C# 实现二叉树各种排序
1. 引言
在实际的项目中,树还是用的比较多的一种,尤其是对于具有层次结构的数据。相信很多人都学过树的遍历,比如先序遍历,后序遍历等,利用递归还是很容易理解的。
今天给大家介绍下二叉树的几种遍历算法,包括递归和非递归的实现。
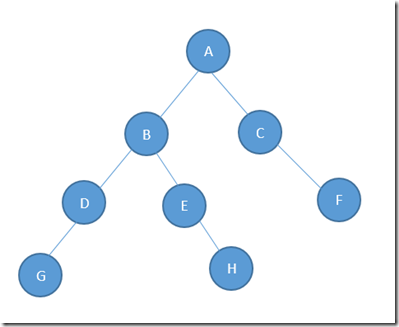
首先建立一棵二叉树 如:
[DebuggerDisplay("Value={Value}")]
public class Tree
{
public string Value;
public Tree Left;
public Tree Right;
}
public static Tree CreatFakeTree()
{
Tree tree = new Tree() {Value = "A"};
tree.Left = new Tree()
{
Value = "B",
Left = new Tree() {Value = "D", Left = new Tree() {Value = "G"}},
Right = new Tree() {Value = "E", Right = new Tree() {Value = "H"}}
};
tree.Right = new Tree() {Value = "C", Right = new Tree() {Value = "F"}};
return tree;
}
一棵简单的二叉树
2. 先序遍历
先序遍历还是很好理解的,一次遍历根节点,左子树,右子数
递归实现
public static void PreOrder(Tree tree)
{
if (tree == null)
return; System.Console.WriteLine(tree.Value);
PreOrder(tree.Left);
PreOrder(tree.Right);
}
非递归实现
public static void PreOrderNoRecursion(Tree tree)
{
if(tree == null)
return; System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>();
Tree node = tree; while (node != null || stack.Any())
{
if (node != null)
{
stack.Push(node);
System.Console.WriteLine(node.Value);
node = node.Left;
}
else
{
var item = stack.Pop();
node = item.Right;
}
}
}
输出结果: 
3. 中序遍历
递归实现
public static void InOrder(Tree tree)
{
if(tree == null)
return; InOrder(tree.Left);
System.Console.WriteLine(tree.Value);
InOrder(tree.Right);
}
非递归实现
public static void InOrderNoRecursion(Tree tree)
{
if (tree == null)
return; System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>();
Tree node = tree; while (node != null || stack.Any())
{
if (node != null)
{
stack.Push(node);
node = node.Left;
}
else
{
var item = stack.Pop();
System.Console.WriteLine(item.Value); node = item.Right;
}
}
}
输出结果:
4. 后序遍历
递归实现
public static void PostOrder(Tree tree)
{
if (tree == null)
return; PostOrder(tree.Left);
PostOrder(tree.Right);
System.Console.WriteLine(tree.Value);
}
非递归实现 比前两种稍微复杂一点。要保证左右节点都被访问后,才能访问根节点。这里给出两种形式。
public static void PostOrderNoRecursion(Tree tree)
{
if (tree == null)
return; System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>();
Tree node = tree;
Tree pre = null;
stack.Push(node); while (stack.Any())
{
node = stack.Peek();
if ((node.Left == null && node.Right == null) ||
(pre != null && (pre == node.Left || pre == node.Right)))
{
System.Console.WriteLine(node.Value);
pre = node; stack.Pop();
}
else
{
if(node.Right != null)
stack.Push(node.Right); if(node.Left != null)
stack.Push(node.Left);
}
}
} public static void PostOrderNoRecursion2(Tree tree)
{
HashSet<Tree> visited = new HashSet<Tree>();
System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree> stack = new System.Collections.Generic.Stack<Tree>();
Tree node = tree; while (node != null || stack.Any())
{
if (node != null)
{
stack.Push(node);
node = node.Left;
}
else
{
var item = stack.Peek();
if (item.Right != null && !visited.Contains(item.Right))
{
node = item.Right;
}
else
{
System.Console.WriteLine(item.Value);
visited.Add(item);
stack.Pop();
}
}
}
}
输出结果: 
5. 层序遍历
层序遍历就是按照层次由左向右输出
public static void LevelOrder(Tree tree)
{
if(tree == null)
return; Queue<Tree> queue = new Queue<Tree>();
queue.Enqueue(tree); while (queue.Any())
{
var item = queue.Dequeue();
System.Console.Write(item.Value); if (item.Left != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(item.Left);
} if (item.Right != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(item.Right);
}
}
}
输出结果:
6. Z-型层序遍历
Z-层序遍历就是奇数层按照由左向右输出,偶数层按照由右向左输出,这里定义了几个辅助函数,比如计算节点所在的层次。算法思想是按照层次保存树形节点,应该是有更加优化的算法,希望大家指出。
public static int GetDepth(Tree tree, Tree node)
{
if (tree == null)
return ; if (tree == node)
return ; if (tree.Left == node || tree.Right == node)
return ; int lDepth = GetDepth(tree.Left, node);
lDepth = lDepth == ? : lDepth + ; int rDepth = GetDepth(tree.Right, node);
rDepth = rDepth == ? : rDepth + ; return lDepth >= rDepth ? lDepth : rDepth;
} public static void Z_LevelOrder(Tree tree, Dictionary<int, List<Tree>> dictionary)
{
if (tree == null)
return; Queue<Tree> queue = new Queue<Tree>();
queue.Enqueue(tree); while (queue.Any())
{
var item = queue.Dequeue();
var depth = GetDepth(tree, item); List<Tree> list;
if (!dictionary.TryGetValue(depth, out list))
{
list = new List<Tree>();
dictionary.Add(depth, list);
}
list.Add(item); if (item.Left != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(item.Left);
} if (item.Right != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(item.Right);
}
}
} public static void Z_LevelOrder(Tree tree)
{
if (tree == null)
return; Dictionary<int, List<Tree>> dictionary = new Dictionary<int, List<Tree>>();
Z_LevelOrder(tree, dictionary); foreach (KeyValuePair<int, List<Tree>> pair in dictionary)
{
if (pair.Key% == )
{
pair.Value.Reverse();
} pair.Value.ForEach(t=> { System.Console.Write(t.Value); });
}
}
输出结果:
C# 实现二叉树各种排序的更多相关文章
- (2)Java数据结构--二叉树 -和排序算法实现
=== 注释:此人博客对很多个数据结构类都有讲解-并加以实例 Java API —— ArrayList类 & Vector类 & LinkList类Java API —— BigDe ...
