流程,注意,此处主要分析的节点的分布式id生成代码!
1、调用JanusGraphBlueprintsGraph类的AddVertex方法
@Override
public JanusGraphVertex addVertex(Object... keyValues) {
// 添加节点
return getAutoStartTx().addVertex(keyValues);
}
2、调用JanusGraphBlueprintsTransaction的addVertex方法
public JanusGraphVertex addVertex(Object... keyValues) {
// 。。。省略了其他的处理
// 该处生成节点对象,包含节点的唯一id生成逻辑
final JanusGraphVertex vertex = addVertex(id, label);
// 。。。省略了其他的处理
return vertex;
}
3、调用StandardJanusGraphTx的addVertex方法
@Override
public JanusGraphVertex addVertex(Long vertexId, VertexLabel label) {
// 。。。省略了其他的处理
if (vertexId != null) {
vertex.setId(vertexId);
} else if (config.hasAssignIDsImmediately() || label.isPartitioned()) {
graph.assignID(vertex,label); // 为节点分配正式的节点id!
}
// 。。。省略了其他的处理
return vertex;
}
4、调用VertexIDAssigner的assignID(InternalElement element, IDManager.VertexIDType vertexIDType)方法
private void assignID(InternalElement element, IDManager.VertexIDType vertexIDType) {
// 开始获取节点分布式唯一id
// 因为一些异常导致获取节点id失败,进行重试,重试此为默认为1000次
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < MAX_PARTITION_RENEW_ATTEMPTS; attempt++) {
// 初始化一个partiiton id
long partitionID = -1;
// 获取一个partition id
// 不同类型的数据,partition id的获取方式也有所不同
if (element instanceof JanusGraphSchemaVertex) {
// 为partition id赋值
}
try {
// 正式分配节点id, 依据partition id 和 节点类型
assignID(element, partitionID, vertexIDType);
} catch (IDPoolExhaustedException e) {
continue; //try again on a different partition
}
assert element.hasId();
// 。。。省略了其他代码
}
}
5、调用了VertexIDAssigner的assignID(final InternalElement element, final long partitionIDl, final IDManager.VertexIDType userVertexIDType)方法
private void assignID(final InternalElement element, final long partitionIDl, final IDManager.VertexIDType userVertexIDType) {
final int partitionID = (int) partitionIDl;
// count为分布式id组成中的一部分,占55个字节
// 分布式id的唯一性保证,就在于`count`基于`partition`维度的唯一性
long count;
if (element instanceof JanusGraphSchemaVertex) { // schema节点处理
Preconditions.checkArgument(partitionID==IDManager.SCHEMA_PARTITION);
count = schemaIdPool.nextID();
} else if (userVertexIDType==IDManager.VertexIDType.PartitionedVertex) { // 配置的热点节点,类似于`makeVertexLabel('product').partition()`的处理
count = partitionVertexIdPool.nextID();
} else { // 普通节点和边类型的处理
// 首先获取当前partition敌营的idPool
PartitionIDPool partitionPool = idPools.get(partitionID);
// 如果当前分区对应的IDPool为空,则创建一个默认的IDPool,默认size = 0
if (partitionPool == null) {
// 在PartitionIDPool中包含多种类型对应的StandardIDPool类型
// StandardIDPool中包含对应的block信息和count信息
partitionPool = new PartitionIDPool(partitionID, idAuthority, idManager, renewTimeoutMS, renewBufferPercentage);
// 缓存下来
idPools.putIfAbsent(partitionID,partitionPool);
// 从缓存中再重新拿出
partitionPool = idPools.get(partitionID);
}
// 确保partitionPool不为空
Preconditions.checkNotNull(partitionPool);
// 判断当前分区的IDPool是否枯竭;已经被用完
if (partitionPool.isExhausted()) {
// 如果被用完,则将该分区id放到对应的缓存中,避免之后获取分区id再获取到该分区id
placementStrategy.exhaustedPartition(partitionID);
// 抛出IDPool异常, 最外层捕获,然后进行重试获取节点id
throw new IDPoolExhaustedException("Exhausted id pool for partition: " + partitionID);
}
// 存储当前类型对应的IDPool,因为partitionPool中保存好几个类型的IDPool
IDPool idPool;
if (element instanceof JanusGraphRelation) {
idPool = partitionPool.getPool(PoolType.RELATION);
} else {
Preconditions.checkArgument(userVertexIDType!=null);
idPool = partitionPool.getPool(PoolType.getPoolTypeFor(userVertexIDType));
}
try {
// 重要!!!! 依据给定的IDPool获取count值!!!!
