SQLSERVER数据库死锁与优化杂谈
死锁杂谈
当数据库死锁时,SqlServer会释放一个优先级较低的锁,让另一个事务运行;所以,即时去捕捉数据库死锁,是挺不容易的。
如果,数据库死锁比较长时间,那么死锁是可以被捕捉的。
可以用SqlServer活动监视器来查看,哪些进程锁了数据库。
首先打开SqlServer活动监视器,然后可以看到,界面里有进程,查看资源,数据文件I/O,最近消耗大量资源的查询四项。
四项显示内容如下:
进程:在进程里可以看到哪些进程被阻塞,查看属性【阻塞者】可以看到,【阻塞者】的会话ID。
等待资源:等待资源里有一些锁,可以看看那些锁累计等待时间较多。
数据文件I/O:数据文件I/O记录一些数据库MDF,LDF的读写速度。
最近消耗大量资源的查询:记录一些消耗资源较大的SQL查询。
查询进程里被死锁的会话ID,然后执行下面的SQL,进行解锁。
declare @spid int Set @spid = 518 --锁表进程会话ID
declare @sql varchar(1000)
set @sql='kill '+cast(@spid as varchar)
exec(@sql)
也可以用下面SQL语句查询死锁进程,这样查询死锁进程,定位比较快。
select request_session_id spid, OBJECT_NAME(resource_associated_entity_id) tableName
from sys.dm_tran_locks where resource_type='OBJECT'
优化杂谈
最近消耗大量资源的查询也可以用SQL查询。
下面SQL是查询最耗时的前10条SQL语句。
SELECT TOP 10 total_worker_time / 1000 AS [自编译以来执行所用的CPU时间总量(ms-毫秒)],
total_elapsed_time/1000 as [完成执行此计划所用的总时间],
total_elapsed_time / execution_count/1000 as [平均完成执行此计划所用时间],
execution_count as [上次编译以来所执行的次数],
creation_time as [编译计划的时间],
deqs.total_worker_time / deqs.execution_count / 1000 AS [平均使用CPU时间(ms)],
last_execution_time AS [上次开始执行计划的时间],
total_physical_reads [编译后在执行期间所执行的物理读取总次数],
total_logical_reads/execution_count [平均逻辑读次数],
min_worker_time /1000 AS [单次执行期间所用的最小CPU时间(ms)],
max_worker_time / 1000 AS [单次执行期间所用的最大 CPU 时间(ms)],
SUBSTRING(dest.text, deqs.statement_start_offset / 2 + 1,
(CASE WHEN deqs.statement_end_offset = -1 THEN DATALENGTH(dest.text) ELSE deqs.statement_end_offset END - deqs.statement_start_offset) / 2 + 1) AS [执行SQL],
dest.text as [完整SQL],
db_name(dest.dbid) as [数据库名称],
object_name(dest.objectid, dest.dbid) as [对象名称]
,deqs.plan_handle [查询所属的已编译计划]
FROM sys.dm_exec_query_stats deqs WITH(NOLOCK)
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(deqs.sql_handle) AS dest --平均使用CPU时间降序
ORDER BY (deqs.total_worker_time / deqs.execution_count / 1000) DESC
在SqlServer活动监视器里,查看资源等待。
通常可以看到等待类别是Latch的排在最上面,如下图:
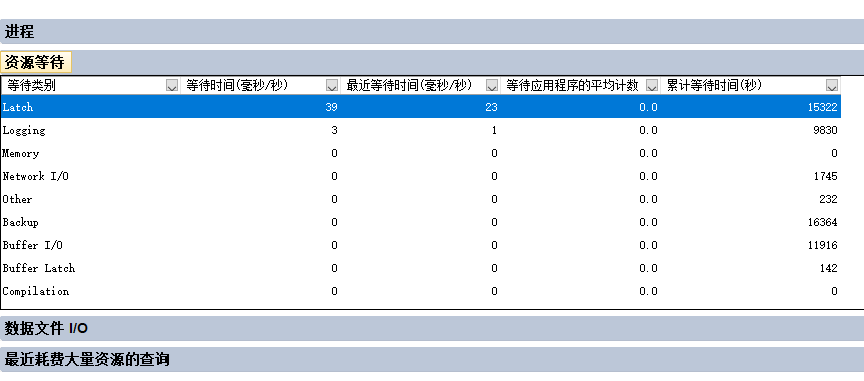
Latch 【闩锁】虽然是一种轻量级的锁,但等待的锁越多,肯定越影响数据库性能。
执行下面SQL,查看下哪些Latch比较耗资源。
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_os_latch_stats
查询结果如下图所示:
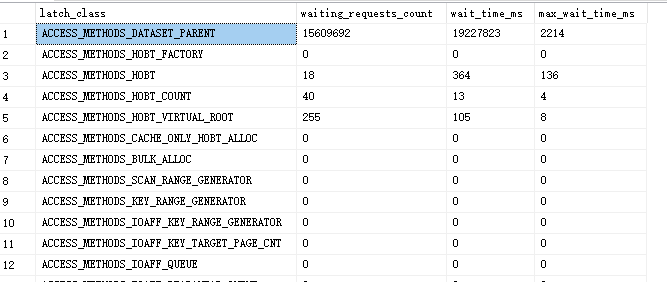
从结果中可以看到各种锁类型的请求的次数,等待时间,最大等待时间(毫秒)。
但这些锁类型都是英文简写,需要使用下面表格查询它们的真实意义。
通过对比表格,我们发现了最消耗资源的ACCESS_METHODS_DATASET_PARENT锁的意义是并发操作时资源访问的锁。那么想降低并发操作,就可以减少ACCESS_METHODS_DATASET_PARENT锁的资源消耗了。
| Latch class | Description |
|---|---|
| ALLOC_CREATE_RINGBUF | Used internally by SQL Server to initialize the synchronization of the creation of an allocation ring buffer. |
| ALLOC_CREATE_FREESPACE_CACHE | Used to initialize the synchronization of internal freespace caches for heaps. |
| ALLOC_CACHE_MANAGER | Used to synchronize internal coherency tests. |
| ALLOC_FREESPACE_CACHE | Used to synchronize the access to a cache of pages with available space for heaps and binary large objects (BLOBs). Contention on latches of this class can occur when multiple connections try to insert rows into a heap or BLOB at the same time. You can reduce this contention by partitioning the object. Each partition has its own latch. Partitioning will distribute the inserts across multiple latches. |
