leetcode 刷题记录(java)-持续更新
题记
感觉说的挺好的,值得学习 1 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liujiaqi12345/article/details/88357041
Leetcode JAVA 题解: https://github.com/mJackie/leetcode
自己日常刷题经过是这样的: 拿到题目,看一眼Difficulty,然后自己思考一下解题思路。如果解不出来,就记下在哪里卡住了,难点在哪。
如果对应的题目有Solution,就看Solution,没有的话就点Discuss,按Most Votes排序,看排名最高的解法。
对比一下自己的解法与最优的解法的差别,总结一下为什么没想起来,记录下来这个思考的过程。
关掉别人的代码,开始Coding,Debug,Submit。
附上自己总结的几条经验: 先刷两个Top专题。Leetcode 上有个List选项,里边有两个专题,分别是Top 100 Liked Questions和Top Interview Questions。这两个List中有很多重复的题,加起来一共150道左右。都是经典的题目,将这150道刷完基本上所有的题型都见过了,而且多数经典题目都会涉及,是提升最快的一个方法。 注意记录、总结与复习。自己写过的代码一定要保存下来,刷题的时候也要记下主要思路和注意点,这样在复习的时候也能对比发现自己哪里还能改进,之前犯得错误有没有重犯。可以将相互关联的题目对比着一起看,方便总结与记忆。一定要时常复习刷过的题,复习比一味的追求数量更重要。 做好Easy,没必要死扣Hard。LeetCode上很多Easy的题目看似简单,实则想要写出Perfect的代码并非易事。多思考如何优化Easy,Medium的解法实际上比花精力解Hard题更能提高自己。况且面试的时候Hard被问的概率太小了。 切忌眼高手低。不要想着自己知道思路解法了就是会了,一定要亲自Coding,手撸出来。我在刷的过程中就经常在Debug的时候才发现自己忘记考虑了某些条件。不把代码写出来,只看别人的答案对自己是没有多大的提高的,只有亲自AC了题目,才能算做过一道题。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Jackie.Liu」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liujiaqi12345/article/details/88357041
还有这注释方式也不错,学习
语言: Java
说明: 每道题在代码头部都添加了我的解题思路和批注,Eg:
/*****
* 287. Find the Duplicate Number
* 题意:n+1个数属于[1~n],找出重复的那个数
* 难度:Medium
* 分类:Array, Two Pointers, Binary Search
* 思路:如果nums[i]不在对应位置,则和对应位置交换。如果对应位置上也为该数,说明这个数就是重复的数字。这个方法改变了数组。是错误的。
* 另一种方法,把问题转换成有环链表,找环的起始节点。O(n) O(1) lc142
* 二分查找,每次看一边数字的个数, O(nlog(n)) O(1)
* Tips:剑指offer原题
*/
1. 两数之和
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
2 int[] result = new int[2];
3 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
4 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
5 if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
6 result[1] = i;
7 result[0] = map.get(target - nums[i]);
8 return result;
9 }
10 map.put(nums[i], i);
11 }
12 return result;
13
14 }
15
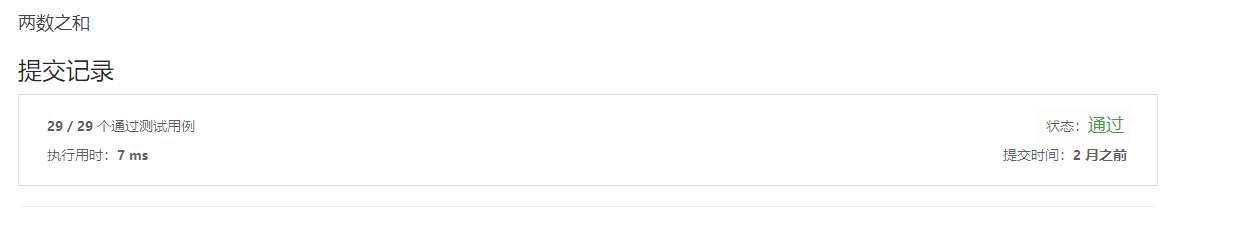
2. Add Two Numbers
/**
* Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8 Explanation: 342 +
* 465 = 807
*
* 题意:对于俩个链表。对应节点相加,满十进一
* 思路:先判断对应节点是否至少存在一个有值,有则相加,然后移动节点向下,循环如此,如果说最后一次相加,进位(carry)不为0,则要显示,其次,返回值要从返回链表的第二个几点开始
*
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode resultNode = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, curr = resultNode;
int carry = 0;
while (p != null || q != null) {
int x = p != null ? p.val : 0;
int y = q != null ? q.val : 0;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
curr.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr.next;
if (p != null) {
p = p.next;
}
if (q != null) {
q = q.next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
curr.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return resultNode.next;
}
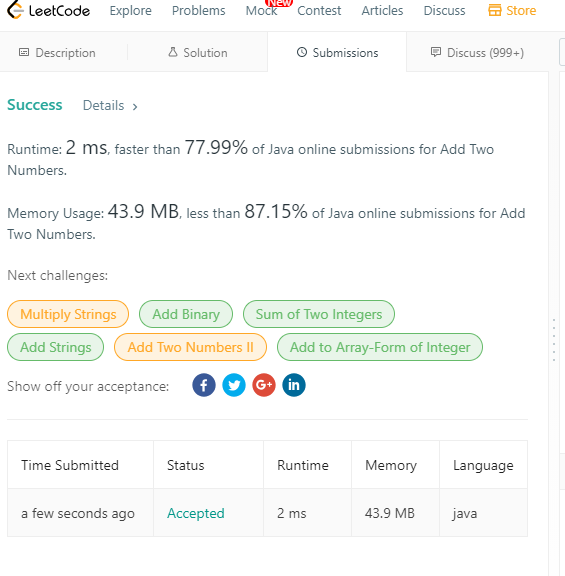
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 String s = "abbabc";
3 System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring(s));
4 }
5
6 public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
7 int max = 0;
8 // ”记录当前重复字母的最新位置“
9 int j = 0;
10 HashMap<Character, Integer> resultMap = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
11 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
12 if (resultMap.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {
13 j = Math.max(resultMap.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1, j);
14 }
15 //”当前位置-上次重复的最大位置+1“
16 max = Math.max(i - j + 1, max);
17 resultMap.put(s.charAt(i), i);
18 }
19
20 return max;
21 }
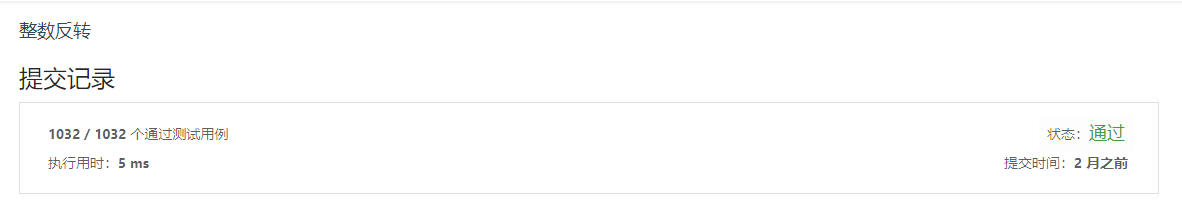
7. 整数反转
1 public int reverse(int x) {
2 int ans = 0;
3 while (x != 0) {
4 int pop = x % 10;
5 if (ans > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 || (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && pop > 7))
6 return 0;
7 if (ans < Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 || (ans == Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 && pop < -8))
8 return 0;
9 ans = ans * 10 + pop;
