Linux-ansible批量管理
1.ansible批量管理服务概念
(1)是基于Python语言开发的自动化软件工具
(2)是基于SSH远程管理服务实现远程主机批量管理
2.ansible批量管理服务意义
(1)提高工作的效率
(2)提高工作准确度
(3)减少维护的成本
(4)减少重复性工作
3.ansible批量管理服务功能
(1)可以实现批量系统操作配置
(2)可以实现批量软件的部署
(3)可以实现批量文件数据分发
(4)可以实现批量系统信息收集
4.ansible批量管理的特点
- 管理端不需要启动服务程序(no server)
- 管理端不需要编写配置文件(/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg)
- 受控端不需要安装软件程序(libselinux-python)
- 被管理端selinux服务没有关闭 — 影响ansible软件的管理
- libselinux-python让selinux开启的状态也可以使用ansible程序
- 受控端不需要启动服务程序(no agent)
- 服务程序管理操作模块众多(module)
- 利用剧本编写来实现自动化(playbook)
5.ansible批量管理服务部署
管理端服务器
(1)安装部署软件
[root@m01 ~]# yum install -y ansible --------需要配置epel源
/etc/ansible -----主程序目录
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg -----配置文件
/etc/ansible/hosts ----- 主机清单配置文件
/etc/ansible/roles ----- 角色目录
(2)编写主机清单文件(/etc/ansible/hosts)
a.根据主机进行编写
[root@m01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
172.16.1.61
172.16.1.7
b.主机分组编写
[shuai]
172.16.1.41
172.16.1.31
172.16.1.7
c.主机名符号匹配编写
[shuai]
172.16.1.[41:43] #代表172.16.1.42-43
web[01:03] #代表web01-03,要做hosts做主机名解析
d.跟上非标准远程端口
[shuai]
172.16.1.41:52113 #52113代表ssh远程管理端口
f.主机使用特殊的变量
[shuai]
172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_port=52113 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456
[shuai]
web01 ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7 ansible_ssh_port=52113 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=123456
g.主机组嵌入式配置
#########################################################
[rsync:children] --- 嵌入子组信息 #
rsync_server #
rsync_client #
#
[rsync_server] #
172.16.1.41 #
#
[rsync_client] #
172.16.1.31 #
172.16.1.7 #
###########################################################
[shuai:vars] --- 对shuai组进行嵌入式变量 #
ansible_ssh_host=172.16.1.7 #
ansible_ssh_port=52113 #
ansible_ssh_user=root #
ansible_ssh_pass=123456 #
[shuai] #
web01 #
###########################################################
(3)测试是否可以管理主机
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -a "hostname"
172.16.1.31 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
nfs01
172.16.1.41 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
backup
172.16.1.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
web01
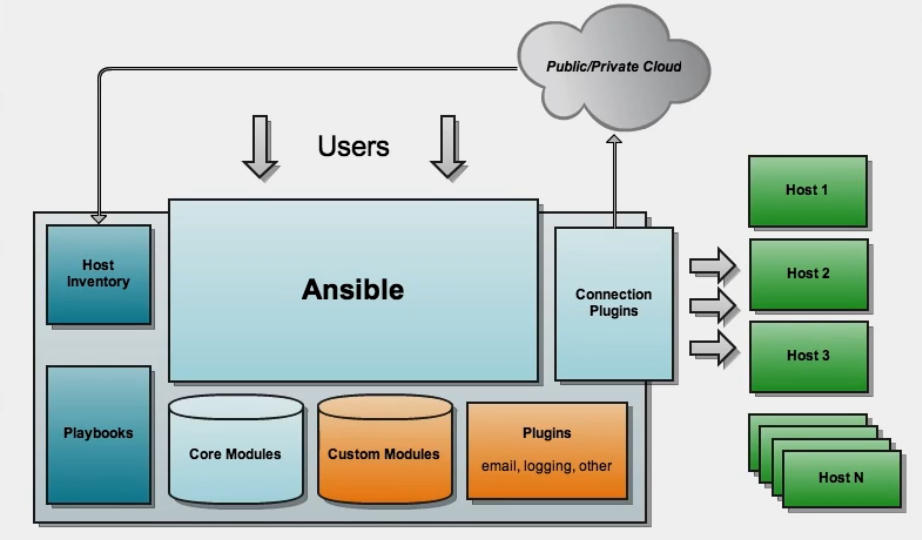
(4)ansible服务架构介绍
a.主机清单信息
b.软件模块信息
c.基于秘钥连接主机
d.软件剧本功能playbook
(5)ansible软件模块应用
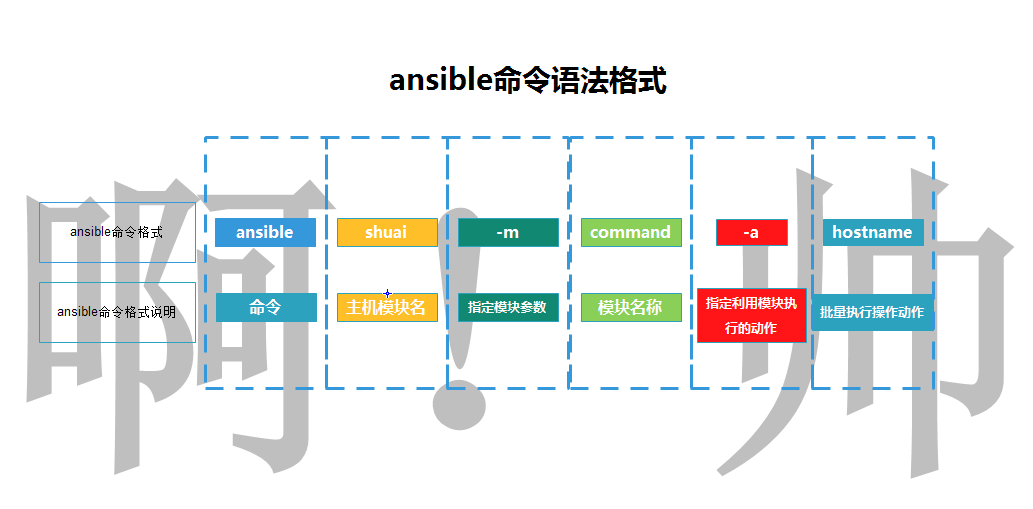
模块应用的语法格式
ansible 主机名称|主机组|主机地址信息|all -m(指定应用的模块信息) 模块名称 -a(指定动作信息) "动作执行"
例如:
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -m command -a "hostname"
6.ansible常用模块介绍
6.1 command模块
a.chdirChange into this directory before running the command #在命令执行之前切换目录
