Funq之Lambda表达式2
Last month I started a series of posts covering some of the new VB and C# language features that are coming as part of the Visual Studio and .NET Framework "Orcas" release. Here are the first two posts in the series:
Today's blog post covers another fundamental new language feature: Lambda Expressions.
What are Lambda Expressions?
C# 2.0 (which shipped with VS 2005) introduced the concept of anonymous methods, which allow code blocks to be written "in-line" where delegate values are expected.
Lambda Expressions provide a more concise, functional syntax for writing anonymous methods. They end up being super useful when writing LINQ query expressions - since they provide a very compact and type-safe way to write functions that can be passed as arguments for subsequent evaluation.
Lambda Expression Example:
In my previous Extension Methods blog post, I demonstrated how you could declare a simple "Person" class like below:
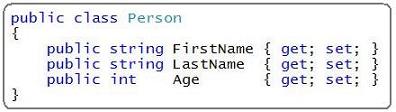
I then showed how you could instantiate a List<Person> collection with values, and then use the new "Where" and "Average" extension methods provided by LINQ to return a subset of the people in the collection, as well as compute the average age of people within the collection:
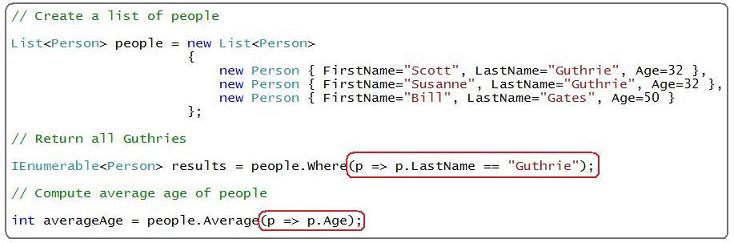
The p => expressions highlighted above in red are Lambda expressions. In the sample above I'm using the first lambda to specify the filter to use when retrieving people, and the second lambda to specify the value from the Person object to use when computing the average.
Lambda Expressions Explained
The easiest way to conceptualize Lambda expressions is to think of them as ways to write concise inline methods. For example, the sample I wrote above could have been written instead using C# 2.0 anonymous methods like so:
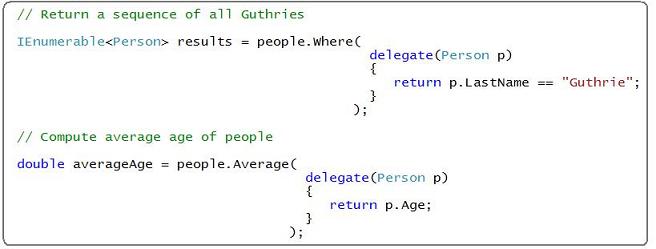
Both anonymous methods above take a Person type as a parameter. The first anonymous method returns a boolean (indicating whether the Person's lastname is Guthrie). The second anonymous method returns an integer (returning the person's age). The lambda expressions we used earlier work the same - both expressions take a Person type as a parameter. The first lambda returns a boolean, the second lambda returns an integer.
In C# a lambda expression is syntactically written as a parameter list, followed by a => token, and then followed by the expression or statement block to execute when the expression is invoked:
params => expression
So when we wrote the lambda expression:
p => p.LastName == "Guthrie"
we were indicating that the Lambda we were defining took a parameter "p", and that the expression of code to run returns whether the p.LastName value equals "Guthrie". The fact that we named the parameter "p" is irrelevant - I could just have easily named it "o", "x", "foo" or any other name I wanted.
Unlike anonymous methods, which require parameter type declarations to be explicitly stated, Lambda expressions permit parameter types to be omitted and instead allow them to be inferred based on the usage. For example, when I wrote the lambda expression p=>p.LastName == "Guthrie", the compiler inferred that the p parameter was of type Person because the "Where" extension method was working on a generic List<Person> collection.
Lambda parameter types can be inferred at both compile-time and by the Visual Studio's intellisense engine (meaning you get full intellisense and compile-time checking when writing lambdas). For example, note when I type "p." below how Visual Studio "Orcas" provides intellisense completion because it knows "p" is of type "Person":

Note: if you want to explicitly declare the type of a parameter to a Lambda expression, you can do so by declaring the parameter type before the parameter name in the Lambda params list like so:

Advanced: Lambda Expression Trees for Framework Developers
One of the things that make Lambda expressions particularly powerful from a framework developer's perspective is that they can be compiled as either a code delegate (in the form of an IL based method) or as an expression tree object which can be used at runtime to analyze, transform or optimize the expression.
This ability to compile a Lambda expression to an expression tree object is an extremely powerful mechanism that enables a host of scenarios - including the ability to build high performance object mappers that support rich querying of data (whether from a relational database, an active directory, a web-service, etc) using a consistent query language that provides compile-time syntax checking and VS intellisense.