| ALLOC_EXTENT_CACHE | Used to synchronize the access to a cache of extents that contains pages that are not allocated. Contention on latches of this class can occur when multiple connections try to allocate data pages in the same allocation unit at the same time. This contention can be reduced by partitioning the object of which this allocation unit is a part. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_DATASET_PARENT | Used to synchronize child dataset access to the parent dataset during parallel operations. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_HOBT_FACTORY | Used to synchronize access to an internal hash table. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_HOBT | Used to synchronize access to the in-memory representation of a HoBt. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_HOBT_COUNT | Used to synchronize access to a HoBt page and row counters. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_HOBT_VIRTUAL_ROOT | Used to synchronize access to the root page abstraction of an internal B-tree. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_CACHE_ONLY_HOBT_ALLOC | Used to synchronize worktable access. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_BULK_ALLOC | Used to synchronize access within bulk allocators. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_SCAN_RANGE_GENERATOR | Used to synchronize access to a range generator during parallel scans. |
| ACCESS_METHODS_KEY_RANGE_GENERATOR | Used to synchronize access to read-ahead operations during key range parallel scans. |
| APPEND_ONLY_STORAGE_INSERT_POINT | Used to synchronize inserts in fast append-only storage units. |
| APPEND_ONLY_STORAGE_FIRST_ALLOC | Used to synchronize the first allocation for an append-only storage unit. |
| APPEND_ONLY_STORAGE_UNIT_MANAGER | Used for internal data structure access synchronization within the fast append-only storage unit manager. |
| APPEND_ONLY_STORAGE_MANAGER | Used to synchronize shrink operations in the fast append-only storage unit manager. |
| BACKUP_RESULT_SET | Used to synchronize parallel backup result sets. |
| BACKUP_TAPE_POOL | Used to synchronize backup tape pools. |
| BACKUP_LOG_REDO | Used to synchronize backup log redo operations. |
| BACKUP_INSTANCE_ID | Used to synchronize the generation of instance IDs for backup performance monitor counters. |
| BACKUP_MANAGER | Used to synchronize the internal backup manager. |
| BACKUP_MANAGER_DIFFERENTIAL | Used to synchronize differential backup operations with DBCC. |
| BACKUP_OPERATION | Used for internal data structure synchronization within a backup operation, such as database, log, or file backup. |
| BACKUP_FILE_HANDLE | Used to synchronize file open operations during a restore operation. |
| BUFFER | Used to synchronize short term access to database pages. A buffer latch is required before reading or modifying any database page. Buffer latch contention can indicate several issues, including hot pages and slow I/Os.
