经典网络流题目模板(P3376 + P2756 + P3381 : 最大流 + 二分图匹配 + 最小费用最大流)
题目来源
最大流
最大流问题是网络流的经典类型之一,用处广泛,个人认为网络流问题最具特点的操作就是建反向边,这样相当于给了反悔的机会,不断地求增广路的,最终得到最大流
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <map>
#include <iomanip>
#define bug cout << "**********" << endl
#define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] "
//#define LOCAL = 1;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod = 1e6 + ;
const int Max = 1e5 + ; struct Edge {
int to, next, flow; //flow记录这条边当前的边残量
}edge[Max << ]; int n, m, s, t;
int head[Max], tot;
bool vis[Max]; void init()
{
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));tot = ;
} void add(int u, int v, int flow)
{
edge[tot].to = v;
edge[tot].flow = flow;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
} //向图中增加一条容量为exp的边(增广路)
int dfs(int u,int exp)
{
if (u == t) return exp; //到达汇点,当前水量全部注入
vis[u] = true; //表示已经到了过了
for(int i = head[u] ; i != - ;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if(!vis[v] && edge[i].flow > )
{
int flow = dfs(v, min(exp, edge[i].flow));
if(flow > ) //形成了增广路
{
edge[i].flow -= flow;
edge[i ^ ].flow += flow;
return flow;
} } }
return ; //无法形成增广路的情况
} //求最大流
int max_flow()
{
int flow = ;
while(true)
{
memset(vis, , sizeof(vis));
int part_flow = dfs(s, inf);
if (part_flow == ) return flow;
flow += part_flow;
}
} int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF)
{
init();
for (int i = , u, v, flow;i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow);
add(u, v, flow);add(v, u, );
}
printf("%d\n", max_flow());
} return ;
}
最简单算法-Ford-Fulkerson
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <map>
#include <iomanip>
#define bug cout << "**********" << endl
#define show(x,y) "["<<x<<","<<y<<"]"
//#define LOCAL = 1;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod = 1e6 + ;
const int Max = 1e5 + ; struct Edge {
int to, next, flow; //flow记录这条边当前的边残量
}edge[Max << ]; int n, m, s, t;
int head[Max], tot;
int dis[Max]; void init()
{
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));tot = ;
} void add(int u, int v, int flow)
{
edge[tot].to = v;
edge[tot].flow = flow;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
} bool bfs() //判断图是否连通
{
queue<int>q;
memset(dis, -, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = ;
q.push(s);
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();q.pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i != -; i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if (dis[v] == - && edge[i].flow > ) //可以借助边i到达新的结点
{
dis[v] = dis[u] + ; //求顶点到源点的距离编号
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return dis[t] != -; //确认是否连通
} int dfs(int u, int flow_in)
{
if (u == t) return flow_in;
int flow_out = ; //记录这一点实际流出的流量
for (int i = head[u]; i != -;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if (dis[v] == dis[u] + && edge[i].flow > )
{
int flow_part = dfs(v, min(flow_in, edge[i].flow));
if (flow_part == )continue; //无法形成增广路
flow_in -= flow_part; //流出了一部分,剩余可分配流入就减少了
flow_out += flow_part; //记录这一点最大的流出 edge[i].flow -= flow_part;
edge[i ^ ].flow += flow_part; //减少增广路上边的容量,增加其反向边的容量
if (flow_in == )
break;
}
}
return flow_out;
} int max_flow()
{
int sum = ;
while (bfs())
{
sum += dfs(s, inf);
}
return sum;
} int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF)
{
init();
for (int i = , u, v, flow;i <= m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow);
add(u, v, flow);add(v, u, );
} printf("%d\n", max_flow());
} return ;
}
常用且高效的算法-Dinic
二分图匹配
要解决这类问题,我们需要先了解什么是二分图?
