postgresql高可用集群部署
一、概况
1、概念
pgsql高可用集群采用postgresql+etcd+patroni+haproxy+keepalived等软件实现,以postgresql做数据库,etcd存储集群状态,patroni与etcd结合实现数据库集群故障切换,
haproxy实现数据库高可用(读读写分离),keepalived实现VIP跳转。
2、拓扑图
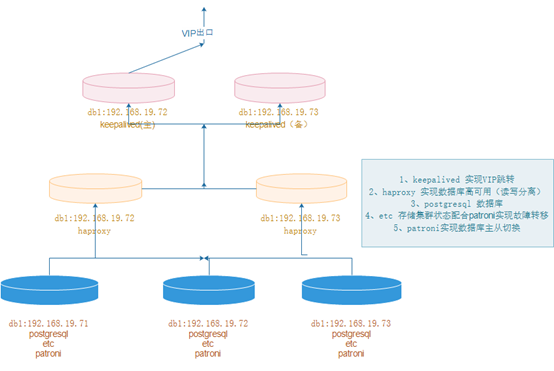
二、postgresql部署(三个节点)
1、下载解压
https://www.enterprisedb.com/download-postgresql-binaries
mkdir -p /data/pg_data
tar xf postgresql-10.18-1-linux-x64-binaries.tar.gz -C /data/
2、创建用户并授权
useradd postgres
passwd postgres
chown -R postgres.postgres /data/
3、初始化数据库(postgres用户下)
切换目录
[root@centos7 ~]# su – postgres
初始化目录
[postgres@centos7 ~]$ /data/pgsql/bin/initdb -D /data/pg_data/
4、配置变量
su – postgres
vim .bash_profile
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin export PATH
export PATH
export PGHOME=/data/pgsql
export PATH=$PATH:$PGHOME/bin
export PGDATA=/data/pg_data
export PGLOG=/data/pg_log/pg.log source .bash_profile
mkdir -p /data/pg_log
chown postgres.postgres /data/pg_data
chown postgres.postgres /data/pg_log
5、配置postgresql启动脚本
vim /etc/systemd/system/postgresql.service
[Unit]
Description=PostgreSQL database server
After=network.target [Service]
Type=forking
User=postgres
Group=postgres
ExecStart= /data/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg_data/ start
ExecReload= /data/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg_data/ restart
ExecStop= /data/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl -D /data/pg_data/ stop
PrivateTmp=true [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
6、启动与关闭
systemctl daemon-reload
开启
systemctl start postgresql
关闭
systemctl stop postgresql
重启
systemctl restart postgresql
7、数据库添加密码
[postgres@pgsql-19 ~]$ psql -U postgres -h localhost
postgres=# alter user postgres with password 'P@sswrd';
8、允许远程连接
vim /data/pg_data/pg_hba.conf
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5

vim /data/pg_data/postgresql.conf
listen_addresses = '*'
password_encryption = on
重启数据库
systemctl restart postgresql
三、etcd部署(三个节点)
1、下载解压
tar xf etcd-v3.1.20-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
ln -s /usr/local/etcd-v3.1.20-linux-amd64 /usr/local/etcd
2、文件配置
mkdir -p /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
vim /usr/local/etcd/conf.yml
name: pgsql_1971
data-dir: /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
listen-client-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
advertise-client-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
listen-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2380
initial-advertise-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.71:2380
initial-cluster: pgsql_1971=http://192.168.19.71:2380,pgsql_1972=http://192.168.19.72:2380,pgsql_1973=http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster-token: etcd-cluster-token
initial-cluster-state: new mkdir -p /usr/local/etcd/data/etc
vim /usr/local/etcd/conf.yml
name: pgsql_1972
data-dir: /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
listen-client-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
advertise-client-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
listen-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2380
initial-advertise-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.72:2380
initial-cluster: pgsql_1971=http://192.168.19.71:2380,pgsql_1972=http://192.168.19.72:2380,pgsql_1973=http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster-token: etcd-cluster-token
initial-cluster-state: new mkdir -p /usr/local/etcd/data/etc
vim /usr/local/etcd/conf.yml
name: pgsql_1973
data-dir: /usr/local/etcd/data/etcd
listen-client-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
advertise-client-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
listen-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-advertise-peer-urls: http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster: pgsql_1971=http://192.168.19.71:2380,pgsql_1972=http://192.168.19.72:2380,pgsql_1973=http://192.168.19.73:2380
initial-cluster-token: etcd-cluster-token
initial-cluster-state: new
3、启动并加入到开机自启中
加入开机自启里边
nohup /usr/local/etcd/etcd --config-file=/usr/local/etcd/conf.yml &
4、集群检查
netstat -lntup|grep etcd
/usr/local/etcd/etcdctl member list
