The following tables show the release dates and key features of all Android operating system updates to date, listed chronologically by their official application programming interface (API) levels.
|
Android 1.0 (API level 1)
Android 1.0 (API level 1)
|
| Android 1.0, the first commercial version of the software, was released on September 23, 2008.[18] The first commercially available Android device was the HTC Dream.[19] Android 1.0 incorporated the following features: |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 1.0 |
September 23, 2008 |
- Android Market application download and updates through the Market application
- Web browser to show, zoom and pan full HTML and XHTML web pages – multiple pages show as windows ("cards")[20][21]
- Camera support – however, this version lacked the option to change the camera's resolution, white balance, quality, etc.[22]
- Folders allowing the grouping of a number of application icons into a single folder icon on the Home screen[23]
- Access to web email servers, supporting POP3, IMAP4, and SMTP[21]
- Gmail synchronization with the Gmail application
- Google Contacts synchronization with the People application
- Google Calendar synchronization with the Calendar application
- Google Maps with Street View to view maps and satellite imagery, as well as find local business and obtain driving directions using GPS[22]
- Google Sync, allowing management of over-the-air synchronization of Gmail, People, and Calendar
- Google Search, allowing users to search the Internet and phone applications, contacts, calendar, etc.
- Google Talk instant messaging
- Instant messaging, text messaging, and MMS
- Media Player, enabling management, importing, and playback of media files – however, this version lacked video and stereo Bluetooth support[21][22]
- Notifications appear in the Status bar, with options to set ringtone, LED or vibration alerts[20][21][24]
- Voice Dialer allows dialing and placing of phone calls without typing a name or number[21]
- Wallpaper allows the user to set the background image or photo behind the Home screen icons and widgets
- YouTube video player[25]
- Other applications include: Alarm Clock, Calculator, Dialer (Phone), Home screen (Launcher), Pictures (Gallery), and Settings
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support
|
|
|
Android 1.1 (API level 2)
Android 1.1 (API level 2)
|
| On February 9, 2009, the Android 1.1 update was released, initially for the HTC Dream only. Android 1.1 was known as "Petit Four" internally, though this name was not used officially.[26] The update resolved bugs, changed the Android API and added a number of features:[27] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 1.1 |
February 9, 2009 |
- Details and reviews available when a user searches for businesses on Maps
- Longer in-call screen timeout default when using the speakerphone, plus ability to show/hide dialpad
- Ability to save attachments in messages
- Support added for marquee in system layouts
|
|
|
Android 1.5 Cupcake (API level 3)
Android 1.5 Cupcake (API level 3)
|
| On April 27, 2009, the Android 1.5 update was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.27.[28][29] This was the first release to officially use a codename based on a dessert item ("Cupcake"), a theme which would be used for all releases henceforth. The update included several new features and UI amendments:[30] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 1.5 |
April 27, 2009[28] |
- Support for third-party virtual keyboards with text prediction and user dictionary for custom words
- Support for Widgets – miniature application views that can be embedded in other applications (such as the Home screen) and receive periodic updates[31]
- Video recording and playback in MPEG-4 and 3GP formats
- Auto-pairing and stereo support for Bluetooth (A2DP and AVRCP profiles)
- Copy and paste features in web browser
- User pictures shown for Favorites in Contacts
- Specific date/time stamp shown for events in call log, and one-touch access to a contact card from call log event
- Animated screen transitions
- Auto-rotation option
- New stock boot animation
- Ability to upload videos to YouTube
- Ability to upload photos to Picasa
|

Android 1.5 on the Android SDK emulator |
|
Android 1.6 Donut (API level 4)
Android 1.6 Donut (API level 4)
|
| On September 15, 2009, the Android 1.6 SDK – dubbed Donut – was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.29.[32][33][34] Included in the update were numerous new features:[32] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 1.6 |
September 15, 2009[33] |
- Voice and text entry search enhanced to include bookmark history, contacts, and the web
- Ability for developers to include their content in search results
- Multi-lingual speech synthesis engine to allow any Android application to "speak" a string of text
