Servlet HTTP Request Response笔记
# 今日内容:
1. Servlet
2. HTTP协议
3. Request
## Servlet:
1. 概念
2. 步骤
3. 执行原理
4. 生命周期
5. Servlet3.0 注解配置
6. Servlet的体系结构
Servlet -- 接口
|
GenericServlet -- 抽象类
|
HttpServlet -- 抽象类
* GenericServlet:将Servlet接口中其他的方法做了默认空实现,只将service()方法作为抽象
* 将来定义Servlet类时,可以继承GenericServlet,实现service()方法即可
* HttpServlet:对http协议的一种封装,简化操作
1. 定义类继承HttpServlet
2. 复写doGet/doPost方法
7. Servlet相关配置
1. urlpartten:Servlet访问路径
1. 一个Servlet可以定义多个访问路径 : @WebServlet({"/d4","/dd4","/ddd4"})
2. 路径定义规则:
1. /xxx:路径匹配
2. /xxx/xxx:多层路径,目录结构
3. *.do:扩展名匹配
## HTTP:
* 概念:Hyper Text Transfer Protocol 超文本传输协议
* 传输协议:定义了,客户端和服务器端通信时,发送数据的格式
* 特点:
1. 基于TCP/IP的高级协议
2. 默认端口号:80
3. 基于请求/响应模型的:一次请求对应一次响应
4. 无状态的:每次请求之间相互独立,不能交互数据
* 历史版本:
* 1.0:每一次请求响应都会建立新的连接
* 1.1:复用连接
* 请求消息数据格式
1. 请求行
请求方式 请求url 请求协议/版本
GET /login.html HTTP/1.1
* 请求方式:
* HTTP协议有7中请求方式,常用的有2种
* GET:
1. 请求参数在请求行中,在url后。
2. 请求的url长度有限制的
3. 不太安全
* POST:
1. 请求参数在请求体中
2. 请求的url长度没有限制的
3. 相对安全
2. 请求头:客户端浏览器告诉服务器一些信息
请求头名称: 请求头值
* 常见的请求头:
1. User-Agent:浏览器告诉服务器,我访问你使用的浏览器版本信息
* 可以在服务器端获取该头的信息,解决浏览器的兼容性问题
2. Referer:http://localhost/login.html
* 告诉服务器,我(当前请求)从哪里来?
* 作用:
1. 防盗链:
2. 统计工作:
3. 请求空行
空行,就是用于分割POST请求的请求头,和请求体的。
4. 请求体(正文):
* 封装POST请求消息的请求参数的
* 字符串格式:
POST /login.html HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:60.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/60.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Referer: http://localhost/login.html
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
username=zhangsan
* 响应消息数据格式
## Request:
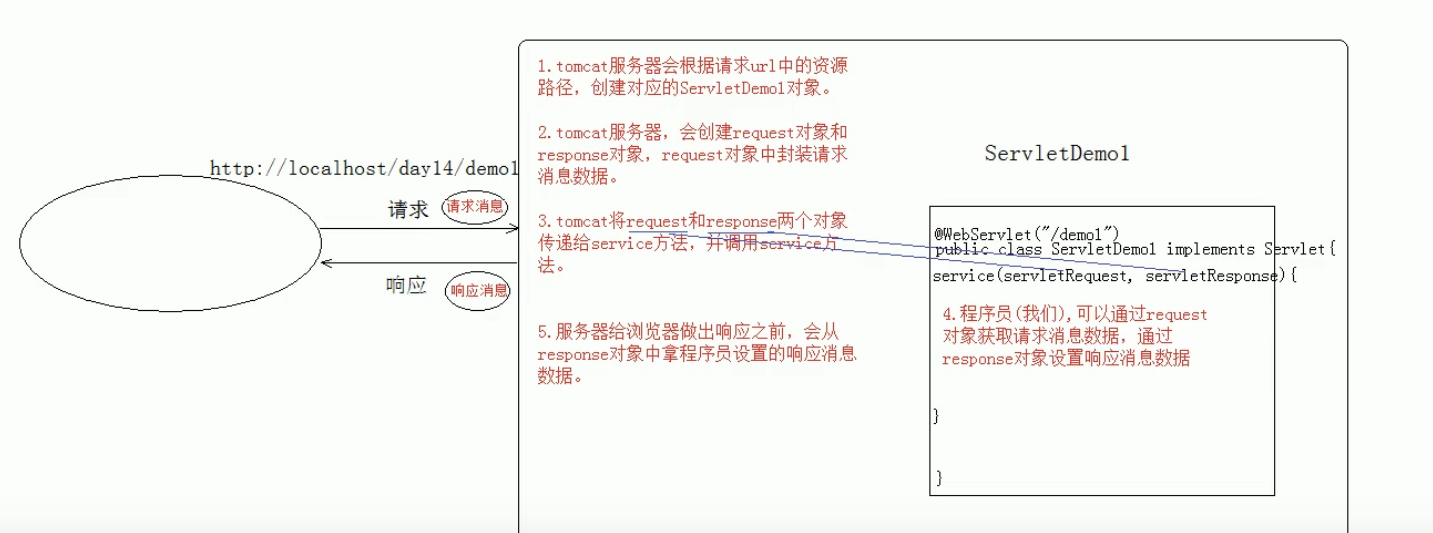
1. request对象和response对象的原理
1. request和response对象是由服务器创建的。我们来使用它们
2. request对象是来获取请求消息,response对象是来设置响应消息
2. request对象继承体系结构:
ServletRequest -- 接口
| 继承
HttpServletRequest -- 接口
| 实现
org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade 类(tomcat)
3. request功能:
1. 获取请求消息数据
1. 获取请求行数据
* GET /day14/demo1?name=zhangsan HTTP/1.1
* 方法:
1. 获取请求方式 :GET
