python 内存监控模块之memory_profiler
0. memory_profiler是干嘛的
This is a python module for monitoring memory consumption of a process as well as line-by-line analysis of memory consumption for python programs. It is a pure python module and has the psutil module as optional (but highly recommended) dependencies.
memory_profiler是监控python进程的神器,它可以分析出每一行代码所增减的内存状况。
1. 入门例子
#del3.py
import time
@profile
def my_func():
a = [1] * (10 ** 6)
b = [2] * (2 * 10 ** 7)
time.sleep(10)
del b
del a
print "+++++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
$python -m memory_profiler del3.py
+++++++++
Filename: del3.py Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
2 10.293 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
3 def my_func():
4 17.934 MiB 7.641 MiB a = [1] * (10 ** 6)
5 170.523 MiB 152.590 MiB b = [2] * (2 * 10 ** 7)
6 170.527 MiB 0.004 MiB time.sleep(10)
7 17.938 MiB -152.590 MiB del b
8 10.305 MiB -7.633 MiB del a
9 10.309 MiB 0.004 MiB print "+++++++++"
代码执行一遍,然后给出具体代码在某一步占用的内存,通过内存加减可以看出某个对象的大小。
2. 对象不删除,直接赋值内存是否会继续增长
#对比1
@profile
def my_func():
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024
a = 'a' * 1024
del a
print "+++++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
1 10.293 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
2 def my_func():
3 1034.301 MiB 1024.008 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
4 11.285 MiB -1023.016 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024
5 11.285 MiB 0.000 MiB a = 'a' * 1024
6 11.285 MiB 0.000 MiB del a
7 11.289 MiB 0.004 MiB print "+++++++++"
#对比2
@profile
def my_func():
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
del a
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024
del a
a = 'a' * 1024
del a
print "+++++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
1 10.293 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
2 def my_func():
3 1034.301 MiB 1024.008 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
4 10.297 MiB -1024.004 MiB del a
5 11.285 MiB 0.988 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024
6 11.285 MiB 0.000 MiB del a
7 11.285 MiB 0.000 MiB a = 'a' * 1024
8 11.285 MiB 0.000 MiB del a
9 11.289 MiB 0.004 MiB print "+++++++++"
结论:是否 del对象没有影响,新赋的值会替代旧的值
3. 对象赋值是否会增加同样的内存
#对比1
@profile
def my_func():
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
b = a
del a
print "+++++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
1 10.293 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
2 def my_func():
3 1034.301 MiB 1024.008 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
4 1034.301 MiB 0.000 MiB b = a
5 1034.301 MiB 0.000 MiB del a
6 1034.305 MiB 0.004 MiB print "+++++++++"
#对比2
@profile
def my_func():
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
b = a
del a
del b
print "+++++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
1 10.297 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
2 def my_func():
3 1034.305 MiB 1024.008 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
4 1034.305 MiB 0.000 MiB b = a
5 1034.305 MiB 0.000 MiB del a
6 10.301 MiB -1024.004 MiB del b
7 10.305 MiB 0.004 MiB print "+++++++++"
