采用C++实现哈夫曼树的创建并输出哈夫曼编码
一、问题源自一道信息论的作业题:

二、完整代码如下 1 #include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
Node *parent, *lchild, *rchild;
pair<float, string> value;
};
class Tree{
public:
int max;
deque<pair<float, string>> leafs; //存放所有叶子
Node *root;
void hfTree(); //将所有叶子组合成哈夫曼树
Tree(deque<pair<float, string>>); //构造函数
bool findLeaf(const pair<float, string> &); //查找叶子
bool deleteLeaf(const pair<float, string> &); //删除叶子
void sortLeafs();
};
//重载pair的加法运算
pair<float, string> operator+(pair<float, string> pr1, pair<float, string> pr2){
return pair<float, string>(pr1.first + pr2.first, pr1.second + pr2.second);
}
//Tree的构造函数
Tree::Tree(deque<pair<float, string>> lf){
int count = ;
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it = lf.begin(); it != lf.end(); it++){
this->leafs.push_front(*it);
count++;
}
this->max = count;
this->root = NULL;
} //根据键值对判断是否存在该叶子
bool Tree::findLeaf(const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it = this->leafs.begin(); it != this->leafs.end(); it++){
if ((*it) == pr){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//根据键值对删除一个叶子
bool Tree::deleteLeaf(const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it = this->leafs.begin(); it != this->leafs.end(); it++){
if ((*it) == pr){
pair<float, string> temp = this->leafs.back();
while (temp != (*it)){
this->leafs.pop_back();
this->leafs.push_front(temp);
temp = this->leafs.back();
}
this->leafs.pop_back();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//删除deque<Node*>中的一个元素
void deleteNode(deque<Node *> &temp, const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<Node *>::iterator it = temp.begin(); it != temp.end(); it++){
if ((*it)->value == pr){
Node *nd = temp.back();
while (nd->value != pr){
temp.pop_back();
temp.push_front(nd);
nd = temp.back();
}
temp.pop_back();
return;
}
}
}
//根据键值对找到节点并返回其地址
Node *findNode(deque<Node *> &temp, const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<Node *>::iterator it = temp.begin(); it != temp.end(); it++){
if ((*it)->value == pr){
return *it;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool isIn(deque<Node *> &temp, const pair<float, string> &pr){
for (deque<Node *>::iterator it = temp.begin(); it != temp.end(); it++){
if ((*it)->value == pr){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//根据所存的叶子节点构造哈夫曼树
void Tree::hfTree(){
deque<Node *> temp;
temp.push_front(NULL);
while (this->leafs.begin() != this->leafs.end()){
//对所有叶子排序并取出概率最小的两个叶子节点
this->sortLeafs();
pair<float, string> pr1;
pair<float, string> pr2;
if (this->leafs.back() == this->leafs.front()){//只剩一个叶子了
pr1 = pr2 = this->leafs.front();
this->leafs.pop_front();
}else{
pr1 = this->leafs.front();
this->leafs.pop_front();
pr2 = this->leafs.front();
this->leafs.pop_front();
}
//首次合并,特殊处理
if (temp.front() == NULL){
temp.pop_front();
Node *node = new Node;
if (pr1 == pr2){
node->lchild = node->parent = node->rchild = NULL, node->value = pr1;
}else{
Node *node1 = new Node;
Node *node2 = new Node;
node1->value = pr1, node2->value = pr2, node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node1->lchild = node1->rchild = node2->rchild = node2->lchild = node->parent = NULL;
node1->parent = node2->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = node2;
}
this->leafs.push_front(node->value);
temp.push_front(node);
}else{
Node *node = new Node;
if (pr1 == pr2){//只剩一个节点了而且是被处理过的,表明所有节点处理完毕,直接退出
break;
}else{//新选出的两个节点都是已经处理后得到的根节点