* String getMethod()
2. (*)获取虚拟目录:/day14
* String getContextPath()
3. 获取Servlet路径: /demo1
* String getServletPath()
4. 获取get方式请求参数:name=zhangsan
* String getQueryString()
5. (*)获取请求URI:/day14/demo1
* String getRequestURI(): /day14/demo1
* StringBuffer getRequestURL() :http://localhost/day14/demo1
* URL:统一资源定位符 : http://localhost/day14/demo1 中华人民共和国
* URI:统一资源标识符 : /day14/demo1 共和国
6. 获取协议及版本:HTTP/1.1
* String getProtocol()
7. 获取客户机的IP地址:
* String getRemoteAddr()
2. 获取请求头数据
* 方法:
* (*)String getHeader(String name):通过请求头的名称获取请求头的值
* Enumeration<String> getHeaderNames():获取所有的请求头名称
3. 获取请求体数据:
* 请求体:只有POST请求方式,才有请求体,在请求体中封装了POST请求的请求参数
* 步骤:
1. 获取流对象
* BufferedReader getReader():获取字符输入流,只能操作字符数据
* ServletInputStream getInputStream():获取字节输入流,可以操作所有类型数据
* 在文件上传知识点后讲解
2. 再从流对象中拿数据
2. 其他功能:
1. 获取请求参数通用方式:不论get还是post请求方式都可以使用下列方法来获取请求参数
1. String getParameter(String name):根据参数名称获取参数值 username=zs&password=123
2. String[] getParameterValues(String name):根据参数名称获取参数值的数组 hobby=xx&hobby=game
3. Enumeration<String> getParameterNames():获取所有请求的参数名称
4. Map<String,String[]> getParameterMap():获取所有参数的map集合
* 中文乱码问题:
* get方式:tomcat 8 已经将get方式乱码问题解决了
* post方式:会乱码
* 解决:在获取参数前,设置request的编码request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
2. 请求转发:一种在服务器内部的资源跳转方式
1. 步骤:
1. 通过request对象获取请求转发器对象:RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path)
2. 使用RequestDispatcher对象来进行转发:forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
2. 特点:
1. 浏览器地址栏路径不发生变化
2. 只能转发到当前服务器内部资源中。
3. 转发是一次请求
3. 共享数据:
* 域对象:一个有作用范围的对象,可以在范围内共享数据
* request域:代表一次请求的范围,一般用于请求转发的多个资源中共享数据
* 方法:
1. void setAttribute(String name,Object obj):存储数据
2. Object getAttitude(String name):通过键获取值
3. void removeAttribute(String name):通过键移除键值对
4. 获取ServletContext:
* ServletContext getServletContext()
## 案例:用户登录
* 用户登录案例需求:
1.编写login.html登录页面
username & password 两个输入框
2.使用Druid数据库连接池技术,操作mysql,day14数据库中user表
3.使用JdbcTemplate技术封装JDBC
4.登录成功跳转到SuccessServlet展示:登录成功!用户名,欢迎您
