LeetCode 解题总结
1. 最长合法括号串
给定只包含'('和')'的字符串,找出最长合法括号串的长度。
Example 1:
Input: "(()" Output: 2 Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()"
Example 2:
Input: ")()())" Output: 4 Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()()"
解法:使用动态规划算法,使用dp数组,其中dp中第i个元素代表以s[i]结尾的最长合法括号串的长度。dp初始化为0,显然,合法的子串必须以')'结尾,所以,以'('结尾的子串在对应的dp下标中总是0。因此只需要在遇到')'时更新dp数组。检查string中相邻的两个字符,如果
1. \(s[i]\) = ')' 且 \(s[i - 1]\) = '(',即"....()"这样的串,有
\(dp[i] = dp[i - 2] + 2\)
2. \(s[i]\) = ')' 且 \(s[i - 1]\) = ')',即"....))"这样的串,有
如果 \(s[i - dp[i - 1] - 1]\) = '(',有 \(dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2] + 2\)
代码如下:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
int maxans = ;
vector<int> dp(s.length());
for (int i = ; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] == ')') {
if (s[i - ] == '(') {
dp[i] = (i >= ? dp[i - ] : ) + ;
} else if (i - dp[i - ] > && s[i - dp[i - ] - ] == '(') {
dp[i] = dp[i - ] + ((i - dp[i - ]) >= ? dp[i - dp[i - ] - ] : ) + ;
}
maxans = max(maxans, dp[i]);
}
}
return maxans;
}
2. 最大乘积子数组
给定整数数组 nums, 找出数组中具有最大乘积的连续的子数组(至少包含一个数字)
Example 1:
Input: [2, 3, -2, 4] Output: 6 Explanation: [2, 3] 具有最大乘积6
Example 2:
Input: [-2, 0, -1] Output: 0 Explanation: 结果不是2,因为 [-2, -1] 不是子数组
代码:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
int r = nums[];
for (int i = , imax = r, imin = r; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] < )
swap(imax, imin);
imax = max(nums[i], imax * nums[i]);
imin = min(nums[i], imin * nums[i]);
r = max(r, imax);
}
return r;
}
3. Rotate Image
给定一个\(n*n\)的二维矩阵,顺时针旋转九十度。
注意:必须就地进行旋转,不能申请一个二维矩阵进行旋转。
解法:旋转图像的一般方法:first reverse up to down, then swap the symmetry
1 2 3 7 8 9 7 4 1
4 5 6 => 4 5 6 => 8 5 2
7 8 9 1 2 3 9 6 3
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
reverse(matrix.begin(), matrix.end());
for (int i = ; i < matrix.size(); i++) {
for (int j = i + ; j < matrix[i].size(); j++) {
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
}
4. 回文数字
判断给定数字是否是回文的。
Example 1:
Input: 121 Output: true
Example 2:
Input: -121 Output: false
Example 3:
Input: 10 Output: false
解法:将原数反转,看是否和原数相等,但反转后的数字有可能溢出。为解决这个问题,考虑仅反转一半数字,如果后一半反转后和前一半相等,则该数为回文的。例如,数字,1221,将后面的21反转后为12,和前一半相等,则该数为回文的。
代码如下:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
if (x < || (x % == && x != ))
return false;
int revertedNumber = ;
while (x > revertedNumber) {
revertedNumber = revertedNumber * + x % ;
x /= ;
}
return (x == revertedNumber || x == revertedNumber / );
}
5. 最长公共前缀
找出数组中字符串的最长公共前缀,如果没有,返回 ""。
Example 1:
Input: ["flower", "flow", "flight"] Output: "fl"
Example 2:
Input: ["dog", "racecar", "car"] Output: ""
解法一:水平扫描,遍历的方式逐步求出两两之间的公共前缀。
代码:
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if (strs.empty()) return "";
string prefix = strs[];
for (int i = ; i < strs.size(); i++) {
while (strs[i].find(prefix) != ) {
prefix = prefix.substr(, prefix.length() - );
if (prefix.empty()) return "";
}
}
return prefix;
}
解法二:垂直扫描,在同一列中从顶至尾比较字符,然后移至下一列。
代码:
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if (strs.empty()) return "";
for (int i = 0; i < strs[0].size(); i++) {
char c = strs[0][i];
for (int j = 1; j < strs.size(); j++) {
if (i == strs[j].length() || strs[j][i] != c)
return strs[0].substr(0, i);
}
}
return strs[0];
}
解法三:分治法。
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if (strs.empty()) return "";
return longestCommonPrefix(strs, , strs.size() - );
}
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return strs[l];
} else {
int mid = (l + r) / ;
string lcpLeft = longestCommonPrefix(strs, l, mid);
string lcpRight = longestCommonPrefix(strs, mid + , r);
return commonPrefix(lcpLeft, lcpRight);
}
}
string commonPrefix(string left, string right) {
int min = min(left.length(), right.length());
for (int i = ; i < min; i++) {
if (left[i] != right[i])
return left.substr(, i);
}
return left.substr(, min);
}
解法四:二分查找法
string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {
if (strs.empty()) return "";
