SkipList算法实现
SkipList是一种快速查找链表,链表元素的是有序的。由W.Pugh发明于1989年。
其算法复杂度如下:
Average Worst case
Space O(n) O(n log n)
Search O(log n) O(n)
Insert O(log n) O(n)
Delete O(log n) O(n)
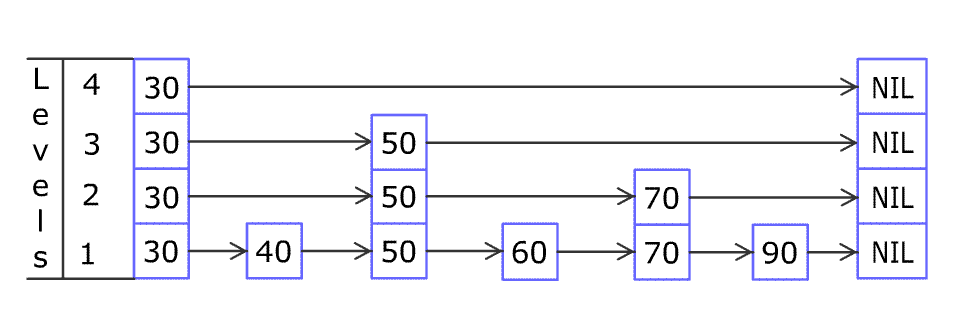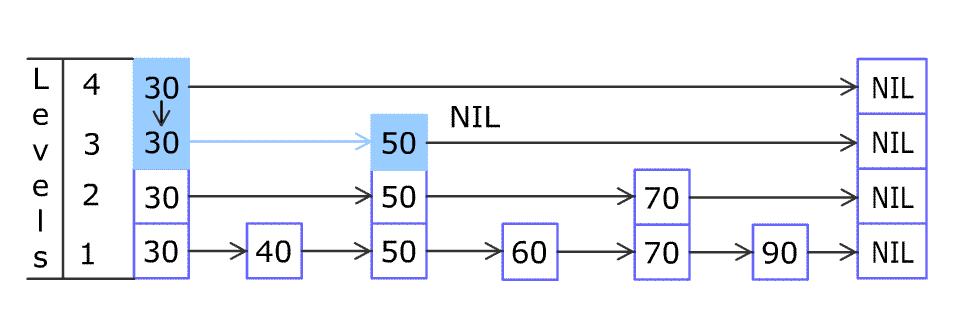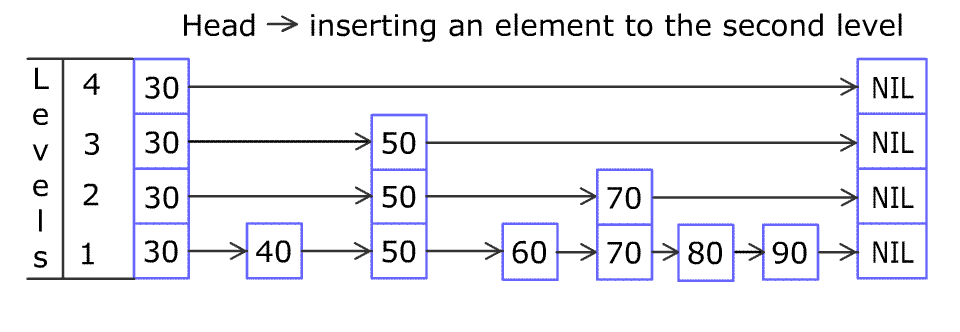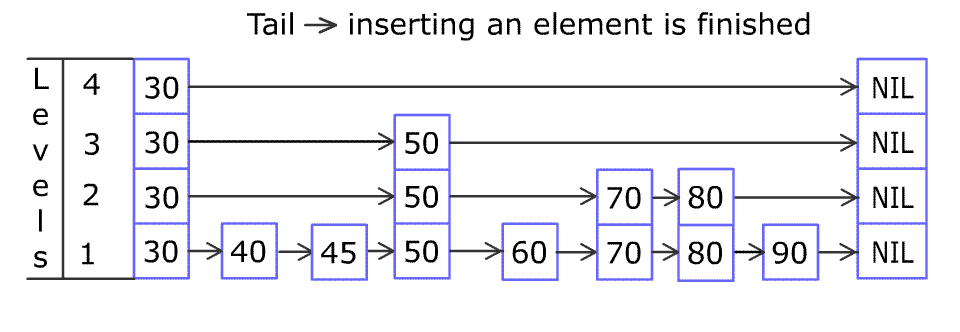
(图片来源于WiKi)
均算法复杂度不亚于AVL和红黑树。其数据结构和操作也简单。AVL树和红黑树为保
持平衡,维护树的平衡代价高。
SkipList 现用于Redis,LevelDB等开源项目, 维基百科可以看它到很多应用场景。
根据W.Pugh的论文,其算法实现如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <random>
using namespace std; #define MaxLevel 5 typedef struct SkipListNode {
int value;
int key;
int level;
SkipListNode* forward[MaxLevel];
} SkipListNode; typedef struct SkipList {
SkipListNode* head;
int level;
int length;
} SkipList; SkipListNode* makeNode(int level, int key, int value)
{
SkipListNode* pNode = (SkipListNode *)malloc(sizeof(SkipListNode));
if (!pNode) {
return NULL;
}
pNode->key = key;
pNode->value = value;
pNode->level = level;
for (int i = ; i < MaxLevel; ++i)
pNode->forward[i] = NULL; return pNode;
} void initSkipList(SkipList *pSkipList)
{
if (!pSkipList)
return;
SkipListNode* head = makeNode(, , );
if (!head)
return;
pSkipList->head = head;
pSkipList->length = ;
pSkipList->level = ; for (int i = ; i < MaxLevel; i++)
pSkipList->head->forward[i] = NULL;
} int randomLevel()
{
int newLevel = ;
while ((rand() & 0xFFFF) < (0.4 * 0xFFFF))
++newLevel;
return newLevel < MaxLevel ? newLevel : MaxLevel;
}
bool insertNode(SkipList *pSkipList, int searchKey, int newValue)
{
SkipListNode* update[MaxLevel];
if (!pSkipList)
return false; SkipListNode* pNode = pSkipList->head;
if (!pNode) {
return false;
}
for (int i = pSkipList->level - ; i >= ; i--) {
while (pNode->forward[i] && pNode->forward[i]->key < searchKey)
pNode = pNode->forward[i]; // pNode->key < searchKey < pNode->forward[i]->key
update[i] = pNode;
}
pNode = pNode->forward[];
if (pNode && pNode->key == searchKey) {
pNode->value = newValue;
}
else {
int level = randomLevel();
if (level > pSkipList->level) {
for (int i = pSkipList->level; i < level; i++) {
update[i] = pSkipList->head;
}
pSkipList->level = level;
}