// 在此语句中设计 block的初始化 和 double buffer block的处理!
count = idPool.nextID();
partitionPool.accessed();
} catch (IDPoolExhaustedException e) { // 如果该IDPool被用完,抛出IDPool异常, 最外层捕获,然后进行重试获取节点id
log.debug("Pool exhausted for partition id {}", partitionID);
placementStrategy.exhaustedPartition(partitionID);
partitionPool.exhaustedIdPool();
throw e;
}
}
// 组装最终的分布式id:[count + partition id + ID padding]
long elementId;
if (element instanceof InternalRelation) {
elementId = idManager.getRelationID(count, partitionID);
} else if (element instanceof PropertyKey) {
elementId = IDManager.getSchemaId(IDManager.VertexIDType.UserPropertyKey,count);
} else if (element instanceof EdgeLabel) {
elementId = IDManager.getSchemaId(IDManager.VertexIDType.UserEdgeLabel, count);
} else if (element instanceof VertexLabel) {
elementId = IDManager.getSchemaId(IDManager.VertexIDType.VertexLabel, count);
} else if (element instanceof JanusGraphSchemaVertex) {
elementId = IDManager.getSchemaId(IDManager.VertexIDType.GenericSchemaType,count);
} else {
elementId = idManager.getVertexID(count, partitionID, userVertexIDType);
}
Preconditions.checkArgument(elementId >= 0);
// 对节点对象赋值其分布式唯一id
element.setId(elementId);
}
上述代码,我们拿到了对应的IdPool,有两种情况:
- 第一次获取分布式id时,分区对应的IDPool初始化为默认的size = 0的IDPool
- 分区对应的IDPool不是初次获取
这两种情况的处理,都在代码count = idPool.nextID()的StandardIDPool类中的nextID()方法中被处理!
在分析该代码之前,我们需要知道 PartitionIDPool 和StandardIDPool的关系:
每个partition都有一个对应的PartitionIDPool extends EnumMap<PoolType,IDPool> 是一个枚举map类型;
每一个PartitionIDPool 都有对应的不同类型的StandardIDPool:
- NORMAL_VERTEX:用于vertex id的分配
- UNMODIFIABLE_VERTEX:用于schema label id的分配
- RELATION:用于edge id的分配
在StandardIDPool中包含多个字段,分别代表不同的含义,抽取几个重要的字段进行介绍:
private static final int RENEW_ID_COUNT = 100;
private final long idUpperBound; // Block的最大值,默认为2的55次幂
private final int partition; // 当前pool对应的分区
private final int idNamespace; // 标识pool为那种类型的pool,上述的三种类型NORMAL_VERTEX、UNMODIFIABLE_VERTEX、RELATION;值为当前枚举值在枚举中的位置
private final Duration renewTimeout;// 重新获取block的超时时间
private final double renewBufferPercentage;// 双buffer中,当第一个buffer block使用的百分比,到达配置的百分比则触发other buffer block的获取
private IDBlock currentBlock; // 当前的block
private long currentIndex; // 标识当前block使用到那一个位置
private long renewBlockIndex; // 依据currentBlock.numIds()*renewBufferPercentage来获取这个值,主要用于在当前的block在消费到某个index的时候触发获取下一个buffer block
private volatile IDBlock nextBlock;// 双buffer中的另外一个block
private final ThreadPoolExecutor exec;// 异步获取双buffer的线程池
6、调用了StandardIDPool类中的nextID方法
经过上述分析,我们知道,分布式唯一id的唯一性是由在partition维度下的count的值的唯一性来保证的;
上述代码通过调用IDPool的nextId来获取count值;
下述代码就是获取count的逻辑;
@Override
public synchronized long nextID() {
// currentIndex标识当前的index小于current block的最大值
assert currentIndex <= currentBlock.numIds();
// 此处涉及两种情况:
// 1、分区对应的IDPool是第一次被初始化;则currentIndex = 0; currentBlock.numIds() = 0;
// 2、分区对应的该IDPool不是第一次,但是此次的index正好使用到了current block的最后一个count
if (currentIndex == currentBlock.numIds()) {
try {
// 将current block赋值为next block
// next block置空 并计算renewBlockIndex
nextBlock();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new JanusGraphException("Could not renew id block due to interruption", e);
}
}
// 在使用current block的过程中,当current index == renewBlockIndex时,触发double buffer next block的异步获取!!!!
