Binder IPC的权限控制
PS:个人理解:当进程1通过Binder调用组件2时,会将进程1的pid及uid赋给组件2,并检测进程1的pid及uid是否有权限调用组件2.而后组件2需要调用组件3,此时组件2保存的pid及uid为进程1的,但是其实际运行在进程2中。此时调用clearCallingIdentity将组件2的保存的pid及uid转换为进程2的pid和uid并return原来保存的进程1的pid及uid的token。此时组件2调用组件3并检查权限。调用完成后,restoreCallingIdentity将组件2的pid及uid恢复为进程1的。
正文:
看过Android系统源代码的朋友,一定看到过Binder.clearCallingIdentity()和Binder.restoreCallingIdentity()这两个方法,其定义在Binder.java文件:
//作用是清空远程调用端的uid和pid,用当前本地进程的uid和pid替代;public static final native long clearCallingIdentity();//作用是恢复远程调用端的uid和pid信息,正好是`clearCallingIdentity`的反过程;public static final native void restoreCallingIdentity(long token);
这两个方法涉及的uid和pid,每个线程都有自己独一无二的IPCThreadState对象,记录当前线程的pid和uid,可通过方法Binder.getCallingPid()和Binder.getCallingUid()获取相应的pid和uid。
clearCallingIdentity(), restoreCallingIdentity()这两个方法使用过程都是成对使用的,这两个方法配合使用,用于权限控制检测功能。
二、原理
从定义这两个方法是native方法,通过Binder的JNI调用,在android_util_Binder.cpp文件中定义了native方法所对应的jni方法。
2.1 clearCallingIdentity
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static jlong android_os_Binder_clearCallingIdentity(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz){//调用IPCThreadState类的方法执行return IPCThreadState::self()->clearCallingIdentity();}
2.1.1 IPC.clearCallingIdentity
[-> IPCThreadState.cpp]
int64_t IPCThreadState::clearCallingIdentity(){int64_t token = ((int64_t)mCallingUid<<32) | mCallingPid;clearCaller();return token;}void IPCThreadState::clearCaller(){mCallingPid = getpid(); //当前进程pid赋值给mCallingPidmCallingUid = getuid(); //当前进程uid赋值给mCallingUid}
- mCallingUid(记为UID),保存Binder IPC通信的调用方进程的Uid;
- mCallingPid(记为PID),保存Binder IPC通信的调用方进程的Pid;
UID和PID是IPCThreadState的成员变量, 都是32位的int型数据,通过移位操作,将UID和PID的信息保存到token,其中高32位保存UID,低32位保存PID。然后调用clearCaller()方法将当前本地进程pid和uid分别赋值给PID和UID,最后返回token。
2.2 restoreCallingIdentity
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static void android_os_Binder_restoreCallingIdentity(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jlong token){//token记录着uid信息,将其右移32位得到的是uidint uid = (int)(token>>32);if (uid > 0 && uid < 999) {//目前Android中不存在小于999的uid,当uid<999则抛出异常。char buf[128];jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalStateException", buf);return;}//调用IPCThreadState类的方法执行IPCThreadState::self()->restoreCallingIdentity(token);}
2.2.1 IPC.restoreCallingIdentity
[-> IPCThreadState.cpp]
void IPCThreadState::restoreCallingIdentity(int64_t token){mCallingUid = (int)(token>>32);mCallingPid = (int)token;}