- Easier searching and ability to view app screenshots in Android Market
- Gallery, camera and camcorder more fully integrated, with faster camera access
- Ability for users to select multiple photos for deletion
- Updated technology support for CDMA/EVDO, 802.1x, VPNs, and a text-to-speech engine
- Support for WVGA screen resolutions
- Speed improvements in searching and camera applications
- Expanded Gesture framework and new GestureBuilder development tool
|

Android 1.6 on the Android SDK emulator |
|
Android 2.0 Eclair (API level 5)
Android 2.0 Eclair (API level 5)
|
| On October 26, 2009, the Android 2.0 SDK – codenamed Eclair – was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.29.[35] Changes included:[36] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 2.0 |
October 26, 2009 |
- Expanded Account sync, allowing users to add multiple accounts to a device for synchronization of email and contacts
- Microsoft Exchange email support, with combined inbox to browse email from multiple accounts in one page
- Bluetooth 2.1 support
- Ability to tap a Contacts photo and select to call, SMS, or email the person
- Ability to search all saved SMS and MMS messages, with delete oldest messages in a conversation automatically deleted when a defined limit is reached
- Numerous new camera features, including flash support, digital zoom, scene mode, white balance, color effect and macro focus
- Improved typing speed on virtual keyboard, with smarter dictionary that learns from word usage and includes contact names as suggestions
- Refreshed browser UI with bookmark thumbnails, double-tap zoom and support for HTML5
- Calendar agenda view enhanced, showing attending status for each invitee, and ability to invite new guests to events
- Optimized hardware speed and revamped UI
- Support for more screen sizes and resolutions, with better contrast ratio
- Improved Google Maps 3.1.2
- MotionEvent class enhanced to track multi-touch events[37]
- Addition of live wallpapers, allowing the animation of home-screen background images to show movement
|
|
|
Android 2.0.1 Eclair (API level 6)
Android 2.0.1 Eclair (API level 6)
|
| |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 2.0.1 |
December 3, 2009[38] |
- Minor API changes, bugfixes and framework behavioral changes
|
|
|
Android 2.1 Eclair (API level 7)
Android 2.1 Eclair (API level 7)
|
| |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 2.1 |
January 12, 2010[39] |
- Minor amendments to the API and bugfixes
|
|
|
Android 2.2–2.2.3 Froyo (API level 8)
Android 2.2–2.2.3 Froyo (API level 8)
|
| On May 20, 2010, the SDK for Android 2.2 (Froyo, short for frozen yogurt) was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.32.[40] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 2.2 |
May 20, 2010 |
- Speed, memory, and performance optimizations[41]
- Additional application speed improvements, implemented through JIT compilation[42]
- Integration of Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine into the Browser application
- Support for the Android Cloud to Device Messaging (C2DM) service, enabling push notifications
- Improved Microsoft Exchange support, including security policies, auto-discovery, GAL look-up, calendar synchronization and remote wipe
- Improved application launcher with shortcuts to Phone and Browser applications
- USB tethering and Wi-Fi hotspot functionality[43]
- Option to disable data access over mobile network.
- Updated Market application with batch and automatic update features.[41]
- Quick switching between multiple keyboard languages and their dictionaries.
- Support for Bluetooth-enabled car and desk docks
- Support for numeric and alphanumeric passwords
- Support for file upload fields in the Browser application[44]
- The browser now shows all frames of animated GIFs instead of just the first frame only
- Support for installing applications to the expandable memory
- Adobe Flash support[45]
- Support for high-PPI displays (up to 320 ppi), such as 4" 720p screens[46]
- Gallery allows users to view picture stacks using a zoom gesture
|
|
| 2.2.1 |
January 18, 2011 |
- Bugfixes, security updates and performance improvements
|
| 2.2.2 |
January 22, 2011 |
- Minor bugfixes, including SMS routing issues that affected the Nexus One[47]
|
| 2.2.3 |
November 21, 2011[48] |
|
|
Android 2.3–2.3.2 Gingerbread (API level 9)
Android 2.3–2.3.2 Gingerbread (API level 9)
|
| On December 6, 2010, the Android 2.3 (Gingerbread) SDK was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.35.[49][50] Changes included:[49] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 2.3 |
December 6, 2010[50] |
- Updated user interface design with increased simplicity and speed
- Support for extra-large screen sizes and resolutions (WXGA and higher)[46]
- Native support for SIP VoIP internet telephony
- Faster, more intuitive text input in virtual keyboard, with improved accuracy, better suggested text and voice input mode