5.登录失败跳转到FailServlet展示:登录失败,用户名或密码错误
* 分析
* 开发步骤
1. 创建项目,导入html页面,配置文件,jar包
2. 创建数据库环境
CREATE DATABASE day14;
USE day14;
CREATE TABLE USER(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(32) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
PASSWORD VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL
);
3. 创建包cn.itcast.domain,创建类User
package cn.itcast.domain;
/**
* 用户的实体类
*/
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4. 创建包cn.itcast.util,编写工具类JDBCUtils
package cn.itcast.util;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.xml.crypto.Data;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* JDBC工具类 使用Durid连接池
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
private static DataSource ds ;
static {
try {
//1.加载配置文件
Properties pro = new Properties();
//使用ClassLoader加载配置文件,获取字节输入流
InputStream is = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
pro.load(is);
//2.初始化连接池对象
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接池对象
*/
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
return ds;
}
/**
* 获取连接Connection对象
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
}
5. 创建包cn.itcast.dao,创建类UserDao,提供login方法
package cn.itcast.dao;
import cn.itcast.domain.User;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
/**
* 操作数据库中User表的类
*/
public class UserDao {
//声明JDBCTemplate对象共用
private JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource());
/**
* 登录方法
* @param loginUser 只有用户名和密码
* @return user包含用户全部数据,没有查询到,返回null
*/
public User login(User loginUser){
try {
//1.编写sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
//2.调用query方法
User user = template.queryForObject(sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class),
loginUser.getUsername(), loginUser.getPassword());
return user;
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();//记录日志
return null;
}
}
}
6. 编写cn.itcast.web.servlet.LoginServlet类
package cn.itcast.web.servlet;
