LinkedHashMap源码
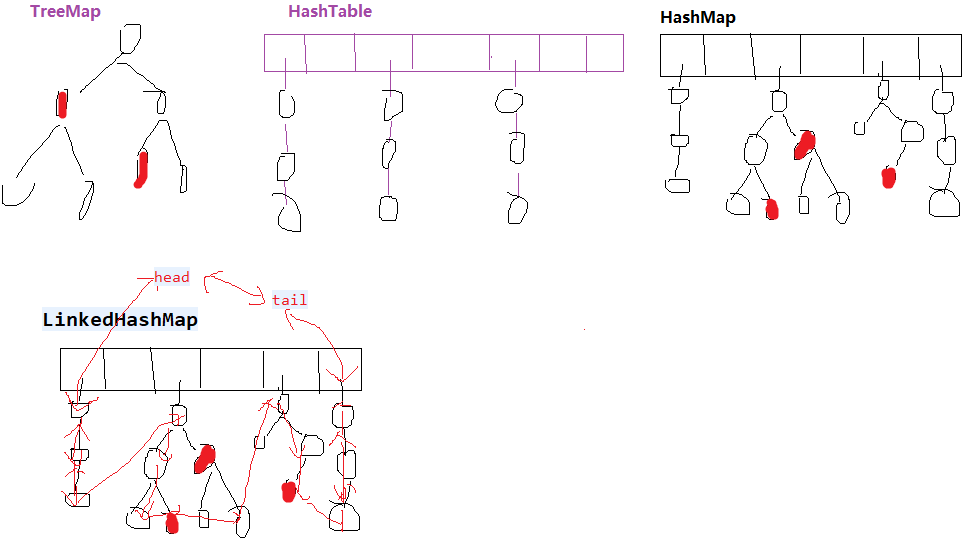
TreeMap是一颗红黑树做Map。HashMap是数组+链表+红黑树。HashTable是数组+链表。
LinkedHashMap底层存储结构与HashMap一样,不同的是LinkedHashMap增加了一个双向链表的头节点,插入的数据除了插入HashMap,还会插入链表中,因而可以保存插入节点的顺序
LinkedHashMap的节点在HashMap节点的基础上增加了前后节点的引用
LinkedHashMap相比HashMap在查找值和删除值时效率要高
LinkedHashMap还可以设置按插入顺序排序或是按访问顺序排序,默认是按插入顺序排序
LinkedHashMap没有put方法,而是覆写了afterNodeAccess方法和afterNodeInsertion方法。当插入的数据已经存在时,会调用afterNodeAccess方法看是否需要将数据插入到链表末尾;当插入的数据是新数据时,会通过afterNodeInsertion方法来根据设置删除近期使用最少的节点
LinkedHashMap可以用来实现LRU算法。首先需要用可以设置accessOrder的构造函数设置accessOrder为true,也就是按照节点访问顺序排序;
而LinkedHashMap还拥有HashMap一样的结构,原因在于其继承自HashMap,因此HashMap中用于存储元素的table也被继承过来,于是乎元素的存储也具备和HashMap一样的规则,所有元素存储在table中,table下的每个索引在原HashMap的结构下也是一个单向链表,同时每个元素中额外增加的before和after引用将table中的元素互连起来。
HashMap链表节点:next,
HashMap红黑树节点TreeNode:parent,left,right,prev,next,
LinkedHashMap链表节点:before,after,next,
LinkedHashMap跟HashMap一样,只不过增加了head,tail把所有元素串联起来了。
- public class testLinkedHashMap1 {
- @SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- LinkedHashMap1<Integer,String> hh = new LinkedHashMap1<Integer,String>();
- //链表添加
- hh.put(, "");//放到LinkedHashMap1的table[0]中,此时是链表(节点有next没有after,before)
- hh.put(, "");
- // hh.remove(4);//链表删除
- // hh.put(4, "4");
- hh.put(, "");
- hh.put(, "");//0位置转成红黑树
- hh.put(, "");
- hh.put(, "");
- hh.put(, "");
- hh.put(, "");//1位置链表添加
- hh.put(, "");
- hh.put(, "");
- hh.get();
- Set s = hh.keySet();//[0, 16, 32, 48, 54, 60, 76, 1, 2, 3]
- Iterator i = s.iterator();
- if(i.hasNext()) System.out.println(i.next());
- // i.remove();
- if(i.hasNext()) System.out.println(i.next());
- }
- }
- //extends HashMap1,table也被继承过来,数组+链表+红黑树。
- public class LinkedHashMap1<K, V> extends HashMap1<K, V> implements Map1<K, V> {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L;
- transient LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> head;// 双向链表的头节点和尾节点
- transient LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> tail;
- final boolean accessOrder;// true,使用节点之后就把节点放到最末尾。false就不放。用于删除第一个最不常用的元素。
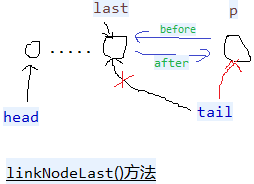
- private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p) {// 链表末尾添加,有before,after
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> last = tail;//保留原来的tail
- tail = p;//修改tail
- if (last == null)// tail=null
- head = p;// tail = head = p
- else {
- p.before = last;
- last.after = p;
- }
- }
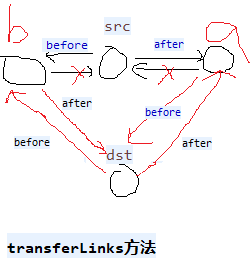
- // dst替换src
- private void transferLinks(LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> src, LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> dst) {
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> b = dst.before = src.before;
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> a = dst.after = src.after;
- if (b == null)// 替换的src是第一个节点
- head = dst;
- else
- b.after = dst;
- if (a == null)// 替换的src是最后一个节点
- tail = dst;
- else
- a.before = dst;
- }
- public void reinitialize() {
- super.reinitialize();// table = null; entrySet = null; keySet = null; values = null;
- head = tail = null;
- }
- //生成一个节点(链表中的节点,不是红黑树中的节点,有hash, key, value, next没有before,after)
- public Node<K, V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> e) {//
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p = new LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>(hash, key, value, e);
- linkNodeLast(p);// 生成新的节点并插入到尾部
- return p;
- }
- public Node<K, V> replacementNode(Node<K, V> p, Node<K, V> next) {
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> q = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) p;