四、patroni部署(三个节点)
1、更新postgresql.conf文件
postgresql.conf配置如下 max_connections = '500'
max_wal_senders = '10'
port = '5432'
listen_addresses = '*'
synchronous_commit = on
full_page_writes = on
wal_log_hints = on
synchronous_standby_names = '*'
max_replication_slots = 10
wal_level = replica
注:这两个参数会导致数据库执行呆滞,后来者欢迎留言看是怎么回事儿
2、更新pg_hba.conf文件
vim /data/pg_data/pg_hba.conf
清理最后配置的配置,新增以下
local all all peer
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host all postgres 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host all all 192.168.19.0/24 md5
host all all ::1/128 md5
local replication replicator peer
host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host replication replicator ::1/128 md5
host replication replicator 192.168.19.71/32 md5
host replication replicator 192.168.19.72/32 md5
host replication replicator 192.168.19.73/32 md5
以上配置完成后,重启数据库
3、在主节点上创建复制槽,很重要,patroni会用到
postgres=# create user replicator replication login encrypted password '1qaz2wsx';
4、配置stream replication(在两个从节点操作)
systemctl stop postgresql
su - postgres
cd /data/ && rm -rf pg_data
/data/pgsql/bin/pg_basebackup -h 192.168.19.71 -D /data/pg_data -U replicator -v -P -R
启动数据库
systemctl start postgresql
5、安装patroni(三个节点)
yum install -y python3 python-psycopg2 python3-devel
pip3 install --upgrade pip
pip3 install psycopg2-binary -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
pip3 install patroni[etcd] -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com 验证是否安装成功 which patroni
patronictl --help
6、创建patroni配置文件
mkdir -p /usr/patroni/conf
cd /usr/patroni/conf/
node1 scope: batman
namespace: /service/
name: postgresql1 restapi:
listen: 192.168.19.71:8008
connect_address: 192.168.19.71:8008
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# authentication:
# username: username
# password: password # ctl:
# insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 192.168.19.71:2379
#Or use "hosts" to provide multiple endpoints
#Could be a comma separated string:
#hosts: host1:port1,host2:port2
#host: 192.168.19.71:2379,192.168.19.71:2379,192.168.19.73:2379
#or an actual yaml list:
#hosts:
#- host1:port1
#- host2:port2
#Once discovery is complete Patroni will use the list of advertised clientURLs
#It is possible to change this behavior through by setting:
#use_proxies: true #raft:
# data_dir: .
# self_addr: 192.168.19.71:2222
# partner_addrs:
# - 192.168.19.71:2223
# - 192.168.19.71:2224 bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
# master_start_timeout: 300
# synchronous_mode: false
#standby_cluster:
#host: 192.168.19.71
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
# use_slots: true
parameters:
# wal_level: hot_standby
# hot_standby: "on"
# max_connections: 100
# max_worker_processes: 8
# wal_keep_segments: 8
# max_wal_senders: 10
# max_replication_slots: 10
# max_prepared_transactions: 0
# max_locks_per_transaction: 64
# wal_log_hints: "on"
# track_commit_timestamp: "off"
# archive_mode: "on"
# archive_timeout: 1800s
# archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
# recovery_conf:
# restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p # some desired options for 'initdb'
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
# For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
#- host replication replicator 192.168.19.71/32 gss include_realm=0
#- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- host replication replicator 192.168.19.71/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# - hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
# post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb postgresql:
listen: 192.168.19.71:5432
connect_address: 192.168.19.71:5432
data_dir: /data/pg_data
bin_dir: /data/pgsql/bin
# config_dir:
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: 1qaz2wsx
superuser:
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
# Server side kerberos spn
# krbsrvname: postgres
parameters:
# Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
# same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
# krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
unix_socket_directories: '.'