[root@m01 ~]# ansible shuai -m command -a "chdir=/tmp touch shuai.txt"
b.creates If it already exists, this step won’t be run. #如果它已经存在,则不会运行此步骤 ,做判断
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m command -a "creates=/tmp/shuai.txt chdir=/tmp touch shuai.txt"
#如果172.16.1.7远程主机的/tmp目录没有shuai.txt文件则在/tmp文件下创建shuai.txt。如果有则跳过
c.removes If it already exists, this step will be run. #如果文件存在,这个步骤将执行
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m command -a "removes=/tmp/shuai.txt chdir=/tmp touch shuai.txt"
command模块注意事项:
1.有些特殊符号无法识别: "<", ">", "|", ";" "&"
2.命令模块后使用空格分隔的参数。
3.命令将在所有选定的节点上执行
6.2 shell模块(万能模块)
a.chdirChange into this directory before running the command #在命令执行之前切换目录
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m shell -a "chdir=/tmp touch shuai01.txt"
b.creates If it already exists, this step won’t be run. #如果它已经存在,则不会运行此步骤 ,做判断
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m shell -a "creates=/tmp/shuai01.txt chdir=/tmp touch shuai02.txt"
c.removes If it already exists, this step will be run. #如果文件存在,这个步骤将执行
c.removes If it already exists, this step will be run. #如果文件存在,这个步骤将执行
6.3script脚本模块
a.chdirChange into this directory before running the command #在命令执行之前切换目录
b.creates If it already exists, this step won’t be run. #如果它已经存在,则不会运行此步骤 ,做判断
c.removes If it already exists, this step will be run. #如果文件存在,这个步骤将执行脚本
[root@m01 /scripts]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m script -a "/scripts/yum.sh"
6.3 copy模块 Copy files to remote locations拷贝文件到远程主机
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.7 -m copy -a "src=/scripts/yum.sh dest=/tmp/"
172.16.1.7 | CHANGED => { ------->在那台主机上操作
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true, ------->是否做了改变(true|false)
"checksum": "de2b2980db930dc11f23774899494c89a8bc4206", ------->生成一个校验码
"dest": "/tmp/yum.sh", ------->显示目标路径信息
"gid": 0, ------->显示文件的gid信息
"group": "root", ------->显示文件的用户组信息
"md5sum": "840212375ea9201ff1aaed70575f1fd5", ------->生成一个校验码
"mode": "0644", ------->显示复制后权限
"owner": "root", ------->显示复制后拥有者
"size": 33, ------->显示文件的大小
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1597911358.94-17987-220899881277199/source",
"state": "file", ------->显示文件的类型信息
"uid": 0 ------->显示文件的uid信息
}
ownerName of the user that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to chown. #在传输文件是改变文件的属主
[root@m01 ~]# ll 1000
-rw-------. 1 root root 884 May 22 2019 1000
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m copy -a "src=/root/1000 dest=/tmp/ owner=shuai"
[root@web01 /tmp]# ll /tmp/1000
-rw-r--r-- 1 shuai root 884 Aug 20 16:28 /tmp/1000