结论,把a赋值给b,内存没有增加。但是只删除其中一个对象的时候,内存不会减。
4. 另一种等价的启动方式
from memory_profiler import profile
@profile(precision=4)
def my_func():
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
del a
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024
del a
a = 'a' * 1024
del a
print "+++++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
$python -m memory_profiler del3.py
+++++++++
Filename: del3.py Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
2 10.3867 MiB 0.0000 MiB @profile(precision=4)
3 def my_func():
4 1034.3945 MiB 1024.0078 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
5 10.3906 MiB -1024.0039 MiB del a
6 11.3789 MiB 0.9883 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024
7 11.3789 MiB 0.0000 MiB del a
8 11.3789 MiB 0.0000 MiB a = 'a' * 1024
9 11.3789 MiB 0.0000 MiB del a
10 11.3828 MiB 0.0039 MiB print "+++++++++"
5. 非python内置对象例子
from memory_profiler import profile
import networkx as nx @profile(precision=4)
def my_func():
a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
del a
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_node(1)
G.add_nodes_from([i for i in range(10000)])
G.add_nodes_from([i for i in range(10000, 20000)])
G.add_edges_from([(1,2), (1,4), (2, 9), (4, 1), (3, 8)])
del G
print "++++++" if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
结果
$python del3.py
++++++
Filename: del3.py Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
4 23.4844 MiB 0.0000 MiB @profile(precision=4)
5 def my_func():
6 1047.4922 MiB 1024.0078 MiB a = 'a' * 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
7 23.4883 MiB -1024.0039 MiB del a
8 23.4883 MiB 0.0000 MiB G = nx.Graph()
9 23.4883 MiB 0.0000 MiB G.add_node(1)
10 31.3359 MiB 7.8477 MiB G.add_nodes_from([i for i in range(10000)])
11 36.9219 MiB 5.5859 MiB G.add_nodes_from([i for i in range(10000, 20000)])
12 36.9219 MiB 0.0000 MiB G.add_edges_from([(1,2), (1,4), (2, 9), (4, 1), (3, 8)])
13 25.9219 MiB -11.0000 MiB del G
14 25.9258 MiB 0.0039 MiB print "++++++"
6. 类怎么使用呢
#del4.py
from memory_profiler import profile class people:
name = ''
age = 0
__weight = 0 def __init__(self,n,a,w):
self.name = n
self.age = a
self.__weight = w @profile(precision=4)
def speak(self):
a = 'a' * 1024
b = 'b' * 1024 * 1024
print("%s is speaking: I am %d years old" % (self.name,self.age)) if __name__ == '__main__':
p = people('tom', 10, 30)
p.speak()
结果
$python del4.py
tom is speaking: I am 10 years old
Filename: del4.py Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
13 9.4219 MiB 0.0000 MiB @profile(precision=4)
14 def speak(self):
15 9.4258 MiB 0.0039 MiB a = 'a' * 1024
16 10.4297 MiB 1.0039 MiB b = 'b' * 1024 * 1024
17 10.4336 MiB 0.0039 MiB print("%s is speaking: I am %d years old" % (self.name,self.age))
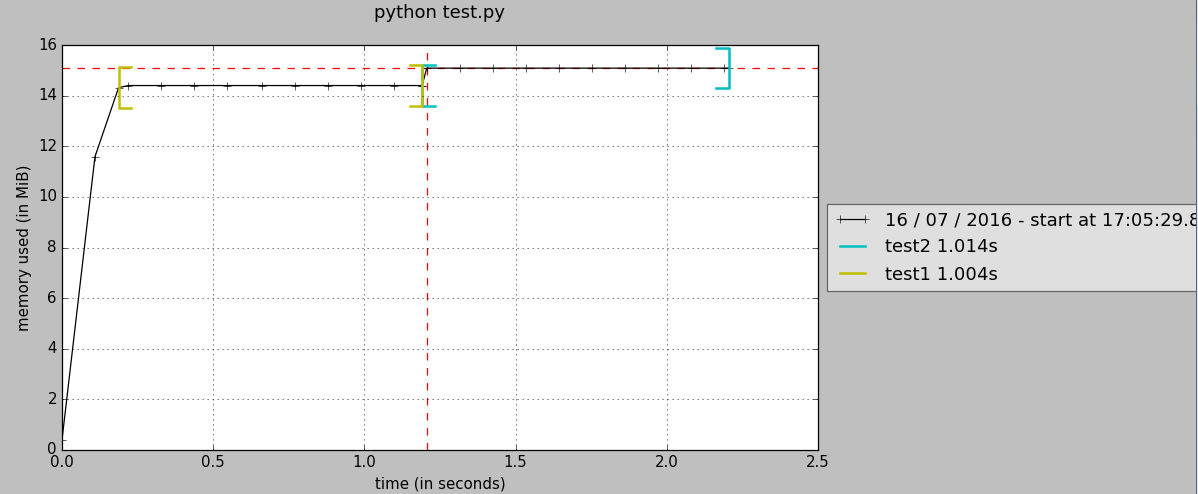
7. 随时间内存统计
#test.py
import time @profile
def test1():
n = 10000
a = [1] * n
time.sleep(1)
return a @profile
def test2():
n = 100000
b = [1] * n
time.sleep(1)
return b if __name__ == "__main__":
test1()
test2()
test.py 里有两个两个待分析的函数(@profile标识),为了形象地看出内存随时间的变化,每个函数内sleep 1s,执行
mprof run test.py
如果执行成功,结果这样
$ mprof run test.py
mprof: Sampling memory every 0.1s
running as a Python program...