- Enhanced copy/paste functionality, allowing users to select a word by press-hold, copy, and paste
- Support for Near Field Communication (NFC), allowing the user to read an NFC tag embedded in a poster, sticker, or advertisement
- New audio effects such as reverb, equalization, headphone virtualization, and bass boost
- New Download Manager, giving users easy access to any file downloaded from the browser, email, or another application
- Support for multiple cameras on the device, including a front-facing camera, if available
- Support for WebM/VP8 video playback, and AAC audio encoding
- Improved power management with a more active role in managing applications that are keeping the device awake for too long
- Enhanced support for native code development
- Switched from YAFFS to ext4 on newer devices[51][52]
- Audio, graphical, and input enhancements for game developers
- Concurrent garbage collection for increased performance
- Native support for more sensors (such as gyroscopes and barometers)
|

Android 2.3 on the Android SDK emulator |
| 2.3.1 |
December 2010 |
- Improvements and bugfixes for the Google Nexus S
|
| 2.3.2 |
January 2011 |
|
Android 2.3.3–2.3.7 Gingerbread (API level 10)
Android 2.3.3–2.3.7 Gingerbread (API level 10)
|
| |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 2.3.3 |
February 9, 2011 |
- Several improvements and API fixes[53]
|
|
| 2.3.4 |
April 28, 2011[54] |
- Support for voice or video chat using Google Talk[55]
- Open Accessory Library support. Open Accessory was introduced in 3.1 (Honeycomb) but the Open Accessory Library grants 2.3.4 added support when connecting to a USB peripheral with compatible software and a compatible application on the device[56]
- Switched the default encryption for SSL from AES256-SHA to RC4-MD5.[57][58]
|
| 2.3.5 |
July 25, 2011 |
- Improved network performance for the Nexus S 4G, among other fixes and improvements
- Fixed Bluetooth bug on Samsung Galaxy S
- Improved Gmail application
- Shadow animations for list scrolling
- Camera software enhancements[59]
- Improved battery efficiency
|
| 2.3.6 |
September 2, 2011[60] |
- Fixed a voice search bug
- (The 2.3.6 update had the side-effect of impairing the Wi-Fi hotspot functionality of many Canadian Nexus S phones. Google acknowledged this problem and fixed it in late September.)[61][62]
|
| 2.3.7 |
September 21, 2011 |
|
|
Android 3.0 Honeycomb (API level 11)
Android 3.0 Honeycomb (API level 11)
|
| On February 22, 2011, the Android 3.0 (Honeycomb) SDK – the first tablet-only Android update – was released, based on Linux kernel 2.6.36.[63][64][65][66] The first device featuring this version, the Motorola Xoom tablet, was released on February 24, 2011.[67] The update's features included:[63] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 3.0 |
February 22, 2011[65] |
- Optimized tablet support with a new “holographic” user interface
- Added System Bar, featuring quick access to notifications, status, and soft navigation buttons, available at the bottom of the screen
- Added Action Bar, giving access to contextual options, navigation, widgets, or other types of content at the top of the screen
- Simplified multitasking – tapping Recent Applications in the System Bar allows users to see snapshots of the tasks underway and quickly jump from one application to another
- Redesigned keyboard, making typing fast, efficient and accurate on larger screen sizes
- Simplified, more intuitive copy/paste interface
- Multiple browser tabs replacing browser windows, plus form auto-fill and a new “incognito” mode allowing anonymous browsing
- Quick access to camera exposure, focus, flash, zoom, front-facing camera, time-lapse, and other camera features
- Ability to view albums and other collections in full-screen mode in Gallery, with easy access to thumbnails for other photos
- New two-pane Contacts UI and Fast Scroll to let users easily organize and locate contacts
- New two-pane Email UI to make viewing and organizing messages more efficient, allowing users to select one or more messages
- Hardware acceleration
- Support for multi-core processors
- Ability to encrypt all user data
- HTTPS stack improved with Server Name Indication (SNI)
- Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE; kernel module)
- Applications' write access to secondary storage (memory cards on devices with internal primary storage) is disabled outside of designated, app-specific directories, while full access to internal primary storage is still allowed through a separate application-level permission.[68][69]
|
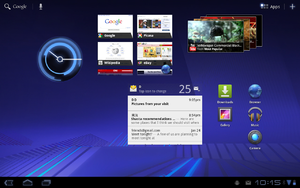
Android 3.0 on the Motorola Xoom tablet |
|
Android 3.1 Honeycomb (API level 12)
Android 3.1 Honeycomb (API level 12)
|
| |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 3.1 |
May 10, 2011[70] |
- UI refinements
- Connectivity for USB accessories (USB On-The-Go).