- Java基础之泛型——使用二叉树进行排序(TryBinaryTree)
控制台程序. 1.实现针对容器类的基于集合的循环 为了让容器类类型的对象能够在基于集合的for循环中可用,类必须并且只需要满足一个要求——必须实现泛型接口java.lang.Iterable<& ...
- 用二叉树进行排序 x (从小到大)
先输入n,表示拥有多少个数: 第二行输入1-n个数,然后开始排序 输出从小到大的排序. ----------------------------------------------代码~------- ...
- 数据结构----二叉树Tree和排序二叉树
二叉树 节点定义 class Node(object): def __init__(self, item): self.item = item self.left = None self.right ...
- [PHP]基本排序(冒泡排序、快速排序、选择排序、插入排序、二分法排序)
冒泡排序: function bubbleSort($array){ $len=count($array); //该层循环控制 需要冒泡的轮数 for($i=1;$i<$len;$i++){ / ...
- 二叉树-二叉查找树-AVL树-遍历
一.二叉树 定义:每个节点都不能有多于两个的儿子的树. 二叉树节点声明: struct treeNode { elementType element; treeNode * left; treeNod ...
- POJ2255二叉树
题目大意就是给出你一个二叉树的前序和中序,要你求后序. 思路:二叉树的排序就是根据根节点的位置来定义的.所以找到二叉树的根节点是最重要的,二叉树的左子树和右子树也可以看成是二叉树,以此递归: #inc ...
- js 前端常用排序算法总结
(冒泡排序.快排顺序.选择排序.插入排序.归并排序) 下面是前端比较常用的五个算法demo: 冒泡算法:比较两个相邻的数值,if第一个>第二个,交换他们的位置元素项向上移动至正确的顺序. fun ...
- python数据结构与算法第十五天【二叉树】
1.树的特点 (1)每个节点有零个或多个子节点: (2)没有父节点的节点称为根节点: (3)每一个非根节点有且只有一个父节点: (4)除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树: 2.树的种类 ...
随机推荐
- XPath高级用法(冰山一角)
运算符+内置函数 使用XPath选择元素时,使用运算符+内置函数来进行筛选: .//div[contains(@class,"ec_desc") or contains(@clas ...
- 记录初学Spring boot中使用GraphQL编写API的几种方式
Spring boot+graphql 一.使用graphql-java-tools方式 <dependency> <groupId>com.graphql-java-kick ...
- Reservoir Sampling-382. Linked List Random Node
Given a singly linked list, return a random node's value from the linked list. Each node must have t ...
- js处理想要得到数据结构
例1 var arr = [ { date: "2018-01-10", time: "11:00" }, { date: "2018-01-10&q ...
- 读取GY-951模块数据(Linux)
参考:https://github.com/Razor-AHRS/razor-9dof-ahrs/wiki/Tutorial#sensor-calibration 链接中使用的硬件是SparkFun“ ...
- python爬虫1——获取网站源代码(豆瓣图书top250信息)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import requests import re import sys reload(sys) sys.setdefaultencoding('utf ...
- easyUI取消选中的所有行
在datagrid选择选中行进行展示后,再返回这个datagrid重新加载数据, 原来选中的数据还是保持选中状态.执行以下的方法还是如此,如图. $("#Table").datag ...
- 微信小程序组件化实践
Do Not Repeat Yourself 如何提高代码质量,方法有许多:抽象.模块.组件化,我认为它们的中心点都是--Do Not Repeat Yourself. 小程序组件化 我们先看看小程序 ...
- 错误处理Cannot load JDBC driver class 'oracle.jdbc.drive
org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.SQLNestedException: Cannot create PoolableConnec是由于<Resource name=&qu ...
- 干货 | 自适应大邻域搜索(Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search)入门到精通超详细解析-概念篇
01 首先来区分几个概念 关于neighborhood serach,这里有好多种衍生和变种出来的胡里花俏的算法.大家在上网搜索的过程中可能看到什么Large Neighborhood Serach, ...