groupName of the group that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to chown. #在传输文件是改变文件的属组
[root@m01 ~]# ll 1000
-rw-------. 1 root root 884 May 22 2019 1000
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m copy -a "src=/root/1000 dest=/tmp/ group=shuai"
[root@web01 /tmp]# ll /tmp/1000
-rw-r--r-- 1 shuai shuai 884 Aug 20 16:28 /tmp/1000
modeThe permissions of the destination file or directory. #在传输文件是改变文件的权限
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m copy -a "src=/root/1000 dest=/tmp/1000 mode=755"
backupCreate a backup file including the timestamp information so you can get the original file back if you somehow clobbered it incorrectly #创建一个包含时间戳信息的备份文件,这样,如果不正确地删除了原始文件,就可以将其取回。 (默认为no)
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m copy -a "src=/root/1000 dest=/tmp/ backup=yes"
content #在远程主机生成文件
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m copy -a "content=你真帅! dest=/tmp/shuai0 2.txt"
[root@web01 ~]# cat /tmp/shuai02.txt
你真帅!
remote_src #scr参数指定文件信息,会从远程主机上进行查找
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m copy -a "src=/root/shuai.txt dest=/tmp/ remote_src=yes"
[root@web01 ~]# echo "你真丑" >> shuai.txt
[root@web01 ~]# cat /tmp/shuai.txt
你真丑
directory_mode #递归的设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限match
follow #当拷贝的文件夹内有link存在的时候,那么拷贝过去的也会有link
local_follow#是否遵循本地机器中的文件系统链接
6.4 file 文件模块
[root@m01 ~/shuai]# ansible a -m file -a "dest=/tmp/shuai/ owner=shuai group=shuai mode=000"
[root@web01 /tmp]# ll
d--------- 7 shuai shuai 155 Aug 21 11:28 shuai
可以利用模块创建数据信息 (文件 目录 链接文件)
state 参数
=absent — 删除数据信息
=directory — 创建一个目录信息
=file — 检查创建的数据信息是否存在 (绿色存在 红色不存在)
=hard — 创建一个硬链接文件
=link — 创建一个软链接文件
=touch — 创建一个文件信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m file -a "dest=/shuai/shuai.txt state=absent"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible 172.16.1.31 -m file -a "dest=/shuai/ state=directory"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m file -a "dest=/shuai state=file"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m file -a "src=/shuai/shuai.txt dest=/shuai/shuai_hard.txt state=hard"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m file -a "src=/shuai/shuai.txt dest=/shuai/shuai_link.txt state=link"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m file -a "dest=/shuai/shuai.txt state=touch"
recurse归修改文件权限
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m file -a "dest=/shuai/ owner=shuai mode=133 recurse=yes"
[root@web01 /shuai]# ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Aug 21 16:09 shuai.txt
[root@web01 /shuai]# ll -d
d--x-wx-wx 2 shuai root 23 Aug 21 16:09 .
