spring源码-事件&监听3.6
一、spring中的发布与监听模式,是我们最常用的一种观察者模式。spring在其中做了很多优化,目的就是让用户更好的使用事件与监听的过程。
二、常用的事件与监听中涉及到的接口和类为:ApplicationEvent、ApplicationListener、ApplicationEventPublisher或者ApplicationContext。ApplicationEventPublisher或者ApplicationContext其实使用的是同一个方法进行发布事件。
三、实现方式
参考:spring源码-Aware-3.4的第二类b点的实现方式,这里不详细解释。
四、源码部分
1)方法实现在:refresh()方法中的
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.registerListeners();
2)initApplicationEventMulticaster
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
//获取本地的beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.getBeanFactory();
//判断是否自己加入applicationEventMulticaster的bean
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean("applicationEventMulticaster")) {
//如果存在则赋值待用
this.applicationEventMulticaster = (ApplicationEventMulticaster)beanFactory.getBean("applicationEventMulticaster", ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
} else {
//如果没用,就直接使用默认的方式加入
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
//加入容器,单例方式
beanFactory.registerSingleton("applicationEventMulticaster", this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name 'applicationEventMulticaster': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
}
可能有点奇怪,这个和事件以及监听有啥关系。后面为具体讲执行过程,留个悬念
3)registerListeners
protected void registerListeners() {
//获取已有监听
Iterator var2 = this.getApplicationListeners().iterator();
//如果存在着添加到缓存中灯带执行
while(var2.hasNext()) {
ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener)var2.next();
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
//获取ApplicationListener类型的beanNames
String[] listenerBeanNames = this.getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
String[] var5 = listenerBeanNames;
int var4 = listenerBeanNames.length;
//同样添加到具体的缓存中
for(int var3 = 0; var3 < var4; ++var3) {
String lisName = var5[var3];
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(lisName);
}
}
//添加到缓存中
//ListenerRetriever
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener listener) {
//这里不详解释,有兴趣可以自己看一下源码,这里就是默认加入缓存的一个过程
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever var2 = this.defaultRetriever;
synchronized(this.defaultRetriever) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
//添加到缓存中
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever var2 = this.defaultRetriever;
synchronized(this.defaultRetriever) {
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
this.retrieverCache.clear();
}
}
//set数据,不详解释
private class ListenerRetriever {
public final Set<ApplicationListener> applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet();
public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet();
private final boolean preFiltered;
public ListenerRetriever(boolean preFiltered) {
this.preFiltered = preFiltered;
}
//具体的获取监听的过程
public Collection<ApplicationListener> getApplicationListeners() {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener> allListeners = new LinkedList();
Iterator var3 = this.applicationListeners.iterator();
while(var3.hasNext()) {
ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener)var3.next();
allListeners.add(listener);
}
if (!this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.this.getBeanFactory();
Iterator var4 = this.applicationListenerBeans.iterator();
label23:
while(true) {
ApplicationListener listenerx;
do {
if (!var4.hasNext()) {
break label23;
}
String listenerBeanName = (String)var4.next();
//获取实例
listenerx = (ApplicationListener)beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
} while(!this.preFiltered && allListeners.contains(listenerx));
allListeners.add(listenerx);
}
}
OrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
}
4)这就是spring中的准备过程,下面就是执行过程了。(publisher为ApplicationEventPublisher,可以参考实现方式)
public void test() {
publisher.publishEvent(new TestEvent(this, "test"));
}
public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Publishing event in " + this.getDisplayName() + ": " + event);
}
//这也就是前面留下悬念的过程
this.getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(event);
if (this.parent != null) {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
看一下注册的ApplicationEventMulticaster
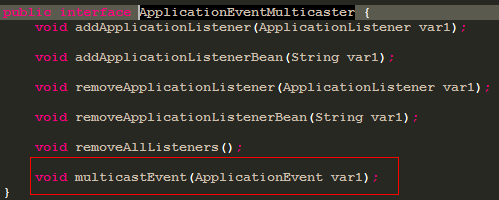
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event) {
//这里获取具体的事件所有关注的监听者
Iterator var3 = this.getApplicationListeners(event).iterator();
while(var3.hasNext()) {
final ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener)var3.next();
//这里如果过存在线程池。则通过线程池执行
Executor executor = this.getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
});
} else {
//或者同步执行
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
}
这里就是具体执行过程了!
