201871010106-丁宣元 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
201871010106-丁宣元 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结
正文开头:
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://home.cnblogs.com/u/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/12031970.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
(1) 掌握Java应用程序的打包操作;
(2) 掌握线程概念; (3) 掌握线程创建的两种技术。 (4) 学习设计应用程序的GUI。 |
正文内容:
第一部分:总结教材14.1-14.3知识内容
第十四章(14.1-14.3) 并发
14.1什么是线程
1.程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本。
2.进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载、执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程。
3.多任务:在同一刻运行多个程序的能力
4.多线程程序:一个程序同时执行多个任务。每一个任务称为一个线程
.多线程与多进程的区别:
多进程:每个进程拥有自己的一套变量
多线程:共享数据
.使用线程可以给其他任务提供机会
7.使用多线程的两种途径:
a.创建Thread类的子类
eg:在Thread类派生出一个子类,在该子类中重写run()方法。
class hand extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
……
}
}
完整:class hand extends Thread
{
public void run()
{……}
}
创建该子类的对象 Lefthand left=new Lefthand();
Righthand right=new Righthand();
用start()方法启动线程 left.start();
right.start();
b.在定义时实现Runnable接口的类
重写run方法-> 创建该类对象,以此为参数建立Thread 类的对象->调用Thread类对象start方法启动线程
eg:class XX implements Runnable
{
public void run()
{
}
}
14-2中断线程
1.没有一个可以强制中断线程的方法,但interrupt方法可以用来请求终止线程
2.详细过程:
当对一个线程调用interrupt方法时,线程的中断状态将被置位。这是boolean的标志,应当不断检查这个标志,以判断是否中断。
判断是否被置位可以调用静态的Thread.currentThread方法获得当前线程,再调用isInterrupted方法:
eg:while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() && more work to do)
{
...
}
若阻塞,则无法检测中断状态,会产生异常。
线程将简单的将中断作为一个终止请求。
14-3 线程状态
1.6种状态:new新创建,
Runnable可运行,
Blocked被阻塞,
Waiting等待,
Timed waiting计时等待,
Terminated被终止
2.新创建线程
线程对象刚创建,没有启动,线程处于不可运行状态
3.可运行线程
调用start方法,线程处于runnable可运行状态
eg:thread.start();
一旦一个线程开始运行,不必始终保持运行。
运行中的线程被中断,目的是为了让其他线程获得运行机会。
4.被阻塞线程和等待线程
此时暂时不活动,不运行任何代码且耗资最少,直至线程调度器重新激活它。
等待阻塞 :调用线程的wait()方法,使线程等待某项工作的完成
同步阻塞 :获取synchronized同步锁失败会进入同步阻塞状态
其他阻塞 :调用线程的sleep(),join() 或发出了I/O请求,线程进入到阻塞状态。
5.被阻塞的线程
a.Terminated终止原因:
run方法正常退出而自然死亡
因为一个没有捕获的异常终止了run方法而意外死亡
注:调用stop方法杀死一个线程,不要用
b.sleep(),wait()是常用的引起线程阻塞的方法

第二部分:实验部分
实验1:测试程序1
实验1: 导入第13章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1
在elipse IDE中调试运行教材585页程序13-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
将所生成的JAR文件移到另外一个不同的目录中,再运行该归档文件,以便确认程序是从JAR文件中,而不是从当前目录中读取的资源。
掌握创建JAR文件的方法;
代码:
package resource; import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.41 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ResourceTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ResourceTestFrame();
frame.setTitle("ResourceTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that loads image and text resources.
