Linux内核0.11 bootsect文件说明
一、总体功能介绍
这是关于Linux-kernel-0.11中boot文件夹下bootsect.s源文件的说明,其中涉及到了一些基础知识可以参考这两篇文章。
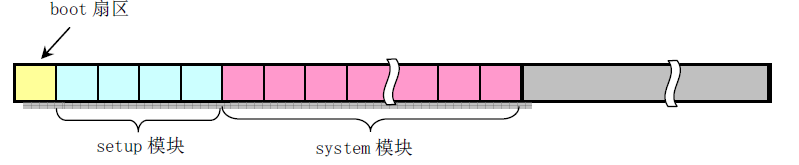
bootsect.s 代码是磁盘引导块程序,存储在磁盘的第一个扇区中(0面0道1扇区),在计算机上电BIOS自检后,BIOS 会吧引导扇区代码bootsect加载到内存0x90000处开并运行。
bootsect代码主要完成以下几项工作:
加载从磁盘第二个扇区开始的4个扇区的内容(由setup.s编译而成)到内存紧接着bootsect后面的0x90200处。
利用BIOS中断 int 13h 获取磁盘参数表中当前启动引导盘的参数。
在屏幕上显示
"Loading system..."字符串。把磁盘上setup模块后面的system模块加载到内存0x10000开始的地方。
确定根文件系统的设备号,若没有指定,则根据所保存的引导盘的每磁道扇区数判别出磁盘的类型和种类(1.2MB 或 1.44MB 软盘),并将其设备号保存在root_dev(引导扇区的508地址出,即第一个扇区的第509个字节处)。
长跳转到setup程序开始处(0x90200)执行setup程序。
在磁盘上,引导块bootsect、setup模块和system模块的扇区位置和大小如下图所示:
二、代码注释
!
! SYS_SIZE is the number of clicks (16 bytes) to be loaded.
! 0x3000 is 0x30000 bytes = 196kB, more than enough for current
! versions of linux
! SYS_SIZE 是要加载的系统模块的长度,单位是节 1节 = 16字节, 0x3000 字节 = 196kB。
!这里定义了system模块长度,所以makefile中的规则就失效了
!
SYSSIZE = 0x3000
!
! bootsect.s (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
!
! bootsect.s is loaded at 0x7c00 by the bios-startup routines, and moves
! iself out of the way to address 0x90000, and jumps there.
!
! It then loads 'setup' directly after itself (0x90200), and the system
! at 0x10000, using BIOS interrupts.
!
! NOTE! currently system is at most 8*65536 bytes long. This should be no
! problem, even in the future. I want to keep it simple. This 512 kB
! kernel size should be enough, especially as this doesn't contain the
! buffer cache as in minix
!
! The loader has been made as simple as possible, and continuos
! read errors will result in a unbreakable loop. Reboot by hand. It
! loads pretty fast by getting whole sectors at a time whenever possible.
! .globl 或 .global 用于定义随后的标识符是外部的或全局的,并且即使不使用也强制引入。
! .text .data .bss 分别定义当前代码段、数据段和未初始化数据段。
.globl begtext, begdata, begbss, endtext, enddata, endbss !定义了6个全局标识符
.text !文本段
begtext:
.data !数据段
begdata:
.bss !未初始化数据段
begbss:
.text
SETUPLEN = 4 ! nr of setup-sectors setup程序的扇区(setup-sectors)值
BOOTSEG = 0x07c0 ! original address of boot-sector bootsect的原始值(是段地址)
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way 将bootsect移到这里
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! setup starts here setup程序从这里开始
SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system loaded at 0x10000 (65536). system模块加载到0x10000(64KB)处
ENDSEG = SYSSEG + SYSSIZE ! where to stop loading 停止加载的段地址
! ROOT_DEV: 0x000 - same type of floppy as boot. 根文件系统设备与引导使用同样的软驱设备
! 0x301 - first partition on first drive etc 根文件系统设备在第一个硬盘的第一个分区上。
ROOT_DEV = 0x306
entry start !告诉链接程序,程序从标号start开始执行
start:
mov ax,#BOOTSEG !设置ds为0x07c0(段地址)
mov ds,ax
mov ax,#INITSEG !设置es为0x9000(段地址)
mov es,ax
mov cx,#256 !移动计数值256个字
sub si,si !源地址 ds:si = 0x07c0:0x0000
sub di,di !目的地址 es:di = 0x9000:0x0000
rep !重复执行并cx的值,直到cx = 0
movw !串传送指令,从[si]移动cx个字到[di]处。从start开始到这里,这段程序将bootsect从0x07c0复制到0x9000处
jmpi go,INITSEG !段间跳转,INITSEG 指跳转到的段地址, 标号go是段内偏移地址。
go: mov ax,cs !设置ds,ss和es为复制代码后代码所在的段。
mov ds,ax
mov es,ax
! put stack at 0x9ff00.