[root@web01 /shuai]# ll
total 0
---x-wx-wx 1 shuai root 0 Aug 21 16:09 shuai.txt
6.5 fetch模块 ( 拉取模块)
| 参数 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| src | 要拉取的目标文件位置 |
| dest | 本地存储目录文章 |
[root@m01 ~/shuai]# ansible a -m fetch -a "src=/root/shuai/fatch.txt dest=/tmp"
[root@m01 ~]# tree /tmp
/tmp
├── 172.16.1.7
│ └── root
│ └── shuai
│ └── fatch.txt
6.6 yum模块 批量安装软件
| 参数 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| name | 安装软件的名称 |
| state | installed 安装 present 安装 latest 安装 absent 卸载 removed 卸载 |
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m yum -a "name=tcpdump state=installed"
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m yum -a "name=tcpdump state=removed" ---卸载软件
6.7 service模块 (管理服务的运行状态)
| 参数 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| name | 服务名称 |
| state | started 开启 stopped 停止 restarted 重启 reloaded 平滑重启 |
| enable |
yes 是 no 否 |
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m service -a "name=nfs state=started enable=yes"
6.8 cron模块 (批量设置多个主机的定时任务模块)
| 参数 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| minute | Minute when the job should run ( 0-59, *, */2, etc ) 分钟 |
| month | Month of the year the job should run ( 1-12, *, */2, etc ) 月 |
| hour | Hour when the job should run ( 0-23, *, */2, etc ) 小时 |
| day | Day of the month the job should run ( 1-31, *, */2, etc ) 天 |
| weekda | Day of the week that the job should run ( 0-6 for Sunday-Saturday, *, etc ) 周 |
| job | 用于定义定时任务需要做的事情 |
| name | 定时任务添加注释信息 |
| state | absent 删除定时任务 present 新建定时任务(默认不用添加) |
| disabled | yes 注释定时任务 no 开启定时任务 |
(1)批量创建定时任务
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m cron -a "minute=*/2 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com > /dev/null 2>&1' name='sync time'"
[root@web01 ~/shuai]# crontab -l
#Ansible: sync time
*/2 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com > /dev/null 2>&1
(2)删除定时任务(只能是ansible创建的才可以批量删除)
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m cron -a "name='sync time' state=absent
(3)注释定时任务(只能是ansible创建的才可以批量注释)
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m cron -a "job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com > /dev/null 2>&1' name='sync time' disabled=yes"
[root@web01 ~/shuai]# crontab -l
#Ansible: sync time
#* * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp1.aliyun.com > /dev/null 2>&1
6.9 mount模块 (批量挂载模块)
| 参数 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| src | 需要挂载的存储设备或文件信息 |
| path | 指定目标挂载点目录 |
| fstype | 指定挂载时的文件系统类型 |
| state | present 不会立即挂载,修改fstab,实现开机自动挂载 mounted 立即挂载,并且实现开机自动挂载 absent 立即卸载,fstab也会删除 unmounted 立即卸载,fstab不会被删除,下次开机自动挂载 |
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m mount -a "src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/mnt fstype=nfs state=mounted"
[root@web01 ~]# df -h | tail -1
172.16.1.7:/data 50G 1.7G 49G 4% /mnt
7. user模块
| 参数 | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
| name | 用户名 |
| uid | 用户uid |
| group | 用户组 |
| groups | 附加到另一个组 |
| password | 密码 |
| shell | 解释器 |
| create_home | yes 创建家目录(默认是yes) no 不创建家目录 |
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m user -a "name=rsync create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin"
[root@web01 ~]# id rsync
uid=1002(rsync) gid=1002(rsync) groups=1002(rsync)