从token中解析出PID和UID,并赋值给相应的变量。该方法正好是clearCallingIdentity的反过程。
2.3 getCallingPid
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static jint android_os_Binder_getCallingPid(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz){return IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingPid();}
2.3.1 IPC.getCallingPid
[-> IPCThreadState.cpp]
pid_t IPCThreadState::getCallingPid() const{return mCallingPid;}uid_t IPCThreadState::getCallingUid() const{return mCallingUid;}
2.4 远程调用
2.4.1 binder_thread_read
binder_thread_read(){while (1) {struct binder_work *w;switch (w->type) {case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION:t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);break;case :...}if (!t)continue; //只有BR_TRANSACTION,BR_REPLY才会往下执行tr.code = t->code;tr.flags = t->flags;tr.sender_euid = t->sender_euid; //mCallingUidif (t->from) {struct task_struct *sender = t->from->proc->tsk;//当非oneway的情况下,将调用者进程的pid保存到sender_pidtr.sender_pid = task_tgid_nr_ns(sender,current->nsproxy->pid_ns);} else {//当oneway的的情况下,则该值为0tr.sender_pid = 0;}...}
2.4.2 IPC.executeCommand
status_t IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int32_t cmd){BBinder* obj;RefBase::weakref_type* refs;status_t result = NO_ERROR;switch ((uint32_t)cmd) {case BR_TRANSACTION:{const pid_t origPid = mCallingPid;const uid_t origUid = mCallingUid;mCallingPid = tr.sender_pid; //设置调用者pidmCallingUid = tr.sender_euid;//设置调用者uid...reinterpret_cast<BBinder*>(tr.cookie)->transact(tr.code, buffer,&reply, tr.flags);mCallingPid = origPid; //恢复原来的pidmCallingUid = origUid; //恢复原来的uid}case :...}}
关于mCallingPid、mCallingUid的修改过程:是在每次Binder Call的远程进程在执行binder_thread_read()过程, 会设置pid和uid. 然后在IPCThreadState的transact收到BR_TRANSACION则会修改mCallingPid、mCallingUid。
这里需要注意的是,当oneway的的情况下mCallingPid=0,不过mCallingUid可以拿到正确值。
三、用途
3.1 场景分析
场景:首先线程A通过Binder远程调用线程B,然后线程B通过Binder调用当前线程的另一个service或者activity之类的组件。
分析:
- 线程A通过Binder远程调用线程B:则线程B的IPCThreadState中的
mCallingUid和mCallingPid保存的就是线程A的UID和PID。这时在线程B中调用Binder.getCallingPid()和Binder.getCallingUid()方法便可获取线程A的UID和PID,然后利用UID和PID进行权限比对,判断线程A是否有权限调用线程B的某个方法。 - 线程B通过Binder调用当前线程的某个组件:此时线程B是线程B某个组件的调用端,则
mCallingUid和mCallingPid应该保存当前线程B的PID和UID,故需要调用clearCallingIdentity()方法完成这个功能。当线程B调用完某个组件,由于线程B仍然处于线程A的被调用端,因此mCallingUid和mCallingPid需要恢复成线程A的UID和PID,这是调用restoreCallingIdentity()即可完成。