- Expanded Recent Applications list
- Resizable Home screen widgets
- Support for external keyboards and pointing devices
- Support for joysticks and gamepads
- Support for FLAC audio playback[71][72]
- High-performance Wi-Fi lock, maintaining high-performance Wi-Fi connections when device screen is off
- Support for HTTP proxy for each connected Wi-Fi access point
|
|
|
Android 3.2 Honeycomb (API level 13)
Android 3.2 Honeycomb (API level 13)
|
| Most first- and second-generation Google TV-enabled devices utilize Honeycomb 3.2.[73] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 3.2 |
July 15, 2011[74] |
- Improved hardware support, including optimizations for a wider range of tablets
- Increased ability of applications to access files on the SD card, e.g. for synchronization
- Compatibility display mode for applications that have not been optimized for tablet screen resolutions
- New display support functions, giving developers more control over display appearance on different Android devices[75]
|
|
| 3.2.1 |
September 20, 2011 |
- Bugfixes and minor security, stability and Wi-Fi improvements
- Update to Android Market with automatic updates and easier-to-read Terms and Conditions text
- Update to Google Books
- Improved Adobe Flash support in browser
- Improved Chinese handwriting prediction
|
| 3.2.2 |
August 30, 2011 |
- Bugfixes and other minor improvements for the Motorola Xoom 4G
|
| 3.2.3 |
|
- Bugfixes and other minor improvements for the Motorola Xoom and Motorola Xoom 4G
|
| 3.2.4 |
December 2011 |
- "Pay as You Go" support for 3G and 4G tablets
|
| 3.2.5 |
January 2012 |
- Bugfixes and other minor improvements for the Motorola Xoom and Motorola Xoom 4G
|
| 3.2.6 |
February 2012 |
- Fixed data connectivity issues when coming out of airplane mode on the US 4G Motorola Xoom
|
|
|
| The SDK for Android 4.0.1 (Ice Cream Sandwich), based on Linux kernel 3.0.1,[76] was publicly released on October 19, 2011.[77] Google's Gabe Cohen stated that Android 4.0 was "theoretically compatible" with any Android 2.3.x device in production at that time.[78] The source code for Android 4.0 became available on November 14, 2011.[79] Ice Cream Sandwich was the last version to officially support Adobe Systems' Flash player.[80] The update introduced numerous new features:[81][82][83] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.0 |
October 18, 2011[81] |
- Major refinements to the "Holo" interface with new Roboto font family
- Soft buttons from Android 3.x are now available for use on phones
- Separation of widgets in a new tab, listed in a similar manner to applications
- Easier-to-create folders, with a drag-and-drop style
- Improved visual voicemail with the ability to speed up or slow down voicemail messages
- Pinch-to-zoom functionality in the calendar
- Integrated screenshot capture (accomplished by holding down the Power and Volume-Down buttons)
- Improved error correction on the keyboard
- Ability to access applications directly from lock screen
- Improved copy and paste functionality
- Better voice integration and continuous, real-time speech to text dictation
- Face Unlock, a feature that allows users to unlock handsets using facial recognition software
- Automatic syncing of browser with users' Chrome bookmarks
- Data Usage section in settings that lets users set warnings when they approach a certain usage limit, and disable data use when the limit is exceeded
- Ability to shut down applications from the recent apps list with a swipe.[84]
- Improved camera application with zero shutter lag, time lapse settings, panorama mode, and the ability to zoom while recording
- Built-in photo editor
- New gallery layout, organized by location and person
- Refreshed "People" application with social network integration, status updates and hi-res images
- Android Beam, a near-field communication feature allowing the rapid short-range exchange of web bookmarks, contact info, directions, YouTube videos and other data
- Support for the WebP image format[71]
- Hardware acceleration of the UI[85]
- Wi-Fi Direct[86]
- 1080p video recording for stock Android devices
- Android VPN Framework (AVF), and TUN (but not TAP) kernel module. Prior to 4.0, VPN software required rooted Android.
|

Android 4.0 on the Samsung Galaxy Nexus |
| 4.0.1 |
October 21, 2011 |
- Fixed minor bugs for the Samsung Galaxy Nexus.