二分图:一个图中的所有顶点可以分为两个集合 V,K ,其实两个集合内部的点彼此之间无边,如下图所示:(蓝色的点和红色的点分属于两个集合V,K)
然后我们回到这个题目上来,这个题目求的是最大可出战人数,实际上就是在二分图中找到两个集合中的最大匹配数,这类问题我们称之为二分图最大匹配数问题
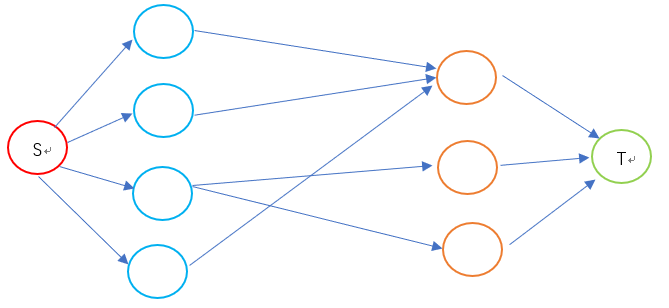
属于网络流经典题目之一,下面说明一下建图的过程
1)由源点向集合V中每个点建一条容量为1的边
2)对于V,K集合之间存在的边e,v 为V中的点,k为K中的点,我们建一条容量为1的边,方向为 v --> k
3)由K中每个点向汇点建一条容量为1的边
当我们将图建好了后,我们求这个图的最大流,这个最大流即为二分图最大匹配数,下面展示一下建成的图:(S代表源点,T代表汇点,蓝色的边代表容量为1的边)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <map>
#include <iomanip>
#define bug cout << "**********" << endl
#define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] "
//#define LOCAL = 1;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod = 1e6 + ;
const int Max = 1e6 + ; struct Edge
{
int to, next, flow;
}edge[Max << ];; int n, m, a, b, s, t;
int head[Max], tot;
int dis[Max];
int ans;
bool vis[Max]; void init()
{
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));tot = ;
ans = ;
} void add(int u, int v, int flow)
{
edge[tot].to = v;
edge[tot].flow = flow;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
} bool bfs()
{
memset(dis, -, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = ;
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();q.pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i != -;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if (dis[v] == - && edge[i].flow > )
{
dis[v] = dis[u] + ;
if (v == t) return true;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return false;
} int dfs(int u, int flow_in)
{
if (u == t) return flow_in;
int flow_out = ;
for (int i = head[u]; i != -;i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if (dis[v] == dis[u] + && edge[i].flow > )
{
int flow_part = dfs(v, min(flow_in, edge[i].flow));
if (flow_part == ) continue;
flow_in -= flow_part;
flow_out += flow_part;
edge[i].flow -= flow_part;
edge[i ^ ].flow += flow_part;
if (flow_in == )break;
}
}
return flow_out;
} int max_val()
{
int sum = ;
while (bfs())
{
sum += dfs(s, inf);
}
return sum;
} int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
while (scanf("%d%d", &m, &n) != EOF)
{
init();
s = , t = n + ;
for (int i = ;i <= m;i++)
{
add(s, i, );add(i, s, ); //由源点向外籍飞行员建边
}
for (int i = m + ; i <= n;i++)
{
add(i, t, );add(t, i, );
}
while (scanf("%d%d", &a, &b) != EOF && a != - && b != -)
{
add(a, b, );add(b, a, );
}
printf("%d\n", max_val());
for (int u = ;u <= m;u++)
{
for (int i = head[u]; i != -;i = edge[i].next)
{
if (edge[i].flow == && edge[i].to != s && edge[i].to != t)
{
printf("%d %d\n", u, edge[i].to);
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
飞行员配对方案-Dinic
最小费用最大流
这类题目相比于最大流问题新增了每天边单位流量的价格,问在最大流的情况下求出最小的费用。
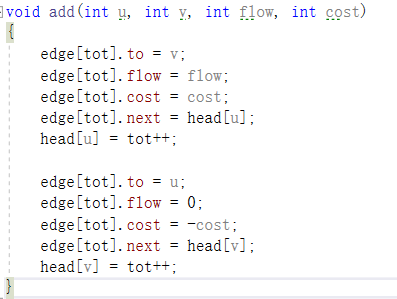
这类题目和最大流很想,不过也有不小区别,对于这类问题,我们为每条边建的反边的价格是每天边的相反数,如图
然后我们的算法也不再是Dinic算法了,而是用spfa或者dijkstra
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <map>
#include <iomanip>
#define bug cout << "**********" << endl
#define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] "
#define LOCAL = 1;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod = 1e9 + ;
const int Max = 5e3 + ; struct Edge
{
int to, rev; //rev记录反向边
int flow, cost;;
}; int n, m, k;
vector<Edge>edge[Max << ];
int h[Max]; //每个结点的势
int dis[Max];
int pre_node[Max], pre_edge[Max]; //前驱结点和对应边 void add(int u, int v, int flow, int cost)
{
edge[u].push_back({ v,(int)edge[v].size(),flow,cost }); edge[v].push_back({ u,(int)edge[u].size() - ,,-cost });
} void min_cost_flow(int s, int t, int& min_cost, int& max_flow)
{
fill(h + , h + + n, );
min_cost = max_flow = ;
int tot = inf; //源点流量无限
while (tot > )
{
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int> >, greater<pair<int, int> > >q;
memset(dis, inf, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = ;q.push({ ,s });
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.top().second;
