[Unity插件]Lua行为树(十一):组合节点Parallel
Parallel节点类似Sequence节点,不同在于Parallel会每帧执行所有的节点。当所有节点返回成功时返回成功,当其中一个节点返回失败时,返回失败并且结束所有的子节点运行。
例如说,给Sequence节点插入一个不断返回Running的行为节点,那么就会造成后面的子节点无法执行,而对于Parallel来说,是不会存在这种阻塞情况的。
Parallel.cs
namespace BehaviorDesigner.Runtime.Tasks
{
[TaskDescription("Similar to the sequence task, the parallel task will run each child task until a child task returns failure. " +
"The difference is that the parallel task will run all of its children tasks simultaneously versus running each task one at a time. " +
"Like the sequence class, the parallel task will return success once all of its children tasks have return success. " +
"If one tasks returns failure the parallel task will end all of the child tasks and return failure.")]
[HelpURL("http://www.opsive.com/assets/BehaviorDesigner/documentation.php?id=27")]
[TaskIcon("{SkinColor}ParallelIcon.png")]
public class Parallel : Composite
{
// The index of the child that is currently running or is about to run.
private int currentChildIndex;
// The task status of every child task.
private TaskStatus[] executionStatus; public override void OnAwake()
{
// Create a new task status array that will hold the execution status of all of the children tasks.
executionStatus = new TaskStatus[children.Count];
} public override void OnChildStarted(int childIndex)
{
// One of the children has started to run. Increment the child index and set the current task status of that child to running.
currentChildIndex++;
executionStatus[childIndex] = TaskStatus.Running;
} public override bool CanRunParallelChildren()
{
// This task can run parallel children.
return true;
} public override int CurrentChildIndex()
{
return currentChildIndex;
} public override bool CanExecute()
{
// We can continue executing if we have more children that haven't been started yet.
return currentChildIndex < children.Count;
} public override void OnChildExecuted(int childIndex, TaskStatus childStatus)
{
// One of the children has finished running. Set the task status.
executionStatus[childIndex] = childStatus;
} public override TaskStatus OverrideStatus(TaskStatus status)
{
// Assume all of the children have finished executing. Loop through the execution status of every child and check to see if any tasks are currently running
// or failed. If a task is still running then all of the children are not done executing and the parallel task should continue to return a task status of running.
// If a task failed then return failure. The Behavior Manager will stop all of the children tasks. If no child task is running or has failed then the parallel
// task succeeded and it will return success.
bool childrenComplete = true;
for (int i = ; i < executionStatus.Length; ++i) {
if (executionStatus[i] == TaskStatus.Running) {
childrenComplete = false;
} else if (executionStatus[i] == TaskStatus.Failure) {
return TaskStatus.Failure;
}
}
return (childrenComplete ? TaskStatus.Success : TaskStatus.Running);
} public override void OnConditionalAbort(int childIndex)
{
// Start from the beginning on an abort
currentChildIndex = ;
for (int i = ; i < executionStatus.Length; ++i) {
executionStatus[i] = TaskStatus.Inactive;
}
} public override void OnEnd()
{
// Reset the execution status and the child index back to their starting values.