pNode = makeNode(level, searchKey, newValue);
if (!pNode) {
return false;
}
for (int i = ; i < pSkipList->level; ++i) {
pNode->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = pNode;
}
pSkipList->length++;
}
return true;
} SkipListNode* searchNode(SkipList *pSkipList, int searchKey) {
if (!pSkipList)
return NULL; SkipListNode *pNode = pSkipList->head;
if (!pNode)
return NULL; for (int i = pSkipList->level - ; i >= ; --i) {
while (pNode->forward[i] && pNode->forward[i]->key < searchKey)
pNode = pNode->forward[i];
} pNode = pNode->forward[];
if (pNode && pNode->key == searchKey)
return pNode;
return NULL;
} bool deleteNode(SkipList* pSkipList, int searchKey) {
if (!pSkipList)
return false; SkipListNode *pNode = pSkipList->head;
SkipListNode *update[MaxLevel]; for (int i = pSkipList->level - ; i >= ; i--) {
while (pNode->forward[i] && pNode->forward[i]->key < searchKey) {
pNode = pNode->forward[i];
}
update[i] = pNode;
} pNode = pNode->forward[];
if (pNode && pNode->key == searchKey) {
for (int i = ; i < pSkipList->level; ++i) {
if (update[i] && update[i]->forward[i] != pNode) {
break;
}
update[i]->forward[i] = pNode->forward[i];
}
free(pNode);
while (pSkipList->level > &&
pSkipList->head->forward[pSkipList->level - ] == NULL) {
pSkipList->level--;
}
pSkipList->length--;
return true;
}
return false;
} void travelList(SkipList* pSkipList)
{
SkipListNode* pNode = pSkipList->head;
if (!pNode)
return; while (pNode->forward[]) {
cout << pNode->forward[]->value << " " << pNode->forward[]->level << endl;
pNode = pNode->forward[];
}
} int main()
{
SkipList list;
initSkipList(&list); insertNode(&list, , );
insertNode(&list, , );
insertNode(&list, , ); travelList(&list); SkipListNode* pNode = searchNode(&list, );
cout << pNode->value << endl; pNode = searchNode(&list, );
cout << pNode->value << endl; cout << "----" << endl;
deleteNode(&list, );
travelList(&list); cout << "----" << endl;
deleteNode(&list, );
travelList(&list); cout << "----" << endl;
deleteNode(&list, );
travelList(&list);
return ;
}
SkipList算法实现的更多相关文章
- 深夜学算法之SkipList:让链表飞
1. 前言 上次写Python操作LevelDB时提到过,有机会要实现下SkipList.摘录下wiki介绍: 跳跃列表是一种随机化数据结构,基于并联的链表,其效率可比拟二叉查找树. 我们知道对于有序 ...