import cn.itcast.dao.UserDao;
import cn.itcast.domain.User;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/loginServlet")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.设置编码
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//2.获取请求参数
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
//3.封装user对象
User loginUser = new User();
loginUser.setUsername(username);
loginUser.setPassword(password);
//4.调用UserDao的login方法
UserDao dao = new UserDao();
User user = dao.login(loginUser);
//5.判断user
if(user == null){
//登录失败
req.getRequestDispatcher("/failServlet").forward(req,resp);
}else{
//登录成功
//存储数据
req.setAttribute("user",user);
//转发
req.getRequestDispatcher("/successServlet").forward(req,resp);
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(req,resp);
}
}
7. 编写FailServlet和SuccessServlet类
@WebServlet("/successServlet")
public class SuccessServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取request域中共享的user对象
User user = (User) request.getAttribute("user");
if(user != null){
//给页面写一句话
//设置编码
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//输出
response.getWriter().write("登录成功!"+user.getUsername()+",欢迎您");
}
}
@WebServlet("/failServlet")
public class FailServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//给页面写一句话
//设置编码
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//输出
response.getWriter().write("登录失败,用户名或密码错误");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request,response);
}
}
8. login.html中form表单的action路径的写法
* 虚拟目录+Servlet的资源路径
9. BeanUtils工具类,简化数据封装
* 用于封装JavaBean的
1. JavaBean:标准的Java类
1. 要求:
1. 类必须被public修饰
2. 必须提供空参的构造器
3. 成员变量必须使用private修饰
4. 提供公共setter和getter方法
2. 功能:封装数据
2. 概念:
成员变量:
属性:setter和getter方法截取后的产物
例如:getUsername() --> Username--> username
3. 方法:
1. setProperty()
2. getProperty()
3. populate(Object obj , Map map):将map集合的键值对信息,封装到对应的JavaBean对象中



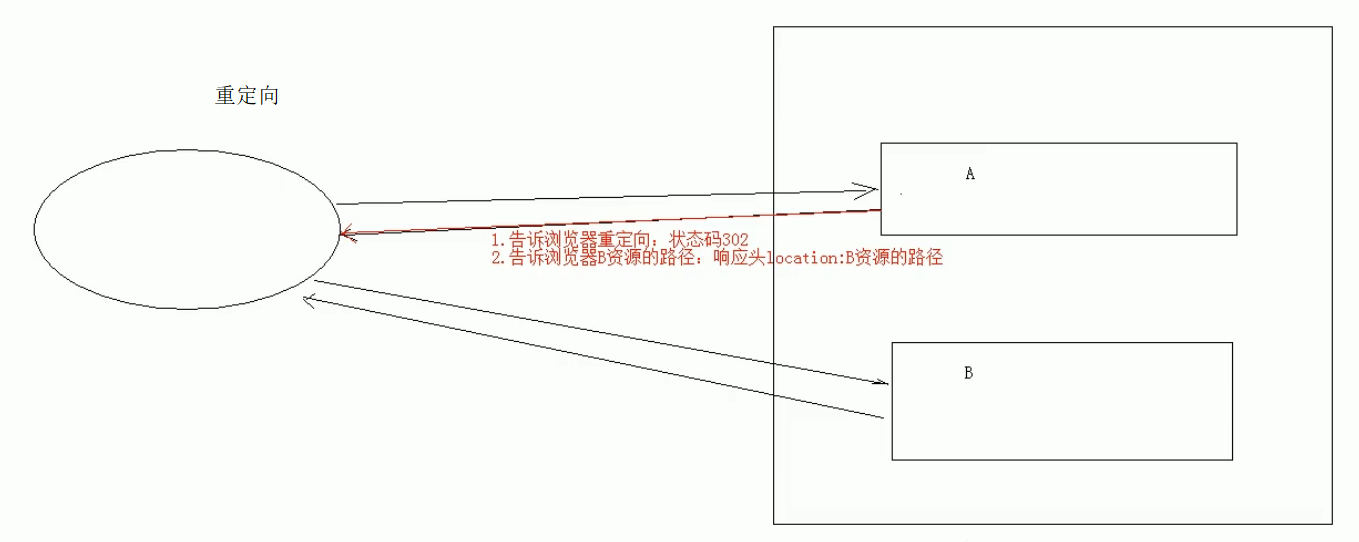
重定向(302):服务器给A发请求,A返回C的地址给服务器,服务器拿着C的地址去访问C