for (int i = ; i < executionStatus.Length; ++i) {
executionStatus[i] = TaskStatus.Inactive;
}
currentChildIndex = ;
}
}
}
BTParallel.lua
BTParallel = BTComposite:New(); local this = BTParallel;
this.name = "BTParallel"; function this:New()
local o = {};
setmetatable(o, self);
self.__index = self;
o.childTasks = {};
o.executionStatus = {};
return o;
end function this:OnUpdate()
if (not self:HasChild()) then
return BTTaskStatus.Failure;
end for i=,#self.childTasks do
local childTask = self.childTasks[i];
if (not self.executionStatus[i]) then --第一次执行
self.executionStatus[i] = childTask:OnUpdate();
if (self.executionStatus[i] == BTTaskStatus.Failure) then
return BTTaskStatus.Failure;
end
elseif (self.executionStatus[i] == BTTaskStatus.Running) then --第二次以及以后执行
self.executionStatus[i] = childTask:OnUpdate();
if (self.executionStatus[i] == BTTaskStatus.Failure) then
return BTTaskStatus.Failure;
end
end
end local childrenComplete = true;
for i=,#self.executionStatus do
if (self.executionStatus[i] == BTTaskStatus.Running) then
childrenComplete = false;
break;
end
end
if (childrenComplete) then
return BTTaskStatus.Success;
else
return BTTaskStatus.Running;
end
end
测试如下:
1.BTSequence和BTParallel的对比
BTSequence:
TestBehaviorTree = BTBehaviorTree:New(); local this = TestBehaviorTree;
this.name = "TestBehaviorTree"; function this:New()
local o = {};
setmetatable(o, self);
self.__index = self;
o:Init();
return o;
end function this:Init()
local sequence = BTSequence:New();
local action = self:GetBTActionUniversal();
local log = BTLog:New("This is log!!!");
log.name = "log"; self:SetStartTask(sequence); sequence:AddChild(action);
sequence:AddChild(log);
end function this:GetBTActionUniversal()
local count = ;
local a = function ()
if (count <= ) then
count = count + ;
print("");
return BTTaskStatus.Running;
else
return BTTaskStatus.Success;
end
end
local universal = BTActionUniversal:New(nil, a);
return universal;
end
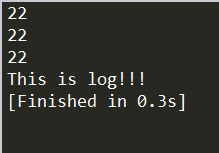
BTParallel:
TestBehaviorTree = BTBehaviorTree:New(); local this = TestBehaviorTree;
this.name = "TestBehaviorTree"; function this:New()
local o = {};
setmetatable(o, self);
self.__index = self;
o:Init();
return o;
end function this:Init()
local parallel = BTParallel:New();
local action = self:GetBTActionUniversal();
local log = BTLog:New("This is log!!!");
log.name = "log"; self:SetStartTask(parallel); parallel:AddChild(action);
parallel:AddChild(log);
end function this:GetBTActionUniversal()
local count = ;
local a = function ()
if (count <= ) then
count = count + ;
print("");
return BTTaskStatus.Running;
else
return BTTaskStatus.Success;
end
end
local universal = BTActionUniversal:New(nil, a);
return universal;
end
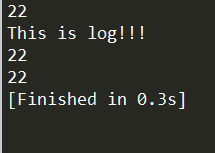
2.BTParallel中返回失败中断执行的情况
TestBehaviorTree = BTBehaviorTree:New(); local this = TestBehaviorTree;
this.name = "TestBehaviorTree"; function this:New()
local o = {};
setmetatable(o, self);
self.__index = self;
o:Init();
return o;
end function this:Init()
local parallel = BTParallel:New();
local action = self:GetBTActionUniversal();
local action2 = self:GetBTActionUniversal2(); self:SetStartTask(parallel); parallel:AddChild(action);
parallel:AddChild(action2);
end function this:GetBTActionUniversal()