if (currentIndex == renewBlockIndex) {
// 异步获取next block
startIDBlockGetter();
}
// 生成最终的count
long returnId = currentBlock.getId(currentIndex);
// current index + 1
currentIndex++;
if (returnId >= idUpperBound) throw new IDPoolExhaustedException("Reached id upper bound of " + idUpperBound);
log.trace("partition({})-namespace({}) Returned id: {}", partition, idNamespace, returnId);
// 返回最终获取的分区维度的全局唯一count
return returnId;
}
上述代码中进行了两次判断:
- currentIndex == currentBlock.numIds():
- 第一次生成分布式id:此处判断即为 0==0;然后生成新的block
- 非第一次生成分布式id:等于情况下标识当前的block已经使用完了,需要切换为next block
- currentIndex == renewBlockIndex
- renew index:标识index使用多少后开始获取下一个double buffer 的next block;有一个默认值100,主要为了兼容第一次分布式id的生成;相等则会触发异步获取下一个next block
下面我们分别对nextBlock();逻辑和startIDBlockGetter();进行分析;
7、调用了StandardIDPool类中的nextBlock方法
private synchronized void nextBlock() throws InterruptedException {
// 在分区对应的IDPool第一次使用时,double buffer的nextBlock为空
if (null == nextBlock && null == idBlockFuture) {
// 异步启动 获取id block
startIDBlockGetter();
}
// 也是在分区对应的IDPool第一次使用时,因为上述为异步获取,所以在执行到这一步时nextBlock可能还没拿到
// 所以需要阻塞等待block的获取
if (null == nextBlock) {
waitForIDBlockGetter();
}
// 将当前使用block指向next block
currentBlock = nextBlock;
// index清零
currentIndex = 0;
// nextBlock置空
nextBlock = null;
// renewBlockIndex用于双buffer中,当第一个buffer block使用的百分比,到达配置的百分比则触发other buffer block的获取
// 值current block 对应的count数量 - (值current block 对应的count数量 * 为renewBufferPercentage配置的剩余空间百分比)
// 在使用current block的时候,当current index == renewBlockIndex时,触发double buffer next block的异步获取!!!!
