剑指offer编程题66道题 26-35
26.二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目描述
中序遍历思路:
按照右中左的顺序,中序遍历对节点的访问顺序和转换完链表从左到右的顺序是一样的。所以在中序遍历时完成相邻两个节点的互指即可。
具体做法是把前一个节点记录下来然后pre->right=cur;cur->left=pre。
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null; public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val; } }
*/
public class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null) return pRootOfTree;
Convert(pRootOfTree.right);
if(pre == null){
pre = pRootOfTree;
} else {
pre.left = pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.right = pre;
pre = pRootOfTree;
}
Convert(pRootOfTree.left);
return pre;
}
}
最开始我采用的是这种解法,有两个问题:
1.采用左中右的中序遍历,遍历完之后头结点还得从右到左挪回来
2.更严重的问题是,我将pre设置为局部传递的变量,由于pre是引用的值传递,在递归回退的时候,pre的引用时上一次遍历pre的副本,而不是遍历后更改的值。解决方法就是讲pre设置为全局变量。
切记!!!java只有值传递!只有值传递!只有值传递!
对于基本类型,java都是传值。而对于引用类型,其实java也是通过值传递的,只是传递的值不是实例本身,而是实例的引用的副本。
参考java的传值与传引用
错误解法:
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null; public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val; } }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null)
return null;
TreeNode pre = null;
ConvertHelper(pRootOfTree,pre);
TreeNode res = pRootOfTree;
while(res.left != null){
res = res.left;
}
return res;
} public void ConvertHelper(TreeNode cur, TreeNode pre){
if(cur == null)
return;
ConvertHelper(cur.left,pre);
cur.left = pre;
if(pre!=null) pre.right = cur;
pre = cur;
ConvertHelper(cur.right,pre);
}
}
非递归实现:
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/947f6eb80d944a84850b0538bf0ec3a5
来源:牛客网 import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null) return pRootOfTree;
TreeNode list = null;
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
while(pRootOfTree != null || !s.isEmpty()){
if(pRootOfTree != null) {
s.push(pRootOfTree);
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.right;
} else {
pRootOfTree = s.pop();
if(list == null)
list = pRootOfTree;
else {
list.left = pRootOfTree;
pRootOfTree.right = list;
list = pRootOfTree;
}
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.left;
}
}
return list;
}
}
27.字符串的排列
题目描述
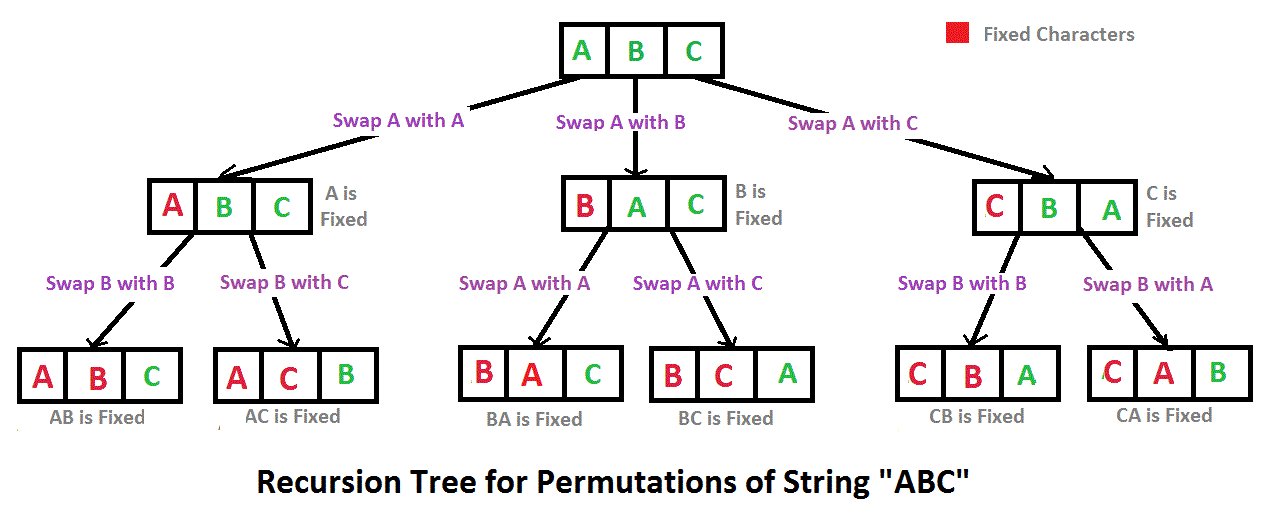
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
if(str !=null && str.length() > ){
PermutationHelper(str.toCharArray(),,list);
Collections.sort(list);
}
return list;
} public void PermutationHelper(char[] cs, int i, ArrayList<String> list){
if(cs.length- == i){
String val = String.valueOf(cs);
if(!list.contains(val)){
list.add(val);
}
}else{
for(int j=i; j<cs.length;j++){
swap(i,j,cs);
PermutationHelper(cs,i+,list);
swap(i,j,cs);
}
}
} public void swap(int i,int j,char[] cs){
char temp = cs[i];
cs[i] = cs[j];
cs[j] = temp;
}
}
最后一个循环是递归调用swap交换前后两个字符,在最后交换完成入List之后再交换回来,回到初始状态再进下一个循环
28.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目描述
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
Map<Integer,Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
if(array.length == )
return array[];
for(int i:array){
if(!count.containsKey(i)){
count.put(i, );
}else{
count.put(i,count.get(i)+);
if(count.get(i) > array.length/)
return i;
}
}
return ;
}
}
第二种解法:耗时10ms
采用阵地攻守的思想:
第一个数字作为第一个士兵,守阵地;count = 1;
遇到相同元素,count++;
遇到不相同元素,即为敌人,同归于尽,count--;当遇到count为0的情况,又以新的i值作为守阵地的士兵,继续下去,到最后还留在阵地上的士兵,有可能是主元素。
再加一次循环,记录这个士兵的个数看是否大于数组一般即可。
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
if(array.length == )
return array[];
int result = array[];
int times = ;
