Adversarial Training with Rectified Rejection
概
通过对置信度进行矫正, 然后再根据threshold (1/2)判断是否拒绝. 有点detection的味道, 总体来说是很有趣的点子.
主要内容
假设一个网络\(f_{\theta}\) 将样本\(x\)映射为概率向量\(f_{\theta}(x)\), 则其置信度(confidence)为
\]
若该样本的真实的标签为\(y\), 进一步定义真实的置信度\(\text{T-Con}\)为
\]
我们进一步定义一个分类器\(F\):
\left \{
\begin{array}{ll}
y^m & \text{if } f_{\theta}(x)[y] \ge \frac{1}{2}, \\
\text{don't know} & \text{if } f_{\theta}(x)[y] < \frac{1}{2}.
\end{array}
\right .
\]
显然这种情况下, 就算\(f\)训练得再糟糕, \(F\)都不会分错(虽然可能大部分都是拒绝判断, 但是拒绝判断在面对对抗样本的时候是有用的).
但是上面的情况是必须知道样本标签\(y\)的, 都知道标签了还弄个分类器不是多次一举. 所以我们现在要做的, 是做一个近似
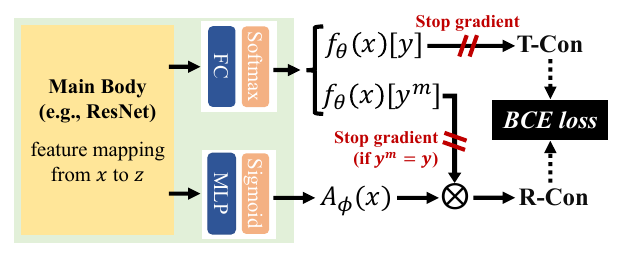
如上图所示, 我们要通过一个近似的\(\text{R-Con}\)来代替\(\text{T-Con}\), Rectified Confidence通过如下的方式构建:
- 通过encoder将\(x\)映为特征\(z\);
- \(z\)通过全连接层和softmax层获得概率向量\(f_{\theta}(x)\);
- \(z\)通过MLP和sigmoid层获得\(A_{\phi}(x) \in [0, 1]\);
- 计算Rectified Confidence:
\[\text{R-Con}(x) = f_{\theta}(x)[y^m]A_{\phi}(x).
\]
显然, 若要\(\text{R-Con}(x) = \text{T-Con}(x)\), 则有
\]
为此, 通过BCE损失:
= \mathbf{BCE}(f_{\theta}(x)[y^m]A_{\phi}(x) \| f_{\theta}(x)[y]) \\
\mathbf{BCE}(f\|g) = g \cdot \log f + (1 - g) \cdot \log (1 - f).
\]
故总的损失为:
x^* = \mathop{\arg \max} \limits_{x' \in B(x)} \mathcal{L}_{A}(x', y; \theta).
\]
注意图中的stop gradient部分, 最上面是为了一个单向的趋近(虽然encoder部分是会依然交涉), 第二个部分作者觉得当\(y^m = y\)时, 该样本比较简单, 而对抗学习应该注中难的样本, 这样不容易陷入局部最优, 经验之谈吧.
rejection
\left \{
\begin{array}{ll}
y^m & \text{if } \text{R-Con}(x) \ge \frac{1}{2}, \\
\text{don't know} & \text{if } \text{R-Con}(x) < \frac{1}{2}.
\end{array}
\right .
\]
现在的疑问是, 什么时候这个分类器是没有错判的.
定义: 当下列界,
- \(|\log (\frac{A_{\phi}(x)}{A_{\phi}^*(x)})| \le \log (\frac{2}{2-\xi})\);
- \(|A_{\phi}(x) - A_{\phi}^*(x)| \le \frac{\xi}{2}\)
至少一个成立时, 称\(A_{\phi}(x)\)在点\(x\)处为\(\xi\text{-error}\), \(\xi \in [0, 1)\).
定理1: 假设\(x_+, x_-\)分别为被\(f\)正判和误判的样本, 即
\]
但均满足(即置信度足够高)
\]
若\(A_{\phi}\)在\(x_+, x_-\)处满足\(\xi\text{-error}\), 则\(\text{R-Con}(x_+) > \frac{1}{2} > \text{R-Con}(x_-)\), 即此时\(F(x_+)\)为正确判断, \(F(x_-)\)拒绝判断.
proof:
界1等价于:
\]
界2等价于
\]
因为
\frac{2-\xi}{2}f(x_+)[y_+] > \frac{1}{2}, \\
f(x)[y] - \frac{\xi}{2} f(x)[y^m] = f(x)[y^m] - \frac{\xi}{2} f(x)[y^m] > \frac{1}{2}.
