android——相对布局,表格布局
1.相对布局
RelativeLayout 又称作相对布局,也是一种非常常用的布局。和LinearLayout 的排列规则不同,RelativeLayout 显得更加随意一些,它可以通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局的任何位置。也正因为如此,RelativeLayout 中的属性非常多,不过这些属性都是有规律可循的,其实并不难理解和记忆。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="Button 3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:text="Button 4" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="Button 5" />
</RelativeLayout>
效果图为

2.表格布局
TableLayout 允许我们使用表格的方式来排列控件,这种布局也不是很常用,你只需要了解一下它的基本用法就可以了。既然是表格,那就一定会有行和列,在设计表格时我们尽量应该让每一行都拥有相同的列数,这样的表格也是最简单的。不过有时候事情并非总会顺从我们的心意,当表格的某行一定要有不相等的列数时,就需要通过合并单元格的方式来应对。
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
tools:context="com.calc.minicalculator.MainActivity" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="109dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal|top"
android:gravity="right|center_vertical"
android:text="" android:textSize="40dp"
android:textStyle="bold" /> <TableRow
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/tableRow1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="清屏" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="space" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="+" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="-" /> </TableRow> <TableRow
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/tableRow2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="7" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="8" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="9" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="*" /> </TableRow> <TableRow
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/tableRow3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button9"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="4" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button10"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="5" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button11"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="6" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button12"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="/" /> </TableRow> <TableRow
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/tableRow4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button13"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="1" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button14"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="2" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button15"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="3" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button19"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="." /> </TableRow> <TableRow
android:layout_weight="1"
android:id="@+id/tableRow5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
> <Button
android:id="@+id/button17"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="0"
android:layout_span="2"
/> <Button
android:id="@+id/button16"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="="
android:layout_span="2"/> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
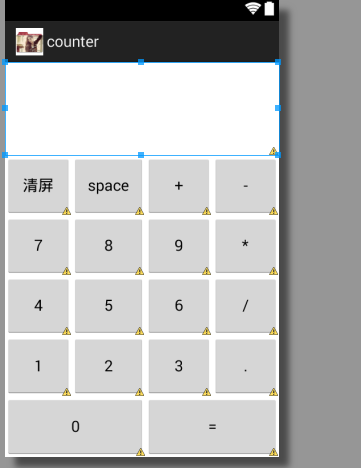
效果图:
android——相对布局,表格布局的更多相关文章
- 第24讲 UI_布局 之帧布局 表格布局 绝对布局
第24讲 UI_布局 之帧布局 表格布局 绝对布局 3. FrameLayout(帧布局) 帧布局是从屏幕的左上角(0,0)坐标开始布局,多个组件层叠排序,后一个组件总会将前一个组件所覆盖,除非最后一 ...
- Android布局— — —表格布局
表格布局 以表格的形式来显示界面中的控件,表格的每一行为一个TableRow,每当一个控件添加到TableRow中,就生成一个单元格. 语法格式: <TableLayout xmlns:andr ...
- .Net程序猿玩转Android开发---(8)表格布局TableLayout
表格布局TableLayout是Android中比較经常使用的一个布局控件,既然是表格,肯定有行和列,TableLayout中的行有TableRow组成.列依据每行控件的数量来确定 假如第一行有3个控 ...
- Android 自学之表格布局 TableLayout
表格布局(TableLayout),表格布局采用行.列的形式来管理UI组件,TableLayout并不需要明确的声明多少行,多少列,而是通过TableRow.其他组件来控制表格的行数和列数. 每次想T ...
- Android中的表格布局TableLayout
表格布局最基本的三个属性: XML代码实例: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLa ...
- Android笔记(十) Android中的布局——表格布局
TableLayout运行我们使用表格的方式来排列控件,它的本质依然是线性布局.表格布局采用行.列的形式来管理控件,TableLayout并不需要明确的声明包含多少行多少列,而是通过添加TableRo ...
- Android之TableLayout表格布局
1.相关属性 1.1.常用属性 android:collapseColumns 设置需要被隐藏的列的序列号 android:shrinkColumns 设置允许被收缩的列的序列号 android:st ...
- android:TableLayout表格布局详解
1.TableLayout简介2.TableLayout行列数的确定3.TableLayout可设置的属性详解4.一个包含4个TableLayout布局的实例及效果图一.Tablelayout简介 ...
- Android开发-之五大布局
在html中大家都知道布局是什么意思了,简单来说就是将页面划分模块,比如html中的div.table等.那么Android中也是这样的.Android五大布局让界面更加美化,开发起来也更加方便.当然 ...
- 【转】TableLayout(表格布局)
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangs1986/archive/2013/01/17/2864536.html TableLayout(表格布局) 表格布局模型以行列的形式管 ...
随机推荐
- 377. Combination Sum IV
问题 Given an integer array with all positive numbers and no duplicates, find the number of possible c ...
- Div 定时移动
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta http ...
- MongoVue中Collections无法显示的问题
问题描述: 通过Python向MongoDB写入数据后,MongoVue中Collections无法显示的问题 原因: Mongodb 3.0之后默认的 storageEngine为wiredTige ...
- locate: can not open `/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db': No such file or directory
# locate zabbix locate: can not open `/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db': No such file or directory locate ...
- 【Java EE 学习 74 下】【数据采集系统第六天】【使用Jfreechart的统计图实现】【将JFreechart整合到项目中】
之前说了JFreechart的基本使用方法,包括生成饼图.柱状统计图和折线统计图的方法.现在需要将其整合到数据采集系统中根据调查结果生成三种不同的统计图. 一.统计模型的分析和设计 实现统计图显示的流 ...
- 让Fiddler 直接抓取java程序的方法
Fiddler官网给出的解决办法(见http://www.fiddler2.com/fiddler/help/hookup.asp#Q-JavaTraffic)是设置jvm参数,如 jre -Dpro ...
- Project Euler欧拉计划
1 If we list all the natural numbers below 10 that are multiples of 3 or 5, we get 3, 5, 6 and 9. Th ...
- SQL Server 得到数据库中所有表的名称及数据条数
--方法一if exists ( select * from dbo.sysobjects where id = object_id(N'[dbo].[TableSpace]') and object ...
- Mysql数据库的使用总结之Innodb简介
最近在对开发的软件的服务器部分制作安装包,但服务器部分需要有mysql数据库的支持.因此,采用免安装版的mysql策略:将mysql数据库需要的文件在安装程序中进行设置和打包即可.但也遇到了很多问题 ...
- ChannelHandler
ChannelHandler功能介绍 ChannelHandler类似于Servlet的Filter过滤器,负责对I/O事件或者I/O操作进行拦截和处理,它可以选择性地拦截和处理自己感兴趣的事件,也可 ...