This latch class covers all possible uses of page latches. sys.dm_os_wait_stats makes a difference between page latch waits that are caused by I/O operations and read and write operations on the page. |
| BUFFER_POOL_GROW | Used for internal buffer manager synchronization during buffer pool grow operations. |
| DATABASE_CHECKPOINT | Used to serialize checkpoints within a database. |
| CLR_PROCEDURE_HASHTABLE | Internal use only. |
| CLR_UDX_STORE | Internal use only. |
| CLR_DATAT_ACCESS | Internal use only. |
| CLR_XVAR_PROXY_LIST | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_CHECK_AGGREGATE | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_CHECK_RESULTSET | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_CHECK_TABLE | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_CHECK_TABLE_INIT | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_CHECK_TRACE_LIST | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_FILE_CHECK_OBJECT | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_PERF | Used to synchronize internal performance monitor counters. |
| DBCC_PFS_STATUS | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_OBJECT_METADATA | Internal use only. |
| DBCC_HASH_DLL | Internal use only. |
| EVENTING_CACHE | Internal use only. |
| FCB | Used to synchronize access to the file control block. |
| FCB_REPLICA | Internal use only. |
| FGCB_ALLOC | Use to synchronize access to round robin allocation information within a filegroup. |
| FGCB_ADD_REMOVE | Use to synchronize access to filegroups for add, drop, grow, and shrink file operations. |
| FILEGROUP_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| FILE_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| FILESTREAM_FCB | Internal use only. |
| FILESTREAM_FILE_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| FILESTREAM_GHOST_FILES | Internal use only. |
| FILESTREAM_DFS_ROOT | Internal use only. |
| LOG_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_DOCUMENT_ID | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_DOCUMENT_ID_TRANSACTION | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_DOCUMENT_ID_NOTIFY | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_LOGS | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_CRAWL_LOG | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_ADMIN | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_AMDIN_COMMAND_CACHE | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_LANGUAGE_TABLE | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_CRAWL_DM_LIST | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_CRAWL_CATALOG | Internal use only. |
| FULLTEXT_FILE_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| DATABASE_MIRRORING_REDO | Internal use only. |
| DATABASE_MIRRORING_SERVER | Internal use only. |
| DATABASE_MIRRORING_CONNECTION | Internal use only. |
| DATABASE_MIRRORING_STREAM | Internal use only. |