size_t minLen = INT_MAX;
for (string str : strs) {
minLen = min(minLen, str.length());
}
int low = ;
int high = minLen;
while (low <= high)
{
int middle = (low + high) / ;
if (isCommonPrefix(strs, middle))
low = middle + ;
else
high = middle - ;
}
return strs[].substr(, (low + high) / );
}
bool isCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs, int len) {
string str1 = strs[].substr(, len);
for (int i = ; i < strs.size(); i++) {
if (strs[i].find(str1) == string::npos)
return false;
}
return true;
}
6. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appear only once and return the new length.
Example 1:
Input: [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4] Output: 5
Solution:
Since the array is already sorted, we can keep two pointers \(i\) and \(j\), where \(i\) is the slow-runner while \(j\) is the fast-runner. As long as \(nums[i] == nums[j]\), we increment \(j\) to skip the duplicate.
When we encounter \(nums[j] \neq nums[i]\), the duplicate run has ended so we must copy its value to \(nums[i+1]\). \(i\) is then incremented and we repeat the same process again until \(j\) reaches the end of array.
lass Solution(object):
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
i = 0
for j in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[j] != nums[i]:
i = i + 1
nums[i] = nums[j]
return i + 1
7. Plus One
Given a non-empty array of digits representing a non-negative integer, plus one to the integer. The digits are sorted such that the most significant digit is at the head of the list, and each element in the array contain a single digit. You may assume the integer does not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: [1, 2, 3] Output: [1, 2, 4]
class Solution(object):
def plusOne(self, digits):
for i in range(len(digits) - 1, -1, -1):
if digits[i] < 9:
digits[i] += 1
return digits
digits[i] = 0
digits = [1] + digits
return digits
8. Sqrt(x)
Implement int sqrt(int x). Compute and return the square root of x, where x is guaranteed to be a non-negative integer. Since the return type is an integer, the decimal digits are truncated and only the integer part of the result is returned.
Example:
Input: 8 Output: 2
class Solution(object):
def mySqrt(self, x):
if x == 0:
return 0
left, right = 1, x
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if mid * mid > x:
right = mid - 1
elif (mid + 1) * (mid + 1) > x:
return mid
else:
left = mid + 1
9. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as: a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example: Given the following tree [3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7], return true.
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
bool help(TreeNode* root, int &height) {
if (root == NULL) {
height = ;
return true;
}
int height1, height2;
if (!help(root->left, height1)) {
return false;
}
if (!help(root->right, height2)) {
return false;
}
height = max(height1, height2) + ;
return (height1 - height2 <= && height2 - height1 <= );
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
int height;
return help(root, height);
}
10. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
Given an array of integers that is already sorted in ascending order, find two number such that they added up to a specific target number. The function twoSum should return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to the target, where index1 must be less than index2.
Example:
Input: numbers = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9 Output: [1, 2]
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, numbers, target):
"""
:type numbers: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
ans = []
l, r = 0, len(numbers) - 1
while numbers[l] + numbers[r] != target:
if numbers[l] + numbers[r] > target:
r -= 1
else:
l += 1
ans.append(l + 1)
ans.append(r + 1)
return ans
11. Excel Sheet Column Title
Given a positive integer, return its corresponding column title as appear in an Excel sheet.