\]
所以\(\text{R-Con}(x_+) > \frac{1}{2}\).
又因为
\]
易证
\]
\]
故\(\text{R-Con}(x_-) < \frac{1}{2}\).
证毕.
实际使用
在实际使用中, threshold 似乎并不是固定为1/2, 而是通过TPR-FPR曲线选择的(TPR-95).
\left \{
\begin{array}{ll}
y^m & \text{if } \text{R-Con}(x) \ge t, \\
\text{don't know} & \text{if } \text{R-Con}(x) < t.
\end{array}
\right .
\]
代码
Adversarial Training with Rectified Rejection的更多相关文章
- Adversarial Training
原于2018年1月在实验室组会上做的分享,今天分享给大家,希望对大家科研有所帮助. 今天给大家分享一下对抗训练(Adversarial Training,AT). 为何要选择这个主题呢? 我们从上图的 ...
- 《C-RNN-GAN: Continuous recurrent neural networks with adversarial training》论文笔记
出处:arXiv: Artificial Intelligence, 2016(一年了还没中吗?) Motivation 使用GAN+RNN来处理continuous sequential data, ...
- LTD: Low Temperature Distillation for Robust Adversarial Training
目录 概 主要内容 Chen E. and Lee C. LTD: Low temperature distillation for robust adversarial training. arXi ...
- Understanding and Improving Fast Adversarial Training
目录 概 主要内容 Random Step的作用 线性性质 gradient alignment 代码 Andriushchenko M. and Flammarion N. Understandin ...
- Boosting Adversarial Training with Hypersphere Embedding
目录 概 主要内容 代码 Pang T., Yang X., Dong Y., Xu K., Su H., Zhu J. Boosting Adversarial Training with Hype ...
- Uncovering the Limits of Adversarial Training against Norm-Bounded Adversarial Examples
Uncovering the Limits of Adversarial Training against Norm-Bounded Adversarial Examples 目录 概 主要内容 实验 ...
- 论文解读(ARVGA)《Learning Graph Embedding with Adversarial Training Methods》
论文信息 论文标题:Learning Graph Embedding with Adversarial Training Methods论文作者:Shirui Pan, Ruiqi Hu, Sai-f ...
- cs231n spring 2017 lecture16 Adversarial Examples and Adversarial Training 听课笔记
(没太听明白,以后再听) 1. 如何欺骗神经网络? 这部分研究最开始是想探究神经网络到底是如何工作的.结果人们意外的发现,可以只改变原图一点点,人眼根本看不出变化,但是神经网络会给出完全不同的答案.比 ...
- Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Via Domain Adversarial Training For Speaker Recognition
年域适应挑战(DAC)数据集的实验表明,所提出的方法不仅有效解决了数据集不匹配问题,而且还优于上述无监督域自适应方法.
随机推荐
- 日常Java 2021/9/21
将Java数组中的元素前后反转.题目要求:已知一个数组arr = {11,12,13,14,15}用程序实现把该数组中的元素值交换,交换后的数组arr = { 15,14,13,12,11},并输出交 ...
- 日常Java 2021/9/19
Math类方法 package m; public class m { public static void main(String args[]) { //计算平方根 System.out.prin ...
- above, abrupt
above 近义词: over, beyond, exceeding反义词: below, beneath, under, underneath 有从右往左写的文字,没有从下往上的.above-men ...
- pymongdb入门
Pymongo入门 安装 pip install pymongo 连接 实际就是实例化一个客户端对象,然后客户端对象中指定一个库作为库对象,库对象中的集合对象就是之后常用来执行操作的对象 1 ''' ...
- Hive(四)【DML 数据导入导出】
目录 一.数据导入 1.1 [load]--向数据中装载数据 案例 1.2 [insert]--查询语句向表中插入数据 案例 1.3 [as select]--查询语句中创建表且加载数据 案例 1.4 ...
- 前端知识,什么是BFC?
BFC全称是Block Formatting Context,即块格式化上下文.它是CSS2.1规范定义的,关于CSS渲染定位的一个概念.要明白BFC到底是什么,首先来看看什么是视觉格式化模型. 视觉 ...
- Android 开源框架Universal-Image-Loader加载https图片
解决方案就是 需要 android https HttpsURLConnection 这个类忽略证书 1,找到 Universal-Image-Loader的library依赖包下面com.nostr ...
- JmxTest
package mbeanTest; import java.util.Set; import javax.management.Attribute; import javax.management. ...
- fastjson过滤多余字段
/** * Description:过滤实体中的字段 * @param src 需要过滤的对象,如 list,entity * @param clazz 实体的class ...
- D3基础入门四-事件处理
6.5.0版 .on("mouseover", function(e,d) e: {"isTrusted":true} 第二个参考才是数据,但这在不同的环境可能 ...