(1) 给指定用户创建密码 PS: 利用ansible程序user模块设置用户密码信息,需要将密码明文信息转换为密文信息进行设置 生成密文密码信息方法: 方法一:
ansible all -i localhost, -m debug -a "msg={{ '密码信息123456' | password_hash('sha512', 'shuai') }}"
##演示
[root@m01 ~]# ansible all -i localhost, -m debug -a "msg={{ '123456' | password_hash('sha512', 'shuai') }}"
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"msg": "$6$shuai$CcqYhe8GgtTbQFxbarWVJAAt.02WAVe03DQEc9tSH0oK0oW3bm6M0gsHUmaw4KDkgul2U9kLzN1Bde54J7nA7/"
}
方法二:
[root@m01 ~]# yum install -y python-pip
[root@m01 ~]# pip install passlib
[root@m01 ~]# python -c "from passlib.hash import sha512_crypt; import getpass; print(sha512_crypt.using(rounds=5000).hash(getpass.getpass()))"
Password:
$6$DUHCNOQ58xnSFVB/$Csd36ECimmg2DPgYfD5doEEfyD.ZBt5zKQeGXyA6fOTrWVinKp7Wy5mx6IEtTKlgIsABoKaRYsadcTKnFPvhG1
[root@m01 ~]# ansible a -m user -a "name=shuai password='$6$oldboy$MVd3DevkLcimrBLdMICrBY8HF82Wtau5cI8D2w4Zs6P1cCfMTcnnyAmmJc7mQaE9zuHxk8JFTRgYMGv9uKW7j1'"
7.剧本的编写方法
7.1剧本的作用:一键化完成多个任务
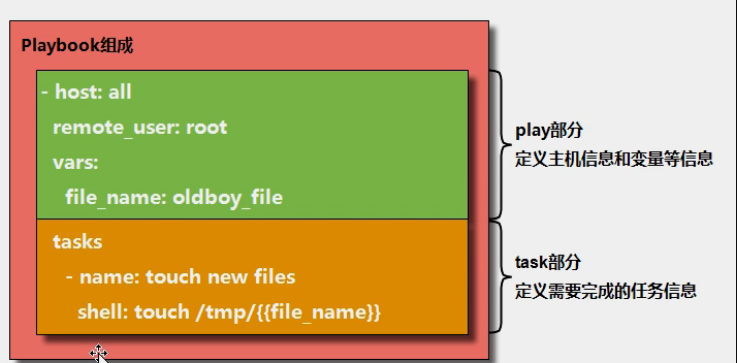
7.2剧本的组成部分:
| 模块 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| hosts | 定义主机 |
| tasks |
任务 |
7.3剧本的编写规范(yaml)
7.3.1.合理的缩进信息,两个空格表示一个缩进关系
标题一
标题二
标题三
7.3.2.冒号的使用方法,冒号后边要跟空格
hosts: 172.16.1.7
tasks:
yum: name=rsync #ps:以冒号结尾,冒号信息出现在注释说明中,后面不需要加上空格
7.3.3.短横线的使用(-)列表功能
- 张三
男
- 打游戏
- 运动
- 李四
女
学习
北京
- 王五
男
运动
天津
#ps:使用短横线构成列表信息,短横线后面需要有空格
7.4开始编写剧本
rsync剧本
[root@m01 /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook]# cat rsync_server.yaml
- hosts: 172.16.1.7
tasks:
- name: 1.服务端安装rsync
yum: name=rsync state=installed
- name: 2.将配置文件推送到客户端
copy: src=/tmp/rsyncd.conf dest=/etc/
- name: 3.创建rsync虚拟用户
user: name=rsync create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin
- name: 创建目录并修改目录属主属组
file: dest=/backup state=directory owner=rsync group=rsync
- name: 创建密码文件并修改权限
copy: content='rsync_backup:shuai123' dest=/etc/rsync.password mode=600
- name: 启动服务并设置为开机自启
service: name=rsyncd.service state=started enabled=yes
- hosts: 172.16.1.61
tasks:
- name: 创建密码文件并修改权限
copy: content='shuai123' dest=/etc/rsync.password mode=600
- name: 检查测试
shell: rsync -avz /etc/hosts rsync_backup@172.16.1.7::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password
7.4.1执行剧本
#######################检查剧本格式#################################
[root@m01 /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check rsync_server.yaml
playbook: rsync_server.yaml
######################模拟执行######################################
[root@m01 /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook]# ansible-playbook -C rsync_server.yaml
######################执行剧本#####################################
[root@m01 /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook]# ansible-playbook rsync_server.yaml
NFS剧本
[root@m01 /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook]# cat nfs_server.yaml
- hosts: 172.16.1.7
tasks:
- name: 1.服务端安装软件
yum:
name=nfs-utils state=installed
name=rpcbind state=installed
- name: 2.推送nfs的配置文件
copy: src=/tmp/exports dest=/etc/
- name: 3.创建目录并修改权限
file: dest=/data state=directory owner=nfsnobody group=nfsnobody
- name: 4.启动服务并设置开机自启
service:
name=rpcbind.service enabled=yes
name=nfs enabled=yes
- hosts: 172.16.1.61
tasks:
- name: 1.客户端下载软件
yum: name=nfs-utils state=installed
- name: 2.远程挂载