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> t = new LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next);
- transferLinks(q, t);// t替换q
- return t;
- }
- public TreeNode<K, V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
- TreeNode<K, V> p = new TreeNode<K, V>(hash, key, value, next);
- linkNodeLast(p);// 末尾添加p
- return p;
- }
- public TreeNode<K, V> replacementTreeNode(Node<K, V> p, Node<K, V> next) {
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> q = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) p;
- TreeNode<K, V> t = new TreeNode<K, V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next);
- transferLinks(q, t);// t替换q
- return t;
- }
- public void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K, V> e) { // 删除节点e
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
- p.before = p.after = null;
- if (b == null)
- head = a;
- else
- b.after = a;
- if (a == null)
- tail = b;
- else
- a.before = b;
- }
- public void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // 添加新的节点时候,有可能删除最老的元素
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> first;
- if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
- K key = first.key;// 删除第一个元素,每次使用元素之后,就会把元素放到最末尾,第一个元素就是最少使用的元素。
- removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);// hashMap方法,
- }
- }
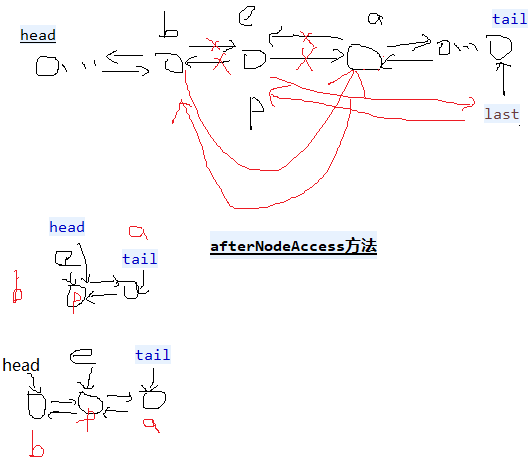
- public void afterNodeAccess(Node<K, V> e) { // 节点e被修改后,e不是尾节点(e是尾节点就不动),把e节点移到最后。
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> last;
- if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> p = (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V>) e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
- p.after = null;// 多个属性指向同一地址值,只是修改其中一个的地址值,其余不变。
- if (b == null)
- head = a;//
- else
- b.after = a;
- if (a != null)
- a.before = b;
- else
- last = b;//
- if (last == null)
- head = p;
- else {
- p.before = last;
- last.after = p;
- }
- tail = p;
- ++modCount;
- }
- }
- public void internalWriteEntries(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
- s.writeObject(e.key);
- s.writeObject(e.value);
- }
- }
- public LinkedHashMap1(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
- super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树
- accessOrder = false;// true,使用节点之后就把节点放到最末尾。false就不放。
- }
- public LinkedHashMap1(int initialCapacity) {
- super(initialCapacity);// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树
- accessOrder = false;
- }
- public LinkedHashMap1() {
- super();// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树
- accessOrder = false;
- }
- public LinkedHashMap1(Map1<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
- super();// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树
- accessOrder = false;
- putMapEntries(m, false);
- }
- public LinkedHashMap1(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) {
- super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);// hashMap方法,构造hashMap的table,一个数组+链表+红黑树
- this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
- }
- public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
- V v = e.value;
- if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- public V get(Object key) {
- Node<K, V> e;
- if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)// hashMap方法
- return null;
- if (accessOrder)
- afterNodeAccess(e);// 把e节点移到最后。
- return e.value;
- }
- public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
- Node<K, V> e;