10 x /= 10;
11 }
12 return ans;
13 }
14
8. String to Integer (atoi)
public static int myAtoi(String str) {
// 1字符串非空判断 ""||" "
if (str.isEmpty() || str.trim().isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
int index = 0;
int sign = 1;
int total = 0;
//1检测第一个非空字符串是什么
while (str.charAt(index) == ' ' && index < str.length()) {
index++;
}
//1判断这个数是正数还是负数
if (str.charAt(index) == '+' || str.charAt(index) == '-') {
sign = str.charAt(index) == '+' ? 1 : -1;
index++;
}
//1判断是否是数字,是否越界,如果越界就取越界的边界值
while (index < str.length()) {
int digit = str.charAt(index) - '0';
if (digit < 0 || digit > 9) {
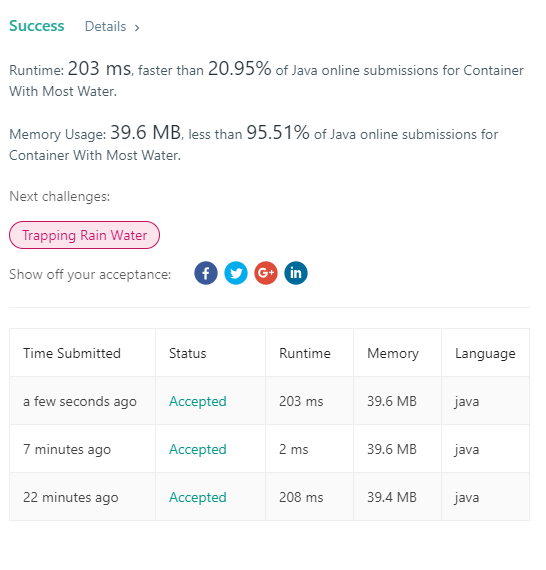
11. Container With Most Water
/**
* 解法1:俩边的边为起点,进行计算,如果左边的边比右边的小,左边第二条边和当前右边的边进行计算,如果右边的边小于左边的边,则右边的第二条便进行计算,依此类推
*
* @param height
* @return
*/
public static int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0, j = height.length - 1, res = 0;
while (i < j) {
// ‘取最大值’
res = Math.max(res, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i));
if (height[i] < height[j]) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return res;
} /**
* 解法2 遍历所有的可能结果n(n-1)/2中情况
*
* @param height
* @return
*/
public int maxArea1(int[] height) {
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < height.length; j++) {
max = Math.max(max, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i));
}
} return max;
}
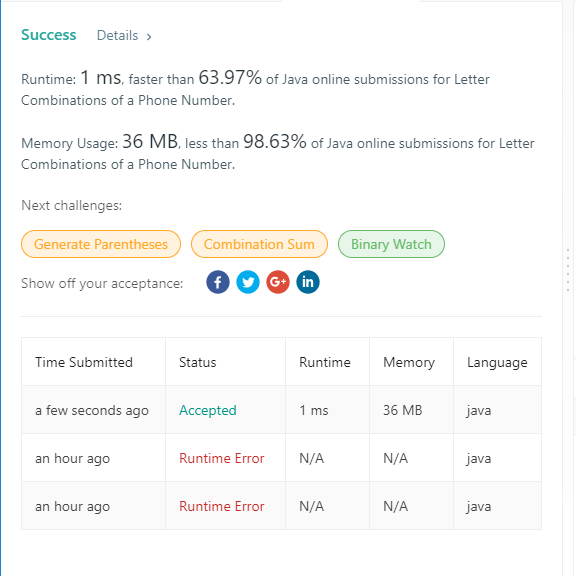
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
public static List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<String>();
Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<Character, String>() {
{
put('2', "abc");
put('3', "def");
put('4', "ghi");
put('5', "jkl");
put('6', "mno");
put('7', "pqrs");
put('8', "tuv");
put('9', "wxyz");
}
};
//‘非空校验’
if (digits == null || "".equals(digits)) {
return ret;
}
dfs(digits, 0, "", map, ret);
return ret;
}
public static void dfs(String digits, int idx, String path, Map<Character, String> map, List<String> ret) {
if (digits.length() == path.length()) {
ret.add(path);
return;
}
//‘循环配合递归’
for (int i = idx; i < digits.length(); i++) {
for (char c : map.get(digits.charAt(i)).toCharArray()) {//这里是第个数字的对应的字母
dfs(digits, i + 1, path + c, map, ret);//这里进行递归,对应的第二个数字的循环,和第一个字母进行拼接
}
}
}
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
/**
*‘本题思路:建立俩个链表,一个是dummy,复制原链表,另一个链表(first)为了计算链表长度;然后在用first链表指向dummy,删掉指定位置的元素’
*‘注意,应为是dummy指向head,所以多了一个节点,在指定删除位置时不用减一;另外返回时应该返回dummy.next,第一个节点是我们自己定义的’
* @param head
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode first = head;
int length = 0;
while (first != null) {
length++;
first = first.next;
}
int position = length - n;
first = dummy;
while (position > 0) {
position--;
first = first.next;
}
first.next = first.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode a1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode a2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode a3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode a4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode a5 = new ListNode(5);
a1.next = a2;
a2.next = a3;
a3.next = a4;
a4.next = a5;
ListNode a6 = removeNthFromEnd(a1, 2);
while (a6 != null) {
System.out.println(a6.val);
a6 = a6.next;
}
}
}

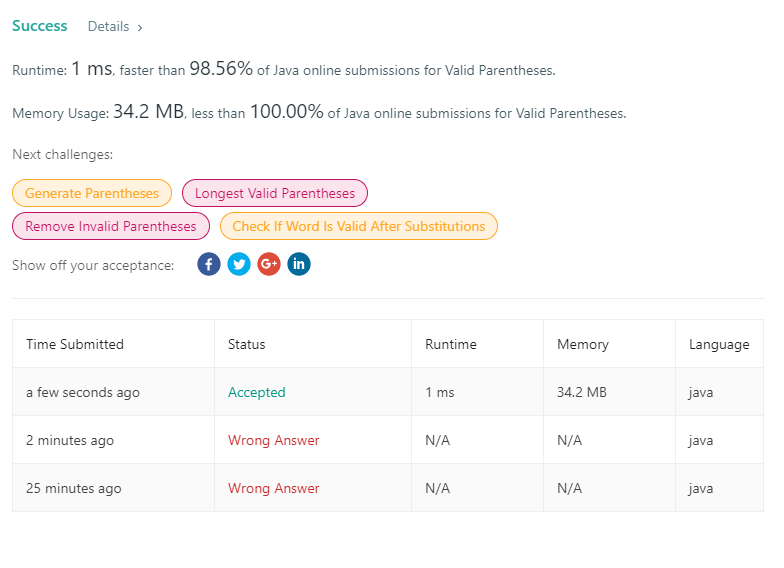
20. Valid Parentheses
/**
* 题意:括号匹配,俩个匹配的括号之间是不允许有为匹配(也就是单个的)括号
* 解题思路:通过入栈的形式,如果未匹配就入栈,匹配就出栈,最后如果栈不为空或者栈顶元素不当前元素不匹配就返回false
*
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '(') {
stack.push(')');
} else if (c == '[') {
stack.push(']');
} else if (c == '{') {
stack.push('}');
} else if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != c) {
return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(isValid("["));
}
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
int val;
ListNode next; ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
} /**