结果会生成一个.dat文件,如"mprofile_20160716170529.dat",里面记录了内存随时间的变化,可用下面的命令以图片的形式展示出来:
mprof plot
8. API
memory_profiler提供很多包给第三方代码,如
>>> from memory_profiler import memory_usage
>>> mem_usage = memory_usage(-1, interval=.2, timeout=1)
>>> print(mem_usage)
[7.296875, 7.296875, 7.296875, 7.296875, 7.296875]
memory_usage(proc=-1, interval=.2, timeout=None)返回一段时间的内存值,其中proc=-1表示此进程,这里可以指定特定的进程号;interval=.2表示监控的时间间隔是0.2秒;timeout=1表示总共的时间段为1秒。那结果就返回5个值。
如果要返回一个函数的内存消耗,示例
def f(a, n=100):
import time
time.sleep(2)
b = [a] * n
time.sleep(1)
return b from memory_profiler import memory_usage
print memory_usage((f, (2,), {'n' : int(1e6)}))
这里执行了 f(1, n=int(1e6)) ,并返回在执行此函数时的内存消耗。
9. 优化实例
对比str & int
from datetime import datetime
@profile
def my_func():
beg = datetime.now()
a = {}
for i in range():
a[i] = i
#a[str(i)] = i
print "+++++++++"
del a
print "+++++++++"
end = datetime.now()
print "time:", end - beg if __name__ == '__main__':
my_func()
用a[i] = i,结果
+++++++++
+++++++++
time: 0:06:14.790899
Filename: int.py Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
2 14.727 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
3 def my_func():
4 14.734 MiB 0.008 MiB beg = datetime.now()
5 14.734 MiB 0.000 MiB a = {}
6 94.031 MiB 79.297 MiB for i in range(1000000):
7 94.031 MiB 0.000 MiB a[i] = i
8 #a[str(i)] = i
9 86.402 MiB -7.629 MiB print "+++++++++"
10 38.398 MiB -48.004 MiB del a
11 38.398 MiB 0.000 MiB print "+++++++++"
12 38.398 MiB 0.000 MiB end = datetime.now()
13 38.406 MiB 0.008 MiB print "time:", end - beg
用a[str(i)] = i,结果
+++++++++
+++++++++
time: 0:06:00.288052
Filename: int.py Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
2 14.723 MiB 0.000 MiB @profile
3 def my_func():
4 14.730 MiB 0.008 MiB beg = datetime.now()
5 14.730 MiB 0.000 MiB a = {}
6 140.500 MiB 125.770 MiB for i in range(1000000):
7 #a[i] = i
8 140.500 MiB 0.000 MiB a[str(i)] = i
9 132.871 MiB -7.629 MiB print "+++++++++"
10 38.539 MiB -94.332 MiB del a
11 38.539 MiB 0.000 MiB print "+++++++++"
12 38.539 MiB 0.000 MiB end = datetime.now()
13 38.547 MiB 0.008 MiB print "time:", end - beg
python 内存监控模块之memory_profiler的更多相关文章
- python内存管理机制
主要分为三部分: (1)内存池机制(2)引用计数(3)垃圾回收 (1)内存池机制对于python来说,对象的类型和内存都是在运行时确定的,所以python对象都是动态类型简单来说,python内存分为 ...
- 解读Python内存管理机制
转自:http://developer.51cto.com/art/201007/213585.htm 内存管理,对于Python这样的动态语言,是至关重要的一部分,它在很大程度上甚至决定了Pytho ...