int dist = q.top().first;
q.pop();
if (dis[u] < dist)continue; //当前的距离不是最近距离
for (int i = ;i < edge[u].size(); i++)
{
Edge &e = edge[u][i];
if (edge[u][i].flow > && dis[e.to] > dis[u] + e.cost + h[u] - h[e.to])
{
dis[e.to] = dis[u] +e.cost + h[u] - h[e.to];
pre_node[e.to] = u;
pre_edge[e.to] = i;
q.push({ dis[e.to],e.to });
}
}
}
if (dis[t] == inf)break; //无法增广了,就是找到答案了
for (int i = ;i <= n;i++) h[i] += dis[i];
int flow = tot; //求这一增广路径的流量
for (int i = t; i != s; i = pre_node[i])
flow = min(flow, edge[pre_node[i]][pre_edge[i]].flow);
for (int i = t; i != s; i = pre_node[i])
{
Edge& e = edge[pre_node[i]][pre_edge[i]];
e.flow -= flow;
edge[i][e.rev].flow += flow;
}
tot -= flow;
max_flow += flow;
min_cost += flow * h[t];
}
} int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int s, t;
while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF)
{
for (int i = , u, v, flow, cost;i <= m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow, &cost);
add(u, v, flow, cost);
}
int min_cost, max_flow;
min_cost_flow(s, t, min_cost, max_flow);
printf("%d %d\n", max_flow, min_cost);
}
return ;
}
无负环图中可用的算法-dijkstra(这里给出的是可以适用于有负环的
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <map>
#include <iomanip>
#define bug cout << "**********" << endl
#define show(x,y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] "
//#define LOCAL = 1;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod = 1e9 + ;
const int Max = 1e5 + ; struct Edge
{
int to, next;
int flow, cost;
}edge[Max << ]; int n, m, s, t;
int head[Max], tot;
int dis[Max];
int pre[Max]; //记录增广路径此点的前一天边
bool vis[Max]; void init()
{
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));tot = ;
} void add(int u, int v, int flow, int cost)
{
edge[tot].to = v;
edge[tot].flow = flow;
edge[tot].cost = cost;
edge[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot++; edge[tot].to = u;
edge[tot].flow = ;
edge[tot].cost = -cost;
edge[tot].next = head[v];
head[v] = tot++;
} bool spfa(int s, int t)
{
memset(dis, inf, sizeof(dis));
memset(vis, , sizeof(vis));
memset(pre, -, sizeof(pre)); queue<int>q;
q.push(s);dis[s] = ;vis[s] = true; while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();q.pop();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = head[u]; i != -; i = edge[i].next)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
if (edge[i].flow > && dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].cost)
{
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].cost;
pre[v] = i; if (!vis[v])
{
vis[v] = true;q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
return pre[t] != -;
} void min_cost_max_flow(int s, int t, int& max_flow, int& min_cost)
{
max_flow = ;
min_cost = ;
while (spfa(s, t))
{
int flow = inf;
for (int i = pre[t]; i != -; i = pre[edge[i ^ ].to]) //沿增广路回溯edge[i^1]即为其反边
{
flow = min(flow, edge[i].flow);
}
for (int i = pre[t]; i != -; i = pre[edge[i ^ ].to])
{
edge[i].flow -= flow;
edge[i ^ ].flow += flow;
min_cost += flow * edge[i].cost;
}
max_flow += flow;
}
} int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF)
{
init();
for (int i = , u, v, flow, cost;i <= m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &u, &v, &flow, &cost);
add(u, v, flow, cost);
}
int max_flow = , min_cost = ;
min_cost_max_flow(s, t, max_flow, min_cost);
printf("%d %d\n", max_flow, min_cost);
}
return ;
}
常用且比较高效的算法-spfa
经典网络流题目模板(P3376 + P2756 + P3381 : 最大流 + 二分图匹配 + 最小费用最大流)的更多相关文章
- Doctor NiGONiGO’s multi-core CPU(最小费用最大流模板)
题目链接:http://acm.nyist.net/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=693 题意:有一个 k 核的处理器和 n 个工作,全部的工作都须要在一个核上处理一个单位的 ...
- P3381 【模板】最小费用最大流
P3381 [模板]最小费用最大流 题目描述 如题,给出一个网络图,以及其源点和汇点,每条边已知其最大流量和单位流量费用,求出其网络最大流和在最大流情况下的最小费用. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 第一行 ...