Lambda Expressions to Code Delegates
The "Where" extension method above is an example of compiling a Lambda expression to a code delegate (meaning it compiles down to IL that is callable in the form of a delegate). The "Where()" extension method to support filtering any IEnumerable collection like above could be implemented using the extension method code below:

The Where() extension method above is passed a filter parameter of type Func<T, bool>, which is a delegate that takes a method with a single parameter of type "T" and returns a boolean indicating whether a condition is met. When we pass a Lambda expression as an argument to this Where() extension method, the C# compiler will compile our Lambda expressions to be an IL method delegate (where the <T> type will be a Person) that our Where() method can then call to evaluate whether a given condition is met.
Lambda Expressions to Expression Trees
Compiling lambdas expressions to code delegates works great when we want to evaluate them against in-memory data like with our List collection above. But consider cases where you want to query data from a database (the code below was written using the built-in LINQ to SQL object relational mapper in "Orcas"):
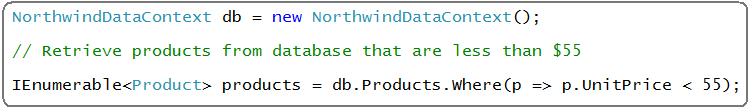
Here I am retrieving a sequence of strongly typed "Product" objects from a database, and I am expressing a filter to use via a Lambda expression to a Where() extension method.
What I absolutely do not want to have happen is to retrieve all of the product rows from the database, surface them as objects within a local collection, and then run the same in-memory Where() extension method above to perform the filter. This would be hugely inefficient and not scale to large databases. Instead, I'd like the LINQ to SQL ORM to translate my Lambda filter above into a SQL expression, and perform the filter query in the remote SQL database. That way I'd only return those rows that match the query (and have a very efficient database lookup).
Framework developers can achieve this by declaring their Lambda expression arguments to be of type Expression<T> instead of Func<T>. This will cause a Lambda expression argument to be compiled as an expression tree that we can then piece apart and analyze at runtime:
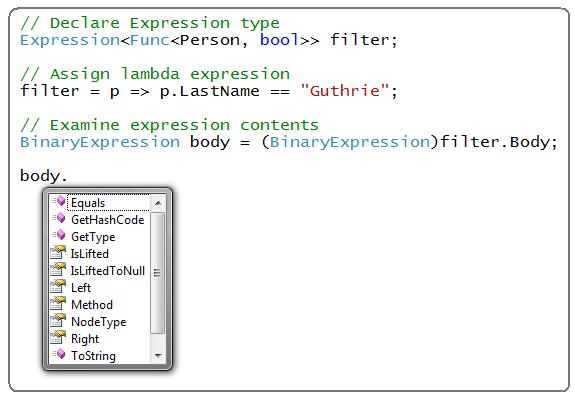
Note above how I took the same p=>p.LastName == "Guthrie" Lambda expression that we used earlier, but this time assigned it to an Expression<Func<Person, bool>> variable instead of aFunc<Person,bool> datatype. Rather then generate IL, the compiler will instead assign an expression tree object that I can then use as a framework developer to analyze the Lambda expression and evaluate it however I want (for example, I could pick out the types, names and values declared in the expression).
In the case of LINQ to SQL, it can take this Lambda filter statement and translate it into standard relational SQL to execute against a database (logically a "SELECT * from Products where UnitPrice < 55").
IQueryable<T> Interface
To help framework developers build query-enabled data providers, LINQ ships with the IQueryable<T> interface. This implements the standard LINQ extension method query operators, and provides a more convenient way to implement the processing of a complex tree of expressions (for example: something like the below scenario where I'm using three different extension methods and two lambdas to retrieve 10 products from a database):
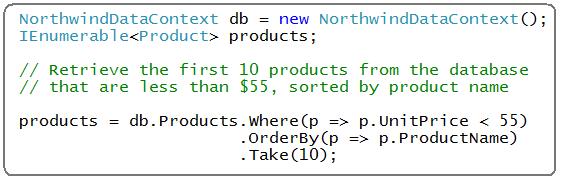
For some great blog post series that cover how to build custom LINQ enabled data providers using IQueryable<T>, please check out these great blog posts from others below:
- LINQ to Amazon: Part 1, Part 2, Part 3
- LINQ to NHibernate: Part 1, Part 2, Part 3
- LINQ to LDAP: Part 0, Part 1, Part 2, Part 3, Part 4, Part 5
Summary
Hopefully the above post provides a basic understanding of how to think about and use Lambda expressions. When combined with the built-in standard query extension methods provided in the System.Linq namespace in "Orcas", they provide a really rich way to query and interact with any type of data while preserving full compile-time checking and intellisense.
By taking advantage of the Expression Tree support provided with Lambdas, and the IQueryable<T> interface, framework developers building data providers can ensure that the clean code that developers write executes fast and efficiently against data sources (whether a database, XML file, in-memory object, web-service, LDAP system, etc).