|
| 4.0.2 |
November 28, 2011 |
- Fixed minor bugs on the Verizon Galaxy Nexus, the US launch of which was later delayed until December 2011
(For Canadian consumers, 4.0.2 reportedly created a bug on the Galaxy Nexus that crashed the application market when users attempted to view details of any Android application. It also inadvertently reduced the NFC capabilities of the Nexus phone.)[87][88]
|
|
|
| |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.0.3 |
December 16, 2011[89] |
- Numerous bugfixes and optimizations
- Improvements to graphics, databases, spell-checking and Bluetooth functionality
- New APIs for developers, including a social stream API in the Contacts provider
- Calendar provider enhancements
- New camera applications enhancing video stabilization and QVGA resolution
- Accessibility refinements such as improved content access for screen readers[90]
|
|
| 4.0.4 |
March 29, 2012[91] |
- Stability improvements
- Better camera performance
- Smoother screen rotation
- Improved phone number recognition[92]
|
|
|
| Google announced Android 4.1 (Jelly Bean) at the Google I/O conference on June 27, 2012. Based on Linux kernel 3.0.31, Jelly Bean was an incremental update with the primary aim of improving the functionality and performance of the user interface. The performance improvement involved "Project Butter", which uses touch anticipation, triple buffering, extended vsync timing and a fixed frame rate of 60 fps to create a fluid and "buttery-smooth" UI.[93] Android 4.1 Jelly Bean was released to the Android Open Source Project on July 9, 2012,[94] and the Nexus 7 tablet, the first device to run Jelly Bean, was released on July 13, 2012. |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.1 |
July 9, 2012 |
- Smoother user interface:
- Vsync timing across all drawing and animation done by the Android framework, including application rendering, touch events, screen composition and display refresh
- Triple buffering in the graphics pipeline
- Enhanced accessibility
- Bi-directional text and other language support
- User-installable keyboard maps
- Expandable notifications
- Ability to turn off notifications on an application-specific basis
- Shortcuts and widgets can automatically be re-arranged or re-sized to allow new items to fit on home screens
- Bluetooth data transfer for Android Beam
- Tablets with smaller screens now use an expanded version of the interface layout and home screen used by phones.[95]
- Improved camera application
- Multichannel audio[93]
- The Fraunhofer FDK AAC codec becomes standard in Android, adding AAC 5.1 channel encoding/decoding.
- USB audio (for external sound DACs)[93]
- Audio chaining (also known as gapless playback)[93][96][97]
- Ability for other launchers to add widgets from the application drawer without requiring root access
|
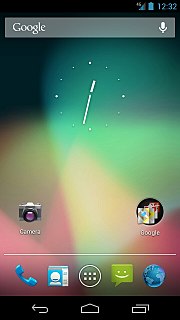
Android 4.1 on the Samsung Galaxy Nexus |
| 4.1.1 |
July 11, 2012[98] |
- Fixed a bug on the Nexus 7 regarding the inability to change screen orientation in any application
|
| 4.1.2 |
October 9, 2012[99] |
- Lock/home screen rotation support for the Nexus 7[100]
- One-finger gestures to expand/collapse notifications[101]
- Bugfixes and performance enhancements
|
|
|
| Google was expected to announce Jelly Bean 4.2 at an event in New York City on October 29, 2012, but the event was cancelled due to Hurricane Sandy.[102] Instead of rescheduling the live event, Google announced the new version with a press release, under the slogan "A new flavor of Jelly Bean". Jelly Bean 4.2 was based on Linux kernel 3.4.0, and debuted on Google's Nexus 4 and Nexus 10, which were released on November 13, 2012.[103][104] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.2 |
November 13, 2012[105] |
- Lock screen improvements, including widget support and the ability to swipe directly to camera[106]
- Notification power controls ("Quick Settings")
- "Daydream" screensavers, showing information when idle or docked
- Multiple user accounts (tablets only)
- Rewritten Bluetooth stack, switching from Bluez to Broadcom open source BlueDroid,[107] allowing improved support for multiple displays and wireless display (Miracast)
- Native right-to-left, always-on VPN and application verification.[108] A new NFC stack was added at the same time.[107]
- Accessibility improvements: triple-tap to magnify the entire screen, pan and zoom with two fingers. Speech output and Gesture Mode navigation for blind users
- New clock application with built-in world clock, stop watch and timer
- All devices now use the same interface layout, previously adapted from phones on 4.1 for smaller tablets (with centered software buttons, the system bar at the top of the screen, and a home screen with a dock and centered application menu), regardless of screen size