For example:
1 -> A 2 -> B ... 26 -> Z 27 -> AA
class Solution(object):
def convertToTitle(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: str
"""
if n == 0:
return ""
return self.convertToTitle((n-1) // 26) + chr((n-1) % 26 + ord('A'))
12. Majority Element
Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element that appears more than \(\lfloor n/2 \rfloor\) times. You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always exist in the array.
Example:
Input: [2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2] Output: 2
Approach 1: Brute Force
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums):
majority_count = len(nums)//2
for num in nums:
count = sum(1 for elem in nums if elem == num)
if count > majority_count:
return num
Approach 2: Hash Map
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums):
counts = collections.Counter(nums)
return max(counts.keys(), key=counts.get)
Approach 3: Sorting
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums):
nums.sort()
return nums[len(nums)//2]
Approach 4: Randomization
import random class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums):
majority_count = len(nums)//2
while True:
candidate = random.choice(nums)
if sum(1 for elem in nums if elem == candidate) > majority_count:
return candidate
Approach 5: Divide and Conquer
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums, lo=0, hi=None):
def majority_element_rec(lo, hi):
# base case; the only element in an array of size 1 is the majority
# element.
if lo == hi:
return nums[lo] # recurse on left and right halves of this slice.
mid = (hi-lo)//2 + lo
left = majority_element_rec(lo, mid)
right = majority_element_rec(mid+1, hi) # if the two halves agree on the majority element, return it.
if left == right:
return left # otherwise, count each element and return the "winner".
left_count = sum(1 for i in range(lo, hi+1) if nums[i] == left)
right_count = sum(1 for i in range(lo, hi+1) if nums[i] == right) return left if left_count > right_count else right return majority_element_rec(0, len(nums)-1)
Approach 6: Boyer-Moore Voting Algorithm
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums):
count = 0
candidate = None for num in nums:
if count == 0:
candidate = num
count += (1 if num == candidate else -1) return candidate
13. Rotate Array
Given an array, rotate the array to the right by \(k\) steps, where \(k\) is non-negative.
Example:
Input: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] and k = 3
Output: [5, 6, 7, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Approach 1: Using extra Array
class Solution(object):
def rotate(self, nums, k):
a = [None] * len(nums)
for i in range(len(nums)):
a[(i + k) % len(nums)] = nums[i]
for i in range(len(nums)):
nums[i] = a[i]
Approach 2: Using Reverse
class Solution(object):
def rotate(self, nums, k):
k %= len(nums)
self.reverse(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
self.reverse(nums, 0, k - 1)
self.reverse(nums, k, len(nums)-1) def reverse(self, nums, start, end):
while start < end:
temp = nums[start]
nums[start] = nums[end]
nums[end] = temp
start += 1
end -= 1
14. Reverse Bits
Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
class Solution(object):
def reverseBits(self, n):
ans = 0
for i in range(32):
ans <<= 1
ans |= (n & 1)
n >>= 1
return ans
15. Number of 1 Bits
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and return the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight).
Example:
Input: 00000000000000000000000000001011 Output: 3
class Solution(object):
def hammingWeight(self, n):
sum = 0
while n:
sum += 1
n &= (n - 1)
return sum
16. Happy Number
Write an algorithm to determine if a number is "happy".
Example:
Input: 19 Output: true
Explanation:
\(1^2 + 9^2 = 82\)
\(8^2 + 2^2 = 68\)
\(6^2 + 8^2 = 100\)
\(1^2 + 0^2 + 0^2 = 1\)
def isHappy(self, n):
mem = set()
while n != 1:
n = sum([int(i) ** 2 for i in str(n)])
if n in mem:
return False
else:
mem.add(n)
else:
return True
17. Invert Binary Tree
Invert a binary tree.
Input:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
Output:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
Approach 1: (Recursive)
def invertTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if root is None:
return None
right = self.invertTree(root.right)
left = self.invertTree(root.left)
root.left = right
root.right = left
return root
Approach 2: (Iterative)
def invertTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if root is None:
return None
q = collections.deque()
q.append(root)
while q:
current = q.popleft()
temp = current.left
current.left = current.right
current.right = temp
if current.left is not None: q.append(current.left)
if current.right is not None: q.append(current.right)
return root
18. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search Tree, find the lowest common ancestor of two given nodes in the BST.