for(int i = ;i<array.length; i++){
if(times == ){
result = array[i];
times = ;
}else if(result == array[i]){
times++;
}else{
times--;
}
}
times=;
for(int i=;i<array.length;i++){
if(result==array[i]){
times++;
}
}
if(times*<=array.length){
result=;
}
return result;
}
}
29.最小的K的个数
题目描述
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(k>input.length)
return list;
Arrays.sort(input);
for(int i:Arrays.copyOfRange(input, , k)){
list.add(i);
}
return list;
}
}
2.创建一个大小为k的数据容器,如果容器还没有有了k个数字,直接放入这个数到容器当中;如果容器中有了k个数字了,找出这已有的k个数字中的最大值,然后拿待插的数和最大值进行比较,小就替换,大就抛弃。如果用二叉树来实现这个容器,那么我们可以在O(logk)实现查找替换操作,对于n个输入数字而言,总的时间效率为O(nlogk)。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int length = input.length;
if(k > length || k == ){
return result;
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
for (int i = ; i < length; i++) {
if (maxHeap.size() != k) {
maxHeap.offer(input[i]);
} else if (maxHeap.peek() > input[i]) {
Integer temp = maxHeap.poll();
temp = null;
maxHeap.offer(input[i]);
}
}
for (Integer integer : maxHeap) {
result.add(integer);
}
return result;
}
}
最大堆直接只用了PriorityQueue实现,它的默认实现是最小堆,改变他的排序方式就可以实现最大堆。
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2.compareTo(o1);
}
});
3.冒泡法
这种方法比较简单,就是时间复杂度为O(n*k),稍高
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf
来源:牛客网 public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (k > input.length) {
return al;
}
for (int i = ; i < k; i++) {
for (int j = ; j < input.length - i - ; j++) {
if (input[j] < input[j + ]) {
int temp = input[j];
input[j] = input[j + ];
input[j + ] = temp;
}
}
al.add(input[input.length - i - ]);
}
return al;
}
30.连续子数组的最大和
HZ偶尔会拿些专业问题来忽悠那些非计算机专业的同学。今天测试组开完会后,他又发话了:在古老的一维模式识别中,常常需要计算连续子向量的最大和,当向量全为正数的时候,问题很好解决。但是,如果向量中包含负数,是否应该包含某个负数,并期望旁边的正数会弥补它呢?例如:{6,-3,-2,7,-15,1,2,2},连续子向量的最大和为8(从第0个开始,到第3个为止)。你会不会被他忽悠住?(子向量的长度至少是1)
1.两个循环遍历,时间复杂度为O(n2)
public class Solution {
public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
double max = -1.0/0.0;
for(int i = ;i<array.length;i++){
double submax = -1.0/0.0;
int sum = ;
for (int j=i;j<array.length;j++){
sum = sum + array[j];
if(sum > submax)
submax = sum;
}
if(submax>max)
max = submax;
}
return (int)max;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
int max = array[];
for(int i = ;i<array.length;i++){
int submax = array[i];
int sum = array[i];
for (int j=i+;j<array.length;j++){
sum = sum + array[j];
if(sum > submax)
submax = sum;
}
if(submax>max)
max = submax;
}
return max;
}
}
2.采用动态规划法,时间复杂度为O(n)
public class Solution {
public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
if(array.length == ) return ;
int sum = array[];
int tempsum = array[];
for(int i = ;i<array.length;i++){
tempsum = (tempsum<)?array[i]:tempsum + array[i];
sum = (tempsum > sum) ? tempsum : sum;
}
return sum;
}
}
31.1—n整数中1出现的次数
时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int number = ;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
number = number+numberOf1(i);
}
return number;
}
public int numberOf1(int i){
int number = ;
while( i!= ){
if(i % ==)
number++;
i = i/;
}
return number;
}
}
时间复杂度为O(logn)
//主要思路:设定整数点(如1、10、100等等)作为位置点i(对应n的各位、十位、百位等等),分别对每个数位上有多少包含1的点进行分析
//根据设定的整数位置,对n进行分割,分为两部分,高位n/i,低位n%i
//当i表示百位,且百位对应的数>=2,如n=31456,i=100,则a=314,b=56,此时百位为1的次数有a/10+1=32(最高两位0~31),每一次都包含100个连续的点,即共有(a%10+1)*100个点的百位为1
//当i表示百位,且百位对应的数为1,如n=31156,i=100,则a=311,b=56,此时百位对应的就是1,则共有a%10(最高两位0-30)次是包含100个连续点,当最高两位为31(即a=311),本次只对应局部点00~56,共b+1次,所有点加起来共有(a%10*100)+(b+1),这些点百位对应为1