* 本题思路:‘将当前节点l1.next和L2的当前节点(第一个节点)进行比较,如果小于等于(注意:等于也是可以的),继续往下走,反之则进行节点替换(l1.next和l2进行替换),当l2为null时(也就是l1.next=null)结束循环’
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
//此处是为了保证第一个节点时最小值
ListNode tmp;
if (l1.val > l2.val) {
tmp = l2;
l2 = l1;
l1 = tmp;
}
ListNode newListNode = l1;
while (l2 != null) {
//遍历节点进行组合
while (newListNode.next != null && newListNode.next.val <= l2.val) {
newListNode = newListNode.next;
}
//比较排序
tmp = newListNode.next;
newListNode.next = l2;
l2 = tmp;
}
return l1; } //展示当前链表的值
public static void sysoListNode(ListNode l1) {
while (l1 != null) {
System.out.format("%d->", l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
System.out.println("===================");
} /**
* 大神的解法:原理和上面一样,只是利用递归的原理
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists2(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null)
return l2;
if (l2 == null)
return l1;
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
//此处时为了更直观看当前链表的状态
sysoListNode(l1);
sysoListNode(l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
//此处时为了更直观看当前链表的状态
sysoListNode(l1);
sysoListNode(l2);
return l2;
}
} //测试数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode l1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode l2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(4);
l1.next = l2;
l2.next = l3; ListNode r1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode r2 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode r3 = new ListNode(4);
r1.next = r2;
r2.next = r3; mergeTwoLists(l1, r1); }
26 break;
27 }
28
29 if (Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 > total
30 || (Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 == total && Integer.MAX_VALUE % 10 >= digit)) {
31 total = total * 10 + digit;
32 index++;
33 } else {
34 return sign > 0 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
35 }
36 }
37 return total * sign;
38
39 }

20. 有效的括号
1 class Solution {
2 public boolean isValid(String s) {
3 int n = s.length();
4 for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
5 if (s.contains("{}"))
6 s = s.replace("{}", "");
7 if (s.contains("()"))
8 s = s.replace("()", "");
9 if (s.contains("[]"))
10 s = s.replace("[]", "");
11 }
12 if ("".equals(s)) {
13 return true;
14 }
15 return false;
16 }
17 }
26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
1 public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
2 int count = 1;
3 for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {//用当前的数字和上一个被比较的数字进行比较,如果大于他就替换,本题默认一排序
4 if (nums[i] > nums[count - 1]) {
5 nums[count++] = nums[i];
6 }
7 }
8 return count;
9
10 }

27. Remove Element
1 public static int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
2 if (nums == null) {
3 return -1;
4 } else if (nums.length == 0) {
5 return 0;
6 } else {
7 int count = 0;//统计几个不相同,同时作为新数组的下标
8 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
9 if (nums[i] != val) {
10 nums[count++] = nums[i];//注意count++的执行顺序
11 }
12 }
13 return count;
14 }
15
16 }
41. First Missing Positive
1 public static int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
2 if (nums.length == 0) {
3 return 1;
4 }
5
6 Set<Integer> numsSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
7 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
8 if (nums[i] < 1) {
9 continue;
10 } else {
11 numsSet.add(nums[i]);
12 }
13 }
14 List<Integer> numsList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
15 numsSet.forEach(n -> numsList.add(n));
16
17 // 1筛选过后的数组为空
18 if (numsList.size() == 0) {
19 return 1;
20 }
21
22 numsList.sort((a, b) -> a.compareTo(b.intValue()));
23
24 int index = 0;// 1当前数组下标
25 for (int i = 1;; i++) {
26 // 1预防数组越界
27 if (index < numsList.size() && numsList.get(index) == i) {
28 index++;
29 } else {
30 return i;
31 }
32 }
33
34 }
46. Permutations
/**
* 本题目标:对于给定数组列出所有的可能排列组合
* 实现方法:利用递归的思路
* 举个例子,当数组为【1,2,3】;先考虑第一个数为1时,后面的可能性,以此类推
* 注意:后面的可能性要以递归的思路去考虑,或者入栈出栈的思路。