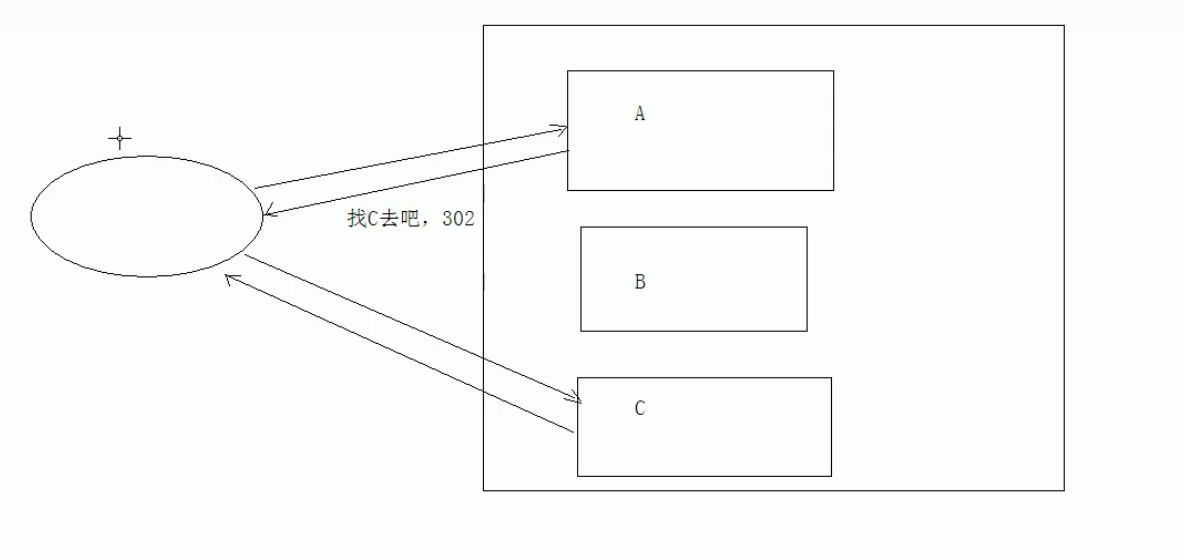
访问缓存(304):请求的时候,返回304 找缓存就行不需要再用别的工序了


# 今日内容
1. HTTP协议:响应消息
2. Response对象
3. ServletContext对象
## HTTP协议:
1. 请求消息:客户端发送给服务器端的数据
* 数据格式:
1. 请求行
2. 请求头
3. 请求空行
4. 请求体
2. 响应消息:服务器端发送给客户端的数据
* 数据格式:
1. 响应行
1. 组成:协议/版本 响应状态码 状态码描述
2. 响应状态码:服务器告诉客户端浏览器本次请求和响应的一个状态。
1. 状态码都是3位数字
2. 分类:
1. 1xx:服务器就收客户端消息,但没有接受完成,等待一段时间后,发送1xx多状态码
2. 2xx:成功。代表:200
3. 3xx:重定向。代表:302(重定向),304(访问缓存)
4. 4xx:客户端错误。
* 代表:
* 404(请求路径没有对应的资源)
* 405:请求方式没有对应的doXxx方法
5. 5xx:服务器端错误。代表:500(服务器内部出现异常)
2. 响应头:
1. 格式:头名称: 值
2. 常见的响应头:
1. Content-Type:服务器告诉客户端本次响应体数据格式以及编码格式
2. Content-disposition:服务器告诉客户端以什么格式打开响应体数据
* 值:
* in-line:默认值,在当前页面内打开
* attachment;filename=xxx:以附件形式打开响应体。文件下载
3. 响应空行
4. 响应体:传输的数据
* 响应字符串格式
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html;charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 101
Date: Wed, 06 Jun 2018 07:08:42 GMT
<html>
<head>
<title>$Title$</title>
</head>
<body>
hello , response
</body>
</html>
## Response对象
* 功能:设置响应消息
1. 设置响应行
1. 格式:HTTP/1.1 200 ok
2. 设置状态码:setStatus(int sc)
2. 设置响应头:setHeader(String name, String value)
3. 设置响应体:
* 使用步骤:
1. 获取输出流
* 字符输出流:PrintWriter getWriter()
* 字节输出流:ServletOutputStream getOutputStream()
2. 使用输出流,将数据输出到客户端浏览器
* 案例:
1. 完成重定向
* 重定向:资源跳转的方式
* 代码实现:
//1. 设置状态码为302
response.setStatus(302);
//2.设置响应头location
response.setHeader("location","/day15/responseDemo2");
//简单的重定向方法
response.sendRedirect("/day15/responseDemo2");
* 重定向的特点:redirect
1. 地址栏发生变化
2. 重定向可以访问其他站点(服务器)的资源
3. 重定向是两次请求。不能使用request对象来共享数据
* 转发的特点:forward
1. 转发地址栏路径不变
2. 转发只能访问当前服务器下的资源
3. 转发是一次请求,可以使用request对象来共享数据

* forward 和 redirect 区别
* 路径写法:
1. 路径分类
1. 相对路径:通过相对路径不可以确定唯一资源
* 如:./index.html
* 不以/开头,以.开头路径
* 规则:找到当前资源和目标资源之间的相对位置关系
* ./:当前目录
* ../:后退一级目录
2. 绝对路径:通过绝对路径可以确定唯一资源
* 如:http://localhost/day15/responseDemo2 /day15/responseDemo2
* 以/开头的路径
* 规则:判断定义的路径是给谁用的?判断请求将来从哪儿发出
* 给客户端浏览器使用:需要加虚拟目录(项目的访问路径)
* 建议虚拟目录动态获取:request.getContextPath()
* <a> , <form> 重定向...