mount: src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/mnt fstype=nfs state=mounted
8.剧本功能实践介绍
8.1编写剧本的重要功能介绍
a. 在剧本中设置变量信息
方式一:直接在剧本文件编写
vars:
shuai01:data01
shuai02:data02 方式二:在命令行中进行指定
ansible-playbook -e shuai01=data01 -e shuai02=data02 rsync_server.yaml
方式三:在主机清单文件编写
[shuai]
172.16.1.61
172.16.1.7
[shuai:vars]
shuai01=/data
####三种方式的优先级####
最优先:命令行变量设置
次优先:剧本中变量设置
最后:主机清单变量设置
如何全局设置变量: roles 剧本整合
b. 在剧本中设置注册信息 (执行剧本时,可以显示输出命令结果信息)
- hosts: 172.16.1.61
tasks:
- name: 1.客户端下载软件
yum: name=nfs-utils state=installed
- name: 2.远程挂载
mount: src=172.16.1.7:/data path=/mnt fstype=nfs state=mounted
- name: 3.查看结果
shell: df -h|tail -1
register: check_mount #将输出及结果定义变量
- name: 显示结果
debug: msg={{ check_mount.stdout_lines }} #调用变量
c. 在剧本中设置判断信息
获取内置变量的方法
[root@m01 /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook]# ansible a -m setup -a "filter=ansible_hostname"
172.16.1.7 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_hostname": "web01",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
#########获取子项的方法#############
ansible_eth0[ipv4] -----添加到剧本才生效
| 主机信息 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| ansible_all_ipv4_addresses: | 仅显示ipv4的信息。 |
| ansible_devices: | 仅显示磁盘设备信息 |
| ansible_distribution: | 显示是什么系统,例:centos,suse等 |
| ansible_distribution_major_version: | 显示是系统主版本 |
| ansible_distribution_version: | 仅显示系统版本。 |
| ansible_machine: | 显示系统类型,例:32位,还是64位。 |
| ansible_eth0: | 仅显示eth0的信息。 |
| ansible_hostname: | 仅显示主机名。 |
| ansible_kernel: | 仅显示内核版本 |
| ansible_lvm: | 显示lvm相关信息 |
| ansible_memtotal_mb: | 显示系统总内存。 |
| ansible_memfree_mb: | 显示可用系统内存 |
| ansible_memory_mb: | 详细显示内存情况。 |
| ansible_swaptotal_mb: | 显示总的swap内存 |
| ansible_swapfree_mb: | 显示swap内存的可用内存 |
| ansible_mounts: | 显示系统磁盘挂载情况 |
| ansible_processor: | 显示cpu个数(具体显示每个cpu的型号) |
| ansible_processor_vcpus: | 显示cpu个数(只显示总的个数)。 |
例子:
- hosts: a
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Check File
file: path=/tmp/this_is_{{ ansible_hostname }}_file state=touch
when: (ansible_hostname == "nfs") or (ansible_hostname == "backup") - name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=installed
when: (系统情况 == "CentOS") - name: install httpd2
yum: name=httpd2 state=installed
when: (系统情况 == "ubuntu")
d. 在剧本中设置循环信息
vim test04.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Add Users
user: name={{ item.name }} groups={{ item.groups }} state=present
with_items:
- { name: 'testuser1', groups: 'bin' }
- { name: 'testuser2', groups: 'root' }
vim test05.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Installed Pkg
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- wget
- tree
- lrzsz
f. 在剧本中设置错误忽略
vim test06.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Ignore False
command: /bin/false
ignore_errors: yes #忽略错误继续执行
- name: touch new file
file: path=/tmp/oldboy_ignore state=touch
g 在剧本中设置标签信息(单独调试某一个name时需要)
- hosts: oldboy
ignore_errors: yes
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Check File
file: path=/tmp/this_is_{{ ansible_hostname }}_file state=touch
when: (ansible_hostname == "nfs01") or (ansible_hostname == "backup")
tags: t1 - name: bad thing
command: ech 123
#ignore_errors: yes
tags: t2 - name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=installed