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Arrays.sort(nums); // not necessary
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums);
return list;
} private static void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int[] nums) {
if (tempList.size() == nums.length) {
//注意这里的细节,是新声明一个集合去保存这个值,如果用tempList会导致最后list为空,原因就是堆被清空啦
list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(tempList));
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (tempList.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
} else {
tempList.add(nums[i]);
//注意是循环中调用递归
backtrack(list, tempList, nums);
//小算法,清空当前递归中的最后一个值
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - 1);
}
} }
}
48. Rotate Image
/**
* 本体题意:顺时针反转90度
* 解题方法:找出通项公式
* @param matrix
*/
public static void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
int[][] rotate = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//通项公式
rotate[i][j] = matrix[n - 1 - j][i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//重新赋值
matrix[i][j] = rotate[i][j];
}
}
}
49. Group Anagrams
/**
* 本题题意:将含有相同字母的字符串归类
*
* 解法:将字符串拆分成字符,然后排序作为key,最后map转化成list
*/
public static List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
if (strs.length == 0) {
return new ArrayList<List<String>>();
}
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<String, List<String>>();
for (String s : strs) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chars);
String key = String.valueOf(chars);
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
map.put(key, new ArrayList<String>());
}
map.get(key).add(s);
}
return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values()); }

53. Maximum Subarray
/**
* 题意:找出一组 最大的数组和,作为结果的数组长度不限但小于等于给定的数组
* 解决方法:二步;
* 第一步找到当前最大(通过(当前最大的+a[i+1]) + a[i+1]比较,找出最大的)(类似贪心)
* 第二步找到当前最大的和之前最大的进行比较,选出最大的
* 注意:maxSum初始值一定要定义最小,可能为负数,如果初始化成0就不行啦
* @param A
* @return
*/
public static int maxSubArray(int[] A) {
if (A == null || A.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
// ‘记录当前数据的最大值’;‘理解成新生成的最大值 和 旧的(已知的最大值比较)’
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// ‘记录(当前)和(当前加下一位)的最大值’
int maxCurrentSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
maxCurrentSum = Math.max(maxCurrentSum + A[i], A[i]);
maxSum = Math.max(maxCurrentSum, maxSum);
}
return maxSum; } /**
* 这个解决思路很好,也很好理解
* 解决思路:‘如果上一次结果为负数,则上一次结果置0,加下一次数’
* 也不需要考虑最小值的问题啦
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static int maxSubArray2(int[] nums) {
int max = nums[0], tmp = max;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (tmp < 0) tmp = 0;//‘精髓’
tmp += nums[i];
max = Math.max(tmp, max);
}
return max;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {-1,1};
System.out.println(maxSubArray2(a));
}
55. Jump Game
/**
* 题意:从a[0]开始跳转当前索引对应数值的步数,看能否跳到最后一步 解题方法:通过
* (i(当前索引)+nums[i](能跳转的最大长度))和当前索引进行比较;如果可达到的位置小于当前位置;则可以判断不可到达
*
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int reachable = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > reachable) {
return false;
}
// i(当前索引)+nums[i](能跳转的最大长度)
reachable = Math.max(reachable, i + nums[i]);
}
return true;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = { 3, 2, 1, 0, 4 };// false
// int[] nums = { 2, 3, 1, 1, 4 };//true
canJump(nums);
}
75. Sort Colors
/**
* 题目:‘将红白蓝归类排序;其实就是012归类排序’
* 解决方法:‘我这里用的冒泡排序,可以尝试一下别的排序方法’
* @param nums
*/
public static void sortColors(int[] nums) {
//‘注意下标’
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
//‘注意下标’
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length - 1; j++) {
if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j + 1];
nums[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = { 2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0 };
sortColors(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
}

78. Subsets
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List; /**
* Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the
* power set).