| QUERY_OPTIMIZER_VD_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| QUERY_OPTIMIZER_ID_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| QUERY_OPTIMIZER_VIEW_REP | Internal use only. |
| RECOVERY_BAD_PAGE_TABLE | Internal use only. |
| RECOVERY_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| SECURITY_OPERATION_RULE_TABLE | Internal use only. |
| SECURITY_OBJPERM_CACHE | Internal use only. |
| SECURITY_CRYPTO | Internal use only. |
| SECURITY_KEY_RING | Internal use only. |
| SECURITY_KEY_LIST | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_CONNECTION_RECEIVE | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_TRANSMISSION | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_TRANSMISSION_UPDATE | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_TRANSMISSION_STATE | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_TRANSMISSION_ERRORS | Internal use only. |
| SSBXmitWork | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_MESSAGE_TRANSMISSION | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_MAP_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_HOST_NAME | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_READ_CACHE | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_WAITFOR_MANAGER | Used to synchronize an instance level map of waiter queues. One queue exists per database ID, Database Version, and Queue ID tuple. Contention on latches of this class can occur when many connections are: In a WAITFOR(RECEIVE) wait state; calling WAITFOR(RECEIVE); exceeding the WAITFOR timeout; receiving a message; committing or rolling back the transaction that contains the WAITFOR(RECEIVE); You can reduce the contention by reducing the number of threads in a WAITFOR(RECEIVE) wait state. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_WAITFOR_TRANSACTION_DATA | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_TRANSMISSION_TRANSACTION_DATA | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_TRANSPORT | Internal use only. |
| SERVICE_BROKER_MIRROR_ROUTE | Internal use only. |
| TRACE_ID | Internal use only. |
| TRACE_AUDIT_ID | Internal use only. |
| TRACE | Internal use only. |
| TRACE_CONTROLLER | Internal use only. |
| TRACE_EVENT_QUEUE | Internal use only. |
| TRANSACTION_DISTRIBUTED_MARK | Internal use only. |
| TRANSACTION_OUTCOME | Internal use only. |
| NESTING_TRANSACTION_READONLY | Internal use only. |
| NESTING_TRANSACTION_FULL | Internal use only. |
| MSQL_TRANSACTION_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| DATABASE_AUTONAME_MANAGER | Internal use only. |
| UTILITY_DYNAMIC_VECTOR | Internal use only. |
| UTILITY_SPARSE_BITMAP | Internal use only. |
| UTILITY_DATABASE_DROP | Internal use only. |
| UTILITY_DYNAMIC_MANAGER_VIEW | Internal use only. |
| UTILITY_DEBUG_FILESTREAM | Internal use only. |
| UTILITY_LOCK_INFORMATION | Internal use only. |