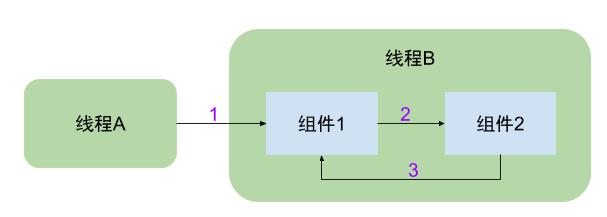
一句话:图中过程2(调用组件2开始之前)执行clearCallingIdentity(),过程3(调用组件2结束之后)执行restoreCallingIdentity()。
3.2 类比分析
看完场景分析,估计还有不少朋友感到迷惑,为何需要这两个方法来多此一举,直接检测最初调用端的权限不就行了吗?为了更加形象明了地说明其用途,下面用一个生活中的场景来类比说明。
场景:假如你的朋友请你帮忙,给她(他)到你的公司以内部价购买公司的某个产品。
分析:这个过程分为两个阶段
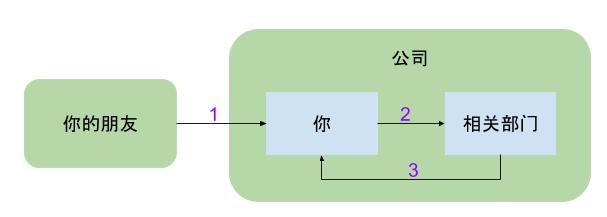
- 第一阶段:你的朋友请你帮忙的过程,这个过程并不一定所有朋友都会帮的,这时就需要一个权限检测,那么在你的朋友”远程调用”你执行任务时,你会记录他的”Identity”信息(比如是性别),有了信息那么就可以权限检测,不妨令权限规则是如果这个朋友是女性则答应帮忙,否则就认定权限不够拒绝执行(可能黑客会想到先去一趟泰国,权限控制可能相应需要打补丁了),若答应帮忙则进入第二阶段,否则直接返回。
- 第二阶段:你向自己所在公司的相关部门内购产品的过程,这个过程也并不是所有人都能权限能够内购的,只有自己公司的员工才行,否则你的朋友也不会找你帮忙了。 这个过程同样需要权限检测,但是”Identity”保存的是性别女的信息,公司内购产品如果也以性别来判断,那岂不是公司的所有男员工没有权限内购,那这公司就有点太坑了,这明显不符合实情。
clearCallingIdentity()是时候该登场了,在第二阶段开始之前,先执行clearCallingIdentity()过程,也就是把”Identity”信息清空,替换为你的信息(比如员工编码ITCode之类的),那公司相关部门通过ITCode就可以直接判断是否允许内购某产品。当第二阶段完成后,也就是你已经购买到了公司产品,这时你需要将产品交付给你的朋友,需要restoreCallingIdentity,恢复”Identity”为女的信息,这样就嗯呢该顺便交付给你的女朋友。如果不恢复信息,还是原来的ITCode,你交付的朋友可能是男的,另有其人,这样就不科学了。
相信到此,大家应该都能明白这两个方法的作用,缺一不可,而且要成对出现。
3.3 实例分析
上述过程主要在system_server进程的各个线程中比较常见(普通的app应用很少出现),比如system_server进程中的ActivityManagerService子线程,代码如下:
[–>ActivityManagerService.java]
@Overridepublic final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {synchronized (this) {//获取远程Binder调用端的pidint callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();//清除远程Binder调用端uid和pid信息,并保存到origId变量final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);//通过origId变量,还原远程Binder调用端的uid和pid信息Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);}}
文章startService流程分析中有讲到attachApplication()的调用。该方法一般是system_server进程的子线程调用远程进程时使用,而attachApplicationLocked方法则是在同一个线程中,故需要在调用该方法前清空远程调用者的uid和pid,调用结束后恢复远程调用者的uid和pid。
转自:http://gityuan.com/2016/03/05/binder-clearCallingIdentity/
Binder IPC的权限控制的更多相关文章
- Android : 跟我学Binder --- (1) 什么是Binder IPC?为何要使用Binder机制?
目录: Android : 跟我学Binder --- (1) 什么是Binder IPC?为何要使用Binder机制? Android : 跟我学Binder --- (2) AIDL分析及手动实现 ...
- SEAndroid安全机制对Binder IPC的保护分析
在SEAndroid安全机制中,除了文件和属性,还有Binder IPC须要保护.Binder IPC是Android系统的灵魂,使用得相当广泛又频繁.比如,应用程序都是Binder IPC请求訪问系 ...
- 尝试asp.net mvc 基于controller action 方式权限控制方案可行性
微软在推出mvc框架不久,短短几年里,版本更新之快,真是大快人心,微软在这种优秀的框架上做了大量的精力投入,是值得赞同的,毕竟程序员驾驭在这种框架上,能够强力的精化代码,代码层次也更加优雅,扩展较为方 ...
- MongoDB 安全和访问权限控制
MongoDB的访问控制能够有效保证数据库的安全,访问控制是指绑定Application监听的IP地址,设置监听端口,使用账户和密码登录 一,访问控制的参数 1,绑定IP地址 mongod 参数:-- ...