//当i表示百位,且百位对应的数为0,如n=31056,i=100,则a=310,b=56,此时百位为1的次数有a/10=31(最高两位0~30)
//综合以上三种情况,当百位对应0或>=2时,有(a+8)/10次包含所有100个点,还有当百位为1(a%10==1),需要增加局部点b+1
//之所以补8,是因为当百位为0,则a/10==(a+8)/10,当百位>=2,补8会产生进位位,效果等同于(a/10+1)
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int count=;
int i=;
for(i=;i<=n;i*=)
{
//i表示当前分析的是哪一个数位
int a = n/i,b = n%i;
if(a%==)
count=count+(a+)/*i+a%*(b+);
else
count=count+(a+)/*i;
}
return count;
}
}
32.把数组排成最小的数
题目描述
* 解题思路: * 先将整型数组转换成String数组,然后将String数组排序,最后将排好序的字符串数组拼接出来。关键就是制定排序规则。 * 排序规则如下: * 若ab > ba 则 a > b, * 若ab < ba 则 a < b, * 若ab = ba 则 a = b; * 解释说明: * 比如 "3" < "31"但是 "331" > "313",所以要将二者拼接起来进行比较import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator; public class Solution {
public String PrintMinNumber(int [] numbers) {
/**
* 1.用list装numbers数组中的数
* 2.使用collection.sort进行排序,排序是将str1+""+str2和str2+""+str1的大小进行比较
* 3.将排序后的数组进行拼接
*/
if(numbers == null || numbers.length==) return "";
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i:numbers){
list.add(i);
}
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>(){
public int compare(Integer str1,Integer str2){
String s1 = str1 + "" + str2;
String s2 = str2 + "" + str1;
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
}); StringBuffer sb= new StringBuffer();
for(int i:list)
sb.append(i); return sb.toString(); }
}
33.丑数
题目描述
2*2 3*1 5*1
2*2 3*2 5*1
2*3 3*2 5*1
2*3 3*2 5*2
2*4 3*3 5*2
2*5 3*3 5*2
2*5 3*4 5*2
2*6 3*4 5*3
2*8 3*5 5*3
2*8 3*6 5*4
public class Solution {
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if(index<)
return index;
int[] ret = new int[index];
ret[] =;
int t2 = ;int t3= ; int t5=;
for(int i=;i<index;i++){
ret[i]=Math.min(Math.min(ret[t2]*, ret[t3]*), ret[t5]*);
if(ret[i] == ret[t2]*) t2++;
if(ret[i] == ret[t3]*) t3++;
if(ret[i] == ret[t5]*) t5++;
}
return ret[index-];
}
}
34.第一次只出现一次的字符
题目描述
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
if(str == null || str.length() == )
return -;
char[] strArray = str.toCharArray();
LinkedHashMap<Character,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<Character,Integer>();
for(char a:strArray){
if(map.containsKey(a)){
map.put(a, map.get(a)+);
}else
map.put(a, );
} for(char key:map.keySet()){
if(map.get(key)==)
return str.indexOf(key);
}
return -;
}
}
35.数组中的逆序对
题目描述
public class Solution {
public int InversePairs(int [] array) {
if(array==null||array.length==)
{
return ;
}
int[] copy = new int[array.length];
for(int i=;i<array.length;i++)
{
copy[i] = array[i];
}
int count = InversePairsCore(array,copy,,array.length-);//数值过大求余
return count;
}
private int InversePairsCore(int[] array,int[] copy,int low,int high)
{
if(low==high)
{
return ;
}
int mid = (low+high)>>;
int leftCount = InversePairsCore(array,copy,low,mid)%;
int rightCount = InversePairsCore(array,copy,mid+,high)%;
int count = ;
int i=mid;
int j=high;
int locCopy = high;
while(i>=low&&j>mid)
{
if(array[i]>array[j])
{
count += j-mid;
copy[locCopy--] = array[i--];
if(count>=)//数值过大求余
{
count%=;
}
}
else
{
copy[locCopy--] = array[j--];
}
}
for(;i>=low;i--)
{
copy[locCopy--]=array[i];
}
for(;j>mid;j--)
{
copy[locCopy--]=array[j];
}
for(int s=low;s<=high;s++)
{
array[s] = copy[s];
}
return (leftCount+rightCount+count)%;
}
}
没看懂。。。
剑指offer编程题66道题 26-35的更多相关文章
- 剑指offer编程题66道题 36-66
36.两个链表的第一个公共节点 题目描述 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点. 1.具有重合节点的两个链表是一个Y字性,用两个堆栈放这两个链表,从尾部开始遍历,直到遍历到最后一个重合节点. 这种算 ...