- if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)// hashMap方法
- return defaultValue;
- if (accessOrder)// 把e节点移到最后。
- afterNodeAccess(e);
- return e.value;
- }
- public void clear() {
- super.clear();
- head = tail = null;
- }
- // 添加一个元素时候是否删除最老的。 map是缓存有用。比如到达100之后,添加一个元素就删除最老的元素。要重写。
- protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map1.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
- return false;
- }
- public Set<K> keySet() {
- Set<K> ks = keySet;
- if (ks == null) {
- ks = new LinkedKeySet();
- keySet = ks;
- }
- return ks;
- }
- final class LinkedKeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
- public final int size() {
- return size;
- }
- public final void clear() {
- LinkedHashMap1.this.clear();
- }
- public final Iterator<K> iterator() {
- return new LinkedKeyIterator();
- }
- public final boolean contains(Object o) {
- return containsKey(o);
- }
- public final boolean remove(Object key) {
- return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;// hashMap方法
- }
- public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() {
- return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.DISTINCT);
- }
- public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) {
- if (action == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- int mc = modCount;
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
- action.accept(e.key);
- if (modCount != mc)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- }
- public Collection<V> values() {
- Collection<V> vs = values;
- if (vs == null) {
- vs = new LinkedValues();
- values = vs;
- }
- return vs;
- }
- final class LinkedValues extends AbstractCollection<V> {
- public final int size() {
- return size;
- }
- public final void clear() {
- LinkedHashMap1.this.clear();
- }
- public final Iterator<V> iterator() {
- return new LinkedValueIterator();
- }
- public final boolean contains(Object o) {
- return containsValue(o);
- }
- public final Spliterator<V> spliterator() {
- return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED);
- }
- public final void forEach(Consumer<? super V> action) {
- if (action == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- int mc = modCount;
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
- action.accept(e.value);
- if (modCount != mc)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- }
- public Set<Map1.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() {
- Set<Map1.Entry<K, V>> es;
- return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new LinkedEntrySet()) : es;
- }
- final class LinkedEntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map1.Entry<K, V>> {
- public final int size() {
- return size;
- }
- public final void clear() {
- LinkedHashMap1.this.clear();
- }
- public final Iterator<Map1.Entry<K, V>> iterator() {
- return new LinkedEntryIterator();
- }
- public final boolean contains(Object o) {
- if (!(o instanceof Map1.Entry))
- return false;
- Map1.Entry<?, ?> e = (Map1.Entry<?, ?>) o;
- Object key = e.getKey();
- Node<K, V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);// hashMap方法
- return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
- }
- public final boolean remove(Object o) {
- if (o instanceof Map1.Entry) {
- Map1.Entry<?, ?> e = (Map1.Entry<?, ?>) o;
- Object key = e.getKey();
- Object value = e.getValue();
- return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;// hashMap方法
- }
- return false;
- }
- public final Spliterator<Map1.Entry<K, V>> spliterator() {