if (isIn(temp, pr1) && isIn(temp, pr2)){
Node *node1 = findNode(temp, pr1);
Node *node2 = findNode(temp, pr2);
node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node->parent = NULL;
node1->parent = node2->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = node2;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2), deleteNode(temp, pr1), deleteNode(temp, pr2); //删除选出来的两个节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value);
}else if (isIn(temp, pr1)){
Node *tp = findNode(temp, pr1);
Node *node2 = new Node;
node2->value = pr2, node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node2->rchild = node2->lchild = node->parent = NULL;
node2->parent = tp->parent = node, node->rchild = node2, node->lchild = tp;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2); //删除选出来的节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value), deleteNode(temp, pr1); //将合并的节点放到生成树和原始集合中
}else if (isIn(temp, pr2)){
Node *tp = findNode(temp, pr2);
Node *node1 = new Node;
node1->value = pr1, node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node1->rchild = node1->lchild = node->parent = NULL;
node1->parent = tp->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = tp;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2); //删除选出来的节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value), deleteNode(temp, pr2); //将合并的节点放到生成树和原始集合中
}else{
Node *node1 = new Node;
Node *node2 = new Node;
node->value = pr1 + pr2;
node->parent = NULL;
node1->value = pr1, node2->value = pr2;
node1->parent = node2->parent = node, node->lchild = node1, node->rchild = node2;
node1->lchild = node2->lchild = node1->rchild = node2->rchild = node->parent = NULL;
this->deleteLeaf(pr1), this->deleteLeaf(pr2); //删除选出来的两个节点
this->leafs.push_front(node->value);
}
}
temp.push_front(node);
}
}
this->root = temp.front();
} //前序遍历一棵树
void prelook(Node *root,string str){
if (root != NULL){
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL){
cout << "weight:\t" << root->value.first << "\tcontent:\t" << root->value.second << "\tcode:\t"<<str<<endl;
}
if (root->lchild != NULL){
str+="";
prelook(root->lchild,str);
str.pop_back();
}
if (root->rchild != NULL){
str+="";
prelook(root->rchild,str);
str.pop_back();
}
}
}
//重载操作符,实现两个集合的笛卡儿积
Tree operator+(Tree tr1, Tree tr2){
deque<pair<float, string>> temp;
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it1 = tr1.leafs.begin(); it1 != tr1.leafs.end(); it1++){
for (deque<pair<float, string>>::iterator it2 = tr2.leafs.begin(); it2 != tr2.leafs.end(); it2++){
temp.push_back(pair<float, string>((*it1).first * (*it2).first, (*it1).second + (*it2).second));
}
}
return Tree(temp);
}
//对一棵树的叶子节点进行排序
void Tree::sortLeafs(){
sort(this->leafs.begin(), this->leafs.end());
}
int main(){
deque<pair<float, string>> temp;
temp.push_front(pair<float, string>(0.5, "a1"));
temp.push_front(pair<float, string>(0.3, "a2"));
temp.push_front(pair<float, string>(0.2, "a3"));
Tree tr = Tree(temp)+Tree(temp)+Tree(temp);
tr.hfTree();
prelook(tr.root,"");
system("pause");
return ;
}
三、修改源代码第276行可以实现对任意次方笛卡尔积结果的编码,第三问输出结果如下:
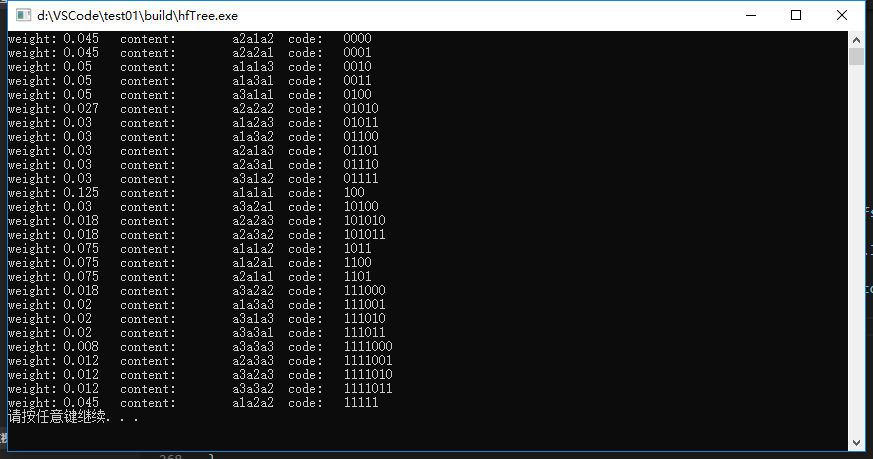
//表明只剩一个叶子了
采用C++实现哈夫曼树的创建并输出哈夫曼编码的更多相关文章
- [C++]哈夫曼树(最优满二叉树) / 哈夫曼编码(贪心算法)
一 哈夫曼树 1.1 基本概念 算法思想 贪心算法(以局部最优,谋求全局最优) 适用范围 1 [(约束)可行]:它必须满足问题的约束 2 [局部最优]它是当前步骤中所有可行选择中最佳的局部选择 3 [ ...
- 数据结构之C语言实现哈夫曼树
1.基本概念 a.路径和路径长度 若在一棵树中存在着一个结点序列 k1,k2,……,kj, 使得 ki是ki+1 的双亲(1<=i<j),则称此结点序列是从 k1 到 kj 的路径. 从 ...