local count = ;
local a = function ()
if (count <= ) then
count = count + ;
print("");
return BTTaskStatus.Running;
else
return BTTaskStatus.Success;
end
end
local universal = BTActionUniversal:New(nil, a);
return universal;
end function this:GetBTActionUniversal2()
local universal = BTActionUniversal:New(nil, function ()
return BTTaskStatus.Failure;
end);
return universal;
end

[Unity插件]Lua行为树(十一):组合节点Parallel的更多相关文章
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(三):组合节点Sequence
Sequence的继承关系如下: Sequence->Composite->ParentTask->Task 上一篇已经实现了简单版本的ParentTask和Task(基于Behav ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(十三):装饰节点完善
之前介绍了组合节点中三大常用的节点:BTSequence.BTSelector和BTParallel,一般来说,这三种就够用了,可以满足很多的需求. 接下来可以完善一下装饰节点,增加几种新的节点. 1 ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(七):行为树嵌套
在上一篇的基础上,可以测试下行为树的嵌套,所谓的行为树嵌套,就是在一棵行为树下的某一个分支,接入另一棵行为树. 以下面这棵行为树为例: TestBehaviorTree2.lua TestBehavi ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(六):打印树结构
经过前面的文章,已经把行为树中的四种基本类型节点介绍了下.接下来可以整理一下,打印一下整棵行为树.注意点如下: 1.可以把BTBehaviorTree也当作一种节点,这样就可以方便地进行行为树嵌套了 ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(二):树结构
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u012740992/article/details/79366251 在行为树中,有四种最基本的节点,其继承结构如下: Action->T ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(四):条件节点和行为节点
条件节点和行为节点,这两种节点本身的设计比较简单,项目中编写行为树节点一般就是扩展这两种节点,而Decorator和Composite节点只需要使用内置的就足够了. 它们的继承关系如下: Condit ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(十):通用行为和通用条件节点
在行为树中,需要扩展的主要是行为节点和条件节点.一般来说,每当要创建一个节点时,就要新建一个节点文件.而对于一些简单的行为节点和条件节点,为了去掉新建文件的过程,可以写一个通用版本的行为节点和条件节点 ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(九):条件节点调整
先看一下之前的条件节点是怎么设计的: BTConditional.lua BTConditional = BTTask:New(); local this = BTConditional; this. ...
- [Unity插件]Lua行为树(八):行为节点扩展
先看一下之前的行为节点是怎么设计的: BTAction.lua BTAction = BTTask:New(); local this = BTAction; this.taskType = BTTa ...
随机推荐
- AXI_LITE源码学习笔记
AXI_LITE源码学习笔记 1. axi_awready信号的产生 准备接收写地址信号 // Implement axi_awready generation // axi_awready is a ...
- 瑞萨S5D9实现UART环形缓冲
队列的常见两种形式,普通队列和环形队列: 普通队列: 环形队列: 当有大量数据的时候,我们不能存储所有的数据,那么计算机处理数据的时候,只能先处理先来的,那么处理完后呢,就会把数据释放掉,再处理下一个 ...
- RTB业务知识之2-Impression概念和关键属性
一.定义-impression This object describes an ad placement or impression being auctioned. A single bid re ...
- VBScript Scripting Techniques: File Open Dialog http://www.robvanderwoude.com/vbstech_ui_fileopen.php
I accept cookies This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website More ...
- 我的ehcache笔记
我的EhcacheUtils类: package com.shinho.bi.utils; import org.ehcache.CacheManager; import org.ehcache.co ...
- Jenkins小试
之前有提到和同事搭建了个Git+Gerrit+Jenkins环境,可惜都在一台机器上,中间IT重装系统后就杯具了,没有备份,只好重来. 6月份项目发布了首个Open API,那时候建了个api uni ...
- 函数,lambda函数,递归函数,内置函数(map,filter),装饰器
1. 集合 主要作用: 去重 关系测试, 交集\差集\并集\反向(对称)差集 2. 元组 只读列表,只有count, index 2 个方法 作用:如果一些数据不想被人修改, 可以存成元组,比如身份证 ...
- (转载)关于java多线程web服务器 以及相关资料转载
1.自己实现的简单的java多线程web服务器: https://blog.csdn.net/chongshangyunxiao321/article/details/51095149 自己实现一个简 ...
- 时间复杂度On和空间复杂度O1是什么意思?
(1).把输入规模看成x轴,所花时间/空间看成y轴 O(n)就是y=x,y随x的增长而线性增长.也就是成正比,一条斜线. O(1)就是y=1,是一个常量,不管x怎么变,y不变,一条与x轴平行的线. ( ...
- 在OpenCV中要练习的一些基本操作
OpenCV上手有一些基本操作要练习下,其实是想把OpenCV玩的像MATLAB一样熟 照着MATLAB的手册从前到后找了下自己经常用到的东西,要完成的操作有: // zeros ones eyes ...