renewBlockIndex = Math.max(0,currentBlock.numIds()-Math.max(RENEW_ID_COUNT, Math.round(currentBlock.numIds()*renewBufferPercentage)));
}
主要是做了三件事:
- 1、block是否为空,为空的话则异步获取一个block
- 2、nextBlock不为空的情况下:next赋值到current、next置空、index置零
- 3、计算获取下一个nextBlock的触发index renewBlockIndex值
8、调用了StandardIDPool类中的startIDBlockGetter方法
private synchronized void startIDBlockGetter() {
Preconditions.checkArgument(idBlockFuture == null, idBlockFuture);
if (closed) return; //Don't renew anymore if closed
//Renew buffer
log.debug("Starting id block renewal thread upon {}", currentIndex);
// 创建一个线程对象,包含给定的权限控制类、分区、命名空间、超时时间
idBlockGetter = new IDBlockGetter(idAuthority, partition, idNamespace, renewTimeout);
// 提交获取double buffer的线程任务,异步执行
idBlockFuture = exec.submit(idBlockGetter);
}
其中创建一个线程任务,提交到线程池exec进行异步执行;
下面看下,线程类的call方法主要是调用了 idAuthority.getIDBlock方法,这个方法主要是基于Hbase来获取还未使用的block;
/**
* 获取double buffer block的线程类
*/
private static class IDBlockGetter implements Callable<IDBlock> {
// 省略部分代码
@Override
public IDBlock call() {
Stopwatch running = Stopwatch.createStarted();
try {
// 此处调用idAuthority 调用HBase进行占用获取Block
IDBlock idBlock = idAuthority.getIDBlock(partition, idNamespace, renewTimeout);
return idBlock;
} catch (BackendException e) {}
}
}
9、调用ConsistentKeyIDAuthority类的getIDBlock方法
@Override
public synchronized IDBlock getIDBlock(final int partition, final int idNamespace, Duration timeout) throws BackendException {
// 开始时间
final Timer methodTime = times.getTimer().start();
// 获取当前命名空间配置的blockSize,默认值10000;可自定义配置
final long blockSize = getBlockSize(idNamespace);
// 获取当前命名空间配置的最大id值idUpperBound;值为:2的55次幂大小
final long idUpperBound = getIdUpperBound(idNamespace);
// uniqueIdBitWidth标识uniqueId占用的位数;uniqueId为了兼容“关闭分布式id唯一性保障”的开关情况,uniqueIdBitWidth默认值=4
// 值:64-1(默认0)-5(分区占用位数)-3(ID Padding占用位数)-4(uniqueIdBitWidth) = 51;标识block中的上限为2的51次幂大小
final int maxAvailableBits = (VariableLong.unsignedBitLength(idUpperBound)-1)-uniqueIdBitWidth;
// 标识block中的上限为2的51次幂大小
final long idBlockUpperBound = (1L <<maxAvailableBits);
// UniquePID用尽的UniquePID集合,默认情况下,randomUniqueIDLimit = 0;
final List<Integer> exhaustedUniquePIDs = new ArrayList<>(randomUniqueIDLimit);
// 默认0.3秒 用于处理TemporaryBackendException异常情况(后端存储出现问题)下:阻塞一断时间,然后进行重试
Duration backoffMS = idApplicationWaitMS;
// 从开始获取IDBlock开始,持续超时时间(默认2分钟)内重试获取IDBlock
while (methodTime.elapsed().compareTo(timeout) < 0) {
final int uniquePID = getUniquePartitionID(); // 获取uniquePID,默认情况下“开启分布式id唯一性控制”,值 = 0; 当“关闭分布式id唯一性控制”时为一个随机值
final StaticBuffer partitionKey = getPartitionKey(partition,idNamespace,uniquePID); // 依据partition + idNamespace + uniquePID组装一个RowKey
try {
long nextStart = getCurrentID(partitionKey); // 从Hbase中获取当前partition对应的IDPool中被分配的最大值,用来作为当前申请新的block的开始值
if (idBlockUpperBound - blockSize <= nextStart) { // 确保还未被分配的id池中的id个数,大于等于blockSize
// 相应处理
}
long nextEnd = nextStart + blockSize; // 获取当前想要获取block的最大值
StaticBuffer target = null;