*/
class ResourceTestFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; public ResourceTestFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);//来自JComponent类
URL aboutURL = getClass().getResource("about.gif");
Image img = new ImageIcon(aboutURL).getImage();//在找到ResourceTest类的地方查找about.gif文件
setIconImage(img); JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea();
InputStream stream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("about.txt");//读取about.txt文件
try (Scanner in = new Scanner(stream, "UTF-8"))//UTF-8文本编码标准
{
while (in.hasNext())
textArea.append(in.nextLine() + "\n");
}
add(textArea);//将文本区添加到框架上
}
}
结果:
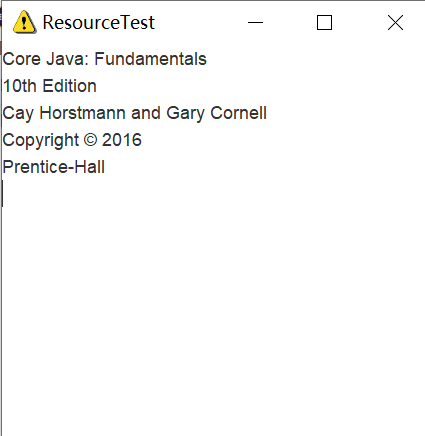 此时:
此时:
归档:Export -> JAR file
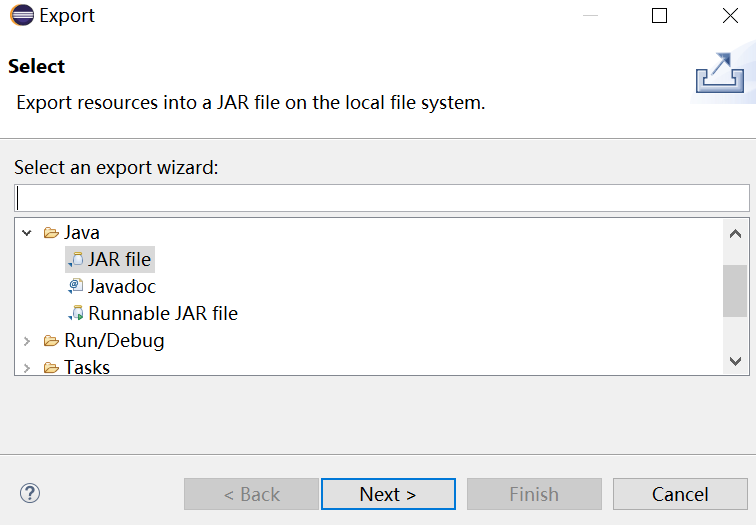
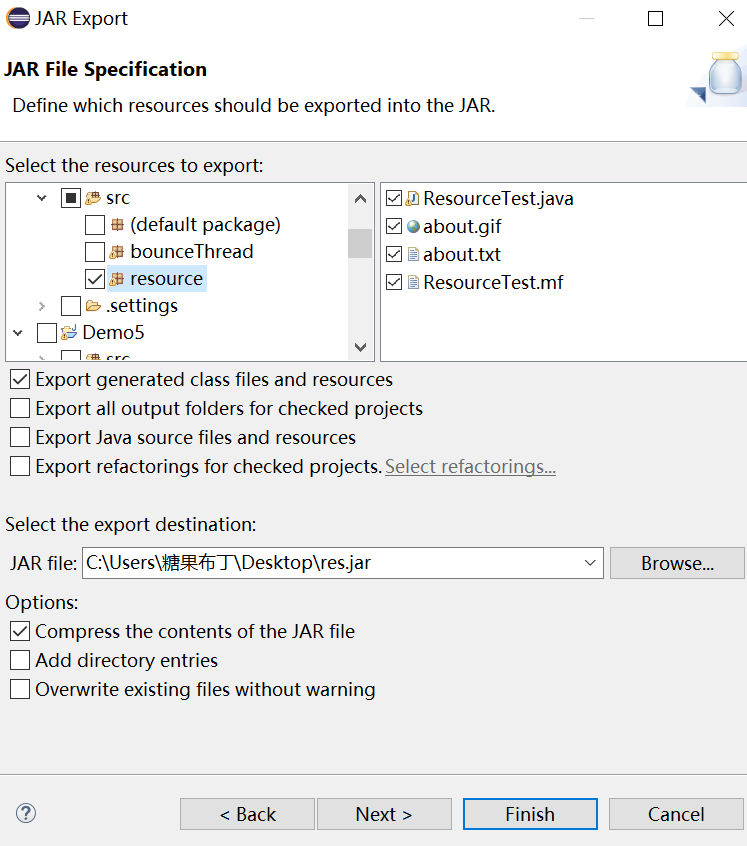

实验1:测试程序2
在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
掌握线程概念;
掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
代码:
class Lefthand extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ sleep(500); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ sleep(300); }
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest
{
static Lefthand left;
static Righthand right;
public static void main(String[] args)
{ left=new Lefthand();
right=new Righthand();
left.start();//启动线程
right.start();
}
}
结果:

利用Runnable接口改造程序
class Lefthand1 implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("You are Students!");
try{ Thread.sleep(500);//休眠500ms
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Lefthand error.");}
}
}
}
class Righthand1 implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{ System.out.println("I am a Teacher!");
try{ Thread.sleep(300);//休眠300ms
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{ System.out.println("Righthand error.");}
}
}
}
public class ThreadT
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Righthand righthand = new Righthand();
Lefthand lefthand = new Lefthand();
Thread right = new Thread(righthand);
right.start();
Thread left=new Thread(lefthand);
left.start();
}
}
结果:
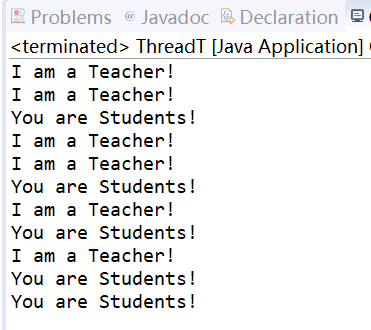
不同方法实现多线程
实验1:测试程序3
在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
对比两个程序,理解线程的概念和用途;
掌握线程创建的两种技术。
14-1、14-2 、14-3代码:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* Shows an animated bouncing ball.
