Spring学习笔记--面向切面编程(AOP)
什么是AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),意为面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
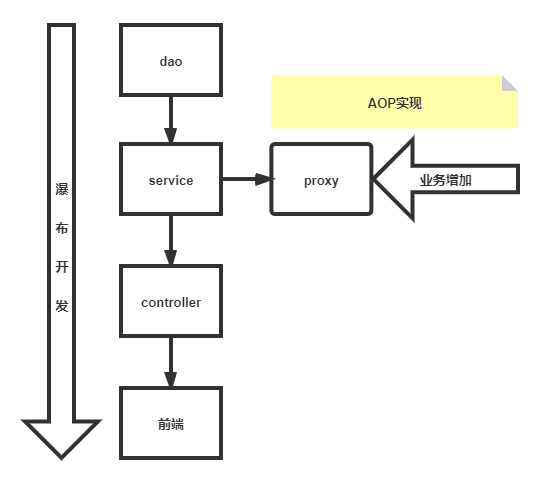
AOP在Spring中的作用
--提供声明式事务:允许用户自定义切面--
- 横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能,即与业务逻辑无关但需要关注的部分(日志、安全、缓存、事务等等)
- 切面(Aspect):【横切关注点】模块化的特殊对象(一个类)
- 通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作(类中方法)
- 目标(Target):被通知目标
- 代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知后创建的对象
- 切入点(PointCut):切面通知执行的“地点”的定义
- 连接点(JoinPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点
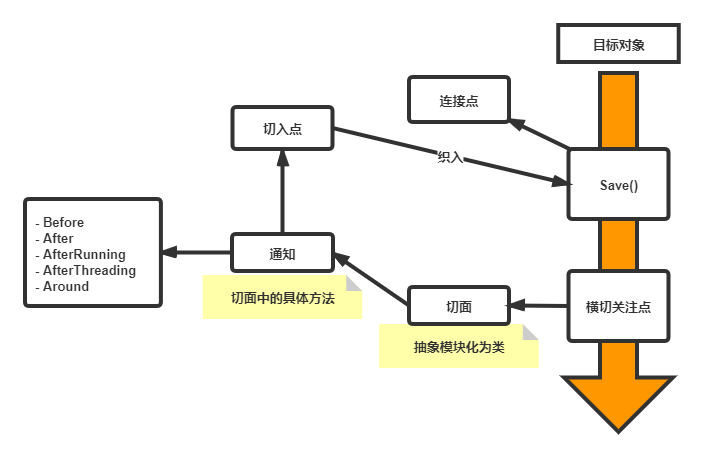
AOP实现
【搭建环境(普通Maven项目)】
【导入依赖】
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
【编写业务类(示例)】
- UserService接口
package cn.iris.service;
/**
* @author Iris 2021/8/12
*/
public interface UserService {
void add();
void del();
void update();
void query();
}
- UserService实现类
package cn.iris.service;
/**
* @author Iris 2021/8/12
*/
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("增加一个用户");
}
@Override
public void del() {
System.out.println("删除一个用户");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("更新一个用户");
}
@Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("查询一个用户");
}
}
- 日志类(示例)
- 前置日志类
package cn.iris.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author Iris 2021/8/12
*/
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
/**
* 前置日志
* @param method 要执行的目标对象的方法
* @param args 参数
* @param target 目标对象
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+ method.getName()+"被执行");
}
}
- 结尾日志类
package cn.iris.log;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author Iris 2021/8/12
*/
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+ method.getName()+"被执行后返回"+returnValue);
}
}
- 测试类
import cn.iris.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author Iris 2021/8/12
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationConfig.xml");
// 动态代理是代理的接口
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
方式一:使用Spring的接口
【Spring API 接口实现】
- Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册Bean-->
<bean class="cn.iris.service.UserServiceImpl" id="userService"/>
<bean class="cn.iris.log.Log" id="log"/>
<bean class="cn.iris.log.AfterLog" id="afterLog"/>
<!--方式一:使用原生Spring API接口-->
<!--配置aop(导入aop约束)-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入点 execution: 要执行的位置-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* cn.iris.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--执行环绕增加-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
方式二:使用自定义类实现
【重点:切面定义】
- Class DiyPointCut
package cn.iris.diy;
/**
* @author Iris 2021/8/13
*/
public class DiyPointCut {
public void before() {
System.out.println("-----Before Method-----");
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("-----After Method-----");
}
}
- applicationConfig.xml
<!--方式二:自定义类-->
<bean class="cn.iris.diy.DiyPointCut" id="diy"/>
<aop:config>
<!--自定义切面,ref引用自定义类-->
<aop:aspect ref="diy">
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* cn.iris.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
方式三:注解实现AOP
- Class AnnotationPointCut
package cn.iris.diy;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
/**
* 方式三:使用注解实现AOP
* @author Iris 2021/8/13
*/
@Aspect //标注该类为一个切面
public class AnnotationPointCut {
@Before("execution(* cn.iris.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("-----Before Method-----");
}
@After("execution(* cn.iris.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("-----After Method-----");
}
@Around("execution(* cn.iris.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
System.out.println("-----Before Around Method-----");
try {
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
System.out.println("Signature : "+signature);
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----After Around Method-----");
}
}
- applicationConfig.xml
<!--方式三:使用注解实现AOP-->
<bean class="cn.iris.diy.AnnotationPointCut" id="anno"/>
<!--开启注解支持 JDK(默认:proxy-target-class="false") cglib(proxy-target-class="true")-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
Spring学习笔记--面向切面编程(AOP)的更多相关文章
- Spring学习笔记-面向切面(AOP)-04
什么是面向切面编程 先大概了解一下部分术语 横切关注点:软件开发中,散布于多出的功能称为横切关注点(cross-cutting concern),简单的可以描述为可以影响应用多处的功能,比如日志.安全 ...
