tsp问题——遗传算法解决
TSP问题最简单的求解方法是枚举法。
它的解是多维的、多局部极值的、趋于无穷大的复杂解的空间。搜索空间是n个点的全部排列的集合。大小为(n-1)!
。能够形象地把解空间看成是一个无穷大的丘陵地带,各山峰或山谷的高度即是问题的极值。求解TSP,则是在此不能穷尽的丘陵地带中攀登以达到山顶或谷底的过程。
这一篇将用遗传算法解决TSP问题。
1)评价。
这个评价算法应该比較简单了,就是找计算总距离,小的为优。目标函数转化为适应度函数能够取倒数。
2)突变。为了防止反复訪问,不能随机的进行突变。由于每一个城市仅仅能訪问一次。我们仅仅须要随意的交换两个城市就可以。
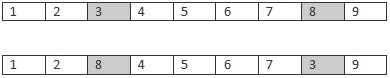
上一行是突变之前。以下一行是突变之后的。
3)交叉。这个操作是个比較关键的步骤。如何交叉才干才干父母的优秀基因呢?对于TSP问题,我们要找的是一个最优的排列。当中排列的顺序应该是最重要的。
因此在交叉的时候。分别随机的取 父母的部分序列,要保持原有的顺序。
Parents
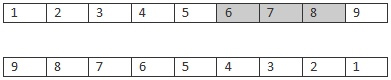
先随机的选取 Parent1 的 一部分。比如 678 部分,。然后把剩下的城市 安装 Parent2 中的顺序,遗传下去。
Chlid
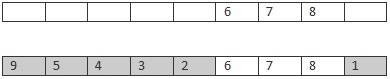
其他基本依照遗传算法的框架来即可了
// TSP.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
// #include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
//#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
//#include <stdlib.h> using namespace std;
#define POPSIZE 200 //种群总数
#define rdint(i)(rand()%(int)(i))
#define rdft()((float)rdint(16384)/(16383.0))
typedef unsigned char BYTE; //31个城市的坐标
int city[31][2] = { { 1304, 2312 }, 3639, 1315, 4177, 2244, 3712, 1399, 3488, 1535, 3326, 1556, 3238, 1229,
4196, 1004, 4312, 790, 4386, 570, 3007, 1970, 2562, 1756, 2788, 1491, 2381, 1676, 1332, 695, 3715, 1678,
3918, 2179, 4061, 2370, 3780, 2212, 3676, 2578, 4029, 2838, 4263, 2931, 3429, 1908, 3507, 2367, 3394, 2643,
3439, 3201, 2935, 3240, 3140, 3550, 2545, 2357, 2778, 2826, 2370, 2975 }; int* my_unrepeat_rand(int L, int H)
{
const int LEN = H - L + 1;
//int n[LEN];
int *n = new int[LEN];
for (int i = 0; i < LEN; ++i)
{
n[i] = L + i;
} for (int j = LEN; j > 0; --j)
{
int m = j*rand() /(RAND_MAX + 1.0);
int temp = n[m];
n[m] = n[j - 1];
n[j - 1] = temp;
}
return n;
} class Chromosome
{
friend class Population;
public:
static const int length = 31; private:
BYTE gene[length];
double fitness;
double distance;
public:
void initial_chromosome()//初始化染色体
{
distance = 0;
fitness = 0;
int*b = my_unrepeat_rand(0, length - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
gene[i] = b[i];
delete[]b;
}
BYTE*get_gene()
{
return this->gene;
}
double get_distance()
{
return distance;
}
void calculate_distance()//计算适应度。这里直接取总距离,越小越好
{
distance = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++)
{
distance += sqrt(pow(double(city[gene[i]][0] - city[gene[i + 1]][0]), double(2)) +
pow(double(city[gene[i]][1] - city[gene[i + 1]][1]), double(2)));
}
distance += sqrt(pow(double(city[gene[0]][0] - city[gene[length - 1]][0]), double(2)) + pow(double(city[gene[0]][1] - city[gene[length - 1]][1]), double(2)));
} pair<Chromosome, Chromosome> cross(Chromosome p1)//交叉操作,选中区间的基因不改变。孩子基因的其它位置的基因从配偶处获得,要保持顺序
{
pair<Chromosome, Chromosome>child;
//srand(time(0));
int m = rand() % length ;
int n = rand() % length;
if (m > n)
{
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
int j = 0,p=0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if (i >= m&&n >= i)
{
child.first.gene[i] = gene[i];
child.second.gene[i] = p1.gene[i];
continue;
}
bool flag = true;
while (flag)
{
flag = false;
for (int k = m; k <= n; k++)
if (p1.gene[j] == gene[k])
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if (flag)
j++;
}
child.first.gene[i] = p1.gene[j];
j++;
flag = true;
while (flag)
{
flag = false;
for (int k = m; k <= n; k++)
if (gene[p] == p1.gene[k])
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if (flag)
p++;
}
child.second.gene[i] = gene[p];