- 转发:[Python]内存管理
本文为转发,原地址为:http://chenrudan.github.io/blog/2016/04/23/pythonmemorycontrol.html 本文主要为了解释清楚python的内存管理 ...
- python 内存泄露的诊断 - 独立思考 - ITeye技术网站
python 内存泄露的诊断 - 独立思考 - ITeye技术网站 python 内存泄露的诊断 博客分类: 编程语言: Python Python多线程Blog.net 对于一个用 python ...
- Python内存优化
实际项目中,pythoner更加关注的是Python的性能问题,之前也写过一篇文章<Python性能优化>介绍Python性能优化的一些方法.而本文,关注的是Python的内存优化,一般说 ...
- 使用gc、objgraph干掉python内存泄露与循环引用!
Python使用引用计数和垃圾回收来做内存管理,前面也写过一遍文章<Python内存优化>,介绍了在python中,如何profile内存使用情况,并做出相应的优化.本文介绍两个更致命的问 ...
- python 内存NoSQL数据库
python 内存NoSQL数据库 来自于网络,经过修改,秉承Open Source精神,回馈网络! #!/usr/bin/python #-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # # memd ...
- [转] 使用gc && objgraph 优化python内存
转自https://www.cnblogs.com/xybaby/p/7491656.html 使用gc.objgraph干掉python内存泄露与循环引用! 目录 一分钟版本 python内存管 ...
- Python内存优化:Profile,slots,compact dict
实际项目中,pythoner更加关注的是Python的性能问题,之前也写过一篇文章<Python性能优化>介绍Python性能优化的一些方法.而本文,关注的是Python的内存优化,一般说 ...
随机推荐
- SecureCRT的相关问题
1. 中文显示乱码的解决方法 2. 显示Linux中的颜色信息 3. 解决终端长时间无输入导致SSH连接中断的问题 4. 以公钥方式代替密码方式登录服务器 在SecureCRT中创建Public Ke ...
- 约跑APP测试报告
用户需求规格说明书URL:http://www.cnblogs.com/liquan/p/6071804.html 组长博客URL:http://www.cnblogs.com/liquan/ 代码g ...
- [办公自动化]PDF大小不一如何调整
最近使用acrobat制作PDF,结果里面的内容因为来自不同文件.有的大,有的小. 选择打印pdf,即可调整正常. 附: PDF页码也可以调整为与目录实际页码一致. 思考: 利用pdf进行问卷调研:或 ...
- Javascript 笔记与总结(2-8)对象2
注意:标签属性与 DOM 对象属性的对应关系,绝大部分 2 者是相同的,例如 imgobj.src 属性对应 <img src=""> 中的 src 属性 例外:< ...
- artDialog ( v 6.0.2 ) content 参数引入页面 html 内容
/*! artDialog v6.0.2 | https://github.com/aui/artDialog */ 将页面某一隐藏的 div 的 html 内容传到 artdialog 的弹窗中,并 ...
- pycharm使用笔记
Basic code completion (the name of any class, method or variable) control + 空格 # 代码补全,如果跟系统spotligh ...
- 正则匹配中文.PHP不兼容的问题
不使用: ^[\u4e00-\u9fa5_a-zA-Z0-9_]+$ 有可能兼容有问题 if(!preg_match_all("/^[\\x7f-\\xff_a-zA-Z0-9]+$/&qu ...
- Delphi深度探索-CodeSite应用指南
Delphi深度探索-CodeSite应用指南 Delphi虽然为我们提供极其强大的调试功能,查找Bug仍然是一项艰巨的工作,通常我们写代码和调试代码的所消耗的时间是大致相同的,甚至有可能更多.为了减 ...
- Java Map遍历方式的选择
[原文] 1. 阐述 对于Java中Map的遍历方式,很多文章都推荐使用entrySet,认为其比keySet的效率高很多.理由是:entrySet方法一次拿到所有key和value的集合:而keyS ...
- Android项目框架升级尝鲜OkHttp
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/liuxian13183/ ,引用必须注明出处! 随着项目日趋稳定,需求不再总是变化,那么是时间来整理下项目了.先简单介绍下,本项目最初使用loop4 ...