5)当然获取具体监听的实现过程还是可以学习一下的,主要是泛型的应用:getApplicationListeners
protected Collection<ApplicationListener> getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent event) {
//获取实际的事件classType
Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType = event.getClass();
//发生地new TestEvent(this, "test")中的this
Class sourceType = event.getSource().getClass();
//查看缓存key
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever retriever = (AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever)this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
//如果存在则直接返回
if (retriever != null) {
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
} else {
//没有则重新声明保存
retriever = new AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever(true);
LinkedList<ApplicationListener> allListeners = new LinkedList();
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.ListenerRetriever var7 = this.defaultRetriever;
synchronized(this.defaultRetriever) {
//查看已有的监听
Iterator var9 = this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.iterator();
//判断是否支持
while(var9.hasNext()) {
ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener)var9.next();
if (this.supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
//如果没有
if (!this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = this.getBeanFactory();
//遍历默认的
Iterator var10 = this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.iterator();
while(var10.hasNext()) {
String listenerBeanName = (String)var10.next();
//获取加入容器的监听
ApplicationListener listener = (ApplicationListener)beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
//判断是否支持
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && this.supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
}
//排序
OrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
//加入缓存方便下次执行
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return allListeners;
}
}
}
//判断方式
protected boolean supportsEvent(ApplicationListener listener, Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType, Class sourceType) {
SmartApplicationListener smartListener = listener instanceof SmartApplicationListener ? (SmartApplicationListener)listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener);
return ((SmartApplicationListener)smartListener).supportsEventType(eventType) && ((SmartApplicationListener)smartListener).supportsSourceType(sourceType);
}
//判断过程
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) {
Class typeArg = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(this.delegate.getClass(), ApplicationListener.class);
if (typeArg == null || typeArg.equals(ApplicationEvent.class)) {
Class targetClass = AopUtils.getTargetClass(this.delegate);
if (targetClass != this.delegate.getClass()) {
typeArg = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(targetClass, ApplicationListener.class);
}
}
return typeArg == null || typeArg.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
}
public static Class<?> resolveTypeArgument(Class clazz, Class genericIfc) {
Class[] typeArgs = resolveTypeArguments(clazz, genericIfc);
if (typeArgs == null) {
return null;
} else if (typeArgs.length != 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Expected 1 type argument on generic interface [" + genericIfc.getName() + "] but found " + typeArgs.length);
} else {
return typeArgs[0];
}
}
public static Class[] resolveTypeArguments(Class clazz, Class genericIfc) {
return doResolveTypeArguments(clazz, clazz, genericIfc);
}
private static Class[] doResolveTypeArguments(Class ownerClass, Class classToIntrospect, Class genericIfc) {
for(; classToIntrospect != null; classToIntrospect = classToIntrospect.getSuperclass()) {
if (genericIfc.isInterface()) {
Type[] ifcs = classToIntrospect.getGenericInterfaces();
Type[] var7 = ifcs;
int var6 = ifcs.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var6; ++var5) {
Type ifc = var7[var5];
Class[] result = doResolveTypeArguments(ownerClass, ifc, genericIfc);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
} else {
Class[] result = doResolveTypeArguments(ownerClass, classToIntrospect.getGenericSuperclass(), genericIfc);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private static Class[] doResolveTypeArguments(Class ownerClass, Type ifc, Class genericIfc) {
if (ifc instanceof ParameterizedType) {
ParameterizedType paramIfc = (ParameterizedType)ifc;
Type rawType = paramIfc.getRawType();
if (genericIfc.equals(rawType)) {
Type[] typeArgs = paramIfc.getActualTypeArguments();
Class[] result = new Class[typeArgs.length];
for(int i = 0; i < typeArgs.length; ++i) {
Type arg = typeArgs[i];
result[i] = extractClass(ownerClass, arg);
}
return result;
}
if (genericIfc.isAssignableFrom((Class)rawType)) {
return doResolveTypeArguments(ownerClass, (Class)rawType, genericIfc);
}
} else if (ifc != null && genericIfc.isAssignableFrom((Class)ifc)) {
return doResolveTypeArguments(ownerClass, (Class)ifc, genericIfc);
}
return null;
}
过程有点复杂,具体可以自己了解一下。大体方向就是通过获取接口的类型,然后具体的泛型类型,然后比对。
6)最后提一点,上面如果我们没有配置applicationEventMulticaster会导致一个问题就是同步问题。在initApplicationEventMulticaster中默认使用的是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的实例来实现具体过程。但是默认情况下是不会有线程池的方式加入的,所以这里需要重新注册名为applicationEventMulticaster的bean。具体实现方式为:
@Configuration
public class PublisherConfiguration { @Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(5);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(60);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setQueueCapacity(3000);
return executor;
} /**
* 事件监听会默认使用改监听器使用线程池执行
* @param executor
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "applicationEventMulticaster")
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster simpleApplicationEventMulticaster(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
applicationEventMulticaster.setTaskExecutor(executor);
return applicationEventMulticaster;
}
}
这里的名字必须为applicationEventMulticaster,至于为什么不用解释了吧!
spring源码-事件&监听3.6的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot实践——事件监听
借鉴:https://blog.csdn.net/Harry_ZH_Wang/article/details/79691994 https://blog.csdn.net/ignorewho/arti ...