- Increased number of extended notifications and Actionable Notifications for more applications, allowing users to respond to certain notifications within the notification bar and without launching the application directly
- SELinux
- Premium SMS confirmation[109]
- Group Messaging
|

Android 4.2 on the Nexus 4 |
| 4.2.1 |
November 27, 2012[110] |
- Fixed a bug in the People application where December was not displayed on the date selector when adding an event to a contact[111]
- Added Bluetooth gamepads and joysticks as supported HID (Human interface device)
|
| 4.2.2 |
February 11, 2013[112] |
- Fixed Bluetooth audio streaming bugs[113]
- Long-pressing the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth icons in Quick Settings now toggles the on/off state
- New download notifications, which now shows the percentage and estimated time remaining for active application downloads
- New sounds for wireless charging and low battery
- New Gallery application animation allows faster loading
- USB debug whitelist
- Bugfixes and performance enhancements
|
|
|
| Google released Jelly Bean 4.3 under the slogan "An even sweeter Jelly Bean" on July 24, 2013, during an event in San Francisco called "Breakfast with Sundar Pichai". Most Nexus devices received the update within a week, although the second-generation Nexus 7 tablet was the first device to officially ship with it.[114] A minor bugfix update was released on August 22, 2013.[115] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.3 |
July 24, 2013[116] |
|

Android 4.3 on the Nexus 7 (2013 version) |
| 4.3.1 |
October 3, 2013[124] |
- Bugfixes and small tweaks for the Nexus 7 LTE[125]
|
|
Android 4.4 KitKat (API level 19)
Android 4.4 KitKat (API level 19)
|
| Google announced Android 4.4 KitKat on September 3, 2013. Although initially under the "Key Lime Pie" ("KLP") codename, the name was changed because "very few people actually know the taste of a key lime pie."[126] Some technology bloggers also expected the "Key Lime Pie" release to be Android 5.[127] KitKat debuted on Google's Nexus 5 on October 31, 2013, and was optimised to run on a greater range of devices than earlier Android versions, having 512 MB of RAM as a recommended minimum; those improvements were known as "Project Svelte" internally at Google.[128] The required minimum amount of RAM available to Android is 340 MB, and all devices with less than 512 MB of RAM must report themselves as "low RAM" devices.[129] |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.4 |
October 31, 2013[130][131] |
- Refreshed interface with white elements instead of blue
- Clock no longer shows bold hours; all digits are thin. The H, M, and S markings for the stopwatch and timer have been removed, leaving just the numbers.
- Ability for applications to trigger translucency in the navigation and status bars[132]
- Ability for applications to use "immersive mode" to keep the navigation and status bars hidden while maintaining user interaction[133]
- Action overflow menu buttons are always visible, even on devices with a "Menu" key, which was officially deprecated by Android 4.0.[134]
- Optimizations for performance on devices with lower specifications, including zRAM support and "low RAM" device API[128]
- Wireless printing capability[128]
- NFC host card emulation, enabling a device to replace smart cards[128]
- WebViews now based on Chromium engine (feature parity with Chrome for Android 30)
- Expanded functionality for notification listener services[128]
- Public API for developing and managing text messaging clients[135]
- New framework for UI transitions
- Storage Access Framework, an API allowing apps to retrieve files in a consistent manner. As part of the framework, a new system file picker allows users to access files from various sources (including those exposed by apps, such as online storage services).[68]
- Sensor batching, step detector and counter APIs[128]
- Settings application now makes it possible to select default text messaging and home (launcher) application
- Audio tunneling, audio monitoring and loudness enhancer[136]
- Built-in screen recording feature (primarily for developers, as usage of ADB is required)[137]
- Native infrared blaster API
- Expanded accessibility APIs and system-level closed captioning settings
- Android Runtime (ART) introduced as a new experimental application runtime environment, not enabled by default, as a replacement for the Dalvik virtual machine[138]
- Bluetooth Message Access Profile (MAP) support[139]
- Disabled access to battery statistics by third-party applications[140]
- Settings application no longer uses a multi-pane layout on devices with larger screens
- Wi-Fi and mobile data activity (TX/RX) indicators are moved to quick settings[141]
- Browser text wrap is disabled.[142]
|

Android 4.4.2 (OmniROM, AOSP-based) |
| 4.4.1 |
December 5, 2013[143] |
- Improvements to auto focus, white balance and HDR+ for the Nexus 5 camera[144][145]