*
* Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
*
* Example:
*
* Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2],[]]
*
*给予一个不重复的整数集合,返回所有的可能的子集
*/
public class Lc78 { public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = new int[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
nums[i] = i + 1;
} for (List<Integer> lists : subsets2(nums)) {
for (Integer i : lists) {
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
}
} /**
* 利用深度优先搜索(dfs)
*/
private static List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>(); public static List<List<Integer>> subsets2(int[] nums) {
dfs(nums, 0, new LinkedList<>());
return results;
} private static void dfs(int[] nums, int start, LinkedList<Integer> list) {
results.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
list.addLast(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, i + 1, list);
//遍历之后删除该节点避免重复
list.removeLast();
}
} }

80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
1 public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
2 int count = 2;
3 for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
4 if (nums[i] > nums[count - 2]) {
5 nums[count++] = nums[i];
6 }
7 }
8 return count;
9 }
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack; public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
} /**
* 题目:‘有序遍历:给你一个二叉树,有序遍历他的节点;有序遍历意味着先便利左子树,之后依次倒叙遍历右子树;
* ’最好集合solution的动图,入栈出栈的形式更好理解
*
* ‘解决方法:利用入栈出栈的形式
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//声明一个栈来存取节点
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode curr = root;
//如果节点没有遍历完或者说栈不为空就继续一下流程
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
//如果当前节点不为空,就继续将当前节点压入栈
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}
//如果当前节点为空,意味着左子树遍历完了,那就出栈存值,然后遍历当前节点的右子树
curr = stack.pop();
res.add(curr.val);
curr = curr.right;
}
return res;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
// [1,null,2,3]
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode treeNode1 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode treeNode2 = new TreeNode(3);
treeNode.right = treeNode1;
treeNode1.left = treeNode2;
inorderTraversal(treeNode);
} }
101. Symmetric Tree
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
/**
* 题意:’判断给定的二叉树是不是对称的二叉树
* 解决方法:‘递归,理解简单。通过递归判断所有的节点是否对称;
* 思路:’将一个给定的二叉树‘复制一份’,从根节点开始,判断对应的节点(以根节点为对称轴)是否相同;
* @param t1
* @param t2
* @return
*/
public static boolean isMirro(TreeNode t1,TreeNode t2) {
if(t1 ==null && t2==null) {
return true;
}
if(t1 == null || t2 == null) {
return false;
}
//判断当前节点以及当前节点的左右树
return (t1.val == t2.val) && isMirro(t1.left, t2.right) && isMirro(t1.right, t2.left);
}
public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isMirro(root, root);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
TreeNode t1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode t2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode t3 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode t4 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode t5 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode t6 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode t7 = new TreeNode(3);
t1.left = t2;t1.right = t3;
t2.left = t4;t2.right = t5;
t3.left = t6;t3.right = t7;
System.out.println(isSymmetric(t1));
}
}
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
/**
* 题意:遍历二叉树得到最大路径的长度
* 解题:遍历可以用递归或者是栈;这里用的是递归,栈我没用明白,
* @param root
* @return
*/
public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1+Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// [0,2,4,1,null,3,-1,5,1,null,6,null,8]
TreeNode t1 = new TreeNode(0);
TreeNode t2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode t3 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode t4 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode t5 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode t6 = new TreeNode(-1);
TreeNode t7 = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode t8 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode t9 = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode t10 = new TreeNode(8);
t1.left = t2;
t1.right = t3;
t2.left = t4;
t4.left = t7;
t4.right = t8;
t3.left = t5;
t3.right = t6;
t5.left = t9;
t6.left = t10;
System.out.println(maxDepth(t1));
}
}
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
public class oneHundredone {
/**
* 题目:卖股票 小卖大卖
* 解题方法:动态找到当前最小的,然后一次判断当前的最大利润
* @param prices
* @return
*/
public static int maxProfit(int prices[]) {
//初始化,
int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxProfit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
//找到最小的买入值
minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, prices[i]);
//找到最大的卖出值
maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, prices[i] - minPrice);
}
return maxProfit;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] stock = { 7, 6, 4, 3, 1 };
System.out.println(maxProfit(stock));
}
}
136. Single Number
1 public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
2
3
4 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
5
6 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
7 if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
8 map.remove(nums[i]);
9 } else {
10 map.put(nums[i], 1);
11 }
12
13 }
14
15 Integer result = 0;
16 for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
17 result = key;
18 break;
19 }
20
21 return result;
22
23
24 }
137. Single Number II
1 public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
2
3
4 Map<Integer, Boolean> map = new HashMap<Integer, Boolean>();
5
6 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
7 if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
8 map.put(nums[i], false);
9 } else {
10 map.put(nums[i], true);
11 }
12
13 }
14
15 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
16 map.forEach((k, v) -> {
17 if (v) {
18 result.add(k);
19 }
20 });
21 return result.get(0);
22
23
24 }
139. Word Break
1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.List;
3
4 /**
5 * 题意:根据给定的字典判断字符串是否可以完全根据字典拆解 思路:利用dp(动态规划:把问题分解成原子级别,求解每个问题的最优解,最后汇聚就是问题的最优解)
6 *
7 *
8 */
9 public class WordBreak {
10 /**
11 * dp1 比较容易理解
12 *
13 * 遍历给定字符串的每一个字符,和字典机型比较,如果符合条件(wordDict.contains(sub) && (j == 0 || dp[j -
14 * 1])),就将该位置设置成true 若遍历所有之后,dp的最后一位是true,代表字符串按照字段拆解完全
15 *
16 * @param s
17 * @param wordDict
18 * @return
19 */
20 public static boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
21 if (s == null || "".equals(s)) {
22 return false;
23 }
24 int n = s.length();
25 boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length()];
26 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
27 for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
28 String sub = s.substring(j, i + 1);
29 if (wordDict.contains(sub) && (j == 0 || dp[j - 1])) {
30 dp[i] = true;
31 }
32 }
33 }
34 return dp[n - 1];
35 }
36
37 /**
38 * dp2
39 * 和dp1思路一样,只是优化了匹配过程,第二次直接遍历字段进行匹配,优化了3ms
40 * @param s
41 * @param wordDict
42 * @return
43 */
44 public static boolean wordBreak2(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
45 int n = s.length();
46 boolean[] dp = new boolean[n + 1];
47 dp[0] = true;
48 for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
49 for (String word : wordDict) {
50 int len = word.length();
51 if (i >= len && dp[i - len] && s.substring(i - len, i).equals(word)) {
52 dp[i] = true;
53 }
54 }
55 }
56 return dp[n];
57
58 }
59
60 /**
61 * dp3递归加dp,还没有完全理解,不过思路都很相似
62 * @param s
63 * @param wordDict
64 * @return
65 */
66 public static boolean wordBreak3(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
67 boolean[] memo = new boolean[s.length()];
68 return wordBreakHelper(s, wordDict, memo, 0);
69 }
70
71 public static boolean wordBreakHelper(String s, List<String> wordDict, boolean[] memo, int i) {
72 if (i >= s.length()) {
73 return true;
74 }
75 if (memo[i]) {
76 return false;
77 }
78 for (String word : wordDict) {
79 if (!s.startsWith(word, i)) {
80 continue;
81 }
82 boolean result = wordBreakHelper(s, wordDict, memo, i + word.length());
83 if (result) {
84 return true;
85 }
86 memo[i] = true;
87 }
88 return false;
89 }
90
91 public static void main(String[] args) {
92 String s = "leetcode";
93 List<String> dict = new ArrayList<String>();
94 dict.add("leet");
95 dict.add("code");
96 // System.out.println(wordBreak(s, dict));
97 System.out.println(wordBreak2(s, dict));
98 }
99 }
152. Maximum Product Subarray
/**
* Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray within an array
* (containing at least one number) which has the largest product.