- 【算法】赫夫曼树(Huffman)的构建和应用(编码、译码)
参考资料 <算法(java)> — — Robert Sedgewick, Kevin Wayne <数据结构> ...
- 20172332 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》Java哈夫曼编码实验--哈夫曼树的建立,编码与解码
20172332 2017-2018-2 <程序设计与数据结构>Java哈夫曼编码实验--哈夫曼树的建立,编码与解码 哈夫曼树 1.路径和路径长度 在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子 ...
- java实现哈弗曼树和哈夫曼树压缩
本篇博文将介绍什么是哈夫曼树,并且如何在java语言中构建一棵哈夫曼树,怎么利用哈夫曼树实现对文件的压缩和解压.首先,先来了解下什么哈夫曼树. 一.哈夫曼树 哈夫曼树属于二叉树,即树的结点最多拥有2个 ...
- C++哈夫曼树编码和译码的实现
一.背景介绍: 给定n个权值作为n个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree).哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的 ...
- 哈夫曼树(三)之 Java详解
前面分别通过C和C++实现了哈夫曼树,本章给出哈夫曼树的java版本. 目录 1. 哈夫曼树的介绍 2. 哈夫曼树的图文解析 3. 哈夫曼树的基本操作 4. 哈夫曼树的完整源码 转载请注明出处:htt ...
- 哈夫曼树(二)之 C++详解
上一章介绍了哈夫曼树的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了哈夫曼树.本章是哈夫曼树的C++实现. 目录 1. 哈夫曼树的介绍 2. 哈夫曼树的图文解析 3. 哈夫曼树的基本操作 4. 哈夫曼树的完整源码 转载 ...
- 哈夫曼树(一)之 C语言详解
本章介绍哈夫曼树.和以往一样,本文会先对哈夫曼树的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现:实现的语言虽不同,但是原理如出一辙,选择其中之一进行了解即可.若 ...
随机推荐
- 一站式自动化测试平台 http://www.Autotestplat.com
Autotestplat 一站式自动化测试平台及解决方案 自动化平台开发 3.1 自动化平台开发方案 3.1.1 功能需求 支持 API.AppUI.WebUI 性能等自动化测试,集成实现测试用例管理 ...
- 部署描述符web.xml
部署描述符应用场景 需要传递初始参数给ServletContext 有多个过滤器,并要指定调用顺序 需要更改会话超时设置 要限制资源的访问,并配置用户身份验证方式 xsi:schemaLocation ...
- BeWhatever
Hadoop Distributed File System:分布式文件系统. HDFS基于流数据模式访问和处理超大文件需求开发,具有高容错性,高可靠性,高可扩展性,多部署在低成本的硬件上.HDFS提 ...
- 面试的绝招(V1.0)
<软件自动化测试开发>出版了 测试开发公开课培训大讲堂 微信公众号:测试开发社区 测试开发QQ群:173172133 咨询QQ:7980068 咨询微信:zouhui1003it
- Android实习生 —— 屏幕适配及布局优化
为什么要进行屏幕适配.对哪些设备进行适配?在近几年的发展当中,安卓设备数量逐渐增长,由于安卓设备的开放性,导致安卓设备的屏幕尺寸大小碎片化极为严重.从[友盟+]2016年手机生态发展报告H1中看截止1 ...
- 微软手机 能靠Surface Phone卷土重来吗?
能靠Surface Phone卷土重来吗?" title="微软手机 能靠Surface Phone卷土重来吗?"> 就算整体大环境再好,就算是站在风口之上,也总是 ...
- ubuntu 代理设置
在学习工作中使用vagrant作为开发环境已经有很长一段时间了,使用ubuntu 作为开发系统 在使用中发现,即使修改了apt的source.list源文件,在面对一些开发中需要的软件工具的时候,不可 ...
- javascript中变量命名规则
前言 变量的命名相对而言没有太多的技术含量,今天整理有关于变量命名相关的规则,主要是想告诉大家,虽然命名没有技术含量,但对于个人编码,或者说一个团队的再次开发及阅读是相当有用的.良好的书写规范可以让你 ...
- SQL注入攻击浅谈
原理 SQL注入攻击指的是通过构建特殊的输入作为参数传入Web应用程序,而这些输入大都是SQL语法里的一些组合,通过执行SQL语句进而执行攻击者所要的操作,其主要原因是程序没有细致地过滤用户输入的数据 ...
- 理解 LinkedList
java -version :jdk 1.8.0_191 构造 类内参数,方法 实现 基于双向链表实现. 插入时间复杂度 O(1) 查找时间复杂度 O(n) 删除时间复杂度 O(1) 修改时间复杂度 ...