- asp.net core启动源码以及监听,到处理请求响应的过程
摘要 asp.net core发布至今已经将近6年了,很多人对于这一块还是有些陌生,或者说没接触过:接触过的,对于asp.net core整个启动过程,监听过程,以及请求过程,响应过程也是一知半解,可 ...
- Spring中的事件监听实现
在spring中我们可以自定义事件,并且可以使用ApplicationContext类型对象(就是spring容器container)来发布这个事件 事件发布之后,所有的ApplicaitonList ...
- spring源码-bean之增强初始化-3
一.ApplicationContext的中文意思是“应用上下文”,它继承自BeanFactory接口,除了包含BeanFactory的所有功能之外,在国际化支持.资源访问(如URL和文件).事件传播 ...
- Spring之事件监听(观察者模型)
目录 Spring事件监听 一.事件监听案例 1.事件类 2.事件监听类 3.事件发布者 4.配置文件中注册 5.测试 二.Spring中事件监听分析 1. Spring中事件监听的结构 2. 核心角 ...
- (转)spring boot实战(第三篇)事件监听源码分析
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/liaokailin/article/details/48194777 监听源码分析 首先是我们自定义的main方法: package com.lkl. ...
- spring boot 源码赏析之事件监听
使用spring Boot已经快1年多了,期间一直想点开springboot源码查看,但由于种种原因一直未能如愿(主要是人类的惰性...),今天就拿springboot 的监听事件祭刀. spring ...
- Spring事件监听机制源码解析
Spring事件监听器使用 1.Spring事件监听体系包括三个组件:事件.事件监听器,事件广播器. 事件:定义事件类型和事件源,需要继承ApplicationEvent. package com.y ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring的事件发布监听机制源码解析
[一]相关源代码类 (1)spring的事件发布监听机制的核心管理类:org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticast ...
随机推荐
- commons dbcp.jar有什么用
主流数据库连接池之一(DBCP.c3p0.proxool),单独使用DBCP需要使用commons-dbpc.jar.commons-collections.jar.commons-pool.jar三 ...
- HDU 1281 棋盘游戏 【二分图最大匹配】
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1281 题意概括: 有N*M大的棋盘,要在里面放尽量多的“车”,求最多能放的车的个数,和为了放最多的车有多 ...
- Linux tmux 使用指南
注意:本文内容适用于 Tmux 2.3 及以上的版本,但是绝大部分的特性低版本也都适用,鼠标支持.VI 模式.插件管理在低版本可能会与本文不兼容. Tmux 快捷键 & 速查表 启动新会话: ...
- Android 复制 粘贴 剪贴板的使用 ClipboardManager
Copy and Paste 版本:Android 4.0 r1 快速查看 用于复制粘贴数据的基于剪贴板的框架. 同时支持简单和复杂的数据,包括文本串.复杂的数据结构.文本和二进制流数据.程序 as ...
- 【题解】洛谷P1074 [NOIP2009TG] 靶形数独(DFS+剪枝)
洛谷P1074:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1074 思路 这道题一看就是DFS 打一个分数表方便后面算分 我用x y z数组分别表示行 列 宫 是否 ...
- C++备忘知识整理
一.设置字体颜色 C++控制台程序运行时输出框默认的文字颜色是白色,所以我常称其输出框为黑白框.但是这个文字样式不是固定不变的,是可以改变颜色的字体的.方法有两种: 1.设置输出框的框体属性.在运行时 ...
- 在js中获取到的页面元素为undefined
在学习js的过程中发现了一个问题就是:在js代码中获取页面元素进行操作的时候发现怎么都没有效果,控制台也不报错,弹出获取的元素结果发现是undefined类型. 后来查找了资料发现:因为我的js是写在 ...
- JQuery手写一个简单的分页
效果图: 大概思路:使用ul进行初始布局,每一次点击事件改变li里的值.完整的代码在gitup上:https://github.com/anxizhihai/Paging.gitcss部分: html ...
- 三层架构,Struts2,SpringMVC实现原理图
三层架构,Struts2,SpringMVC实现原理图 三层架构实现原理 Struts2实现原理 SpringMVC实现原理
- axios和ajax,fetch的区别
1,传统 Ajax 指的是 XMLHttpRequest(XHR), 最早出现的发送后端请求技术,隶属于原始js中,核心使用XMLHttpRequest对象,多个请求之间如果有先后关系的话,就会出现回 ...