*
* 给一整数,求解最大的连续乘积,数组包含至少一个整数
*
*/
public class Lc152 {
/**
* 思路:dp
* 最优子结构,之前最大值乘当前值为最大值
* 边界值,初始值为nums[0]
*公式: 最大值 为 当前值 和 之前最大值乘以当前值 中的一个
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 1) {
return 0;
} int max = nums[0];
int dpMax = nums[0];
int dpMin = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
dpMax = Math.max(nums[i], Math.max(dpMax * nums[i], dpMin * nums[i]));
dpMin = Math.min(nums[i], Math.min(dpMax * nums[i], dpMin * nums[i]));
max = Math.max(max, dpMax);
} return max;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = { 2, 3, -2, 4 };
System.out.println(maxProduct(nums));
}
}

167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
2
3 int[] position = new int[2];
4 for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
5 for (int j = i + 1; j < numbers.length; j++) {
6 if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) {
7 position[0] = ++i;
8 position[1] = ++j;
9 break;
10 }
11 }
12 }
13
14 return position;
15
16 }
169. Majority Element
import java.util.Arrays;
public class majorityElement {
/**
* 题目: Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element
* is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times.
*
* You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always
* exist in the array.
*
* 解题: 利用测试用例数据
*
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
/**
* 摩尔投票 是你就给你加一,不是你就减一,如果你是0就替换
*/
public static int majorityElement2(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int count = 1;
for (int i : nums) {
if (i == res) {
count++;
} else {
count--;
}
if (count == 0) {
res = i;
count++;
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = { 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
// System.out.println(majorityElement(a));
System.out.println(majorityElement2(a));
}
}
198. House Robber
/**
* You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each
* house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you
* from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security system
* connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses
* were broken into on the same night.
*
* Given a list of non-negative integers representing the amount of money of
* each house, determine the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without
* alerting the police.
*
* @author 5109v12458
*
*/
public class HouseRobbe { /**
* 每次求得的now都是相隔的俩个数相加
* @param nums
* @return
*/
public static int rob(int[] nums) {
int last = 0;
int now = 0;
int temp = 0;
//an = (a(n-1)+n,an)
for (int i : nums) {
temp = now;
now = Math.max(last + i, now);
last = temp;
}
return now;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int nums[] = { 1, 2, 4, 6 };
System.out.println(rob(nums));
}
}

204. 计数质数
1 class Solution {
2 public int countPrimes(int n) {
3 int[] num = new int[n];
4
5 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
6 num[i] = 1;
7 }
8
9 for (int j = 2; j < n; j++) {
10 if (num[j] == 1) {
11 for (int k = 2; k * j < n; k++) {
12 num[j * k] = 0;
13 }
14 }
15 }
16 int sum = 0;
17 for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
18 if (num[i] == 1) {
19 sum++;
20 }
21 }
22 return sum;
23 }
24
25 }
206. Reverse Linked List
/**
* Reverse a singly linked list.
*
* Example:
*
* Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL Follow up:
*
* A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you
* implement both?
*
*/
public class ReverseLinkedList {
public static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next; ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
} /**
* 解法,通过另一条链表实现反转链表
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode temp = curr.next;
/*
* 目的是将当前节点的下一个几点作为prev的上一个节点,当前节点作为prev的当前节点
* 其他的步骤就是单纯的置换
*/
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
return prev;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2); node.next = node1;
node1.next = node2; reverseList(node);
}
}
226. Invert Binary Tree