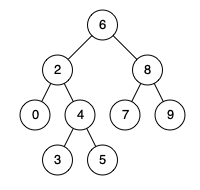
Example:
Input: root = [6, 2, 8, 0, 4, 7, 9, null, null, 3, 5], p = 2, q = 8
Output: 6
Approach 1: Recursive Approach
Algorithm:
1. Start traversing the tree from the root node.
2. If both the nodes \(p\) and \(q\) are in the right subtree, then continue the search with right subtree starting step 1.
3. If both the nodes \(p\) and \(q\) are in the left subtree, then continue the search with left subtree starting step 1.
4. If both step 2 and step 3 are not true, this means we have found the node which is common to node \(p\)'s and \(q\)'s subtrees, and hence we return this common node as the LCA.
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# Value of current node or parent node.
parent_val = root.val # Value of p
p_val = p.val # Value of q
q_val = q.val # If both p and q are greater than parent
if p_val > parent_val and q_val > parent_val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
# If both p and q are lesser than parent
elif p_val < parent_val and q_val < parent_val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
# We have found the split point, i.e. the LCA node.
else:
return root
Approach 2: Iterative Approach
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
""" # Value of p
p_val = p.val # Value of q
q_val = q.val # Start from the root node of the tree
node = root # Traverse the tree
while node: # Value of current node or parent node.
parent_val = node.val if p_val > parent_val and q_val > parent_val:
# If both p and q are greater than parent
node = node.right
elif p_val < parent_val and q_val < parent_val:
# If both p and q are lesser than parent
node = node.left
else:
# We have found the split point, i.e. the LCA node.
return node
19. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
Given the following binary tree: root = [3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4]
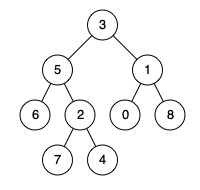
Example:
Input: root = [3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 0, 8, null, null, 7, 4], p = 5, q = 1 . Output: 3
Approach 1: Recursive Approach
从 \(root\) 开始遍历,如果找到了\(p\)或者\(q\),就返回\(true\),如果对某个节点,左右子树都返回了\(true\),则此节点就是 LCA。如果某节点就是\(p\)或\(q\)节点,该节点的子树递归结果仍为 true。
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
# Variable to store LCA node.
self.ans = None
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
def recurse_tree(current_node):
# If reached the end of a branch, return False.
if not current_node:
return False
# Left Recursion
left = recurse_tree(current_node.left)
# Right Recursion
right = recurse_tree(current_node.right)
# If the current node is one of p or q
mid = current_node == p or current_node == q
# If any two of the three flags left, right or mid become True.
if mid + left + right >= 2:
self.ans = current_node
# Return True if either of the three bool values is True.
return mid or left or right
# Traverse the tree
recurse_tree(root)
return self.ans
Approach 2: Iterative using parent pointer
在遍历过程中保存各个节点的父节点,然后从\(p\)和\(q\)节点往上找父节点,第一个公共节点就是 LCA.(找父节点时,只需要找到\(p\)和\(q\)为止)
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# Stack for tree traversal
stack = [root]
# Dictionary for parent pointers
parent = {root: None}
# Iterate until we find both the nodes p and q
while p not in parent or q not in parent:
node = stack.pop()
# While traversing the tree, keep saving the parent pointers.
if node.left:
parent[node.left] = node
stack.append(node.left)
if node.right:
parent[node.right] = node
stack.append(node.right)
# Ancestors set() for node p.
ancestors = set()
# Process all ancestors for node p using parent pointers.
while p:
ancestors.add(p)
p = parent[p]
# The first ancestor of q which appears in
# p's ancestor set() is their lowest common ancestor.
while q not in ancestors:
q = parent[q]
return q
Approach 3: Iterative without parent pointers
使用栈保存遍历路径。
class Solution:
# Three static flags to keep track of post-order traversal.
# Both left and right traversal pending for a node.
# Indicates the nodes children are yet to be traversed.
BOTH_PENDING = 2
# Left traversal done.
LEFT_DONE = 1
# Both left and right traversal done for a node.
# Indicates the node can be popped off the stack.
BOTH_DONE = 0
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# Initialize the stack with the root node.