# Additional fencing script executed after acquiring the leader lock but before promoting the replica
#pre_promote: /path/to/pre_promote.sh #watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: /dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5 tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
node2 scope: batman
namespace: /service/
name: postgresql2 restapi:
listen: 192.168.19.72:8008
connect_address: 192.168.19.72:8008
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# authentication:
# username: username
# password: password # ctl:
# insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 192.168.19.72:2379
#Or use "hosts" to provide multiple endpoints
#Could be a comma separated string:
#hosts: host1:port1,host2:port2
#host: 192.168.19.71:2379,192.168.19.72:2379,192.168.19.73:2379
#or an actual yaml list:
#hosts:
#- host1:port1
#- host2:port2
#Once discovery is complete Patroni will use the list of advertised clientURLs
#It is possible to change this behavior through by setting:
#use_proxies: true #raft:
# data_dir: .
# self_addr: 192.168.19.72:2222
# partner_addrs:
# - 192.168.19.72:2223
# - 192.168.19.72:2224 bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
# master_start_timeout: 300
# synchronous_mode: false
#standby_cluster:
#host: 192.168.19.72
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
# use_slots: true
parameters:
# wal_level: hot_standby
# hot_standby: "on"
# max_connections: 100
# max_worker_processes: 8
# wal_keep_segments: 8
# max_wal_senders: 10
# max_replication_slots: 10
# max_prepared_transactions: 0
# max_locks_per_transaction: 64
# wal_log_hints: "on"
# track_commit_timestamp: "off"
# archive_mode: "on"
# archive_timeout: 1800s
# archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
# recovery_conf:
# restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p # some desired options for 'initdb'
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
# For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
#- host replication replicator 192.168.19.72/32 gss include_realm=0
#- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- host replication replicator 192.168.19.72/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# - hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
# post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb postgresql:
listen: 192.168.19.72:5432
connect_address: 192.168.19.72:5432
data_dir: /data/pg_data
bin_dir: /data/pgsql/bin
# config_dir:
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: 1qaz2wsx
superuser:
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
# Server side kerberos spn
# krbsrvname: postgres
parameters:
# Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
# same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
# krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
unix_socket_directories: '.'
# Additional fencing script executed after acquiring the leader lock but before promoting the replica
#pre_promote: /path/to/pre_promote.sh #watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: /dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5 tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
node3 scope: batman
namespace: /service/
name: postgresql3 restapi:
listen: 192.168.19.73:8008
connect_address: 192.168.19.73:8008
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# keyfile: /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
# authentication:
# username: username
# password: password # ctl:
# insecure: false # Allow connections to SSL sites without certs
# certfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
# cacert: /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cacert-snakeoil.pem etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 192.168.19.73:2379
#Or use "hosts" to provide multiple endpoints
#Could be a comma separated string:
#hosts: host1:port1,host2:port2
#host: 192.168.19.73:2379,192.168.19.73:2379,192.168.19.73:2379
#or an actual yaml list:
#hosts:
#- host1:port1
#- host2:port2
#Once discovery is complete Patroni will use the list of advertised clientURLs
#It is possible to change this behavior through by setting:
#use_proxies: true #raft:
# data_dir: .
# self_addr: 192.168.19.73:2222
# partner_addrs:
# - 192.168.19.73:2223
# - 192.168.19.73:2224 bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
# master_start_timeout: 300
# synchronous_mode: false
#standby_cluster:
#host: 192.168.19.73
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
# use_slots: true
parameters:
# wal_level: hot_standby
# hot_standby: "on"
# max_connections: 100
# max_worker_processes: 8
# wal_keep_segments: 8
# max_wal_senders: 10
# max_replication_slots: 10
# max_prepared_transactions: 0
# max_locks_per_transaction: 64
# wal_log_hints: "on"
# track_commit_timestamp: "off"
# archive_mode: "on"
# archive_timeout: 1800s
# archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
# recovery_conf:
# restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p # some desired options for 'initdb'
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
# For kerberos gss based connectivity (discard @.*$)
#- host replication replicator 192.168.19.73/32 gss include_realm=0
#- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 gss include_realm=0
- host replication replicator 192.168.19.73/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
# - hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 # Additional script to be launched after initial cluster creation (will be passed the connection URL as parameter)
# post_init: /usr/local/bin/setup_cluster.sh # Some additional users users which needs to be created after initializing new cluster
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb postgresql:
listen: 192.168.19.73:5432
connect_address: 192.168.19.73:5432
data_dir: /data/pg_data
bin_dir: /data/pgsql/bin
# config_dir:
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: 1qaz2wsx
superuser:
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: postgres
password: P@sswrd
# Server side kerberos spn
# krbsrvname: postgres
parameters:
# Fully qualified kerberos ticket file for the running user
# same as KRB5CCNAME used by the GSS
# krb_server_keyfile: /var/spool/keytabs/postgres
unix_socket_directories: '.'
# Additional fencing script executed after acquiring the leader lock but before promoting the replica
#pre_promote: /path/to/pre_promote.sh #watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: /dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5 tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
7、依次启动patroni服务
Postgres用户下启动
nohup patroni /usr/patroni/conf/patroni_postgresql.yml &
8、patroni配置启动脚本
为了方便开机自启,故配置成 patroni.service,3个node都需要进行配置,配置好patroni.service后就可以直接在root用户下切换Leader以及重启postgres节点等操作
[root@pgsql_1971 ~]$ vim /etc/systemd/system/patroni.service
[Unit]
Description=patroni - a high-availability PostgreSQL
Documentation=https://patroni.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
After=syslog.target network.target etcd.target
Wants=network-online.target [Service]
Type=simple
User=postgres
Group=postgres
PermissionsStartOnly=true
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/patroni /usr/patroni/conf/patroni_postgresql.yml
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
LimitNOFILE=65536
KillMode=process
KillSignal=SIGINT
Restart=on-abnormal
RestartSec=30s
TimeoutSec=0 [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
9、禁用postgresql脚本采用patroni服务启动数据库
禁止 postgresql 的自启动,通过 patroni 来管理 postgresql systemctl stop postgresql
systemctl status postgresql
systemctl disable postgresql systemctl status patroni
systemctl start patroni
systemctl enable patroni
五、集群检查
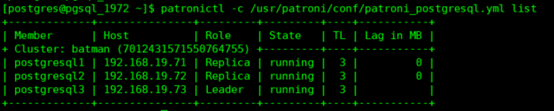
1、数据库集群检查
patronictl -c /usr/patroni/conf/patroni_postgresql.yml list
2、etcd检查
root@pgsql_1971 ~]# /usr/local/etcd/etcdctl ls /service/batman
root@pgsql_1971 ~]# /usr/local/etcd/etcdctl get /service/batman/members/postgresql1
六、haproxy部署(两个从节点)
七、keepalived部署(两个从节点)
postgresql高可用集群部署的更多相关文章
- hbase高可用集群部署(cdh)
一.概要 本文记录hbase高可用集群部署过程,在部署hbase之前需要事先部署好hadoop集群,因为hbase的数据需要存放在hdfs上,hadoop集群的部署后续会有一篇文章记录,本文假设had ...
- (十)RabbitMQ消息队列-高可用集群部署实战
原文:(十)RabbitMQ消息队列-高可用集群部署实战 前几章讲到RabbitMQ单主机模式的搭建和使用,我们在实际生产环境中出于对性能还有可用性的考虑会采用集群的模式来部署RabbitMQ. Ra ...
- RocketMQ的高可用集群部署
RocketMQ的高可用集群部署 标签(空格分隔): 消息队列 部署 1. RocketMQ 集群物理部署结构 Rocket 物理部署结构 Name Server: 单点,供Producer和Cons ...