Invert a binary tree.
Example:
Input:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
Output:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node. public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode
* left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } }
*/
class Lc226 {
public static class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
} /**
*
* 反转二叉树:先按照左子树反转,在右子树反转,在左右字数反转
*
* @return
*/
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
260. Single Number III
1 public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
2
3 Map<Integer, Boolean> map = new HashMap<Integer, Boolean>();
4
5 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
6 if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
7 map.put(nums[i], false);
8 } else {
9 map.put(nums[i], true);
10 }
11
12 }
13
14 List<Integer> resultTemp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
15
16 map.forEach((k, v) -> {
17 if (v) {
18 resultTemp.add(k);
19 }
20 });
21
22 int[] result = new int[resultTemp.size()];
23
24 for (int i = 0; i < resultTemp.size(); i++) {
25 result[i] = resultTemp.get(i);
26 }
27 return result;
28
29 }
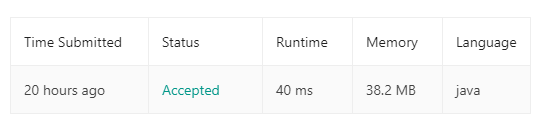
283. Move Zeroes
1 public static void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
2 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
3 if (nums[i] != 0) {
4 continue;
5 } else {
6 int count = 0;
7 do {
8 swap(nums, i);//如果当前位置为0,则置换到最后一位
9 count++;
10 } while (nums[i] == 0 && count < nums.length - i);//如果当前位置是0,并且之前也没有0啦,则终止循环,终止条件有待优化
11 }
12 }
13 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
14 System.out.print(nums[i]);
15 }
16 }
17
18 public static void swap(int[] nums, int position) {//普通的置换算法,冒泡排序里的一段
19 for (int i = position; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
20 int temp = nums[i];
21 nums[i] = nums[i + 1];
22 nums[i + 1] = temp;
23 }
24 }
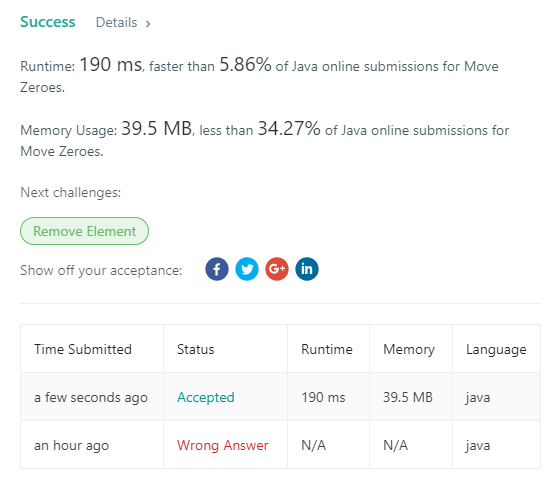
412. Fizz Buzz
1 class Solution {
2 public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) {
3 List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
4 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
5 if (i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
6 result.add("FizzBuzz");
7 } else if (i % 3 == 0) {
8 result.add("Fizz");
9 } else if (i % 5 == 0) {
10 result.add("Buzz");
11 } else {
12 result.add("" + i);
13 }
14
15 }
16 return result;
17 }
18 }
448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array
1 public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
2
3
4 Map<Integer, Integer> numsMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
5 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
6 numsMap.put(nums[i], i);
7 }
8
9 // 1给定数组应该有的大小
10 int size = nums.length;
11
12 List<Integer> disappearedNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
13 for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
14 if (!numsMap.containsKey(i)) {
15 disappearedNumbers.add(i);
16 }
17 }
18
19 return disappearedNumbers;
20
21 }

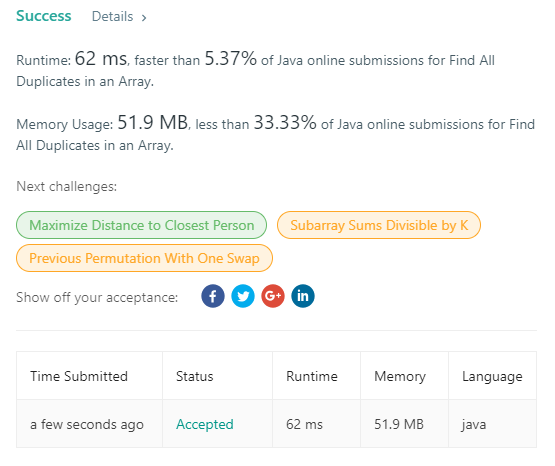
442. Find All Duplicates in an Array
1 public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
2
3 // 1对于给定数组进行排序
4 Map<Integer, Integer> numsMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
5 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
6 if(numsMap.containsKey(nums[i])) {
7 numsMap.put(nums[i], 2);
8 }else {
9 numsMap.put(nums[i], 1);
10 }
11 }
12
13 List<Integer> disappearedNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
14 numsMap.forEach((k,v)->{
15 if(v==2) {
16 disappearedNumbers.add(k);
17 }
18 });
19
20 return disappearedNumbers;
21
22
23 }
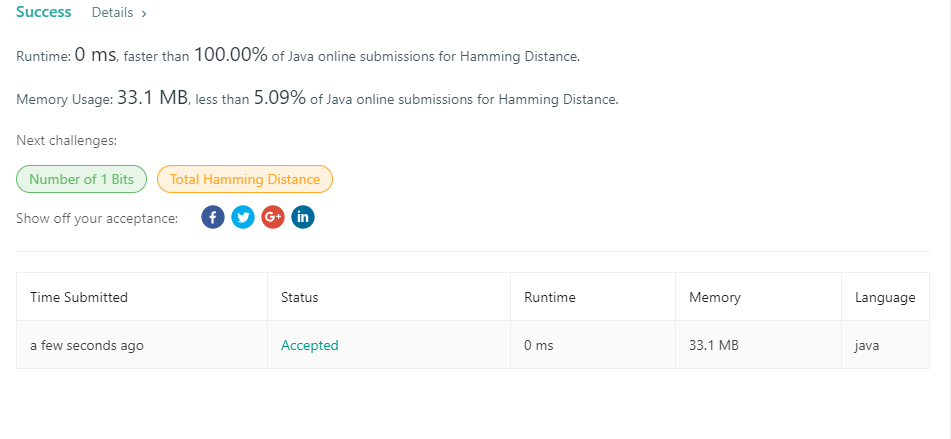
461. Hamming Distance
/**
* Hamming Distance
*
* The Hamming distance between two integers is the number of positions at which
* the corresponding bits are different. Given two integers x and y, calculate
* the Hamming distance.