- WebGIS中快速整合管理多源矢量服务以及服务权限控制的一种设计思路
文章版权由作者李晓晖和博客园共有,若转载请于明显处标明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/naaoveGIS/ 1.背景 在真实项目中,往往GIS服务数据源被其他多个信息中心或者第三方 ...
- ASP.NET MVC实现权限控制
这篇分享一下 ASP.NET MVC权限控制.也就是说某一用户登录之后,某一个用户是否有权限访问Controller,Action(操作),视图等 想实现这些功能,需要在数据库创建好几个表:[User ...
- springmvc+spring+mybatis+maven项目集成shiro进行用户权限控制【转】
项目结构: 1.maven项目的pom中引入shiro所需的jar包依赖关系 ? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ...
- Appfuse:权限控制
Appfuse的权限控制依赖于Struts的Menu机制,common下的menu.jsp是对菜单顺序的定义,详细的菜单项和菜单链接及权限再menu-config.xml中控制,如下: <Men ...
- .NET WebAPI 用ActionFilterAttribute实现token令牌验证与对Action的权限控制
项目背景是一个社区类的APP(求轻吐...),博主主要负责后台业务及接口.以前没玩过webAPI,但是领导要求必须用这个(具体原因鬼知道),只好硬着头皮上了. 最近刚做完权限这一块,分享出来给大家.欢 ...
随机推荐
- JavaEE-07 过滤器和监听器
学习要点 过滤器 监听器 过滤器Filter 过滤器的概念 过滤器位于客户端和web应用程序之间,用于检查和修改两者之间流过的请求和响应. 在请求到达Servlet/JSP之前,过滤器截获请求. 在响 ...
- 阿里云ECS搭建node/mongodb开发环境及部署
一.前端的er在window或mac上安装开发环境应该再清楚不过了.但在服务器上安装还是有点不同的,毕竟是 centOS,从此不得不走上用命令操作…… 二.前期准备 1.首先,我们去阿里云网站阿里云服 ...
- IOS学习笔记2—Objective C—类、属性、方法
以下是我学习IOS开发的一些笔记和心得,贴出来和大家一同分享,也希望大家能补充和纠错,共同进步 有Android和IOS开发问题也希望能和大家交流! Objective-C 1.OC是一门基于C的面向 ...
- 任务一:零基础HTML编码
面向人群: 零基础或初学者 难度: 简单 重要说明 百度前端技术学院的课程任务是由百度前端工程师专为对前端不同掌握程度的同学设计.我们尽力保证课程内容的质量以及学习难度的合理性,但即使如此,真正决定课 ...
- [题解] cogs 1669 神秘的咒语
http://cogs.pro:8080/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=1669 "The Real Incantation is Their Common In ...
- hdu5126 stars
题目描述 题解: 和二维的比起来差不多. 但是这是四维偏序. 所以搞一下CDQ套CDQ. CDQ是维度a已经有序,按维度b排序,然后将维度c存入一维数据结构. 所以我们在第一层CDQ中分治处理,将合法 ...
- 关闭 macOS Google Chrome 黑暗模式风格
终端执行命令 defaults write com.google.Chrome NSRequiresAquaSystemAppearance -bool YES 恢复 defaults write c ...
- (5) openssl speed(测试算法性能)和openssl rand(生成随机数)
1.1 openssl speed 测试加密算法的性能 支持的算法有: openssl speed [md2] [mdc2] [md5] [hmac] [sha1] [rmd160] [idea-cb ...
- 【HIHOCODER 1605】小Hi的生成树计数
描述 小Hi最近对生成树(包含所有顶点的联通无环子图.)非常的感兴趣,他想知道对于特定的简单平面无向图是不是存在求生成树个数的简单方法. 小Hi定义了这样的图:一个以{0,1,2--n}为顶点的图,顶 ...
- java环境配置——工具下载地址
每次官网找个下载地址都是 费劲巴拉的 整理了一下几个下载地址分享给大家 eclipse:http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/packages/release/Kepler ...