stack = [(root, Solution.BOTH_PENDING)]
# This flag is set when either one of p or q is found.
one_node_found = False
# This is used to keep track of LCA index.
LCA_index = -1
# We do a post order traversal of the binary tree using stack
while stack:
parent_node, parent_state = stack[-1]
# If the parent_state is not equal to BOTH_DONE,
# this means the parent_node can't be popped of yet.
if parent_state != Solution.BOTH_DONE:
# If both child traversals are pending
if parent_state == Solution.BOTH_PENDING:
# Check if the current parent_node is either p or q.
if parent_node == p or parent_node == q:
# If one_node_found is set already, this means we have found both the nodes.
if one_node_found:
return stack[LCA_index][0]
else:
# Otherwise, set one_node_found to True,
# to mark one of p and q is found.
one_node_found = True
# Save the current top index of stack as the LCA_index.
LCA_index = len(stack) - 1
# If both pending, traverse the left child first
child_node = parent_node.left
else:
# traverse right child
child_node = parent_node.right
# Update the node state at the top of the stack
# Since we have visited one more child.
stack.pop()
stack.append((parent_node, parent_state - 1))
# Add the child node to the stack for traversal.
if child_node:
stack.append((child_node, Solution.BOTH_PENDING))
else:
# If the parent_state of the node is both done,
# the top node could be popped off the stack.
# i.e. If LCA_index is equal to length of stack. Then we decrease LCA_index by 1.
if one_node_found and LCA_index == len(stack) - 1:
LCA_index -= 1
stack.pop()
return None
20. Word Pattern
Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same pattern.
Example:
Input: pattern = 'abba', str = "dog cat cat dog" Output: true
class Solution(object):
def wordPattern(self, pattern, str):
"""
:type pattern: str
:type str: str
:rtype: bool
"""
s = pattern
t = str.split()
return map(s.find, s) == map(t.index, t)
21. Intersection of Two Arrays
Given two arrays, write a function to compute their intersection.
Example:
Input: nums1 = [1, 2, 2, 1], nums2 = [2, 2] . Output: [2]
Approach 1: Two Sets
class Solution:
def set_intersection(self, set1, set2):
return [x for x in set1 if x in set2] def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
set1 = set(nums1)
set2 = set(nums2) if len(set1) < len(set2):
return self.set_intersection(set1, set2)
else:
return self.set_intersection(set2, set1)
Approach 2: Built-in Set Intersection
class Solution:
def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
set1 = set(nums1)
set2 = set(nums2)
return list(set2 & set1)
22. Intersection of Two Arrays II
Given two arrays, write a function to compute their intersection.
Example:
Input: nums1 = [1, 2, 2, 1], nums2 = [2, 2] . Output: [2, 2]
class Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
a,b = collections.Counter(nums1),collections.Counter(nums2)
return [i for i in a if i in b for _ in range(min(a[i], b[i]))]
更高级的写法:
class Solution:
def intersect(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> List[int]:
a, b = map(collections.Counter, (nums1, nums2))
return list((a & b).elements())
LeetCode 解题总结的更多相关文章
- Leetcode解题思想总结篇:双指针
Leetcode解题思想总结篇:双指针 1概念 双指针:快慢指针. 快指针在每一步走的步长要比慢指针一步走的步长要多.快指针通常的步速是慢指针的2倍. 在循环中的指针移动通常为: faster = f ...
- LeetCode解题报告:Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II
LeetCode解题报告:Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II 1题目 Linked List Cycle Given a linked ...
- leetcode解题报告(2):Remove Duplicates from Sorted ArrayII
描述 Follow up for "Remove Duplicates": What if duplicates are allowed at most twice? For ex ...
- LeetCode解题记录(贪心算法)(二)
1. 前言 由于后面还有很多题型要写,贪心算法目前可能就到此为止了,上一篇博客的地址为 LeetCode解题记录(贪心算法)(一) 下面正式开始我们的刷题之旅 2. 贪心 763. 划分字母区间(中等 ...