* 给服务器使用:不需要加虚拟目录
* 转发路径
2. 服务器输出字符数据到浏览器
* 步骤:
1. 获取字符输出流
2. 输出数据
* 注意:
* 乱码问题:
1. PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();获取的流的默认编码是ISO-8859-1
2. 设置该流的默认编码
3. 告诉浏览器响应体使用的编码
//简单的形式,设置编码,是在获取流之前设置
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
3. 服务器输出字节数据到浏览器
* 步骤:
1. 获取字节输出流
2. 输出数据
4. 验证码
1. 本质:图片
2. 目的:防止恶意表单注册
## ServletContext对象:
1. 概念:代表整个web应用,可以和程序的容器(服务器)来通信
2. 获取:
1. 通过request对象获取
request.getServletContext();
2. 通过HttpServlet获取
this.getServletContext();
3. 功能:
1. 获取MIME类型:
* MIME类型:在互联网通信过程中定义的一种文件数据类型
* 格式: 大类型/小类型 text/html image/jpeg
* 获取:String getMimeType(String file)
2. 域对象:共享数据
1. setAttribute(String name,Object value)
2. getAttribute(String name)
3. removeAttribute(String name)
* ServletContext对象范围:所有用户所有请求的数据
3. 获取文件的真实(服务器)路径
1. 方法:String getRealPath(String path)
String b = context.getRealPath("/b.txt");//web目录下资源访问
System.out.println(b);
String c = context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/c.txt");//WEB-INF目录下的资源访问
System.out.println(c);
String a = context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/a.txt");//src目录下的资源访问
System.out.println(a);
## 案例:
* 文件下载需求:
1. 页面显示超链接
2. 点击超链接后弹出下载提示框
3. 完成图片文件下载
* 分析:
1. 超链接指向的资源如果能够被浏览器解析,则在浏览器中展示,如果不能解析,则弹出下载提示框。不满足需求
2. 任何资源都必须弹出下载提示框
3. 使用响应头设置资源的打开方式:
* content-disposition:attachment;filename=xxx
* 步骤:
1. 定义页面,编辑超链接href属性,指向Servlet,传递资源名称filename
2. 定义Servlet
1. 获取文件名称
2. 使用字节输入流加载文件进内存
3. 指定response的响应头: content-disposition:attachment;filename=xxx
4. 将数据写出到response输出流
* 问题:
* 中文文件问题
* 解决思路:
1. 获取客户端使用的浏览器版本信息
2. 根据不同的版本信息,设置filename的编码方式不同
Servlet HTTP Request Response笔记的更多相关文章
- request&response笔记
一.HttpServletResponse 1.代表了一个响应 2.应用: 2.1输出中文 字节流输出中文 //拿到输出字节流对象 ServletOutputStream oos = response ...
- Server,Servlet,ServletConfig,ServletContext,Session,Request,Response
Server流程 解析URL->找到应用->找到Servlet->实例化Servlet->调用init->调用service->返回响应->调用destroy ...
- javaWeb中 servlet 、request 、response
1.Servlet (1)Servlet是JavaEE的一个动态web资源开发技 术,就是在服务器上运行的小程序,这个小程序是由服务器调用的,服务器为了能调用这个小程序,就要求这样的程序必须实现一个S ...
- JavaWeb 后端 <三> 之 Response Request 学习笔记
一.响应对象 Response(重点:HTTP协议响应部分) 查看
- JavaWeb学习笔记四 request&response
HttpServletResponse 我们在创建Servlet时会覆盖service()方法,或doGet()/doPost(),这些方法都有两个参数,一个为代表请求的request和代表响应res ...