- return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.DISTINCT);
- }
- public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map1.Entry<K, V>> action) {
- if (action == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- int mc = modCount;
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
- action.accept(e);
- if (modCount != mc)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- }
- public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
- if (action == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- int mc = modCount;
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
- action.accept(e.key, e.value);
- if (modCount != mc)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
- if (function == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- int mc = modCount;
- for (LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
- e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value);
- if (modCount != mc)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- }
- public static class Entry<K, V> extends HashMap1.Node<K, V> {
- public Entry<K, V> before, after;// hash, key, value, next
- public Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
- super(hash, key, value, next);// before和after引用节点以支持双向链表
- }
- }
- abstract class LinkedHashIterator {//头结点head开始一路after到末尾
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> next;
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> current;
- int expectedModCount;
- LinkedHashIterator() {
- next = head;// 初始化时下一个是head
- expectedModCount = modCount;
- current = null;
- }
- public final boolean hasNext() {
- return next != null;
- }
- final LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> nextNode() {
- LinkedHashMap1.Entry<K, V> e = next;
- if (modCount != expectedModCount)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- if (e == null)
- throw new NoSuchElementException();
- current = e;
- next = e.after;// before和after遍历链表
- return e;
- }
- public final void remove() {
- Node<K, V> p = current;
- if (p == null)
- throw new IllegalStateException();
- if (modCount != expectedModCount)
- throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
- current = null;
- K key = p.key;
- removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);// hashMap方法
- expectedModCount = modCount;
- }
- }
- final class LinkedKeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator implements Iterator<K> {
- public final K next() {
- return nextNode().getKey();
- }
- }
- final class LinkedValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator implements Iterator<V> {
- public final V next() {
- return nextNode().value;
- }
- }
- final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator implements Iterator<Map1.Entry<K, V>> {
- public final Map1.Entry<K, V> next() {
- return nextNode();
- }
- }
- }
LinkedHashMap源码的更多相关文章
- 转:【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedHashmap源码剖析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/37867985 前言:有网友建议分析下LinkedHashMap的源码,于是花了一晚上时 ...
- Java集合系列[4]----LinkedHashMap源码分析
这篇文章我们开始分析LinkedHashMap的源码,LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,也就是说LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上扩展而来的,因此在看LinkedHas ...
- linkedHashMap源码解析(JDK1.8)
引言 关于java中的不常见模块,让我一下子想我也想不出来,所以我希望以后每次遇到的时候我就加一篇.上次有人建议我写全所有常用的Map,所以我研究了一晚上LinkedHashMap,把自己感悟到的解释 ...
- LRU算法实现,HashMap与LinkedHashMap源码的部分总结
关于HashMap与LinkedHashMap源码的一些总结 JDK1.8之后的HashMap底层结构中,在数组(Node<K,V> table)长度大于64的时候且链表(依然是Node) ...