when: (ansible_all_ipv4_addresses == ["172.16.1.7","10.0.0.7"])
tags: t3 - name: install httpd2
yum: name=httpd2 state=installed
when: (ansible_distribution == "ubuntu")
tags: t4 #指定执行哪个标签任务: ansible-playbook --tags=t2 test05.yml
#跳过指定标签任务: ansible-playbook --skip-tags=t2 test05.yml
h.在剧本中设置触发信息
- hosts: backup
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: 01 Install rsync
yum: name=rsync state=present - name: 02 push config file
copy: src=./file/{{ item.src }} dest=/etc/{{ item.dest }} mode={{ item.mode }}
with_items:
- { src: "rsyncd.conf", dest: "rsyncd.conf", mode: "0644" }
- { src: "rsync.password", dest: "rsync.password", mode: "0600" }
notify: restart rsync server #触发条件
handlers:
- name: restart rsync server #触发器
service: name=rsyncd state=restarted
i. 在剧本中进行剧本整合
方式一:include_tasks: f1.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: f1.yml
- include_tasks: f2.yml
方式二:include: f1.yml
- include:f1.yml
- include:f2.yml
方式三:- import_playbook:
[root@m01 ansible-playbook]# cat main.yml
- import_playbook: base.yml
- import_playbook: rsync.yml
- import_playbook: nfs.yml
- import_playbook: oxxx.yml
- import_playbook: rsync.yml
- import_playbook: nfs.yml
9.ansible角色配置roles
第一个历程: 规范目录结构
cd /etc/ansible/roles
mkdir {rsync,nfs} --- 创建相应角色目录
mkdir {nfs,rsync}/{vars,tasks,templates,handlers,files} --- 创建角色目录下面的子目录
[root@m01 roles]# tree
.
├── nfs
│ ├── files --- 保存需要分发文件目录
│ ├── handlers --- 保存触发器配置文件信息
│ ├── tasks --- 保存要执行的动作信息文件
│ ├── templates --- 保存需要分发模板文件 模板文件中可以设置变量信息
│ └── vars --- 保存变量信息文件
└── rsync
├── files
├── handlers
├── tasks
├── templates
└── vars
第二个历程: 在roles目录中创建相关文件
编写文件流程图:
1) 编写tasks目录中的main.yml文件
vim main.yml
- include_tasks: copy_info.yml
- include_tasks: create_dir.yml
- include_tasks: boot_server.yml
vim copy_info.yml
- name: 01-copy conf file
copy: src=exports dest=/etc
notify: restart nfs server
vim create_dir.yml
- name: 02-create data dir
file: path={{ Data_dir }} state=directory owner=nfsnobody group=nfsnobody
vim boot_server.yml
- name: 03-boot server
service: name={{ item }} state=started enabled=yes
with_items:
- rpcbind
- nfs
2) 编写vars目录中的main.yml文件
[root@m01 vars]# vim main.yml
Data_dir: /data
3) 编写files目录中的文件
[root@m01 files]# ll
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 29 May 17 15:23 exports
4) 编写handlers目录中的main.yml文件
vim main.yml
- name: restart nfs server
service: name=nfs state=restarted
目录中文件编写好汇总结构
[root@m01 nfs]# tree
.
├── files
│ └── exports
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── templates
└── vars
└── main.yml 第三个历程: 编写一个主剧本文件
[root@m01 roles]# cat site.yml
- hosts: nfs_server
roles:
- nfs-server
- hosts: rsync_server
roles:
- rsync
补充:ansible学习帮助手册如何查看
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -l --模块简介
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc -s command --模块的详细信息
[root@m01 ~]# ansible-doc file --查询模块在剧本中的应用方法
Linux-ansible批量管理的更多相关文章
- Linux(11):期中架构(3)--- SSH远程管理服务 & ansible 批量管理服务
SSH远程管理服务 1. 远程管理服务知识介绍 # 1.1 SSH远程登录服务介绍说明 SSH是Secure Shell Protocol的简写,由 IETF 网络工作小组(Network Worki ...
- 六.ansible批量管理服务
期中集群架构-第六章-ansible批量管理服务介绍====================================================================== 01. ...
- Ansible 批量管理Windows Server服务器
Ansible批量管理Windows Server Ansible是一款为类Unix系统开发的自由开源的配置和自动化工具, 它用Python写成,类似于saltstack和Puppe ...