mov ss,ax
mov sp,#0xFF00 ! arbitrary value >>512 设置栈顶指针,远大于512个字节偏移。
! load the setup-sectors directly after the bootblock.
! Note that 'es' is already set up.
!加载 setup 模块代码数据,注意 es已经指向了 0x9000处,不用再设置。
!将setup从磁盘第二个扇区读到0x90200开始处,共读4个扇区。如果读出错,则复位驱动器并重读。
load_setup:
mov dx,#0x0000 ! drive 0, head 0 对驱动器0进行操作
mov cx,#0x0002 ! sector 2, track 0
mov bx,#0x0200 ! address = 512, in INITSEG
mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN ! service 2, nr of sectors
int 0x13 ! read it
jnc ok_load_setup ! ok - continue
mov dx,#0x0000
mov ax,#0x0000 ! reset the diskette
int 0x13
j load_setup ! j 即jmp指令
ok_load_setup:
! Get disk drive parameters, specifically nr of sectors/track
! 获取磁盘参数,尤其是每道的扇区数量
mov dl,#0x00
mov ax,#0x0800 ! AH=8 is get drive parameters
int 0x13
mov ch,#0x00
seg cs
mov sectors,cx
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
! Print some inane message 在屏幕上显示msg1指向的字符串,"Loading system ..."
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#24
mov bx,#0x0007 ! page 0, attribute 7 (normal)
mov bp,#msg1
mov ax,#0x1301 ! write string, move cursor
int 0x10 ! 写字符串并将光标移动到字符串结尾处。
! ok, we've written the message, now 现在开始将system模块加载到 0x10000处(64KB处)
! we want to load the system (at 0x10000)
mov ax,#SYSSEG
mov es,ax ! segment of 0x010000
call read_it ! 读磁盘上的system模块,es为输入参数
call kill_motor ! 关闭驱动马达,这样就可以知道驱动器的状态了。
! After that we check which root-device to use. If the device is
! defined (!= 0), nothing is done and the given device is used.
! Otherwise, either /dev/PS0 (2,28) or /dev/at0 (2,8), depending
! on the number of sectors that the BIOS reports currently.
! 确定选用哪个根文件系统
seg cs
mov ax,root_dev
cmp ax,#0
jne root_defined
seg cs
mov bx,sectors
mov ax,#0x0208 ! /dev/ps0 - 1.2Mb
cmp bx,#15 ! 判断每磁道扇区数是否为15
je root_defined
mov ax,#0x021c ! /dev/PS0 - 1.44Mb
cmp bx,#18 ! 判断每磁道扇区数是否为18
je root_defined
undef_root:
jmp undef_root 如果根文件系统设备都不对,则死循环。
root_defined:
seg cs
mov root_dev,ax ! 将检查过的设备号保存到 root_dev 中
! after that (everyting loaded), we jump to
! the setup-routine loaded directly after
! the bootblock:
jmpi 0,SETUPSEG ! 到这里所有的文件都已经加载完毕,程序跳转到setup文件中去执行。
!!!!! bootsect.s 执行到这里就结束了。 下面是两个子程序。
! This routine loads the system at address 0x10000, making sure
! no 64kB boundaries are crossed. We try to load it as fast as
! possible, loading whole tracks whenever we can.