// attempt to write our claim on the next id block
boolean success = false;
try {
Timer writeTimer = times.getTimer().start(); // ===开始:开始进行插入自身的block需求到Hbase
target = getBlockApplication(nextEnd, writeTimer.getStartTime()); // 组装对应的Column: -nextEnd + 当前时间戳 + uid(唯一标识当前图实例)
final StaticBuffer finalTarget = target; // copy for the inner class
BackendOperation.execute(txh -> { // 异步插入当前生成的RowKey 和 Column
idStore.mutate(partitionKey, Collections.singletonList(StaticArrayEntry.of(finalTarget)), KeyColumnValueStore.NO_DELETIONS, txh);
return true;
},this,times);
writeTimer.stop(); // ===结束:插入完成
final boolean distributed = manager.getFeatures().isDistributed();
Duration writeElapsed = writeTimer.elapsed(); // ===获取方才插入的时间耗时
if (idApplicationWaitMS.compareTo(writeElapsed) < 0 && distributed) { // 判断是否超过配置的超时时间,超过则报错TemporaryBackendException,然后等待一断时间进行重试
throw new TemporaryBackendException("Wrote claim for id block [" + nextStart + ", " + nextEnd + ") in " + (writeElapsed) + " => too slow, threshold is: " + idApplicationWaitMS);
} else {
assert 0 != target.length();
final StaticBuffer[] slice = getBlockSlice(nextEnd); // 组装下述基于上述Rowkey的Column的查找范围:(-nextEnd + 0 : 0nextEnd + 最大值)
final List<Entry> blocks = BackendOperation.execute( // 异步获取指定Rowkey和指定Column区间的值
(BackendOperation.Transactional<List<Entry>>) txh -> idStore.getSlice(new KeySliceQuery(partitionKey, slice[0], slice[1]), txh),this,times);
if (blocks == null) throw new TemporaryBackendException("Could not read from storage");
if (blocks.isEmpty())
throw new PermanentBackendException("It seems there is a race-condition in the block application. " +
"If you have multiple JanusGraph instances running on one physical machine, ensure that they have unique machine idAuthorities");
if (target.equals(blocks.get(0).getColumnAs(StaticBuffer.STATIC_FACTORY))) { // 如果获取的集合中,当前的图实例插入的数据是第一条,则表示获取block; 如果不是第一条,则获取Block失败
// 组装IDBlock对象
ConsistentKeyIDBlock idBlock = new ConsistentKeyIDBlock(nextStart,blockSize,uniqueIdBitWidth,uniquePID);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
idBlock, partition, idNamespace, uid);
}
success = true;
return idBlock; // 返回
} else { }
}
} finally {
if (!success && null != target) { // 在获取Block失败后,删除当前的插入; 如果没有失败,则保留当前的插入,在hbase中标识该Block已经被占用
//Delete claim to not pollute id space
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < ROLLBACK_ATTEMPTS; attempt++) { // 回滚:删除当前插入,尝试次数5次
}
}
}
} catch (UniqueIDExhaustedException e) {
// No need to increment the backoff wait time or to sleep
log.warn(e.getMessage());
} catch (TemporaryBackendException e) {
backoffMS = Durations.min(backoffMS.multipliedBy(2), idApplicationWaitMS.multipliedBy(32));
sleepAndConvertInterrupts(backoffMS); \
}
}
throw new TemporaryLockingException();
}
主要的逻辑就是:
组装Rowkey:partition + idNameSpace+unquePId组装Column:-nextEnd+now time+uid- 将
RowKey+Column插入Hbase - 获取的上述组装的RowKey 基于(-nextEnd + 0 : -nextEnd + max)范围的所有Column集合