- spring学习 八 面向切面编程(AOP)概述
注:本文大部分参考 --------------------- 本文来自 -望远- 的CSDN 博客 ,全文地址请点击:https://blog.csdn.net/yanquan345/artic ...
- Spring框架系列(4) - 深入浅出Spring核心之面向切面编程(AOP)
在Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心中向你展示了AOP的基础含义,同时以此发散了一些AOP相关知识点; 本节将在此基础上进一步解读AOP的含义以及AOP的使用方式.@pd ...
- Spring中的面向切面编程(AOP)简介
一.什么是AOP AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming, 面向切面编程): 是一种新的方法论, 是对传统 OOP(Object-Oriented Programming, 面 ...
- Spring学习笔记:面向切面编程AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)
一.面向切面编程AOP 目标:让我们可以“专心做事”,避免繁杂重复的功能编码 原理:将复杂的需求分解出不同方面,将公共功能集中解决 *****所谓面向切面编程,是一种通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现 ...
- Spring框架学习笔记(2)——面向切面编程AOP
介绍 概念 面向切面编程AOP与面向对象编程OOP有所不同,AOP不是对OOP的替换,而是对OOP的一种补充,AOP增强了OOP. 假设我们有几个业务代码,都调用了某个方法,按照OOP的思想,我们就会 ...
- Spring学习手札(二)面向切面编程AOP
AOP理解 Aspect Oriented Program面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术. 但是,这种说法有些片面,因为在软件工程中,AOP的价值体现的并 ...
- Spring之控制反转——IoC、面向切面编程——AOP
控制反转——IoC 提出IoC的目的 为了解决对象之间的耦合度过高的问题,提出了IoC理论,用来实现对象之间的解耦. 什么是IoC IoC是Inversion of Control的缩写,译为控制 ...
- 04 Spring:01.Spring框架简介&&02.程序间耦合&&03.Spring的 IOC 和 DI&&08.面向切面编程 AOP&&10.Spring中事务控制
spring共四天 第一天:spring框架的概述以及spring中基于XML的IOC配置 第二天:spring中基于注解的IOC和ioc的案例 第三天:spring中的aop和基于XML以及注解的A ...
随机推荐
- nohup启动 jar 不输出日志
简单暴力:nohup java -jar xxx.jar >/dev/null 2>&1 &
- centos 8 chown命令详解
chown命令简介 chown将指定文件的拥有者改为指定的用户或组,用户可以是用户名或者用户ID:组可以是组名或者组ID: 文件是以空格分开的要改变权限的文件列表,支持通配符. 系统管理员经常使用ch ...
- python 两种排序方法 sort() sorted()
python中有两种排序方法,list内置sort()方法或者python内置的全局sorted()方法 区别为: sort()方法对list排序会修改list本身,不会返回新list.sort()只 ...
- FastTunnel-开源内网穿透框架
FastTunnel - 打造人人都能搭建的内网穿透工具 FastTunnel是用.net core开发的一款跨平台内网穿透工具,它可以实现将内网服务暴露到公网供自己或任何人访问. 与其他穿透工具不同 ...
- SoapUI Pro 最新版本和最新功能
专为整个后端的端到端测试而构建 创建全面的端到端测试,以从API定义或实时端点验证API的整个工作流程.只需单击几下即可传递响应数据并添加断言-无需编码. 综合生成或配置数据 通过简单的数据驱动测试来 ...
- ESP32省电模式连接WIFI笔记
基于ESP-IDF4.1版本 main.c文件如下: #include <string.h> #include "freertos/FreeRTOS.h" #inclu ...
- JS高阶函数的使用
1.何为高阶函数呢? JavaScript的函数其实都指向某个变量.既然变量可以指向函数,函数的参数能接收变量,那么一个函数就可以接收另一个函数作为参数,这种函数就称之为高阶函数.简单来说,就是对其他 ...
- 「AGC020D」 Min Max Repetition
「AGC020D」 Min Max Repetition 传送门 首先这个东西的连续字符个数你可以二分.但事实上没有必要,这是可以直接算出来的. 即 \(k=\max\{\lceil\frac{A}{ ...
- Django基础06篇 分页
1.导入Django自带的分页类 from django.core.paginator import Paginator 2.分页类的使用 def index(request): # return H ...
- C语言:\t\b\n应用
#include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("123\n"); printf("%c\n",'\177'); pr ...