!
! in: es - starting address segment (normally 0x1000)
!
sread: .word 1+SETUPLEN ! sectors read of current track 当前磁道中已读扇区数
head: .word 0 ! current head 当前磁头号
track: .word 0 ! current track 当前磁道号
read_it:
mov ax,es
test ax,#0x0fff
die: jne die ! es must be at 64kB boundary
xor bx,bx ! bx is starting address within segment
rp_read:
mov ax,es
cmp ax,#ENDSEG ! have we loaded all yet?
jb ok1_read
ret
ok1_read:
seg cs
mov ax,sectors
sub ax,sread
mov cx,ax
shl cx,#9
add cx,bx
jnc ok2_read
je ok2_read
xor ax,ax
sub ax,bx
shr ax,#9
ok2_read:
call read_track
mov cx,ax
add ax,sread
seg cs
cmp ax,sectors
jne ok3_read
mov ax,#1
sub ax,head
jne ok4_read
inc track
ok4_read:
mov head,ax
xor ax,ax
ok3_read:
mov sread,ax
shl cx,#9
add bx,cx
jnc rp_read
mov ax,es
add ax,#0x1000
mov es,ax
xor bx,bx
jmp rp_read
read_track:
push ax
push bx
push cx
push dx
mov dx,track
mov cx,sread
inc cx
mov ch,dl
mov dx,head
mov dh,dl
mov dl,#0
and dx,#0x0100
mov ah,#2
int 0x13
jc bad_rt
pop dx
pop cx
pop bx
pop ax
ret
bad_rt: mov ax,#0
mov dx,#0
int 0x13
pop dx
pop cx
pop bx
pop ax
jmp read_track
/*
* This procedure turns off the floppy drive motor, so
* that we enter the kernel in a known state, and
* don't have to worry about it later.
*/
kill_motor:
push dx
mov dx,#0x3f2 !软驱控制卡的数字输出寄存器(DOR)端口,只写
mov al,#0 !A驱动器,关闭FDC,禁止DMA和中断请求,关闭马达。
outb !将al中的内容输出到dx指定的端口。
pop dx
ret
sectors:
.word 0 !存放当前启动软盘每磁道的存储扇区数。
msg1: !调用BIOS中断显示的信息
.byte 13,10 !回车,换行的ASCⅡ码
.ascii "Loading system ..."
.byte 13,10,13,10 !共24个ASCⅡ码字符
.org 508 !表示语句从地址508(0x01fc)开始,所以root_dev在启动扇区的第508开始的2个字节中。
root_dev:
.word ROOT_DEV !这里存放根文件系统所在设备号(init/main.c 中会用到)
boot_flag:
.word 0xAA55 !启动盘具有有效引导扇区的标志,仅供BIOS中程序加载引导扇区时识别使用。
!它必须位于引导扇区的最后两个字节中。
.text
endtext:
.data
enddata:
.bss
endbss:
Linux内核0.11 bootsect文件说明的更多相关文章
- Linux内核0.11 setup文件说明
一.总体功能介绍 这是关于Linux-kernel-0.11中boot文件夹下setup.s源文件的实现功能的总结说明. setup.s是一个操作系统加载程序,它的主要功能是利用BIOS中断读取机器系 ...
- Linux内核0.11 makefile文件说明
# # if you want the ram-disk device, define this to be the # size in blocks. # 如果要使用 RAM 就定义块的大小(注释掉 ...
- Linux内核0.11体系结构 ——《Linux内核完全注释》笔记打卡
0 总体介绍 一个完整的操作系统主要由4部分组成:硬件.操作系统内核.操作系统服务和用户应用程序,如图0.1所示.操作系统内核程序主要用于对硬件资源的抽象和访问调度. 图0.1 操作系统组成部分 内核 ...
- Linux内核0.11代码阅读(转)
最近决定开始阅读Linux 0.11的源代码. 学习Linux操作系统的核心概念最好的方法莫过于阅读源代码.而Linux当前最新的源代码包已经有70MB左右,代码十分庞大,要想深入阅读十分困难.而Li ...