- Better application compatibility for the experimental Android Runtime (ART)
- Camera application now loads Google+ Photos instead of Gallery when swiping away from the camera view
- Miscellaneous improvements and bugfixes
|
| 4.4.2 |
December 9, 2013[146] |
- Further security enhancements and bugfixes
- Removal of the "App Ops" application permissions control system, introduced in Android 4.3[147]
|
| 4.4.3 |
June 2, 2014[148] |
- Refreshed Dialer app interface[149]
- Updated the Chromium based WebView to version 33 (screencasting to DevTools, HTML5 Canvas hardware acceleration performance improvements, vibration API, HTML5 form validation, HTML5 datalist)[150]
- Miscellaneous improvements and bugfixes
|
| 4.4.4 |
June 19, 2014[151] |
|
|
Android 4.4 KitKat with wearable extensions (API level 20)
Android 4.4 KitKat with wearable extensions (API level 20)
|
| |
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 4.4W[153] |
June 25, 2014[154] |
- Initial release of Android Wear platform for smartwatches: the same as Android 4.4 "KitKat", but with wearable extensions added
|
|
| 4.4W.1 |
September 6, 2014[155] |
- UI updates for Google Maps navigation and alarms
|
|
| 4.4W.2 |
October 21, 2014[156] |
- Offline music playback
- GPS support
|
|
|
|
| Android 5.0 "Lollipop" was unveiled under the codename "Android L" on June 25, 2014, during Google I/O. It became available as official over-the-air (OTA) updates on November 12, 2014, for select devices that run distributions of Android serviced by Google, including Nexus and Google Play edition devices. Its source code was made available on November 3, 2014.[157][158]
Lollipop features a redesigned user interface built around a responsive design language referred to as "material design". Other changes include improvements to the notifications, which can be accessed from the lockscreen and displayed within applications as top-of-the-screen banners. Furthermore, Google made internal changes to the platform, with the Android Runtime (ART) officially replacing Dalvik for improved application performance, and with changes intended to improve and optimize battery usage, known internally as Project Volta.[159][160][161][162]
|
| Version |
Release date |
Features |
Image(s) |
| 5.0[163] |
November 12, 2014[164] |
- Android Runtime (ART) with ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation and improved garbage collection (GC), replacing Dalvik that uses just-in-time (JIT) compilation[163]
- Support for 64-bit CPUs
- OpenGL ES 3.1 and Android Extension Pack (AEP) on supported GPU configurations
- Recent activities screen with tasks instead of applications, up to a configured maximum of tasks per application
- Vector drawables, which scale without losing definition
- Support for print previews
- Material design, bringing a restyled user interface
- Refreshed lock screen, no longer supporting widgets[165]
- Refreshed notification tray and quick settings pull-down
- Project Volta, for battery life improvements
- Searches can be performed within the system settings for quicker access to particular settings
- Lock screen provides shortcuts to application and notification settings[166]
- Guest logins and multiple user accounts are available on more devices, such as phones.[167]
- Audio input and output through USB devices
- Third-party applications regain the ability to read and modify data located anywhere on external storage, such as on SD cards.[168][169]
- Pinning of an application's screen for restricted user activity.[166]
- Recently used applications are remembered even after restarting the device.[166]
- WebViews receive updates independently through Google Play for security reasons, instead of relying on system-wide vendor updates[170]
- Addition of 15 new languages: Basque, Bengali, Burmese, Chinese (Hong Kong), Galician, Icelandic, Kannada, Kyrgyz, Macedonian, Malayalam, Marathi, Nepali, Sinhala, Tamil and Telugu[171]
- Tap and Go allows users to quickly migrate to a new Android device, using NFC and Bluetooth to transfer Google Account details, configuration settings, user data and installed applications.[166]
- A flashlight-style application is included, working on supported devices with a camera flash.[166]
- User-customizable priorities for application notifications[172]
|

Android 5.0 developer preview |
| 5.0.1 |
December 2, 2014[173] |
- A few bugfixes, including resolving issues with video playback and password failures handling
|
| 5.0.2 |
December 19, 2014[174] |
- Fixes a bug with TRIM support, which prevented devices from the nightly on-charger cleanups of file system allocations if the device was turned off while being charged, or if it was charged during the day
- Changes how alarms wake the CPU, and how alarms compete for system resources[175]
|
- 获取 Android APP 版本信息工具类(转载)
获取 Android APP 版本信息工具类 获取手机APP版本信息工具类 1.获取版本名称 2.获取版本号 3.获取App的名称 package com.mingyue.nanshuibeidiao ...