*
* 转换为2进制,有几个位置上的值不同,就叫做Hamming distance
*
*/
public class Lc461 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(hammingDistance(1, 4));
} public static int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int sum = x ^ y;
int res = 0;
res += sum % 2;
sum /= 2;
return res;
}
}
560. Subarray Sum Equals K
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
*找出最大连续子序列的个数
*
*/
public class Lc560 { /**
* 如果存在 sum-k=subArrayCount,則存在对应count的连续子序列
*
* @param nums
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int count = 0;
int sum = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();// map<sum,count(该sum-k出现的次数)>
map.put(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(sum - k)) {
count += map.get(sum - k);
}
map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int nums[] = { 3, 4, 7, 2, -3, 1, 4, 2 };
System.out.println(subarraySum(nums, 7));
}
}
581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
* 581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
* 题意:找出数组中需要排序的长度
* 难度:Easy
* 分类:Array
* 思路:
* Tips:可以考虑八大排序
*/
public class Lc581 {
public static int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {
int copyFromNums[] = new int[nums.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
copyFromNums[i] = nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(copyFromNums);
int startPosition = 0;
int endPosition = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (copyFromNums[i] != nums[i]) {
startPosition = i;
break;
}
} for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (copyFromNums[i] != nums[i]) {
endPosition = i;
}
} int count = 0;
if (endPosition != startPosition) {
count = endPosition - startPosition + 1;
}
return count;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int nums[] = { 2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 9, 15 };
System.out.println(findUnsortedSubarray(nums));
}
}

617. Merge Two Binary Trees
1 /**
2 * 题意:将俩个二叉树及进行合并,如果同一位置节点都存在,则合并,否则旧直接放上去
3 * 思路:相同位置进行合并,有则相加,无责这届放上去,注意用递归
4 * @param t1
5 * @param t2
6 * @return
7 */
8 public static TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
9 if (t1 == null && t2 == null) {
10 return null;
11 }
12 if (t1 == null) {
13 return t2;
14 }
15 if (t2 == null) {
16 return t1;
17 }
18
19 TreeNode t = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
20 t.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
21 t.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
22 return t;
23 }
771. Jewels and Stones
public class Lc771 {
public static int numJewelsInStones(String J, String S) {
String[] strJ = convertToAscall(J);
String[] strS = convertToAscall(S);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strS.length; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k < strJ.length; k++) {
if (strS[i].equals(strJ[k])) {
count++;
break;
}
}
}
return count;
}
private static String[] convertToAscall(String s) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars) {
sb.append((int) c).append(",");
}
return sb.toString().split(",");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String S = "aAAbbbddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddb";
String J = "addddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddA";
System.out.println(numJewelsInStones(J, S));
}
}

leetcode 刷题记录(java)-持续更新的更多相关文章
- leetcode刷题记录--js
leetcode刷题记录 两数之和 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标. 你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案.但 ...
- Leetcode刷题记录(python3)
Leetcode刷题记录(python3) 顺序刷题 1~5 ---1.两数之和 ---2.两数相加 ---3. 无重复字符的最长子串 ---4.寻找两个有序数组的中位数 ---5.最长回文子串 6- ...
- LeetCode刷题记录(python3)
由于之前对算法题接触不多,因此暂时只做easy和medium难度的题. 看完了<算法(第四版)>后重新开始刷LeetCode了,这次决定按topic来刷题,有一个大致的方向.有些题不止包含 ...
- LeetCode 刷题记录(二)
写在前面:因为要准备面试,开始了在[LeetCode]上刷题的历程.LeetCode上一共有大约150道题目,本文记录我在<http://oj.leetcode.com>上AC的所有题目, ...
- LeetCode 刷题记录
写在前面:因为要准备面试,开始了在[LeetCode]上刷题的历程.LeetCode上一共有大约150道题目,本文记录我在<http://oj.leetcode.com>上AC的所有题目, ...
- LeetCode动态规划题总结【持续更新】
以下题号均为LeetCode题号,便于查看原题. 10. Regular Expression Matching 题意:实现字符串的正则匹配,包含'.' 和 '*'.'.' 匹配任意一个字符,&quo ...
- leetcode刷题记录——树
递归 104.二叉树的最大深度 /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * Tree ...
- 算法进阶之Leetcode刷题记录
目录 引言 题目 1.两数之和 题目 解题笔记 7.反转整数 题目 解题笔记 9.回文数 题目 解题笔记 13.罗马数字转整数 题目 解题笔记 14.最长公共前缀 题目 解题笔记 20.有效的括号 题 ...
- leetcode刷题记录——字符串
242.有效地字母异位词 由于本题的字符串只包含 26 个小写字符,因此可以使用长度为 26 的整型数组对字符串出现的字符进行统计,并对比字母出现的次数是否一致.不再使用 HashMap. toCha ...
随机推荐
- JSP+java上传图片到服务器,并将地址保存至MYSQL + JSP网页显示服务器的图片
这两天遇到个需求——用户头像修改功能. 查了好多资料,不是代码不全,就是某些高端框架,卡了好久,今已实现,分享给大家,如果有更好的方法,非常感谢可以在下方评论区写出 一.整体项目架构 二.web.xm ...
- HTML5-新增语义化结构标签
总结目录结构: 1.简洁的DOCTYPE声明 2.新的布局结构标签 header,article,section,aside,footer 3.新的其它常用标签: nav,hgroup,figure, ...
- 使用.csv文件
引用自:https://blog.csdn.net/vision_tung/article/details/79845758 通用爬虫:https://blog.csdn.net/Vision_Tun ...
- kudu集群高可用搭建
首先咱得有KUDU安装包 这里就不提供直接下载地址了(因为有5G,我 的服务器网卡只有4M,你们下的很慢) 这里使用的是CDH版本 官方下载地址http://archive.cloudera.com/ ...
- 【iOS】copy 关键字
以前没注意过 iOS 的 copy, nonatomic, assign, weak, strong 等关键字. 偏偏今天遇到了一个问题,恰恰是关键字的问题,如图: 之前用的是 assign, 没有用 ...
- 疯子的算法总结(二) STL Ⅰ 算法 ( algorithm )
写在前面: 为了能够使后续的代码具有高效简洁的特点,在这里讲一下STL,就不用自己写堆,写队列,但是做为ACMer不用学的很全面,我认为够用就好,我只写我用的比较多的. 什么是STL(STl内容): ...
- sqoop 密码别名模式 --password-alias
sqoop要使用别名模式隐藏密码 1.首先使用命令创建别名 hadoop credential create xiaopengfei -provider jceks://hdfs/user/pass ...
- linux安装MySQL后输入mysql显示 ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket
我是小白,大佬勿喷 *** linux安装MySQL后输入mysql显示 ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through ...
- opencv3 编程入门学习笔记(一): 基本函数介绍
滤波 blur (均值滤波) 均值滤波是典型的线性滤波算法, 主要方法为领域平均法(即用一片图像区域的各个像素的平均值来代替原图像中的各个像素值) 缺点: 不能很好的保护图像细节, 在图像去噪的同时也 ...
- Python模块之pexpect
一.pexpect模块介绍 Pexpect使Python成为控制其他应用程序的更好工具.可以理解为Linux下的expect的Python封装,通过pexpect我们可以实现对ssh,ftp,pass ...