p++;
} return child;
} Chromosome mutation()//变异。选择两个位置交换基因
{
int m = rand() % (length - 1);
int n = rand() % (length - 1);
while (n == m)
{
n = rand() % (length - 1);
}
int temp = gene[m];
gene[m] = gene[n];
gene[n] = temp;
return *this;
} }; class Population
{
private:
Chromosome pop[POPSIZE];
Chromosome best;
Chromosome worst;
unsigned int Generation;
unsigned int maxgeneration;
double m_dCrossoverRate;//交叉率0.6
double m_dMutationRate;//变异率0.01
bool elitism;//是否在新一代中保存前一代的最优个体
double m_dTotalFitnessScore;
void initial_pop()
{
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
pop[i].initial_chromosome();
};
public:
Population(double pc, double pM, bool ISelitism, unsigned int maxgen) :m_dCrossoverRate(pc), m_dMutationRate(pM), elitism(ISelitism), maxgeneration(maxgen)//构造函数
{
Generation = 1;
initial_pop();
}
void Calcu_fit()//计算适应值
{
m_dTotalFitnessScore = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
pop[i].calculate_distance();
}
find_best_worst();
//sort_by_distance(POPSIZE);
double mindis = best.distance;
double maxdis = worst.distance;
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
pop[i].fitness = 1 - (pop[i].distance - mindis) / (maxdis - mindis + 0.0001);//double(1000) / pop[i].distance;//
m_dTotalFitnessScore += pop[i].fitness;
} }
//fitness(i,1)=(1-((len(i,1)-minlen)/(maxlen-minlen+0.0001)))
void sort_by_distance(int k)
{
if (k == 1)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < k-1; i++)
{
if (pop[i].distance < pop[i + 1].distance)
{
double temp = pop[i].distance;
pop[i].distance = pop[i + 1].distance;
pop[i + 1].distance = temp;
}
}
sort_by_distance(k - 1);
}
void find_best_worst()
{
double mindis = 100000000;
double maxdis = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
if (pop[i].distance > maxdis)
{
maxdis = pop[i].distance;
worst = pop[i];
}
if (pop[i].distance < mindis)
{
mindis = pop[i].distance;
best = pop[i];
}
}
} int RouletteWheelSelection()
{
double fSlice = rdft() * m_dTotalFitnessScore;
double cfTotal = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i<POPSIZE; ++i)
{
cfTotal += pop[i].fitness;
if (cfTotal > fSlice)
{
return i;
}
}
}
void Epoch()
{
Calcu_fit();
Chromosome new_pop[POPSIZE+1];
int NewBabies = 0;
if (elitism)
{
NewBabies = 1;
new_pop[0] = best;
} while (NewBabies < POPSIZE)
{
//select 2 parents
int mum = RouletteWheelSelection();
int dad = RouletteWheelSelection();
while (dad == mum)
{
dad = RouletteWheelSelection();
}pair<Chromosome, Chromosome>child;
if (rdft() < m_dCrossoverRate)
{
child = pop[mum].cross(pop[dad]);
}
else
{
child.first = pop[mum];
child.second = pop[dad];
}
if (rdft() < m_dMutationRate)
{
child.first.mutation();
}
if (rdft() < m_dMutationRate)
{
child.second.mutation();
}
new_pop[NewBabies]=child.first;
new_pop[NewBabies+1] = child.second;
NewBabies += 2;
} for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
pop[i] = new_pop[i];
++Generation;
} Chromosome get_best()
{
return best;
}
void run()
{
while (Generation < maxgeneration)
{
Epoch();
}
} }; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
time_t t;
srand((unsigned)time(&t)); Population tsp(0.6,0.1,true,1000);
tsp.run(); cout << tsp.get_best().get_distance()<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
tsp问题——遗传算法解决的更多相关文章
- 遗传算法解决旅行商问题(TSP)
这次的文章是以一份报告的形式贴上来,代码只是简单实现,难免有漏洞,比如循环输入的控制条件,说是要求输入1,只要输入非0就行.希望会帮到以后的同学(*^-^*) 一.问题描述 旅行商问题(Traveli ...