* @version 1.34 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bounce
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BounceFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* The frame with ball component and buttons.
*/
class BounceFrame extends JFrame
{
private BallComponent comp;
public static final int STEPS = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 3; /**
* Constructs the frame with the component for showing the bouncing ball and
* Start and Close buttons
*/
public BounceFrame()
{
setTitle("Bounce");
comp = new BallComponent();
add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER);//边框布局显示在中心位置
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall());//添加两个按钮
addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0));
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
} /**
* Adds a button to a container.
* @param c the container
* @param title the button title
* @param listener the action listener for the button
*/
public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(title);
c.add(button);
button.addActionListener(listener);
} /**
* Adds a bouncing ball to the panel and makes it bounce 1,000 times.加一个球
*/
public void addBall()
{
try//异常处理
{
Ball ball = new Ball();
comp.add(ball); for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++)
{
ball.move(comp.getBounds());
comp.paint(comp.getGraphics());
Thread.sleep(DELAY);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
}
}
import java.awt.geom.*; /**
* A ball that moves and bounces off the edges of a rectangle
* @version 1.33 2007-05-17
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Ball
{
private static final int XSIZE = 15;
private static final int YSIZE = 15;
private double x = 0;
private double y = 0;
private double dx = 1;
private double dy = 1; /**
* 将球移动至下一个位置,若碰到一边,变向
*/
public void move(Rectangle2D bounds)
{
x += dx;
y += dy;
if (x < bounds.getMinX())//四个方向
{
x = bounds.getMinX();
dx = -dx;
}
if (x + XSIZE >= bounds.getMaxX())
{
x = bounds.getMaxX() - XSIZE;
dx = -dx;
}
if (y < bounds.getMinY())
{
y = bounds.getMinY();
dy = -dy;
}
if (y + YSIZE >= bounds.getMaxY())
{
y = bounds.getMaxY() - YSIZE;
dy = -dy;
}
} /**
*球在当前位置
*/
public Ellipse2D getShape()
{
return new Ellipse2D.Double(x, y, XSIZE, YSIZE);
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* The component that draws the balls.
* @version 1.34 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BallComponent extends JPanel
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 450;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; private java.util.List<Ball> balls = new ArrayList<>(); /**
* Add a ball to the component.
* @param b the ball to add
*/
public void add(Ball b)
{
balls.add(b);
} public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
super.paintComponent(g); // 擦除背景
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
for (Ball b : balls)
{
g2.fill(b.getShape());
}
} public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
}
}
结果:
14-4
package bounceThread; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /**
* Shows animated bouncing balls.
* @version 1.34 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class BounceThread
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new BounceFrame();
frame.setTitle("BounceThread");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* The frame with panel and buttons.
*/
class BounceFrame extends JFrame
{
private BallComponent comp;
public static final int STEPS = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 5; /**
* Constructs the frame with the component for showing the bouncing ball and
* Start and Close buttons
*/
public BounceFrame()
{
comp = new BallComponent();
add(comp, BorderLayout.CENTER);//加在中间
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();//容器
addButton(buttonPanel, "Start", event -> addBall());//start加ball
addButton(buttonPanel, "Close", event -> System.exit(0));//colse退出程序
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();//自适应窗口大小
} /**
* Adds a button to a container.