- 判断集合的第一个Column是不是当前插入的Column,是的话则占用block成功,不是的话则占用失败,删除刚才占用并进行重试
最终:异步获取到了唯一占用的Block,然后生成对应的唯一count,组装最后的唯一id
整体的调用流程如下:
四:其他类型的id生成
上述我们主要依据生成节点id(vertex id)的过程来进行分析
在JanusGraph中还包含edge id、property id、schema label id等几种的分布式id生成
所有类型的分布式id的生成主要思想和逻辑都几乎相同,只是一些具体的逻辑可能有所不同,我们理解了vertex id的分布式id生成流程,其他的也可以理解了。
1、property id的生成
在JanusGraph中的property的分布式唯一id的生成,整体逻辑和vertex id的生成逻辑大体相同;
property id的 生成和 vertex id有两点不同:
- ID的组成部分: 在
vertex id中组成部分包含count+partition+ID Padding; 而在property id中没有ID Padding部分,其组成为count + partition
long id = (count<<partitionBits)+partition;
if (type!=null) id = type.addPadding(id); // 此时,type = null
return id;
- partition id的获取方式:在生成
vertex id时,partition id是随机获取的;而在生成property id时,partition id是获取的当前节点对应的partition id,如果节点获取不到分区id,则随机生成一个;
if (element instanceof InternalRelation) { // 属性 + 边
InternalRelation relation = (InternalRelation)element;
if (attempt < relation.getLen()) {
InternalVertex incident = relation.getVertex(attempt);
Preconditions.checkArgument(incident.hasId());
if (!IDManager.VertexIDType.PartitionedVertex.is(incident.longId()) || relation.isProperty()) { // 获取对应节点已有的partition id
partitionID = getPartitionID(incident);
} else {
continue;
}
} else { // 如果对应的节点都没有,则随机获取一个partition id
partitionID = placementStrategy.getPartition(element);
}
2、Edge id的生成
在JanusGraph中的edge的分布式唯一id的生成,整体逻辑和vertex id的生成逻辑大体相同;
edge id的 生成和 vertex id有两点不同:
- ID的组成部分: 在
vertex id中组成部分包含count+partition+ID Padding; 而在edge id中没有ID Padding部分,其组成为count + partition,代码同property id的生成代码 - partition id的获取方式:在生成
vertex id时,partition id是随机获取的;而在生成edge id时,partition id是获取的当前source vertex或者target vertex对应的partition id,如果节点获取不到分区id,则随机生成一个,代码同property id的生成代码;
3、Schema相关id的生成
在JanusGraph中的schema相关id的分布式唯一id的生成,整体逻辑和vertex id的生成逻辑大体相同;
schema相关id的生成分为四种:PropertyKey、EdgeLabel、VertexLabel、JanusGraphSchemaVertex
- ID的组成部分: 在
vertex id中组成部分包含count+partition+ID Padding; 在schema对应的id生成,这四种产生的id对应的结构都是一样的:count + 对应类型的固定后缀
return (count << offset()) | suffix();
- partition id的获取方式:在生成
vertex id时,partition id是随机获取的;而在生成schema id时,partition id是默认的partition id = 0;
public static final int SCHEMA_PARTITION = 0;
if (element instanceof JanusGraphSchemaVertex) {
partitionID = IDManager.SCHEMA_PARTITION; // 默认分区
}
总结
本文总结了JanusGraph的分布式唯一id的生成逻辑,也进行的源码分析;
下一篇,JanusGraph的锁机制分析,包含本地锁和分布式锁相关的分析,我是“洋仔”,我们下期见~
图解Janusgraph系列-分布式id生成策略分析的更多相关文章
- 分布式ID生成策略 · fossi
分布式环境下如何保证ID的不重复呢?一般我们可能会想到用UUID来实现嘛.但是UUID一般可以获取当前时间的毫秒数再加点随机数,但是在高并发下仍然可能重复.最重要的是,如果我要用这种UUID来生成分表 ...
- Hibernate系列之ID生成策略
一.概述 hibernate中使用两种方式实现主键生成策略,分别是XML生成id和注解方式(@GeneratedValue),下面逐一进行总结. 二.XML配置方法 这种方式是在XX.hbm.xml文 ...
- 分布式ID生成策略之ZK
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFramework; import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFra ...
- 分布式系统下的全局id生成策略分析
对于分布式系统而言,意味着会有很多个instance会并发的生成很多业务数据,比如订单.不同的机房.不同的机器.不同的应用实例会同时生成.所以,如何生成一个好用的全局id并不是一个简单的uuid就能够 ...