- 遗传算法解决寻路问题——Python描述
概要 我的上一篇写遗传算法解决排序问题,当中思想借鉴了遗传算法解决TSP问题,本质上可以认为这是一类问题,就是这样认为:寻找到一个序列X,使F(X)最大. 详解介绍 排序问题:寻找一个序列,使得这个序 ...
- 【高级算法】遗传算法解决3SAT问题(C++实现)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhoubin1992/article/details/46910079 1 SAT问题描写叙述 命题逻辑中合取范式 (CNF) 的可满足性问 ...
- 遗传算法解决TSP问题实现以及与最小生成树的对比
摘要: 本实验采用遗传算法实现了旅行商问题的模拟求解,并在同等规模问题上用最小生成树算法做了一定的对比工作.遗传算法在计算时间和占用内存上,都远远优于最小生成树算法. 程序采用Microsoft vi ...
- 遗传算法解决TSP问题
1实验环境 实验环境:CPU i5-2450M@2.50GHz,内存6G,windows7 64位操作系统 实现语言:java (JDK1.8) 实验数据:TSPLIB,TSP采样实例库中的att48 ...
- 转:遗传算法解决TSP问题
1.编码 这篇文章中遗传算法对TSP问题的解空间编码是十进制编码.如果有十个城市,编码可以如下: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 这条编码代表着一条路径,先经过0,再经过1,依次下去. 2.选 ...
- 用遗传算法解决TSP问题
浅谈遗传算法:https://www.cnblogs.com/AKMer/p/9479890.html Description \(小m\)在踏上寻找\(小o\)的路程之后不小心碰到了大魔王\(fat ...
- [POJ 3311]Hie with the Pie——谈论TSP难题DP解决方法
主题连接: id=3311">http://poj.org/problem?id=3311 题目大意:有n+1个点,给出点0~n的每两个点之间的距离,求这个图上TSP问题的最小解 ...
- TSP问题 遗传算法 智能优化算法
写了半天,效率还是有点低的,以后有空再优化下: //用次序表示法来表示个体编码 #include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include< ...
随机推荐
- [SDOI2010] 古代猪文 (快速幂+中国剩余定理+欧拉定理+卢卡斯定理) 解题报告
题目链接:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P2480 题目背景 “在那山的那边海的那边有一群小肥猪.他们活泼又聪明,他们调皮又灵敏.他们自由自在生活在那绿色 ...
- vue -- 7 个 有用的 Vue 开发技巧
1 状态共享 随着组件的细化,就会遇到多组件状态共享的情况, Vuex当然可以解决这类问题,不过就像 Vuex官方文档所说的,如果应用不够大,为避免代码繁琐冗余,最好不要使用它,今天我们介绍的是 vu ...
- WebView的坑[持续更新]
返回错误的 innerHeight,如 240(WebView returns bad window.innerHeight) http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1 ...
- Git放弃本地更改恢复到资源库版本
使用git版本控制工具在本地clone一份代码后,如果发现修改错误想恢复到资源库版本,下面两行可以轻松加愉快的搞定: git clean -xdf git checkout -f git的更多详细用法 ...
- Android 自定义viewpager 三张图片在同一屏幕轮播的效果
github:https://github.com/nickeyCode/RoundImageViewPager 说实话不知道怎么描述这个效果,在网页上见得跟多,公司要求做这个效果得时候不知道怎么用文 ...
- 比起 Windows,怎样解读 Linux 的文件系统与目录结构?
Linux 和 Windows 的文件系统有些不同,在学习使用 Linux 之前,若能够了解这些不同,会有助于后续学习. 本文先对 Windows 和 Linux 上面文件系统原理.组织概念进行区分, ...
- Linux下通过rdesktop连接Windows远程桌面
rdesktop是linux下支持Windows远程桌面连接的客户端程序,在linux系统下可通过它远程访问Windows桌面,支持多种版本.rdesktop是sourceforge下支持GPL协议的 ...
- SSD-实现
一.制作voc数据集 1.数据集文件夹 新建一个文件夹,用来存放整个数据集,或者和voc2007一样的名字:VOC2007 然后像voc2007一样,在文件夹里面新建如下文件夹: 2.将训练图片放到J ...
- JAVA-截取字符串两边指定字符
工具类: /** * 工具类 */ public class Tool { /** * 截取两边指定的字符 * @param character * @param symbol * @return * ...
- mysql主从同步错误恢复
Mysql主从同步集群在生成环境使用过程中,如果主从服务器之间网络通信条件差或者数据库数据量非常大,容易导致MYSQL主从同步延迟. MYSQL主从产生延迟之后,一旦主库宕机,会导致部分数据没有及时同 ...