- LinkedHashMap源码详解
序言 本来是不打算先讲map的,但是随着对set集合的认识,发现如果不先搞懂各种map,是无法理解set的.因为set集合很多的底层就是用map来存储的.比如HashSet就是用HashMap,Lin ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(5)-LinkedHashMap源码解析
前面分析了HashMap的实现,我们知道其底层数据存储是一个hash表(数组+单向链表).接下来我们看一下另一个LinkedHashMap,它是HashMap的一个子类,他在HashMap的基础上维持 ...
- LinkedHashMap 源码详细分析(JDK1.8)
1. 概述 LinkedHashMap 继承自 HashMap,在 HashMap 基础上,通过维护一条双向链表,解决了 HashMap 不能随时保持遍历顺序和插入顺序一致的问题.除此之外,Linke ...
- LinkedHashMap源码分析
hashMap源码分析:hashMap源码分析 版本说明:jdk1.7LinkedHashMap继承于HashMap,是一个有序的Map接口的实现.有序指的是元素可以按照一定的顺序排列,比如元素的插入 ...
- LinkedHashMap源码分析及实现LRU
概述 从名字上看LinkedHashMap相比于HashMap,显然多了链表的实现.从功能上看,LinkedHashMap有序,HashMap无序.这里的顺序指的是添加顺序或者访问顺序. 基本使用 @ ...
- 死磕 java集合之LinkedHashMap源码分析
欢迎关注我的公众号"彤哥读源码",查看更多源码系列文章, 与彤哥一起畅游源码的海洋. 简介 LinkedHashMap内部维护了一个双向链表,能保证元素按插入的顺序访问,也能以访问 ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu与centos系统对比
CentOS与Ubuntu该如何选择,哪个更好用.笔者在自媒体平台收集了一些网友的观点,较为经典,分享给大家.至于应该选择哪个,希望看完本文章后,读者心中有数. 观点1:CentOS适用于服务器,Ub ...
- spring AOP的两种配置
xml配置 定义要被代理的方法的接口 public interface TestAop { public void print(String s); } 实现上述接口 public class Tes ...
- ./configure & make & make install 知其所以然
最近一直在类unix系统上(Ubuntu和Mac OS)上调研第三方的一些开源库,要涉及到开源库的编译安装工作,接触最多的就是./configure & make & make ins ...
- Jpa的简介
Jpa:是用于数据持久化的一组标准接口. 1.HelloWorld的编写 创建EntityManagerFactory 创建EntityManager 开启事务 数据持久化 提交事务 关闭Entity ...
- Spark GraphX图计算核心源码分析【图构建器、顶点、边】
一.图构建器 GraphX提供了几种从RDD或磁盘上的顶点和边的集合构建图形的方法.默认情况下,没有图构建器会重新划分图的边:相反,边保留在默认分区中.Graph.groupEdges要求对图进行重新 ...
- java 使用网建SMS发送短信验证码
首先, 注册并登录网建用户, 新注册用户将获得5条的测试短信 网建短信通地址: http://sms.webchinese.cn/default.shtml 注册账号在此就不多做赘述了, 直接上代码 ...
- 安装docker后,导致qemu的桥接网络出现问题
按照Qemu-4.1 桥接网络设置中介绍的方法建立起桥接网络后,可以实现虚拟机和host的相互ping,但是在虚拟机里去ping其他跟host处于同一个网段的ip地址时却失败了,然后ifconfig后 ...
- 设置linux代理完成apt-get
最近ubuntu的服务器被公司关闭了外网使用权限,但是安装软件又需要连接外网,那么就只能通过代理来连接了. 先按照下面的这篇帖子来设置windows端的代理. https://blog.csdn.ne ...
- scikit-learn 中的 KMeans
语法 sklearn.cluster.KMeans(n_clusters=8, # 簇的个数, 默认为 8 init='k-means++', # 初始簇中心的获取方法 n_init=10, # 初始 ...
- MySQL体系结构与存储引擎
MySQL 体系结构 先看 MySQL 数据库的体系结构,如下图所示. MySQL 体系结构由 Client Connectors 层.MySQL Server 层及存储引擎层组成. Client C ...
