NLP(三) 预处理
原文链接:http://www.one2know.cn/nlp3/
- 分词
from nltk.tokenize import LineTokenizer,SpaceTokenizer,TweetTokenizer
from nltk import word_tokenize
# 根据行分词,将每行作为一个元素放到list中
lTokenizer = LineTokenizer()
print('Line tokenizer output :',lTokenizer.tokenize('hello hello\npython\nworld'))
# 根据空格分词
rawText = 'hello python,world'
sTokenizer = SpaceTokenizer()
print('Space tokenizer output :',sTokenizer.tokenize(rawText))
# word_tokenize分词
print('Word tokenizer output :',word_tokenize(rawText))
# 能使特殊符号不被分开
tTokenizer = TweetTokenizer()
print('Tweet tokenizer output :',tTokenizer.tokenize('This is a cooool #dummysmiley: :-) :-p <3'))
输出:
Line tokenizer output : ['hello hello', 'python', 'world']
Space tokenizer output : ['hello', 'python,world']
Word tokenizer output : ['hello', 'python', ',', 'world']
Tweet tokenizer output : ['This', 'is', 'a', 'cooool', '#dummysmiley', ':', ':-)', ':-p', '<3']
- 词干提取
去除词的后缀,输出词干,如wanted=>want
from nltk import PorterStemmer,LancasterStemmer,word_tokenize
# 创建raw并将raw分词
raw = 'he wants to be loved by others'
tokens = word_tokenize(raw)
print(tokens)
# 输出词干
porter = PorterStemmer()
pStems = [porter.stem(t) for t in tokens]
print(pStems)
# 这种方法去除的多,易出错
lancaster = LancasterStemmer()
lTems = [lancaster.stem(t) for t in tokens]
print(lTems)
输出:
['he', 'wants', 'to', 'be', 'loved', 'by', 'others']
['he', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'love', 'by', 'other']
['he', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'lov', 'by', 'oth']
- 词形还原
词干提取只是去除后缀,词形还原是对应字典匹配还原
from nltk import word_tokenize,PorterStemmer,WordNetLemmatizer
raw = 'Tom flied kites last week in Beijing'
tokens = word_tokenize(raw)
# 去除后缀
porter = PorterStemmer()
stems = [porter.stem(t) for t in tokens]
print(stems)
# 还原器:字典找到才还原,特殊大写词不还原
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
lemmas = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(t) for t in tokens]
print(lemmas)
输出:
['tom', 'fli', 'kite', 'last', 'week', 'in', 'beij']
['Tom', 'flied', 'kite', 'last', 'week', 'in', 'Beijing']
- 停用词
古登堡语料库:18个未分类的纯文本
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import gutenberg
# nltk.download('gutenberg')
# nltk.download('stopwords')
print(gutenberg.fileids())
# print(stopwords)
# 获得bible-kjv.txt的所有单词,并过滤掉长度<3的单词
gb_words = gutenberg.words('bible-kjv.txt')
words_filtered = [e for e in gb_words if len(e) >= 3]
# 加载英文的停用词,并用它过滤
stopwords = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english')
words = [w for w in words_filtered if w.lower() not in stopwords]
# 处理的词表和未做处理的词表 词频的比较
fdistPlain = nltk.FreqDist(words)
fdist = nltk.FreqDist(gb_words)
# 观察他们的频率分布特征
print('Following are the most common 10 words in the bag')
print(fdistPlain.most_common(10))
print('Following are the most common 10 words in the bag minus the stopwords')
print(fdist.most_common(10))
输出:
['austen-emma.txt', 'austen-persuasion.txt', 'austen-sense.txt', 'bible-kjv.txt', 'blake-poems.txt', 'bryant-stories.txt', 'burgess-busterbrown.txt', 'carroll-alice.txt', 'chesterton-ball.txt', 'chesterton-brown.txt', 'chesterton-thursday.txt', 'edgeworth-parents.txt', 'melville-moby_dick.txt', 'milton-paradise.txt', 'shakespeare-caesar.txt', 'shakespeare-hamlet.txt', 'shakespeare-macbeth.txt', 'whitman-leaves.txt']
Following are the most common 10 words in the bag
[('shall', 9760), ('unto', 8940), ('LORD', 6651), ('thou', 4890), ('thy', 4450), ('God', 4115), ('said', 3995), ('thee', 3827), ('upon', 2730), ('man', 2721)]
Following are the most common 10 words in the bag minus the stopwords
[(',', 70509), ('the', 62103), (':', 43766), ('and', 38847), ('of', 34480), ('.', 26160), ('to', 13396), ('And', 12846), ('that', 12576), ('in', 12331)]
- 编辑距离 Levenshtein_distance
从一个字符串变到另外一个字符串所需要最小的步骤,衡量两个字符串的相似度
动态规划算法:创建一个二维表,若相等,则=左上;否则=min(左,上,左上)+1
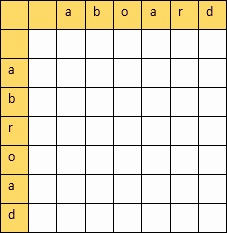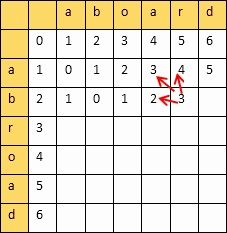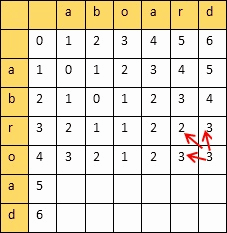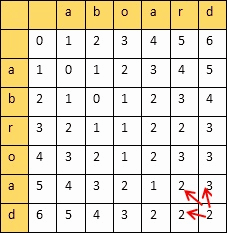
填完表计算编辑距离和相似度:
设两个字符串的长度分别是m,n,填的二维表为A
则
编辑距离 = A[m][n]
相似度 = 1 - 编辑距离/max(m,n)
代码实现:
from nltk.metrics.distance import edit_distance
def my_edit_distance(str1,str2):
m = len(str1) + 1
n = len(str2) + 1
# 创建二维表,初始化第一行和第一列
table = {}
for i in range(m): table[i,0] = i
for j in range(n): table[0,j] = j
# 填表
for i in range(1,m):
for j in range(1,n):
cost = 0 if str1[i-1] == str2[j-1] else 1
table[i,j] = min(table[i,j-1]+1,table[i-1,j]+1,table[i-1,j-1]+cost)
return table[i,j],1-table[i,j]/max(i,j)
print('My Algorithm :',my_edit_distance('aboard','abroad'))
print('NLTK Algorithm :',edit_distance('aboard','abroad'))
输出:
My Algorithm : (2, 0.6666666666666667)
NLTK Algorithm : 2
- 提取两个文本共有词汇
story1 = open('story1.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read()
story2 = open('story2.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read()
# 删除特殊字符,所有字符串小写
story1 = story1.replace(',',' ').replace('\n',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('"',' ')\
.replace("'",' ').replace('!',' ').replace('?',' ').casefold()
story2 = story2.replace(',',' ').replace('\n',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('"',' ')\
.replace("'",' ').replace('!',' ').replace('?',' ').casefold()
# 分词
story1_words = story1.split(' ')
story2_words = story2.split(' ')
# 去掉重复词
story1_vocab = set(story1_words)
story2_vocab = set(story2_words)
# 找共同词
common_vocab = story1_vocab & story2_vocab
print('Common Vocabulary :',common_vocab)
输出:
Common Vocabulary : {'', 'got', 'for', 'but', 'out', 'you', 'caught', 'so', 'very', 'away', 'could', 'to', 'not', 'it', 'a', 'they', 'was', 'of', 'and', 'said', 'ran', 'the', 'saw', 'have'}
NLP(三) 预处理的更多相关文章
- NLP 文本预处理
1.不同类别文本量统计,类别不平衡差异 2.文本长度统计 3.文本处理,比如文本语料中简体与繁体共存,这会加大模型的学习难度.因此,他们对数据进行繁体转简体的处理. 同时,过滤掉了对分类没有任何作用的 ...
- DeepLearning (三) 预处理:主成分分析与白化
[原创]Liu_LongPo 转载请注明出处 [CSDN]http://blog.csdn.net/llp1992 PCA算法前面在前面的博客中已经有介绍,这里简单在描述一下,更详细的PCA算法请参考 ...