| VERSIONING_TRANSACTION | Internal use only. |
| VERSIONING_TRANSACTION_LIST | Internal use only. |
| VERSIONING_TRANSACTION_CHAIN | Internal use only. |
| VERSIONING_STATE | Internal use only. |
| VERSIONING_STATE_CHANGE | Internal use only. |
| KTM_VIRTUAL_CLOCK | Internal use only. |
DBCC杂谈
DBCC 语句是SQL Server 的数据库控制台命令,共有以下四种类型。
维护:对数据库、索引或文件组进行维护的任务。
杂项:杂项任务,如启用跟踪标志或从内存中删除 DLL。
信息:收集并显示各种类型信息的任务。
验证:对数据库、表、索引、目录、文件组或数据库页的分配进行的验证操作。
DBCC shrinkdatabase
DBCC shrinkdatabase用于收缩数据库,SQL语句如下:
DBCC shrinkdatabase (N'库名' , 1)
执行结果如下:
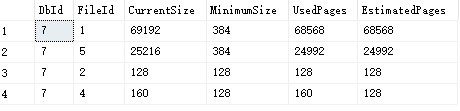
各字段含义如下:
DbId:数据库引擎试图收缩的文件的数据库标识号。
FileId:数据库引擎尝试收缩的文件的文件标识号。
CurrentSize:文件当前占用的 8 KB 页数。
MinimumSize:文件最低可以占用的 8 KB 页数。 这与文件的最小大小或最初创建时的大小相对应。
UsedPages:文件当前使用的 8 KB 页数。
EstimatedPages:数据库引擎估计文件能够收缩到的 8 KB 页数。
如果收缩不成功,可以查看下数据库是否有可以收缩的空间。
SQL如下:
SELECT name ,size/128.0 - CAST(FILEPROPERTY(name, 'SpaceUsed') AS int)/128.0 AS AvailableSpaceInMB
FROM sys.database_files;
如果有空间还收缩不成功,则可能是别原因。
数据库日志杂谈
SqlServer数据库日志对执行的SQL语句进行了加密,所以,在日志里,我们看不到真正执行的SQL语句。
如果想查看SQL语句,需要借助一些工具,如ApexSQLLog。
不过,虽然看不到SQL语句,也可以通过日志看出一些数据库问题,比如,可以查看数据库执行了多少次插入,更新等操作。
查看数据库日志的SQL如下:
SELECT * FROM [sys].[fn_dblog](NULL,NULL)
查询结果如下:
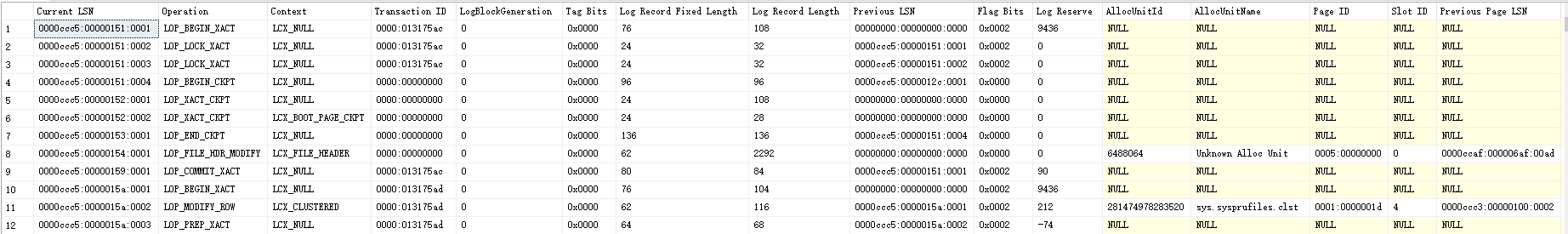
查询结果各字段含义如下:
|
Operation |
Context |
解释 |
|
LOP_SET_BITS |
LCX_DIFF_MAP |
设置位图,资料: 差异(Differential)备份:只备份上次完整备份后,做修改的部分。备份单位是区(Extent)。意味着某个区内即使只有一页做了变动,则在差异备份里会被体现.差异备份依靠一个BitMap进行维护,一个Bit对应一个区,自上次完整备份后,被修改的区会被置为1,而BitMap中被置为1对应的区会被差异备份所备份。而到下一次完整备份后,BitMap中所有的Bit都会被重置为0 而这个BitMap在数据库第7页: DCM页 差异变更(Differential Changed Map,DCM)页面他跟踪一个文件中的哪一个区在最新一次完整数据库备份之后被修改过。SQLSERVER用在增量备份时只对已发生数据变更的分区进行增量备份即可 |
| LOP_BEGIN_XACT | 事务开始 | |
| LOP_MODIFY_ROW | LCX_HEAP | 修改堆表中的某一行记录 |
| LOP_PREP_XACT | 准备启动数据库 | |
| LOP_COMMIT_XACT | 提交事务 | |
| LOP_MODIFY_ROW | LCX_BOOT_PAGE | 修改数据库启动页 |
| LOP_MODIFY_HEADER | LCX_PFS | 修改PFS页的页头部信息 |
| LOP_INSERT_ROWS | LCX_CLUSTERED | 插入数据到聚集索引的索引页 |
| LOP_INSERT_ROWS | LCX_INDEX_LEAF | 插入数据到索引的叶子节点即数据页 |
| LOP_FORMAT_PAGE | LCX_CLUSTERED | 重新组织聚集索引 |
| LOP_DELETE_SPLIT | LCX_CLUSTERED | 删除聚集索引表的一行记录引起页拆分 |
| LOP_MODIFY_HEADER | LCX_HEAP | 修改堆表的某页的页头信息 |
| LOP_BEGIN_CKPT | LCX_NULL | 检查点开始 |
| LOP_END_CKPT | LCX_NULL | 检查点结束 |
| LOP_SET_FREE_SPACE | LCX_PFS | 修改PFS页设置那个数据页是空闲的 |
| LOP_ROOT_CHANGE | LCX_CLUSTERED | 聚集索引的根节点改变 |
| LOP_INSERT_ROWS | LCX_HEAP | 插入数据到堆表 |
| LOP_FORMAT_PAGE | LCX_HEAP | 格式化堆里的数据页 |
| LOP_LOCK_XACT | 在事务里获取锁 | |
| LOP_FORMAT_PAGE | LCX_HEAP | 格式化堆里的数据页 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注:此文章为原创,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处!
若您觉得这篇文章还不错,请点击下方的【推荐】,非常感谢!

SQLSERVER数据库死锁与优化杂谈的更多相关文章
- 查询Sqlserver数据库死锁的一个存储过程(转)
使用sqlserver作为数据库的应用系统,都避免不了有时候会产生死锁, 死锁出现以后,维护人员或者开发人员大多只会通过sp_who来查找死锁的进程,然后用sp_kill杀掉.利用sp_who ...
- 查询Sqlserver数据库死锁的一个存储过程
From:http://www.cnblogs.com/mzhanker/archive/2011/06/04/2072739.html 使用sqlserver作为数据库的应用系统,都避免不了有时候会 ...