- LeetCode 解题报告索引
最近在准备找工作的算法题,刷刷LeetCode,以下是我的解题报告索引,每一题几乎都有详细的说明,供各位码农参考.根据我自己做的进度持续更新中...... ...
- leetCode解题报告5道题(六)
题目一: Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters Given a string, find the length of the longest s ...
- LeetCode解题中位运算的运用
位运算是我最近才开始重视的东西,因为在LeetCode上面刷题的时候发现很多题目使用位运算会快很多.位运算的使用包含着许多技巧(详细可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/zmazon/ar ...
- Leetcode解题思路总结(Easy篇)
终于刷完了leetcode的前250道题的easy篇.好吧,其实也就60多道题,但是其中的套路还是值得被记录的. 至于全部code,请移步github,题目大部分采用python3,小部分使用C,如有 ...
- LeetCode解题思路
刷完题后,看一下其他人的solution,受益匪浅. 可以按不同的topic刷题,比如数组.字符串.集合.链表等等.先做十道数组的题,接着再做十道链表的题. 刷题,最主要的是,学习思路. 多刷几遍.挑 ...
- LeetCode解题报告—— Longest Valid Parentheses
Given a string containing just the characters '(' and ')', find the length of the longest valid (wel ...
随机推荐
- KVM宿主机上虚拟机动态添加新磁盘
(1)KVM宿主机查看运行的虚拟机 $ virsh list --all (2)将qcow2的磁盘移动到/var/lib/libvirt/images/,比如为centos.qcow2 (3)进入/e ...
- Linux下ansible的group模块
一.概述 group 模块可以帮助我们管理远程主机上的组. 二.常用参数 name参数:必须参数,用于指定要操作的组名称. state参数:用于指定组的状态,两个值可选,present,absent, ...
- Python网络爬虫精要
目的 学习如何从互联网上获取数据.数据科学必须掌握的技能之一. 本文所用到的第三方库如下: requests, parsel, selenium requests负责向网页发送HTTP请求并得到响应, ...
- centos6.5之phpmyadmin安装
PhpMyAdmin 首先我们看一下百度百科,看一下phpmyadmin是做什么的. phpMyAdmin 是一个以PHP为基础,以Web-Base方式架构在网站主机上的MySQL的数据库管理工具,让 ...
- 2019-04-04 Mybatis学习知识点
1. 比较#和$的区别 #是占位符?,$是字符串拼接.因此使用$的时候,如果参数是字符串类型,那么要使用引号 尽量使用#而不是$ 当参数表示表名或列名的时候,只能使用$ 2. 多参数时候 配置文件中使 ...
- Spring Boot 2.x 编写 RESTful API (五) 单元测试
用Spring Boot编写RESTful API 学习笔记 概念 驱动模块 被测模块 桩模块 替代尚未开发完毕的子模块 替代对环境依赖较大的子模块 (例如数据访问层) 示例 测试 Service @ ...
- CF802C Heidi and Library (hard)
题目描述 你有一个容量为k的空书架,现在共有n个请求,每个请求给定一本书ai,如果你的书架里没有这本书,你就必须以ci的价格购买这本书放入书架.当然,你可以在任何时候丢掉书架里的某本书.请求出完成这n ...
- Linux-I/O重定向和管道
Linux I/O重定向 标准输入(stdin):文件描述符0 标准输入(stdout):文件描述符1 标准错误(stderr):文件描述符2 file descriptors(FD,文件描述符 或 ...
- 微信小程序onLaunch、onLoad执行生命周期
原文转载自:微信小程序onLaunch.onLoad执行生命周期 1.需求:先执行App的onLaunch添加验证权限等,再执行Page里的onLoad. 2.问题:还没有等onLaunch执行完成, ...
- 第二篇--PCI设备解析
介绍:参考 一个系统上最多有256个PCI总线,每个总线最多有32个设备,每个设备最多有8个功能,每个功能最多有256字节的配置地址空间,所以总的配置地址空间是16M. PCI设备有物理设备和逻辑设备 ...