- 算法: skiplist 跳跃表代码实现和原理
SkipList在leveldb以及lucence中都广为使用,是比较高效的数据结构.由于它的代码以及原理实现的简单性,更为人们所接受. 所有操作均从上向下逐层查找,越上层一次next操作跨度越大.其 ...
- ssdb底层实现——ssdb底层是leveldb,leveldb根本上是skiplist(例如为存储多个list items,必然有多个item key,而非暴力string cat),用它来做redis的list和set等,势必在数据结构和算法层面上有诸多不适
我已经在用ssdb的hash结构,存储了很多数据了,但是我现在的用法正确吗? 我使用hash结构合理吗? 1. ssdb数据库说是类似redis,而且他们都有hash结构,但是他们的命名有点不同,ss ...
- 探索c#之跳跃表(SkipList)
阅读目录: 基本介绍 算法思想 演化步骤 实现细节 总结 基本介绍 SkipList是William Pugh在1990年提出的,它是一种可替代平衡树的数据结构. SkipList在实现上相对比较简单 ...
- [转载] 跳表SkipList
原文: http://www.cnblogs.com/xuqiang/archive/2011/05/22/2053516.html leveldb中memtable的思想本质上是一个skiplist ...
- 浅析SkipList跳跃表原理及代码实现
本文将总结一种数据结构:跳跃表.前半部分跳跃表性质和操作的介绍直接摘自<让算法的效率跳起来--浅谈“跳跃表”的相关操作及其应用>上海市华东师范大学第二附属中学 魏冉.之后将附上跳跃表的源代 ...
- 跳表SkipList
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuqiang/archive/2011/05/22/2053516.html 跳表SkipList 1.聊一聊跳表作者的其人其事 2. 言归正 ...
- skiplist 跳表(2)-----细心学习
快速了解skiplist请看:skiplist 跳表(1) http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_693f08470101n2lv.html 本周我要介绍的数据结构,是我非常非 ...
- skiplist 跳表(1)
最近学习中遇到一种新的数据结构,很实用,搬过来学习. 原文地址:skiplist 跳表 为什么选择跳表 目前经常使用的平衡数据结构有:B树,红黑树,AVL树,Splay Tree, Treep等. ...
随机推荐
- 关于xib文件和storyboard文件的那些事儿
在ios中,一般建议使用代码布局,因为使用代码布局,后期维护容易,拓展容易,并且可以实现动态加载很多数据,但是代码布局比较繁琐,不适合初学者.Xib布局或者Storyboard布局比较方便.下面介绍一 ...
- Ms sql将首字母大写
--辅助表 create table a ( a int ) declare @b int begin insert into a values(@b) end; go --表数据 ),id int) ...
- PCI Express(二) - Topology
原文出处:http://www.fpga4fun.com/PCI-Express2.html Point-to-point architecture At 2.5Gbps, the PCI Expre ...
- Java利用aspose-words将word文档转换成pdf(破解 无水印)
首先下载aspose-words-15.8.0-jdk16.jar包 http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nvbJwnv 引入jar包,编写Java代码 package doc; impo ...
- 32、shiro框架入门3.授权
一. 授权,也叫访问控制,即在应用中控制谁能访问哪些资源(如访问页面/编辑数据/页面操作等).在授权中需了解的几个关键对象:主体(Subject).资源(Resource).权限(Permission ...
- IIS7中配置FastCGI运行PHP
环境说明: 操作系统:使用windows 2008 server 64位系统,IIS7.5PHP版本:官方下载PHP 5.4.16 VC9 x86 Non Thread SafeZIP版本.PHP路径 ...
- 编程范式 epesode7,8 stack存放指针类型and heap,register
这一节从后往前写. ____stack and heap ___stack由 汇编语言操控管理,数据先入后出. 栈是存放局部变量,函数调用子函数时,该函数在栈中占用的空间会增大,用于存放子函数的局部变 ...
- Spring JDBC常用方法详细示例
Spring JDBC使用简单,代码简洁明了,非常适合快速开发的小型项目.下面对开发中常用的增删改查等方法逐一示例说明使用方法 1 环境准备 启动MySQL, 创建一个名为test的数据库 创建Mav ...
- Brn系列商城4.1正式发布,欢迎大家下载体验
此次升级内容如下: 独立IP搜索策略 独立文件上传策略 添加退换货功能 重构支付方式 常规性修复和改进 下载地址:http://www.brnshop.com
- left join ,right join ,inner join ,cross join 区别
left join ,right join ,inner join ,cross join 区别(参考:http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=gpOl9HXZR0OrQuy ...
