Matlab实现线性回归和逻辑回归: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7732417
本讲内容:
Matlab 实现各种回归函数
=========================
基本模型
Y=θ0+θ1X1型---线性回归(直线拟合)
解决过拟合问题---Regularization
Y=1/(1+e^X)型---逻辑回归(sigmod 函数拟合)
在解决拟合问题的解决之前,我们首先回忆一下线性回归和逻辑回归的基本模型。
设待拟合参数 θn*1 和输入参数[ xm*n, ym*1 ] 。
对于各类拟合我们都要根据梯度下降的算法,给出两部分:
① cost function(指出真实值y与拟合值h<hypothesis>之间的距离):给出cost function 的表达式,每次迭代保证cost function的量减小;给出梯度gradient,即cost function对每一个参数θ的求导结果。
function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction ( theta )
② Gradient_descent(主函数):用来运行梯度下降算法,调用上面的cost function进行不断迭代,直到最大迭代次数达到给定标准或者cost function返回值不再减小。
function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
线性回归:拟合方程为hθ(x)=θ0x0+θ1x1+…+θnxn,当然也可以有xn的幂次方作为线性回归项(如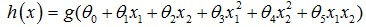 ),这与普通意义上的线性不同,而是类似多项式的概念。
),这与普通意义上的线性不同,而是类似多项式的概念。
其cost function 为: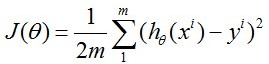
逻辑回归:拟合方程为hθ(x)=1/(1+e^(θTx)),其cost function 为:
cost function对各θj的求导请自行求取,看第三章最后一图,或者参见后文代码。
后面,我们分别对几个模型方程进行拟合,给出代码,并用matlab中的fit函数进行验证。
在Matlab 线性拟合 & 非线性拟合中我们已经讲过如何用matlab自带函数fit进行直线和曲线的拟合,非常实用。而这里我们是进行ML课程的学习,因此研究如何利用前面讲到的梯度下降法(gradient descent)进行拟合。
- function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction2( theta )
- %COSTFUNCTION2 Summary of this function goes here
- % linear regression -> y=theta0 + theta1*x
- % parameter: x:m*n theta:n* y:m* (m=,n=)
- %
- %Data
- x=[;;;];
- y=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
- m=size(x,);
- hypothesis = h_func(x,theta);
- delta = hypothesis - y;
- jVal=sum(delta.^);
- gradient()=sum(delta)/m;
- gradient()=sum(delta.*x)/m;
- end
其中,h_func是hypothesis的结果:
- function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta)
- %H_FUNC Summary of this function goes here
- % Detailed explanation goes here
- %cost function
- res= theta()+theta()*inputx;function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta)
- end
Gradient_descent:
- function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
- %GRADIENT_DESCENT Summary of this function goes here
- % Detailed explanation goes here
- options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',);
- initialTheta = zeros(,);
- [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction2,initialTheta,options);
- end
result:
- >> [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
- Local minimum found.
- Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
- the default value of the function tolerance.
- <stopping criteria details>
- optTheta =
- 0.3000
- 0.8600
- functionVal =
- 0.0720
- exitFlag =
- function [ parameter ] = checkcostfunc( )
- %CHECKC2 Summary of this function goes here
- % check if the cost function works well
- % check with the matlab fit function as standard
- %check cost function
- x=[;;;];
- y=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
- EXPR= {'x',''};
- p=fittype(EXPR);
- parameter=fit(x,y,p);
- end
运行结果:
- >> checkcostfunc()
- ans =
- Linear model:
- ans(x) = a*x + b
- Coefficients (with % confidence bounds):
- a = 0.86 (0.4949, 1.225)
- b = 0.3 (-0.6998, 1.3)
和我们的结果一样。下面画图:
- function PlotFunc( xstart,xend )
- %PLOTFUNC Summary of this function goes here
- % draw original data and the fitted
- %===================cost function ====linear regression
- %original data
- x1=[;;;];
- y1=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
- %plot(x1,y1,'ro-','MarkerSize',);
- plot(x1,y1,'rx','MarkerSize',);
- hold on;
- %fitted line - 拟合曲线
- x_co=xstart:0.1:xend;
- y_co=0.3+0.86*x_co;
- %plot(x_co,y_co,'g');
- plot(x_co,y_co);
- hold off;
- end
过拟合问题解决方法我们已在第三章中讲过,利用Regularization的方法就是在cost function中加入关于θ的项,使得部分θ的值偏小,从而达到fit效果。
在每次迭代中,按照gradient descent的方法更新参数θ:θ(i)-=gradient(i),其中gradient(i)是J(θ)对θi求导的函数式,在此例中就有gradient(1)=2*(theta(1)-5), gradient(2)=2*(theta(2)-5)。
函数costFunction, 定义jVal=J(θ)和对两个θ的gradient:
- function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction( theta )
- %COSTFUNCTION Summary of this function goes here
- % Detailed explanation goes here
- jVal= (theta()-)^+(theta()-)^;
- gradient = zeros(,);
- %code to compute derivative to theta
- gradient() = * (theta()-);
- gradient() = * (theta()-);
- end
Gradient_descent,进行参数优化
- function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
- %GRADIENT_DESCENT Summary of this function goes here
- % Detailed explanation goes here
- options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',);
- initialTheta = zeros(,)
- [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction,initialTheta,options);
- end
matlab主窗口中调用,得到优化厚的参数(θ1,θ2)=(5,5)
- [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
- initialTheta =
- Local minimum found.
- Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
- the default value of the function tolerance.
- <stopping criteria details>
- optTheta =
- functionVal =
- exitFlag =
第四部分:Y=1/(1+e^X)型---逻辑回归(sigmod 函数拟合)
hypothesis function:
- function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta)
- %cost function
- tmp=theta()+theta()*inputx;%m*
- res=./(+exp(-tmp));%m*
- end
cost function:
- function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction3( theta )
- %COSTFUNCTION3 Summary of this function goes here
- % Logistic Regression
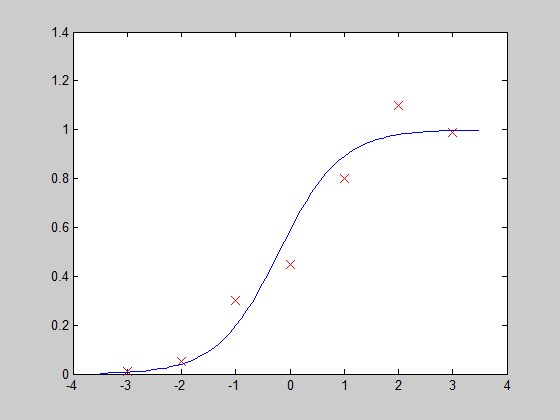
- x=[-; -; -; ; ; ; ];
- y=[0.01; 0.05; 0.3; 0.45; 0.8; 1.1; 0.99];
- m=size(x,);
- %hypothesis data
- hypothesis = h_func(x,theta);
- %jVal-cost function & gradient updating
- jVal=-sum(log(hypothesis+0.01).*y + (-y).*log(-hypothesis+0.01))/m;
- gradient()=sum(hypothesis-y)/m; %reflect to theta1
- gradient()=sum((hypothesis-y).*x)/m; %reflect to theta
- end
Gradient_descent:
- function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
- options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',);
- initialTheta = [;];
- [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction3,initialTheta,options);
- end
运行结果:
- [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
- Local minimum found.
- Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
- the default value of the function tolerance.
- <stopping criteria details>
- optTheta =
- 0.3526
- 1.7573
- functionVal =
- 0.2498
- exitFlag =
画图验证:
Matlab实现线性回归和逻辑回归: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression的更多相关文章
- 逻辑回归模型(Logistic Regression)及Python实现
逻辑回归模型(Logistic Regression)及Python实现 http://www.cnblogs.com/sumai 1.模型 在分类问题中,比如判断邮件是否为垃圾邮件,判断肿瘤是否为阳 ...
- 斯坦福机器学习视频笔记 Week3 逻辑回归与正则化 Logistic Regression and Regularization
我们将讨论逻辑回归. 逻辑回归是一种将数据分类为离散结果的方法. 例如,我们可以使用逻辑回归将电子邮件分类为垃圾邮件或非垃圾邮件. 在本模块中,我们介绍分类的概念,逻辑回归的损失函数(cost fun ...
- 斯坦福CS229机器学习课程笔记 part2:分类和逻辑回归 Classificatiion and logistic regression
Logistic Regression 逻辑回归 1.模型 逻辑回归解决的是分类问题,并且是二元分类问题(binary classification),y只有0,1两个取值.对于分类问题使用线性回归不 ...