* @param c the container
* @param title the button title
* @param listener the action listener for the button
*/
public void addButton(Container c, String title, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(title);
c.add(button);
button.addActionListener(listener);
} /**
* Adds a bouncing ball to the canvas and starts a thread to make it bounce
*/
public void addBall()
{
Ball ball = new Ball();
comp.add(ball);
Runnable r = () -> { //lambda表达式,回调程序设计
try
{
for (int i = 1; i <= STEPS; i++)
{
ball.move(comp.getBounds());
comp.repaint();//重绘
Thread.sleep(DELAY);//延迟
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();//启动
}
}
结果:
并发式设计:点一次可以再点一次,可以出现多个小球。start键可以点击多次,同时引入多个小球运动。
普通设计:只能出现一个小球,只能这个球结束后,再出现下一个球
实验总结:
通过本次实验,我了解了:1.Java应用程序的打包操作 2.了解线程的基本知识及概念 3.掌握线程创建的两种技术 4.学习设计应用程序的GUI
通过本次实验,加深对线程新概念的理解。程序一不会归档,求助于同学,明白了如何做。结对编程一直是难点,搜索资料知识,参照例码,还存在一些问题,需再修改。编程一直是最弱的地方,要多加练习。
201871010106-丁宣元 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十六周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201571030332 扎西平措 《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计Java>第八周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https: ...
- 201771010118马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.接口 在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成.Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第七周学习总结
第七周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1.继承是面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming-OOP)中软件重用的关键技术.继承机制使用已经定义的类作为基础建立新的类定义,新 ...
- 201771010128 王玉兰《面象对象程序设计 (Java) 》第六周学习总结
---恢复内容开始--- 第一部分:基础知识总结: 1.继承 A:用已有类来构建新类的一种机制,当定义了一个新类继承一个类时,这个新类就继承了这个类的方法和域以适应新的情况: B:特点:具有层次结构. ...
- 201871010126 王亚涛《面向对象程序设计 JAVA》 第十三周学习总结
内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/ ...
- 马凯军201771010116《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一,理论知识学习部分 6.1.1 接口概念 两种含义:一,Java接口,Java语言中存在的结构,有特定的语法和结构:二,一个类所具有的方法的特征集合,是一种逻辑上的抽象.前者叫做“Java接口”,后 ...
- 周强201771010141《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一.理论知识学习部分 Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个接口. 接口体中包含常量定义和方法定义,接口中只进行方法的声明,不提供方法的实现. 类似建立类的继承关系 ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010126 王亚涛 《面向对象程序设计 (Java)》第十七周学习总结
内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/12 ...
随机推荐
- leetcode 排序问题
1.堆排序 //大顶堆的构造,传入的i是父节点 void HeapAdjust(int k[],int p,int n) { int i,temp; temp = k[p]; * p; i <= ...
- jenkins构建:通过testng.xml构建项目
1.项目的pom.xml中build下添加maven插件,xmlFileName为可变参数 2.jenkins新建maven项目 构建脚本: 原文:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ ...
- 使用Appium进行微信公众号自动化测试
查看Android的webview视图版本:手机链接电脑后在电脑Chrome打开页面chrome://inspect/#devices查看Android的Chrome内核版本 下载与该版本相对 ...
- CF613B Skills
CF613B Skills 洛谷评测传送门 题目描述 Lesha plays the recently published new version of the legendary game hack ...
- 《京东到家订单中心 Elasticsearch 演进历程》----阅读
上篇通过阅读文章对京东到家的架构分析有了初步了解,这次对文章(https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU1MzE2NzIzMg==&mid=2247486889& ...
- ubuntu 安装rocketmq
RocketMQ环境要求 ) 64bit OS,linux/Unix/Max ) 64bit JDK 1.8+ ) Maven 3.2.x ) Git 一.下载并构建 git clone https: ...
- JavaScript forEach() 方法
JavaScript forEach() 方法 JavaScript Array 对象 实例 列出数组的每个元素: <button onclick="numbers.forEach( ...
- Python 小案例实战 —— 简易银行存取款查询系统
Python 小案例实战 -- 简易银行存取款查询系统 涉及知识点 包的调用 字典.列表的混合运用 列表元素索引.追加 基本的循环与分支结构 源码 import sys import time ban ...
- windows10 启动安卓模拟器会蓝屏的解决方案
最近突然想用win10装个安卓模拟器玩游戏,然后提示vt被占用. 查了一下,了解到在windows 10 系统上,我们会用vmware,virtual box ,hyper-v,安卓模拟器,360安全 ...
- asp.net core系列 63 领域模型架构 eShopOnWeb项目分析 上
一.概述 本篇继续探讨web应用架构,讲基于DDD风格下最初的领域模型架构,不同于DDD风格下CQRS架构,二者架构主要区别是领域层的变化. 架构的演变是从领域模型到CQRS, 一开始DDD是用领域 ...