- 洛谷P3381 最小费用最大流模板
https://www.luogu.org/problem/P3381 题目描述 如题,给出一个网络图,以及其源点和汇点,每条边已知其最大流量和单位流量费用,求出其网络最大流和在最大流情况下的最小费用 ...
- P3381 【模板】最小费用最大流(MCMF)
P3381 [模板]最小费用最大流 题目描述 如题,给出一个网络图,以及其源点和汇点,每条边已知其最大流量和单位流量费用,求出其网络最大流和在最大流情况下的最小费用. 输入格式 第一行包含四个正整数N ...
- Luogu P3381 (模板题) 最小费用最大流
<题目链接> 题目大意: 给定一张图,给定条边的容量和单位流量费用,并且给定源点和汇点.问你从源点到汇点的最带流和在流量最大的情况下的最小费用. 解题分析: 最小费用最大流果题. 下面的是 ...
- P3381 【模板】最小费用最大流 题解
CSDN同步 原题链接 前置知识: 从三种算法剖析网络流本质 简要题意: 给定网络图,求图的最大流,以及流量为最大流时的最小费用. 现在假设你们看了那篇网络流博客之后,所有人都会了 \(\text{E ...
- 【网络流#2】hdu 1533 - 最小费用最大流模板题
最小费用最大流,即MCMF(Minimum Cost Maximum Flow)问题 嗯~第一次写费用流题... 这道就是费用流的模板题,找不到更裸的题了 建图:每个m(Man)作为源点,每个H(Ho ...
- 洛谷P3381 - 【模板】最小费用最大流
原题链接 题意简述 模板题啦~ 题解 每次都以费用作为边权求一下最短路,然后沿着最短路增广. Code //[模板]最小费用最大流 #include <cstdio> #include & ...
- poj2135最小费用最大流经典模板题
Farm Tour Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 13509 Accepted: 5125 Descri ...
随机推荐
- 查找:find、locate、which、whereis
有find . locate . which . whereis 一.find 命令格式:[root@localhost ~]# find 搜索路径 [选项] 搜索内容 find是比较特殊的命令,它有 ...
- [CSP-S模拟测试]:B(DP+数学)
题目传送门(内部题45) 输入格式 第一行$3$个整数$n,m,P$.第二行$m$个整数,表示$m$次询问. 输出格式 一行$m$个整数表示答案. 样例 样例输入1: 2 4 40 1 2 3 样例输 ...
- JavaWeb页面静态化之使用freemarker模板生成一个html静态页面
题外话: 页面静态化(展示数据从JSP页面变成HTML页面)实现方式-->模板技术 从本质上来讲,模板技术是一个占位符动态替换技术.一个完整的模板技术需要四个元素:①模板语言(使 ...
- php项目权限系统设计
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/u013090676/article/details/77893237 说起php的权限,很多人都容易想起rbac,这里不多介绍.下面介绍一种通用 ...
- Linux编程之文件锁
1. 使用 fcntl() 给记录加锁 使用 fcntl() 能够在一个文件的任意部分上放置一把锁,这个文件部分既可以是一个字节,也可以是整个文件.这种形式的文件加锁通常被称为记录加锁,但这种称谓是不 ...
- Python 之 subprocess模块
一.subprocess以及常用的封装函数运行python的时候,我们都是在创建并运行一个进程.像Linux进程那样,一个进程可以fork一个子进程,并让这个子进程exec另外一个程序.在Python ...
- php post请求
public function file_get_contents_post($url, $post){ $options = array( 'http'=> array( 'method'=& ...
- 卸载apache
1.查看httpd相关软件包 rpm -qa|grep httpd 2.卸载命令, “rpm -e 软件或服务名” 如果出现类似“httpd >= 2.2.0 is needed by (ins ...
- Zabbix - 实现对磁盘动态监控
回到目录 前言 zabbix一直是小规模互联网公司服务器性能监控首选,首先是免费,其次,有专门的公司和社区开发维护,使其稳定性和功能都在不断地增强和完善.zabbix拥有详细的UI界面和分组策 ...
- 什么叫DMZ区?DMZ区有什么作用?应该怎样构建DMZ
您的公司有一堆电脑,但可以归为两大类:客户机.服务器.所谓客户机就是主动发起连接请求的机器,所谓服务器就是被动响应提供某些服务的机器.服务器又可以分仅供企业内网使用和为外网提供服务两种. 所以,如果把 ...
