javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树
javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树
树是计算机科学中经常用到的一种数据结构。树是一种非线性的数据结构,以分成的方式存储数据,树被用来存储具有层级关系的数据,比如文件系统的文件,树还被用来存储有序列表。我们要研究的是二叉树,在二叉树上查找元素非常快,为二叉树添加元素或者删除元素,也是非常快的。
树的基本结构示意图如下:
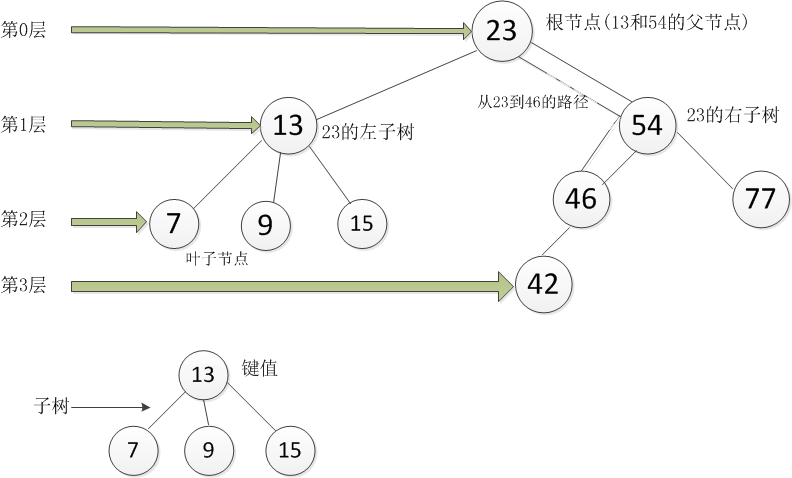
我们现在最主要的是要来学习二叉树,二叉树是一种特殊的树,它的特征是 子节点个数不超过2个。如下图就是二叉树的基本结构示意图如下:

二叉树是一种特殊的树,相对较少的值保存在左节点上,较大的值保存在右节点中。这一特性使得查找的效率非常高,对于数值型和非数值型的数据,比如单词和字符串都是一样。
下面我们来学习插入节点的操作吧!
1. 二叉树是由节点组成的,所以我们需要定义一个对象node,可以保存数据,也可以保存其他节点的链接(left 和 right),show()方法用来显示保存在节点中的数据。Node代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
插入节点分析如下:
代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
初始代码如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
示意图如下:
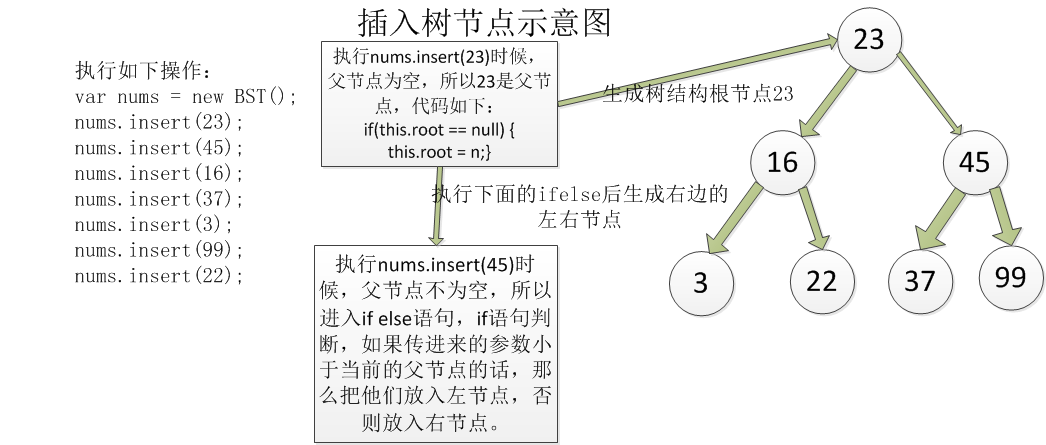
1. 执行insert(23)时候,由于根节点== null 所以 根节点为23.
2. 执行insert(45)的时候,根节点不等于null,因此进入while语句;由于45 > 大于根节点23 所以就进入else语句,当前current的值如下图:

当执行 current = current.right; 这句代码时候,当前current值变为null了,然后进行if判断代码如下:
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
所以45为根节点的右节点了。跳出循环语句;
3. 执行insert(16)的时候,根节点不等于null,因此进入while语句,由于16 < 小于根节点23,所以就进入if语句,那么当前的current值如下:

当执行到 current = current.left; 的时候,current的值就变为null,所以接着往下执行代码:
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
就把当前的节点16插入到根节点的左节点上。
4. 接着执行 insert(37) 的时候,根节点不等于null,因此进入else语句中的while语句,由于37 大于根节点23,所以就进入while语句中的else语句,当前的current值为:

当执行current = current.right;这句代码的时候,那么当前current = 45的那个节点(如上图所示);当再执行下面的代码:
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
那么current != null 所以接着进入下一次while循环,执行这句代码后;parent = current;
那么parent = 45的那个节点了,current值如下所示:

接着进入if语句判断,由于当前的根节点是45,所以37 小于根节点 45了,所以就进入if语句代码如下:
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}
Current = current.left 因此current = null; 继续执行上面的if语句判断是否为null的时候,因此就把37放入根节点为45的左节点上了。
5. 直接执行insert(3); 的时候,根节点不为空,所以就进入else语句的while语句中,由于当前的data = 3,所以执行如下if判断代码:
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}
插入的节点值3 小于 根节点23,进入if语句里面执行,但是当前的current值如下:
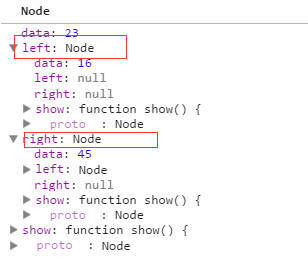
所以当执行 current = current.left 的时候,那么current = 16的那个节点了,如下所示:
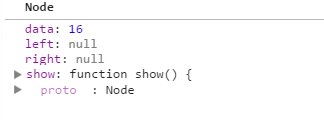
因此current 不等于null,所以就执行到下一次while循环,继续进入while中的if判断,由于当前的根节点是16,所以也就进入了if里面的代码去执行,在执行这句代码后:
current = current.left; 由上图可知:current = null;current就等于null了;再执行代码如下:
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
就把节点3 插入到当前的根节点为16的左节点了。
6. 执行insert(99)的时候;当前的根节点23 小于 99,那么就进入else语句了,那么current值就等于如下:

当执行 current = current.right; 的时候 ,那么current 就等于如下:
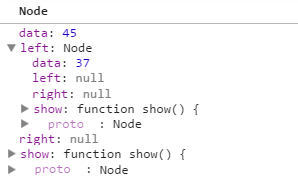
再接着执行代码:
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
如上图所示,current并不等于null,所以执行下一次while循环,继续进入while中的else语句,那么当前的current值如下:
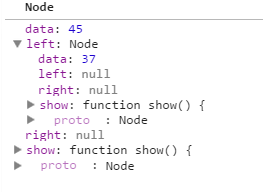
当执行current = current.right;这句代码的时候,那么current 就等于 null了,所以执行if语句代码如下:
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
就把99节点插入到当前的根节点为45节点的右节点了。
7. 执行 insert(22);的时候,由于根节点为23,所以节点22 小于 23,所以进入while中的if语句里面了,那么当前current值如下:

当执行 current = current.left; 的时候,那么current值变为如下所示:
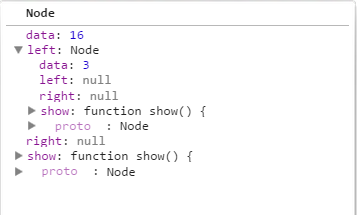
所以执行 if语句代码如下:
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
不等于null,所以斤进入while下一次循环,由于当前的根节点16 小于插入的节点22 ,所以就进入else语句了,那么当前的current值如下:
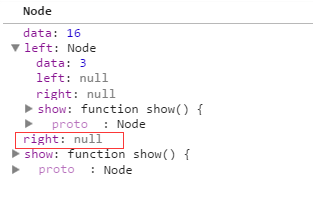
再执行这句代码 current = current.right; 那么current就等于null了;因此就把节点22插入到根节点为16上面的右节点上了;
以上是插入节点的整个流程!
二:遍历二叉查找树;
遍历二叉树的方法有三种,中序,先序和后序。
1. 中序;
如下图所示:
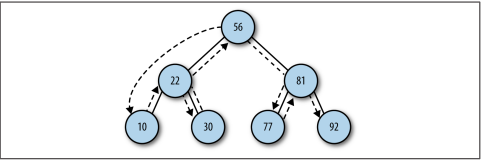
中序遍历使用递归的方式实现,该方法需要以升序访问树中的所有节点,先访问左子树,再访问根节点,最后访问右子树。
代码如下:
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
代码分析如下:



JS所有代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
代码初始化如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
inOrder(nums.root);
2. 先序:先序遍历先访问根节点,然后以同样方式访问左子树和右子树。如下图所示:
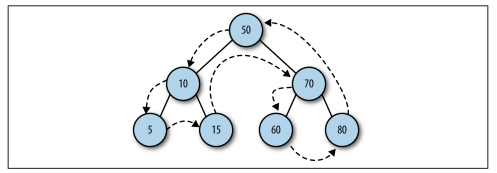
代码如下:
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
JS所有代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
初始化代码如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
console.log("--------------");
preOrder(nums.root);
先序遍历打印如下:

3. 后序:后序遍历先访问叶子节点,从左子树到右子树,再到根节点,如下所示:
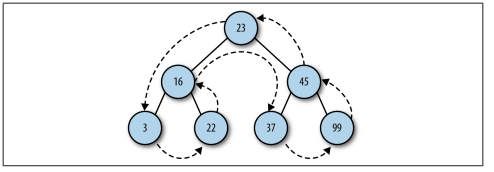
JS代码如下:
// 后序遍历
function postOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
console.log("后序遍历"+node.show());
}
}
所有的JS代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
function postOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
console.log("后序遍历"+node.show());
}
}
页面初始化如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
console.log("--------------");
postOrder(nums.root);
打印如下:
在二叉查找树上进行查找
查找二叉树上的最小值与最大值非常简单,因为较小的值总是在左子节点上,在二叉树上查找最小值,只需要遍历左子树,直到找到最后一个节点。
1. 二叉树查找最小值
代码如下:
// 二叉树查找最小值
function getMin(){
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.left == null)) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
所有JS代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
this.getMin = getMin;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
function postOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
console.log("后序遍历"+node.show());
}
}
// 二叉树查找最小值
function getMin(){
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.left == null)) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
测试代码初始化如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
var min = nums.getMin();
console.log(min); // 打印出3
代码分析如下:
1 当执行到getMin()方法内的 var current = this.root的时候,当前的this.root的值为如下:
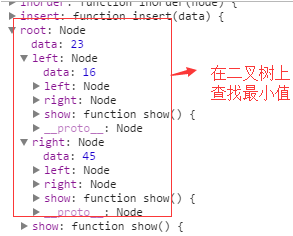
因此进入while内的循环,执行到代码:
current = current.left,current.left值如下:
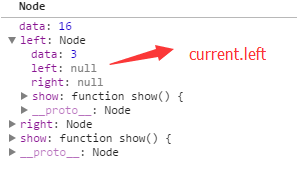
赋值给current,因此current等于上面的节点。接着继续循环遍历while,执行到代码 current = current.left , current.left值变成如下:

然后值赋值给current。再继续遍历,进入while循环,while(!(current.left == null)) {}代码判断,由上图可知;current.left = null,因此就跳出整个while循环,因此打印3出来。
2.在二叉树上查找最大值;只需遍历右子树,直到查到最后一个节点,该节点上保存的值即为最大值。
JS代码如下:
// 二叉树上查找最大值
function getMax() {
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.right == null)) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
下面是所有的JS代码:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
this.getMin = getMin;
this.getMax = getMax;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
function postOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
console.log("后序遍历"+node.show());
}
}
// 二叉树查找最小值
function getMin(){
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.left == null)) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
// 二叉树上查找最大值
function getMax() {
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.right == null)) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
HTML初始化如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
var min = nums.getMin();
console.log(min);
var max = nums.getMax();
console.log(max);
分析还是和上面最小值分析一个道理,这里就不分析了。
上面2个方法返回最小值和最大值,但是有时候,我们希望方法返回存储最小值和最大值的节点,这很好实现,只需要修改方法,让它返回当前节点,而不是节点中存储的数据即可。
在二叉树上查找给定值
在二叉树上查找给定值,需要比较该值和当前节点上的值得大小。通过比较,就能确定如果给定值不在当前节点时,就要向左遍历和向右遍历了。
代码如下:
// 查找给定值
function find(data) {
var current = this.root;
while(current != null) {
if(current.data == data) {
return current;
}else if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
}else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return null;
}
代码分析如下:
比如现在的二叉树是如下这个样子:

页面初始化 查找二叉树上的45 节点,代码初始化如下:
var value = nums.find("45");
截图如下:

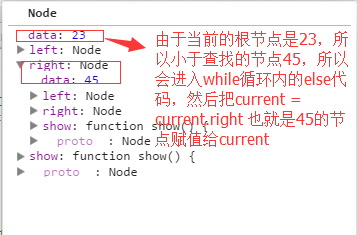

然后就return 45的节点上了。
所有的JS代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
this.getMin = getMin;
this.getMax = getMax;
this.find = find;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
function postOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
console.log("后序遍历"+node.show());
}
}
// 二叉树查找最小值
function getMin(){
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.left == null)) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
// 二叉树上查找最大值
function getMax() {
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.right == null)) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
// 查找给定值
function find(data) {
var current = this.root;
while(current != null) {
if(current.data == data) {
return current;
}else if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
}else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return null;
}
从二叉查找树上删除节点。
原理:从二叉树上删除节点首先要判断当前节点是否包含待删除的数据,如果包含,则删除该节点;如果不包含,则要比较当前节点上的数据和待删除的数据。如果待删除数据小于当前节点上的数据,则要移到当前节点的左子节点继续比较;如果删除的数据大于当前节点上的数据,则移至当前节点的右子节点继续比较。
如果待删除节点是叶子节点(没有子节点的节点),那么只需要将父节点指向它的链接指向null;
如果待删除的节点只包含一个子节点,那么原本指向它的节点就得做点调整,使其指向它的子节点。
最后,如果待删除节点包含2个子节点,正确的做法有2种,1:要么查找待删除节点左子树上的最大值,要么查找其右子树上的最小值。这里我们选择后一种;
下面是我们删除节点的JS代码如下:
function remove(data) {
root = removeNode(this.root,data);
}
function getSmallest(node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
else {
return getSmallest(node.left);
}
}
function removeNode(node,data) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
if(data == node.data) {
// 没有子节点的节点
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
// 没有左子节点的节点
if(node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
// 没有右子节点的节点
if(node.right == null) {
return node.left;
}
// 有2个子节点的节点
var tempNode = getSmallest(node.right);
node.data = tempNode.data;
node.right = removeNode(node.right,tempNode.data);
return node;
}else if(data < node.data) {
node.left = removeNode(node.left,data);
return node;
}else {
node.right = removeNode(node.right,data);
return node;
}
}
我们还是以上面的二叉树来分析下代码原理:
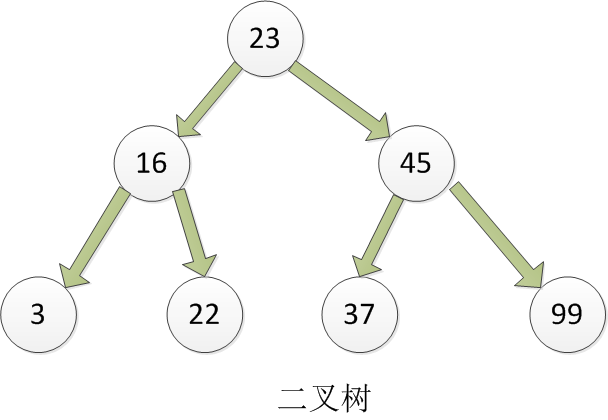
1. 比如我现在要删除根节点为23的节点,代码初始化如下:
nums.remove(23);
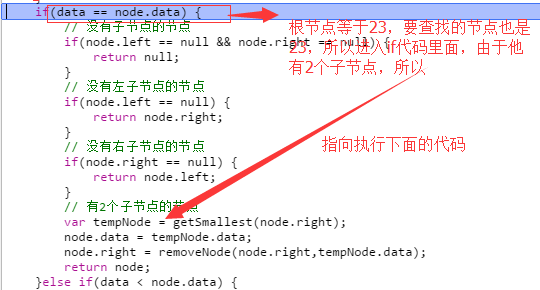