- linux kernel 0.11 bootsect
bootsect作用 ①将自己移动到0x90000处 ②将setup从磁盘读到0x90200处 ③将system从磁盘读到0x10000处 寄存器 汇编代码中存在:数据段data seg 栈段 sta ...
- 在windows下解压缩Linux内核源代码出现重复文件原因
在windows下解压缩Linux内核源代码出现重复文件原因 2009年06月30日 13:35 来源:ChinaUnix博客 作者:embededgood 编辑:周荣茂 原因一.因为在Lin ...
- linux内核驱动中对文件的读写 【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-13059007-id-5766941.html 有时候需要在Linux kernel--大多是在需要调试的驱动程序--中读写文 ...
- Linux mysql8.0.11安装
准备:检查是否已安装过mysql,若有便删除(linux系统自带的) rpm -qa | grep mariadb rpm -e nodeps mariadb-libs-5.5.56-2.el7.x8 ...
- Linux内核3.11的socket busy poll机制避免睡眠切换
Linux的网络协议栈很独立,上下通过两个接口分别和用户态以及设备相连.也能够看作是北向和南向接口...北向通过socket接口,南向通过qdisc接口(你能够觉得是上层的netdev queue,对 ...
随机推荐
- Python码农福音,GitHub增加Python语言安全漏洞告警
在 2017 年 GitHub 开始对托管在其网站的代码仓库和依赖库开始提供安全漏洞检查和告警,开始时候只支持 Ruby 和 JavaScript 语言的项目.根据 GitHub 官方数据显示截止目前 ...
- 手动搭建openstack的痛苦经历
openstack真的是一个十分痛苦的东西,好在有自动部署工具,虽然有自动部署工具可以方便我们部署使用,但是学习的话,第一次最好手动部署,因为手动部署更能我们了解openstack的工作流程和各组建之 ...
- JUC——线程同步锁(Condition精准控制)
在进行锁处理的时候还有一个接口:Condition,这个接口可以由用户来自己进行锁的对象创建. Condition的作用是对锁进行更精确的控制. Condition的await()方法相当于Objec ...
- oracle的多表合并查询-工作心得
本随笔文章,由个人博客(鸟不拉屎)转移至博客园 发布时间: 2018 年 11 月 29 日 原地址:https://niaobulashi.com/archives/oracle-select-al ...
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 实现摄像头实时人脸检测和平铺显示
1. 引言 在某些场景下,我们不仅需要进行实时人脸检测追踪,还要进行再加工:这里进行摄像头实时人脸检测,并对于实时检测的人脸进行初步提取: 单个/多个人脸检测,并依次在摄像头窗口,实时平铺显示检测到的 ...
- Windows本地上传源码到Gitee远程仓库
1.下载Git,并安装. 安装时一路默认即可 https://git-scm.com/downloads 验证Git安装成功否 cmd 下输入,出现版本号即成功 git --version 2.生成s ...
- Python从菜鸟到高手:格式化字符串
1. 字符串格式化基础 字符串格式化相当于字符串模板.也就是说,如果一个字符串有一部分是固定的,而另一部分是动态变化的,那么就可以将固定的部分做成模板,然后那些动态变化的部分使用字符串格式化操作符(% ...
- 使用OpenCV通过摄像头捕获实时视频并探测人脸
在Opencv初接触,图片的基本操作这篇手记中,我介绍了一些图片的基本操作,视频可以看作是一帧一帧的图片,因此图片操作其实是视频操作的基础,这篇手记就来讲讲OpenCV中的视频操作,并实现一个用笔记本 ...
- CentOS赋予一个普通用户root权限
http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-07/64530.htm
- wdatepicker控件de使用小方法汇总
在总结wdatepicker控件的使用前,先插播一条吧,下午刚心血来潮百度的一条 问?C#中Int16.Int32.Int64.之间的区别,:::嘿嘿其实百度知道就有,但还是写上吧! Int16 表示 ...