Over the next few weeks I'll complete this language series covering the new core language concepts from a theoretical level, and then move on to cover some super practical examples of using them in action (especially using LINQ against databases and XML files).
Hope this helps,
Funq之Lambda表达式2的更多相关文章
- Funq之Lambda表达式入门
今天接受了一个Tranning关于.net3.5 framework中的new feature. 其中最不明白的还是Lambda表达式.回来后又仔细的思考了一番,总算有点体会在这里写一下.既然是入门, ...
- 你知道C#中的Lambda表达式的演化过程吗?
那得从很久很久以前说起了,记得那个时候... 懵懂的记得从前有个叫委托的东西是那么的高深难懂. 委托的使用 例一: 什么是委托? 个人理解:用来传递方法的类型.(用来传递数字的类型有int.float ...
- Linq表达式、Lambda表达式你更喜欢哪个?
什么是Linq表达式?什么是Lambda表达式? 如图: 由此可见Linq表达式和Lambda表达式并没有什么可比性. 那与Lambda表达式相关的整条语句称作什么呢?在微软并没有给出官方的命名,在& ...
- 背后的故事之 - 快乐的Lambda表达式(一)
快乐的Lambda表达式(二) 自从Lambda随.NET Framework3.5出现在.NET开发者眼前以来,它已经给我们带来了太多的欣喜.它优雅,对开发者更友好,能提高开发效率,天啊!它还有可能 ...
- Kotlin的Lambda表达式以及它们怎样简化Android开发(KAD 07)
作者:Antonio Leiva 时间:Jan 5, 2017 原文链接:https://antonioleiva.com/lambdas-kotlin/ 由于Lambda表达式允许更简单的方式建模式 ...
- java8中lambda表达式的应用,以及一些泛型相关
语法部分就不写了,我们直接抛出一个实际问题,看看java8的这些新特性究竟能给我们带来哪些便利 顺带用到一些泛型编程,一切都是为了简化代码 场景: 一个数据类,用于记录职工信息 public clas ...
- 背后的故事之 - 快乐的Lambda表达式(二)
快乐的Lambda表达式 上一篇 背后的故事之 - 快乐的Lambda表达式(一)我们由浅入深的分析了一下Lambda表达式.知道了它和委托以及普通方法的区别,并且通过测试对比他们之间的性能,然后我们 ...
- CRL快速开发框架系列教程二(基于Lambda表达式查询)
本系列目录 CRL快速开发框架系列教程一(Code First数据表不需再关心) CRL快速开发框架系列教程二(基于Lambda表达式查询) CRL快速开发框架系列教程三(更新数据) CRL快速开发框 ...
- Lambda 表达式递归用法实例
注意: 使用Lambda表达式会增加额外开销,但却有时候又蛮方便的. Windows下查找子孙窗口实例: HWND FindDescendantWindows(HWND hWndParent, LPC ...
随机推荐
- c++ virtual 和 pure virtual的区别
参考资料: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1306778/c-virtual-pure-virtual-explained 验证代码: #include < ...
- redhat5.8系统学习
# redhat5.8系统学习 ### 简介-----------------------------redhat操作系统是红帽公司的收费版操作系统 ### 查看系统版本号-------------- ...
- 彻底解决maven Cannot change version of project facet Dynamic Web Module to 3.0?
这个问题是由于maven默认的jdk和默认的Dynamic Web Module版本问题引起的. 这个问题断断续续解决了复发了,今天找打了一个方法 第一,首先要在maven中配置这个插件 <pl ...
- ASP.NET:把ashx写到类库里并在页面上调用的具体方法
在类库中建Http Handler的操作很简单,就是添加一个普通的类,然后把之前ashx里的代码几乎一模一样贴到这个类中.但要注意命名空间和类名,因为之后我们会用 到.样例Handler: names ...
- 关闭QQ看点
手机qq联系人 然后右上角公众号 然后看到看点 取消关注!!!
- mysql 年龄计算(根据生日)
生日(DATE) 计算方法1: ))) 计算方法2: year( from_days( datediff( now( ), birthdate))) now() 当前时间,精确到秒 datediff( ...
- python3基础知识学习记录
学习地址:http://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-tutorial.html ------------------------------ 为什么要学python: ...
- Android程序执行shell脚本
在做Android应用时,经常需要执行shell脚本,以快速实现某些功能: 在Android应用程序中执行shell脚本可以省去一大堆繁琐的代码,还可以避免不必要的错误: 比如:拷贝文件夹时,可以执行 ...
- Android无线测试之—UiAutomator UiSelector API介绍之七
对象搜索—索引与实例 一.索引与实例说明: 1)index:在同一级中的编号,在兄弟类中组件的编号,index从0开始 2)instance:同一个布局中同一类组件的编号,instance从0开始 二 ...
- 关于mysql联合索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 CREATE TABLE `uniontest` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `menuname` varcha ...