- RabbitMQ的高可用集群部署
RabbitMQ的高可用集群部署 标签(空格分隔): 消息队列 部署 1. RabbitMQ部署的三种模式 1.1 单一模式 单机情况下不做集群, 仅仅运行一个RabbitMQ. # docker-c ...
- rocketmq高可用集群部署(RocketMQ-on-DLedger Group)
rocketmq高可用集群部署(RocketMQ-on-DLedger Group) rocketmq部署架构 rocketmq部署架构非常多,都是为了解决一些问题,越来越高可用,越来越复杂. 单ma ...
- MySQL MHA 高可用集群部署及故障切换
MySQL MHA 高可用集群部署及故障切换 1.概念 2.搭建MySQL + MHA 1.概念: a)MHA概念 : MHA(MasterHigh Availability)是一套优秀的MySQL高 ...
- Kubernetes容器集群 - harbor仓库高可用集群部署说明
之前介绍Harbor私有仓库的安装和使用,这里重点说下Harbor高可用集群方案的部署,目前主要有两种主流的Harbor高可用集群方案:1)双主复制:2)多harbor实例共享后端存储. 一.Harb ...
- 【转】harbor仓库高可用集群部署说明
之前介绍Harbor私有仓库的安装和使用,这里重点说下Harbor高可用集群方案的部署,目前主要有两种主流的Harbor高可用集群方案:1)双主复制:2)多harbor实例共享后端存储. 一.Harb ...
- Centos6.9下RocketMQ3.4.6高可用集群部署记录(双主双从+Nameserver+Console)
之前的文章已对RocketMQ做了详细介绍,这里就不再赘述了,下面是本人在测试和生产环境下RocketMQ3.4.6高可用集群的部署手册,在此分享下: 1) 基础环境 ip地址 主机名 角色 192. ...
随机推荐
- Linux centos 安装 maven 3.5.4
一.maven下载 1.官方下载 打开网址:http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi 下拉滚动条,找到标记处并点击 选择自己想要的版本,我这里选择的是 3.5.4,然后 ...
- IDEA 创建Maven Web工程
一.Maven环境搭建 二.Maven常用命令 mvn clean 清除生成的target文件 mvn install 生成target文件 mvn clean install 相当于先删除targe ...
- 刷题-力扣-168. Excel表列名称
168. Excel表列名称 题目链接 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/excel-sheet-column-title 著作权 ...
- IMO 1977 第 2 题探析
原题:在一个有限的实数数列中,任意 7 个连续项之和为负数,且任意 11 个连续项之和为正数.求这个数列最多有多少项. 解法一:记这个数列为 a1, a2, ..., ak,问题等价于求 k 的最大值 ...
- k8s笔记0528-基于KUBERNETES构建企业容器云手动部署集群记录-7
Kubernetes Dashboard 创建CoreDNS [root@linux-node1 ~]# kubectl create -f coredns.yaml [root@linux-node ...
- Spring笔记(4)
集成Web环境 1.步骤 导入Spring-web坐标 <!-- spring-web--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springfra ...
- Spring(一)——概述
一.概述 1.介绍 struts 是 web 框架 (jsp/action/actionfrom).hibernate是orm (Object Relational Mapping) 框架,处于持久层 ...
- Java基础(一)——面向对象
一.对象 1.成员变量和局部变量的区别 两类变量同名时,局部变量具有更高的优先级. 作用域不同:局部变量的作用域仅限于定义它的方法,作用于函数或者语句中:成员变量的作用域在整个类中. 初始值不同:Ja ...
- java基础之ThreadLocal
早在JDK 1.2的版本中就提供java.lang.ThreadLocal,ThreadLocal为解决多线程程序的并发问题提供了一种新的思路.使用这个工具类可以很简洁地编写出优美的多线程程序.Thr ...
- aes加解密前后端-前端
一.ajax请求前端 f12请求和响应参数效果: 1.在前端封装ajax的公共Util的js中,封装ajax请求的地方,在beforeSend方法和成功之后的回调函数success方法中: var p ...