- 查询Sqlserver数据库死锁的一个存储过程(转)
链接 :http://www.cnblogs.com/mzhanker/archive/2011/06/04/2072739.html 使用sqlserver作为数据库的应用系统,都避免不了有时候会产 ...
- SqlServer定时备份数据库和定时杀死数据库死锁解决
上周五组长对我说了一句要杀死数据库的死锁进程,有时候同一时刻不停写入数据库会造成这种情况的发生,因为自己对数据库不是很熟悉,突然组长说了我也就决定一定要倒腾一下,不然自己怎么提高呢?现在不研究,说不定 ...
- 【转载】 Sqlserver查看数据库死锁的SQL语句
在Sqlsever数据库中,有时候操作数据库过程中会进行锁表操作,在锁表操作的过程中,有时候会出现死锁的情况出现,这时候可以使用SQL语句来查询数据库死锁情况,主要通过系统数据库Master数据库来查 ...
- MySQL 性能优化-数据库死锁监控
MySQL性能优化-数据库死锁监控 by:授客 QQ:1033553122 1)表锁定 通过检查 table_locks_waited 和 table_locks_immediate 状态变量来分析表 ...
- SQLSERVER查询数据库死锁的存储过程
USE [IdentityDemo] GO /****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[sp_who_lock] Script Date: 2019/1/17 10: ...
- SqlServer 数据库引擎优化顾问优化数据库
现在一直在做的项目,数据量相对也不小,开始的时候没有觉得,因为是刚开始,数据量还很小,在程序使用过程中速度还挺快,但是随着数据量的不停的增长,发现程序越来越慢,甚至出现了超时的问题,因此要对程序和数据 ...
- sqlserver 数据库阻塞和死锁
参考原文:http://blog.csdn.net/ha196200/article/details/44985597 (1) 数据库阻塞: 假设第一个连接T1占有且没有释放资源,第二个连接T2请求同 ...
随机推荐
- [ SSH框架 ] Struts2框架学习之三(OGNl和ValueStack值栈学习)
一.OGNL概述 1.1 什么是OGNL OGNL的全称是对象图导航语言( object-graph Navigation Language),它是一种功能强大的开源表达式语言,使用这种表达式语言,可 ...
- hadoop 2.x 简单实现wordCount
简单实现hadoop程序,包括:hadoop2.x的实现写法 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured; import org.apache.hadoop.fs ...
- C#System.Text.RegularExpressions.Regex使用(二) .
(6)特殊字符的匹配 string x = "//"; Regex r1 = new Regex("^////$"); Console.WriteLine(&q ...
- python之Flask实现登录功能
网站少不了要和数据库打交道,归根到底都是一些增删改查操作,这里做一个简单的用户登录功能来学习一下Flask如何操作MySQL. 用到的一些知识点:Flask-SQLAlchemy.Flask-Logi ...
- git merge与 git rebase区别及实例
接Git分支创建与合并,在分支合并时,有两种方式:git merge 和git rebase. git merge:将两个分支,合并提交为一个新提交,并且新提交有2个parent. git rebas ...
- Java反射-修改private final成员变量值,你知道多少?
大家都知道使用java反射可以在运行时动态改变对象的行为,甚至是private final的成员变量,但并不是所有情况下,都可以修改成员变量.今天就举几个小例子说明. 基本数据类型 String类型 ...
- R 网络图 nodes,edges属性计算
前面提到了用R画网络图,免不了要对网络图nodes和edges的特征做一些统计.分享下我的代码: ########## nodes edges的统计########### # ####nodes的度有 ...
- 重写equals时,遵守的规定
0 正确的equals方法 public class MyClass { // 主要属性1 private int primaryAttr1; // 主要属性2 private int prima ...
- DoxygenToolKit.vim 插件配置
如何才能既享受 Doxygen 的强大功能,同时又避免大量的重复性的注释内容? 解决思路: 让编辑器来替我们写那些格式和内容固定的部分,我们只负责写真正的有效内容. 所以,答案就是:Vim + Dox ...
- Redis配置文件中关于bind参数
在配置文件redis.conf中,默认的bind 接口是127.0.0.1,也就是本地回环地址.这样的话,访问redis服务只能通过本机的客户端连接,而无法通过远程连接,这样可以避免将redis服务暴 ...