执行这个代码后 var tempNode = getSmallest(node.right); 就指向45的那个节点了,如下:

然后执行下面的获取右子树上的最小值的方法;
function getSmallest(node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
else {
return getSmallest(node.left);
}
}
里面使用递归的方式执行代码,当node.left == null 时候,就返回当前node节点;如下:

如上所示,当node等于37的时候 就返回node为37的节点。
下面继续执行第二句代码;如下:
node.data = tempNode.data; 那么node.data = 37了;下面是node节点的截图如下:
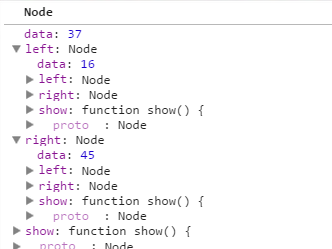
接着继续执行下面的代码
node.right = removeNode(node.right,tempNode.data);
同时又使用递归的方式removeNode()方法;返回如下节点:

所有的JS代码如下:
function Node(data,left,right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.show = show;
}
function show() {
return this.data;
}
function BST() {
this.root = null;
this.insert = insert;
this.inOrder = inOrder;
this.getMin = getMin;
this.getMax = getMax;
this.find = find;
this.remove = remove;
}
function insert(data) {
var n = new Node(data,null,null);
if(this.root == null) {
this.root = n;
}else {
var current = this.root;
var parent;
while(current) {
parent = current;
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if(current == null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
}else {
current = current.right;
if(current == null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
function inOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show());
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 先序遍历
function preOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
console.log(node.show());
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
// 后序遍历
function postOrder(node) {
if(!(node == null)) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
console.log("后序遍历"+node.show());
}
}
// 二叉树查找最小值
function getMin(){
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.left == null)) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
// 二叉树上查找最大值
function getMax() {
var current = this.root;
while(!(current.right == null)) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
// 查找给定值
function find(data) {
var current = this.root;
while(current != null) {
if(current.data == data) {
return current;
}else if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
}else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return null;
}
function remove(data) {
root = removeNode(this.root,data);
}
function getSmallest(node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
else {
return getSmallest(node.left);
}
}
function removeNode(node,data) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
if(data == node.data) {
// 没有子节点的节点
if(node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
// 没有左子节点的节点
if(node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
// 没有右子节点的节点
if(node.right == null) {
return node.left;
}
// 有2个子节点的节点
var tempNode = getSmallest(node.right);
node.data = tempNode.data;
node.right = removeNode(node.right,tempNode.data);
return node;
}else if(data < node.data) {
node.left = removeNode(node.left,data);
return node;
}else {
node.right = removeNode(node.right,data);
return node;
}
}
代码初始化如下:
var nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(22);