- 分类和逻辑回归(Classification and logistic regression)
分类问题和线性回归问题问题很像,只是在分类问题中,我们预测的y值包含在一个小的离散数据集里.首先,认识一下二元分类(binary classification),在二元分类中,y的取值只能是0和1.例 ...
- 逻辑回归(分类问题)(Logistic Regression、罗杰斯特回归)
逻辑回归:问题只有两项,即{0, 1}.一般而言,回归问题是连续模型,不用在分类问题上,且噪声较大,但如果非要引入,那么采用逻辑回归模型. 对于一般训练集: 参数系统为: 逻辑回归模型为: ...
- 吴恩达机器学习笔记22-正则化逻辑回归模型(Regularized Logistic Regression)
针对逻辑回归问题,我们在之前的课程已经学习过两种优化算法:我们首先学习了使用梯度下降法来优化代价函数
- 机器学习算法笔记1_2:分类和逻辑回归(Classification and Logistic regression)
形式: 採用sigmoid函数: g(z)=11+e−z 其导数为g′(z)=(1−g(z))g(z) 如果: 即: 若有m个样本,则似然函数形式是: 对数形式: 採用梯度上升法求其最大值 求导: 更 ...
- 逻辑回归原理 面试 Logistic Regression
逻辑回归是假设数据服从独立且服从伯努利分布,多用于二分类场景,应用极大似然估计构造损失函数,并使用梯度下降法对参数进行估计.
- 吴恩达深度学习:2.9逻辑回归梯度下降法(Logistic Regression Gradient descent)
1.回顾logistic回归,下式中a是逻辑回归的输出,y是样本的真值标签值 . (1)现在写出该样本的偏导数流程图.假设这个样本只有两个特征x1和x2, 为了计算z,我们需要输入参数w1.w2和b还 ...
随机推荐
- jdbc基础 (五) 连接池与数据源 DBCP以及C3P0的使用
一.连接池的概念和使用 在实际应用开发中,特别是在WEB应用系统中,如果JSP.Servlet或EJB使用JDBC直接访问数据库中的数据,每一次数据访问请求都必须经历建立数据库连接.打开数据库.存取数 ...
- xsd、wsdl生成C#类的命令行工具使用方法
1.xsd生成C#类命令 示例:xsd <xsd文件路径> /c /o:<生成CS文件目录> <其他参数> 参数说明: /c 生成为cs文件,/d 生成DataSe ...
- 第三十一课:JSDeferred详解2
这一课,我们先接着上一课讲一下wait方法,以及wait方法是如何从静态方法变化实例方法的. 首先我们先看wait方法为啥可以从静态方法变成实例方法,请看register源码: Deferred.re ...
- AngularJs-MVC之路由、模块以及依赖注入
前面呢,我们大概的了解了下AngularJs的入门,也做过了hello world的一个demo,不知道大家有没有掌握呢?在下面我们需要讲一些AngularJS的一些干货. 1,一个完整项目的目录结构 ...
- 5.9-3 用正则表达式判断字符串text是否为合法的手机号
package zfc; public class Zfc { public static void main(String[] args) { //判断手机号格式是否合法 String text = ...
- Java 关键字 native
native 关键字说明其修饰的方法是一个原生态方法,方法对应的实现不是在当前文件中,而是在用其他语言实现的文件中.Java语言本身不能对操作系统底层进行访问和操作,但是可以通过JNI接口调用其他语言 ...
- Linux operation strucutre
Under the /usr/src directory. 1.arch目录包括了所有和体系结构相关的核心代码.它下面的每一个子目录都代表一种Linux支持的体系结构,例如i386就是Intel CP ...
- 浅谈Logistic回归及过拟合
判断学习速率是否合适?每步都下降即可.这篇先不整理吧... 这节学习的是逻辑回归(Logistic Regression),也算进入了比较正统的机器学习算法.啥叫正统呢?我概念里面机器学习算法一般是这 ...
- CVE-2014-4877 && wget: FTP Symlink Arbitrary Filesystem Access
目录 . 漏洞基本描述 . 漏洞带来的影响 . 漏洞攻击场景重现 . 漏洞的利用场景 . 漏洞原理分析 . 漏洞修复方案 . 攻防思考 1. 漏洞基本描述 0x1: Wget简介 wget是一个从网络 ...
- Xcode的一些有用的插件
** --Alcatraz:Xcode插件管理 ** 安装:curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/supermarin/Alcatraz/master/Scripts/ ...