- 百度NLP三面
首先,面试官根据项目经验进行提问,主要是自然语言处理相关的问题:然后写代码题,字符串处理和数字运算居多:再者是一些语言基础知识,百度用的linux平台,C++和python居多.下面列出我面试中的一些 ...
- 史上最详尽的NLP预处理模型汇总
文章发布于公号[数智物语] (ID:decision_engine),关注公号不错过每一篇干货. 转自 | 磐创AI(公众号ID:xunixs) 作者 | AI小昕 编者按:近年来,自然语言处理(NL ...
- 浅谈NLP 文本分类/情感分析 任务中的文本预处理工作
目录 浅谈NLP 文本分类/情感分析 任务中的文本预处理工作 前言 NLP相关的文本预处理 浅谈NLP 文本分类/情感分析 任务中的文本预处理工作 前言 之所以心血来潮想写这篇博客,是因为最近在关注N ...
- C预编译, 预处理, C/C++头文件, 编译控制,
在所有的预处理指令中,#Pragma 指令可能是最复杂的了,它的作用是设定编译器的状态或者是指示编译器完成一些特定的动作.#pragma指令对每个编译器给出了一个方法,在保持与C和C++语言完全兼容的 ...
- C中的预编译宏定义
可以用宏判断是否为ARC环境 #if _has_feature(objc_arc) #else //MRC #endif C中的预编译宏定义 -- 作者: infobillows 来源:网络 在将一 ...
- 一些基础的.net用法
一.using 用法 using 别名设置 using 别名 = System.web 当两个不同的namespace里有同名的class时.可以用 using aclass = namespace1 ...
- 学习笔记之自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing)
自然语言处理 - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E8%87%AA%E7%84%B6%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E5%A4%84%E7 ...
随机推荐
- JSP使用分层实现业务处理
在Java开发中,使用JDBC操作数据库的四个步骤如下: ①加载数据库驱动程序(Class.forName("数据库驱动类");) ②连接数据库(Connection co ...
- On The Way—Step 1 :python入门之Python的历程
1.python的历史 2004 Django框架 python2 和 python3的区别 python2 源码不统一 有重复功能代码 python3 源码统一 没有重复功能代码 Python的发展 ...
- Python 之父撰文回忆:为什么要创造 pgen 解析器?
花下猫语: 近日,Python 之父在 Medium 上开通了博客,并发布了一篇关于 PEG 解析器的文章(参见我翻的 全文译文).据我所知,他有自己的博客,为什么还会跑去 Medium 上写文呢?好 ...
- Promise异步编程解决方案
Promise是ES6中新增的异步编程解决方案,体现在代码中它是一个对象,可以通过 Promise 构造函数来实例化. 其最基本的使用 new Promise(function(resolve,rej ...
- oracle一条语句插入多个值的方法
今天在实践过程中遇到一个问题, 我想往数据库插入多条数据时,使用了如下语句: insert into 表1 (字段1,字段2) values (1,2),(2,3),(3,4); 这条语句在mysql ...
- 经典SQL(sqlServer)
一.基础 .说明:创建新表create table tabname(col1 type1 [not null] [primary key],col2 type2 [not null],..) .分组: ...
- (转)Linux LVM逻辑卷配置过程详解(创建、扩展、缩减、删除、卸载、快照创建)
一.预备知识 LVM全称为Logical Volume Manager 逻辑卷管理器,LVM是Linux环境中对磁盘分区进行管理的一种机制,是建立在硬盘和分区之上.文件系统之下的一个逻辑层,可提高磁盘 ...
- 有容云-PPT | 当微服务遇见容器
编者注: 本文为10月29日有容云高级技术顾问龙淼在Docker Live时代线下系列-广州站中演讲的PPT,本次线下沙龙为有容云倾力打造Docker Live时代系列主题线下沙龙,每月一期畅聊容器技 ...
- Kafka学习(四)-------- Kafka核心之Producer
通过https://www.cnblogs.com/tree1123/p/11243668.html 已经对consumer有了一定的了解.producer比consumer要简单一些. 一.旧版本p ...
- python基础之循环与迭代器
循环 python 循环语句有for循环和while循环. while循环while循环语法 while 判断条件: 语句 #while循环示例 i = 0 while i < 10: i += ...