- servlet dispatcher .forward(request, response); 进入其它servlet【原】
dispatcher .forward(request, response); 进入其它servlet 假如我们的web.xml配置如下 <servlet> <servlet-nam ...
- servlet中request和response
一.HttpServletRequest介绍 HttpServletRequest对象代表客户端的请求,当客户端通过HTTP协议访问服务器时,HTTP请求头中的所有信息都封装在这个对象中,通过这个对象 ...
- JSP Servlet中Request与Response所有成员方法的研究
HttpServletRequest与HttpServletResponse作为Servlet中doGet.doPost等方法中传递的参数,承接了Http请求与响应中的大部分功能,请求的解析与响应的返 ...
- JavaWeb -- 服务器传递给Servlet的对象 -- ServletConfig, ServletContext,Request, Response
1. ServletConfig 有一些东西不合适在程序中写死,应该写在web.xml中,比如 文字怎么显示, 访问数据库名 和 密码, servlet要读取的配置文件 等等.. l在Servle ...
- javaWeb核心技术第七篇之HTTP、Tomcat、Servlet、Request和Response
- Web服务器 - 概念: - web资源: "英文直译"网"的意思 资源:一切数据文件 web资源:通过网络可以访问到的资源,通常指的是一切放在服务器上的文件&quo ...
随机推荐
- nacos集群搭建和反向代理
搭建环境 安装ngin https://www.linuxprobe.com/linux-install-nginx.html 配置jdk1.8 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42 ...
- Latex数学公式学习
要想博客写的更详细,更好,那么具体详细的数学推导这一部分是少不了的,不仅要好看还要方便输入那些更为复杂的符号,因此学习Latex就是必不可少的啦,说不定过几天就要用嘞! 本篇文章参考自超详细 LaTe ...
- C温故补缺(二):volatile
volatile 参考:CSDN volatile也是一个类型修饰符,被其修饰的变量意味着可以被某些编译器未知的因素修改,如操作系统,硬件,线程等. 当遇到volatile修饰的变量时,编译器对访问该 ...
- 解决redmi airdots 2右耳充不进电,灯不亮
解决方案 在放入充电盒并插入数据线充电状态下,长按按钮
- 关于vlc"编解码器暂不支持: VLC 无法解码格式“MIDI” (MIDI Audio)"解决
解决办法 sudo apt install vlc-plugin-fluidsynth
- python-函数的参数与返回值
Python函数 4.1.函数初识 在编写程序的过程中,有某一功能代码块出现多次,但是为了提高编写的效率以及代码的重用,所以把具有独立功能的代码块组织为一个小模块,这就是函数 就是一系列Python语 ...
- SLM6500电磁干扰认证设计PCB
SLM6500 是一款面向5V交充适配器的2A离子电池充电器.它是采用1.5MHz固定频率的步降压型转换器,利用芯片内部的功率晶体管电池进行涓流.恒流和恒压充电.充电电流可用外部电阻编程设定,持续充电 ...
- MSTN CE和MSTN SDK安装经验及技巧
MSTN CE和MSTN SDK安装经验及技巧 本文介绍了MSTN CE及MSTN CE SDK安装的流程以及在安装时可能会遇到的问题 一.MSTN CE安装 1.MSTN CE即Microstati ...
- web框架推导 wsgiref模块 jinja2模板语法 django框架简介 django基本操作
目录 纯手撸web框架 web框架的本质 手写web框架 存在的问题 基于wsgiref模块 基本介绍 推导流程 代码封装优化 总结 动静态网页 jinja2模块 前端.后端.数据库三者联动 推导流程 ...
- ORM常用字段与参数(自定义字段)
目录 一:orm中常用字段及参数 1.说明 2.自定义字段使用 3.ORM字段参数 一:orm中常用字段及参数 1.说明 id字段是自动添加的,如果你想要指定自定义主键,只需在其中一个字段中指定pri ...