var min = nums.getMin();
console.log(min);
var max = nums.getMax();
console.log(max);
var value = nums.find("45");
console.log(value);
nums.remove(23);
javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树的更多相关文章
- javascript数据结构与算法---二叉树(删除节点)
javascript数据结构与算法---二叉树(删除节点) function Node(data,left,right) { this.data = data; this.left = left; t ...
- javascript数据结构与算法---二叉树(查找最小值、最大值、给定值)
javascript数据结构与算法---二叉树(查找最小值.最大值.给定值) function Node(data,left,right) { this.data = data; this.left ...
- javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树遍历(后序)
javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树遍历(后序) 后序遍历先访问叶子节点,从左子树到右子树,再到根节点. /* *二叉树中,相对较小的值保存在左节点上,较大的值保存在右节点中 * * * */ ...
- javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树遍历(先序)
javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树遍历(先序) 先序遍历先访问根节点, 然后以同样方式访问左子树和右子树 代码如下: /* *二叉树中,相对较小的值保存在左节点上,较大的值保存在右节点中 * ...
- javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树遍历(中序)
javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树遍历(中序) 中序遍历按照节点上的键值,以升序访问BST上的所有节点 代码如下: /* *二叉树中,相对较小的值保存在左节点上,较大的值保存在右节点中 * ...
- javascript数据结构与算法--二叉树(插入节点、生成二叉树)
javascript数据结构与算法-- 插入节点.生成二叉树 二叉树中,相对较小的值保存在左节点上,较大的值保存在右节点中 /* *二叉树中,相对较小的值保存在左节点上,较大的值保存在右节点中 * * ...
- javascript数据结构与算法--散列
一:javascript数据结构与算法--散列 一:什么是哈希表? 哈希表也叫散列表,是根据关键码值(key,value)而直接进行访问的数据结构,它是通过键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录的,散列 ...
- 为什么我要放弃javaScript数据结构与算法(第八章)—— 树
之前介绍了一些顺序数据结构,介绍的第一个非顺序数据结构是散列表.本章才会学习另一种非顺序数据结构--树,它对于存储需要快速寻找的数据非常有用. 本章内容 树的相关术语 创建树数据结构 树的遍历 添加和 ...
- JavaScript 数据结构与算法之美 - 线性表(数组、栈、队列、链表)
前言 基础知识就像是一座大楼的地基,它决定了我们的技术高度. 我们应该多掌握一些可移值的技术或者再过十几年应该都不会过时的技术,数据结构与算法就是其中之一. 栈.队列.链表.堆 是数据结构与算法中的基 ...
随机推荐
- Hibernate内测总结
1.在Hibernate中,以下关于主键生成器说法错误的是( ). A.increment可以用于类型为long.short或byte的主键 B.identity用于如SQL Server.DB2.M ...
- Struts2 Ajax校验
Ajax(Asynchronous javascript and xml):异步刷新技术 技术组成: CSS + xml +JavaScript +DOM Ajax核心对象: XMLHttpRequ ...
- Visual Studio 2013支持Xamarin的解决方案
转自博客园[遗忘的代码] Xamarin的Visual Studio插件目前还不支持VS 2013,所以需要在安装Xamarin的VS插件时把2010和2012全选上 (由于我的电脑里只剩2013,而 ...
- jmeter(八)断言
jmeter中有个元件叫做断言(Assertion),它的作用和loadrunner中的检查点类似: 用于检查测试中得到的响应数据等是否符合预期,用以保证性能测试过程中的数据交互与预期一致. 使用断言 ...
- 分布式监控系统Zabbix-3.0.3-完整安装记录(2)-添加mysql监控
Zabbix3.0 Server以后就自带了MySQL插件来监控mysql数据库的模板,只需要配置好agent客户端,然后在web端给主机增加模板就行了. 以下是公司线上的zabbix3.0环境下添加 ...
- Microsoft Client Development MVP 2013 - 2014
周末一直沉浸在醉意中,为婚礼忙忙碌碌了一个月,终于完成了人生一大喜事. 清晨仍旧有一些宿醉得感觉, 看到来自微软的邮件,获得Microsoft Client Development MVP 2013 ...
- ZooKeeper 笔记(1) 安装部署及hello world
先给一堆学习文档,方便以后查看 官网文档地址大全: OverView(概述) http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/r3.4.6/zookeeperOver.html Get ...
- 兼容firefox的 keyCode
<script language = "javascript"> document.onkeydown=inLogin function inLogin(e) { va ...
- PHP操作MySQL数据库5个步骤
PHP操作MySQL数据库一般可分为5个步骤:1.连接MySQL数据库服务器:2.选择数据库:3.执行SQL语句:4.关闭结果集:5断开与MySQL数据库服务器连接. 1.用mysql_connect ...
- 利用python将二值csv格式转换为矩阵
#!/usr/bin/env python # coding:utf-8 #import pandas as pd, numpy as np; ''' 将csv文件转换为对应的邻接矩阵mat ''' ...