- 剑指offer编程题66道题 1-25
1.二维数组中的查找 题目描述 在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数. ...
- 剑指Offer编程题2——替换空格
剑指Offer编程题2——替换空格 题目描述 请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”.例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happ ...
- 剑指Offer编程题1——二维数组中的查找
剑指Offer编程题1---------------二维数组中的查找 题目描述 在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完 ...
- 剑指offer编程题Java实现——面试题12打印1到最大的n位数
题目:打印1到最大的n位数 输入数字n,按顺序打印输出从1到最大的n位十进制数,比如输入3,打印从1到999. 这道题考察的地方是如何表示大数问题.由于n是任意大的数组,如果n太大的话n位数就超过了l ...
- 剑指offer编程题Java实现——面试题12相关题大数的加法、减法、乘法问题的实现
用字符串或者数组表示大数是一种很简单有效的表示方式.在打印1到最大的n为数的问题上采用的是使用数组表示大数的方式.在相关题实现任意两个整数的加法.减法.乘法的实现中,采用字符串对大数进行表示,不过在具 ...
- 剑指offer编程题Java实现——替换空格
题目描述 请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的空格替换成"%20".例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy. package ...
- 剑指offer编程题Java实现——面试题5从头到尾打印链表
题目描述* 剑指offer面试题5:从尾到头打印链表 输入一个链表的头结点,从尾到头打印出每个结点的值 解决方案一:首先遍历链表的节点后打印,典型的"后进先出",可以使用栈来实现这 ...
- 剑指offer编程题Java实现——面试题6重建二叉树
题目: 输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树.假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历结果中都不含重复的数字.例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2, ...
随机推荐
- oracle 里 插入空字符串会被转成null插入
oracle 里 插入空字符串会被转成null插入 因为非空列如果要插入空字符串数据,最好是插个空格,因为空字符串会报错
- C#获取CPU编号
//System.Management;//需要添加引用(系统自带) /// <summary> /// 获取cpu编号 /// </summary> /// <retu ...
- 快速开发微信小程序
image.png 最近婷主在做微信小程序.自己的微信公众号也需要添加点料,乘着这次放假,把微信小程序研究了下.虽然没有做什么很强大的功能,不过好歹自己的公众号也有了微信小程序.够用即可. 1.需要先 ...
- jquery js 动态加载 js文件
jquery方法 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://ww ...
- hdu4691(后缀数组)
算是后缀数组的入门题吧. 思路无比简单,要是直接套模板的话应该很容易秒掉. 关于后缀数组看高中神犇的论文就可以学会了 算法合集之<后缀数组——处理字符串的有力工具> 话说这题暴力是可以过了 ...
- 第一只python爬虫
import urllib.request response = urllib.request.urlopen("http://www.baidu.com") html = res ...
- 修改sudoers权限之后无法sudo的最简单解决方法
网上百度一下进入recovery模式或是单用户模式仍然修改不了sudoers的权限, 后来终于在网上找到了一种最简单的方法,那就是 pkexec chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers
- log4j中将SocketAppender将日志内容发送到远程服务器
1.服务端配置 1)服务端配置文件log4j-server.properties #Define a narrow log category. A category like debug will p ...
- 页面的日志服务 web页面渲染 服务 ; 服务耦合带来的问题
情景: 虽然对web服务做了3节点的负载均衡,但是由于埋点数据的落盘的代码也在相同服务器上,导致当flume处理日志的吞吐量达到瓶颈时,3节点的请求积压,挤占服务器资源,导致接口数据处理迟缓,页面加载 ...
- 文件下载(StreamingHttpResponse流式输出)
文件下载(StreamingHttpResponse流式输出) HttpResponse会直接使用迭代器对象,将迭代器对象的内容存储成字符串,然后返回给客户端,同时释放内存.可以当文件变大看出这是一个 ...