- ansible批量管理服务 上
1 ansible简介 1.1 ansible批量管理服务概述 (1)是基于python语言开发的自动化软件工具(2)是基于SSH远程管理服务实现远程主机批量管理(3)并行管理,部署简单,应用也简单方 ...
- windows下运行的linux服务器批量管理工具(带UI界面)
产生背景: 由于做服务器运维方面的工作,需要一人对近千台LINUX服务器进行统一集中的管理,如同时批量对LINUX服务器执行相关的指令.同时批量对LINUX服务器upload程序包.同时批量对LINU ...
- 使用ansible批量管理远程服务器
使用ansible批量管理远程服务器 背景 本地需要管理远程的一批服务器,主要执行以下任务: 1) 将本地的文件复制到远端所有服务器: 2) 需要在远程服务器中执行一个个命令: 远端服务器路径并非完全 ...
- Linux下批量管理工具pssh安装和使用
Linux下批量管理工具pssh安装和使用 pssh工具包 安装:yum -y install pssh pssh:在多个主机上并行地运行命令 pscp:把文件并行地复制到多个主机上 prsync:通 ...
- Linux中ansible批量管理软件部署及剧本编写
服务器版本信息: Centos6.9 [root@db02 ~]# uname -a Linux db02 2.6.32-696.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue Mar 21 19:29: ...
- Linux系统——Ansible批量管理工具
批量管理工具: (1)ansible 操作简单(适用于500台以下服务器) (2)saltstack 比较复杂(一般适用于1000-4w台服务器) (3)puppet超级复杂 systemctl(统一 ...
- linux运维、架构之路-ansible批量管理
一.ansible软件 1.介绍 ①ansible是一个基于Python开发的自动化运维工具 ②其功能实现基于SSH远程连接服务 ③ansible可以实现批量系统配置.批量软件部署.批量文件拷贝.批量 ...
随机推荐
- golang:net/http理解总结
Go语言标准库内建提供了net/http包,涵盖了HTTP客户端和服务端的具体实现.使用net/http包,我们可以很方便地编写HTTP客户端或服务端的程序. http服务端的创建流程 在使用http ...
- [OS] 汇编语言
操作系统 每个进程拥有一片连续的内存空间(地址空间),空间中的每个字节都可以用一个32位无符号整数定位,每个字节的位置称为地址 CPU 32位:能够处理的数据最大为32bit,地址空间2^32< ...
- 7.12-7.19 id、w、who、last、lastb、lastlog
7.12-7.19 id.w.who.last.lastb.lastlog 目录 7.12 id:显示用户与用户组的信息 7.13 w:显示已登录用户信息 7.14 who:显示已登录用户信息 显示最 ...
- 嵌入式Boa服务器上CGI开发-(转自Bryce.Xiao)
嵌入式WEB服务器常见的有lighttpd shttpd thttpdboa mathopd minihttpdappwebgoahead=============================== ...
- unity ab包打包和加载的简单学习示例
闲着没事结合项目看了下unity AssetBundle打包和使用,写了一些测试例子,需要的可以拿去,导入一个空项目即可 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1H85dnMNkRoW ...
- Django中数据库操作相关的错误
问题:字段修改属性发生错误 1> >python manage.py makemigrations You are trying to add a non-nullable field ' ...
- 使用指定源安装python包
对于经常需要按照那个python包的同学,外网下载比较慢的话,可以使用公司内部的镜像进行安装 eg: pip install django -i http://mirrors.***.com.cn/p ...
- Jupyter Notebook出现kernel error情况
今天重新装了anaconda,在运行时发现真快,可是在运行selenium的代码时候,发现自己按照以前写得帖子得步骤做,同样还是出现了错误,心里不免大吃一惊,难道我的做法是错的?等到发现有个 ker ...
- Lidar激光雷达市场
Lidar激光雷达市场 近年来,激光雷达技术在飞速发展,从一开始的激光测距技术,逐步发展了激光测速.激光扫描成像.激光多普勒成像等技术,如今在无人驾驶.AGV.机器人等领域已相继出现激光雷达的身影. ...
- MLIR多级中间表示概述
MLIR多级中间表示概述 MLIR项目是构建可重用和可扩展的编译器基础设施的一种新方法.MLIR旨在解决软件碎片化问题,改进异构硬件的编译,显著降低构建特定领域编译器的成本,并帮助将现有编译器连接在一 ...