- Disruptor分布式id生成策略
需要的pom文件: <!-- 顺序UUID --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.uuid</groupId> ...
- 分布式ID生成策略
策略一.UUID 策略二.数据库自增序列 策略三.snowflake算法 策略四.基于redis自增 思路:利用增长计数API,业务系统在自增长的基础上,配合其他信息组装成为一个唯一ID. redis ...
- 图解Janusgraph系列-图数据底层序列化源码分析(Data Serialize)
图解Janusgraph系列-图数据底层序列化源码分析(Data Serialize) 大家好,我是洋仔,JanusGraph图解系列文章,实时更新~ 图数据库文章总目录: 整理所有图相关文章,请移步 ...
- 图解JanusGraph系列 - 关于JanusGraph图数据批量快速导入的方案和想法(bulk load data)
大家好,我是洋仔,JanusGraph图解系列文章,实时更新~ 图数据库文章总目录: 整理所有图相关文章,请移步(超链):图数据库系列-文章总目录 源码分析相关可查看github(码文不易,求个sta ...
- 业务ID 生成策略
业务ID 生成策略,从技术上说,基本要借助一个集中式的引擎来帮忙实现. 为了扩大业务ID生成策略的并发问题,还有更为技巧性的提升. 先来介绍普遍的分布式ID生成策略: 1. 利用DB的自增主键 这里又 ...
随机推荐
- navicat for mysql 连接报错1251的解决方法
这是因为比较新的mysql版本采用新的保密方式,若要用navicat连接需要改使用到的用户的密码方式:use mysql:ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIE ...
- ios 常用的正则表达式(手机号邮箱md5加密验证空字符串等)
可以写一个nssring的category 给nsstring 增加一些方法,而这些方法就是一些正则表达式. 比如写一个叫做Helper的类 创建完了就是 NSString+Helper 然后在进行 ...
- vue中模块局部刷新
父组件: 一. 父组件中引入子组件 data中定义变量 二. 定义provide函数 三.写reload方法 需要刷新的那个子组件: 一.引入 ...
- JavaScript calss语法糖
JavaScript calss语法糖 基础知识 严格意义上来讲,在Js中是没有类这一概念的. 我们可以运用前面章节提到的构造函数来模拟出类这一概念,并且可以通过原型对象的继承来完美的实现实例对象方法 ...
- java目前常用的几种定时任务
java目前常用的几种定时任务 JDK自带的Timer spring的Task Quartz elastic-job分布式定时任务 一.JDK自带的Timer Timer是jdk中提供的一个定时器工具 ...
- Docker容器网络-实现篇
通常,Linux容器的网络是被隔离在它自己的Network Namespace中,其中就包括:网卡(Network Interface).回环设备(Loopback Device).路由表(Routi ...
- 【JAVA】java中int转成String位数不足前面补零例如:1->001
String.format("%03d", 1); 0代表前面要补的字符3代表字符串长度d表示参数为整数类型 测试完数据:循环了100次 截取了一部分:
- tableau用户留存分析
1.数据源 这是个母婴产品的购买流水数据 2.数据处理 字段拆分.创建购买点会员生命周期 3.分析不同省份的留存率情况 根据第12个月的留存率对省市进行分组 实际业务中也可以通过类似的方法对用户年龄组 ...
- JDK8 String类知识总结
一.概述 java的String类可以说是日常实用的最多的类,但是大多数时候都只是简单的拼接或者调用API,今天决定深入点了解一下String类. 要第一时间了解一个类,没有什么比官方的javaDoc ...
- Java并发---并发理论
一.如何理解线程安全 在多线程中稍微不注意就会出现线程安全问题,那么什么是线程安全问题? 我的认识是.在多线程下代码执行的结果和预期的正确的结果不一致,该代码就是线程不安全的,否则就是线程安全的 在深 ...