- 安装使用离线版本的维基百科(Wikipedia)
1 相关背景 平常大家在上网查询一些基本概念的时候常常会参考维基百科上面的资料,但是由于方校长研制的GFW(长城防火墙系统)强大的屏蔽功能,好多链接打开以后,不出意外会出现著名的“404NOT FOU ...
- 获取Android版本信息和电话信息
Android的版本信息可以通过android.os.Build获得,电话信息可以通过TelephonyManager获得,代码如下: private void get_infor(){ sd ...
- Android APP 读取 AndroidManifest.xml 中的版本信息详解
APP都会涉及到版本的问题,Android APP的版本信息保存在AndroidManifest.xml文件的顶部.如下图: 有2个属性表示,“android:versionCode”和“androi ...
- Android 获取包名,版本信息
Android 获取包名,版本信息及VersionName名称 <span style="font-size: 14px;">private String ge ...
- Android版本信息及与Linux和Java的关系
1.Android与Linux和Java的关系 Android严格来说,不能算是Linux,Android是一个统称,具体来说,是Google用了Linux的一个核心,用这个核心来管理进程,控制硬件. ...
- android API版本对应的系统版本及Android获取手机和系统版本等信息的代码
学了这么久的Android,竟然一直对其API对应的名称关系一值搞不清楚,现在网上认真看了下资料,转载一个觉得写得不错的作者的文章,记下来: [背景] 之前折腾android期间,慢慢地知道了,And ...
- 维基百科 MediaWiki API 解析
使用开放的 API 做一个自己的小项目,是一个很好的学习方法.但好像开放的 API 选择并不多.这里给大家多一个选择,简单介绍一下维基百科使用的 MediaWiki API. 简介 先简单介绍几个容易 ...
- 使用JWPL (Java Wikipedia Library)操作维基百科数据
使用JWPL (Java Wikipedia Library)操作维基百科数据 1. JWPL介绍 JWPL(Java Wikipedia Library)是一个开源的访问wikipeida数据的Ja ...
随机推荐
- 再回首,Java温故知新(二):Java基本数据类型
Java作为一种强类型语言,意味着每一个变量都会有特定的类型,Java共有8种基本类型,其中有4种整型(byte.short.int.long).两种浮点型(float.double).1种字符型(c ...
- svcutil 生成代理类时的问题
如果有这个的xsd, group内嵌choice的结构: <xs:complexType name="CreateType"> <xs:sequen ...
- navicat导入mysql数据库sql时报错或数据不完全问题
错误详情:[Err] [Imp] 2006 - MySQL server has gone away 或无提示错误,但是导入数据明显缺少字段和数据 找到服务器上的MYSQL安装目录下的my.ini文件 ...
- Linux学习笔记共享
从学习到现在,已经3个月了,还有不到一个月linux课程就要结束,大概的情况如下: 预科一周,主要是学习了网络,思科的内容 linux基础课程,从无到有 linux shell 脚本 linux项目实 ...
- 基于Bootstrap实现下图所示效果的页面,一个白底的带有两个菜单项、一个下拉菜单和一个登录表单的基本导航条
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8& ...
- 关于<:if>没有<c:else>解决方案
<c:if>没有<c:else>可以用<c:choose>来取代结构: <c:choose> <c:when test=""& ...
- Ajax请求传递参数遇到的问题
想写个同类型的,代码未测. 什么是WebAPI?我的理解是WebAPI+JQuery(前端)基本上能完成Web MVC的功能,即:这么理解吧,WebAPI相当于Web MVC的后台部分. 接下来直接上 ...
- jvm-初探
目录 1,Java体系结构 2.jvm执行引擎 3,ClassLoader的体系结构 4,java class文件 概述 其实,学java不算新手了,但是却感觉很多基本的知识,我们一开始也许是记住而不 ...
- ASP.NET性能优化小结
一.返回多个数据集 检查你的访问数据库的代码,看是否存在着要返回多次的请求.每次往返降低了你的应用程序的每秒能够响应请求的次数.通过在单个数据库请求中返回多个结果集,可以减少与数据库通信的时间,使你的 ...
- $(document).ready(function(){}),$().ready(function(){})和$(function(){})三个有区别么
三者都是一样的,最完整的写法是:$(document).ready(function(){})ready() 函数仅能用于当前文档,因此无需选择器.所以document选择器可以不要,那么就可以写成: ...










