201871010126 王亚涛 《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十一周学习总结
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11815810.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
学习目标 1.掌握java异常处理技术; 2.了解断言的用法; 3.了解日志的用途; 4.掌握程序基础调试技巧。 |
第八章 泛型程序设计
8.1 为什么要使用泛型程序设计
8.1.1泛型类的定义
一个泛型类(generic class)就是具有一个或多个类型变量的类,即创建用类型作为参数的类。如一个泛型类定义格式如下:
class Generics<K,V>
其中K和V是类的可变类型参数。
1).Pair类引入了一个类型变量T,用尖括号(<>)括起来,并放在类名的后面。
2).泛型类可以有多个类型变量。例如:
public class Pair<T, U> { … }
3).类的类型变量用于指定方法的返回类型以及域、
局部变量的类型。
8.1.2泛型方法的声明
1).除了泛型类外,还可以只单独定义一个方法作为泛型方法,用于指定方法参数或者返回值为泛型类型,留待方法调用时确定。
2).泛型方法可以声明在泛型类中,也可以声明在普通类中。
8.1.3泛型接口的定义
1).定义

2).定义泛型变量的上界
public class NumberGeneric< T extends Number>
a.上述声明规定了NumberGeneric类所能处理的泛型变量类型需和Number有继承关系;
b.extends关键字所声明的上界既可以是一个类,也可以是一个接口。
3).定义泛型变量的下界
泛型变量下界的说明
“?”符号表明参数的类型可以是任何一种类型,它和参数T的含义是有区别的。T表示一种未知类型,而“?”表示任何一种类型。这种通配符一般有以下三种用法:
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型类的定义与使用;
(3) 了解泛型方法的声明与使用;
(4) 掌握泛型接口的定义与实现;
(5) 理解泛型程序设计,理解其用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第8章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、调试、运行教材311、312页代码,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型类定义及使用代码处添加注释;
掌握泛型类的定义及使用。
实验代码如下:
package pair1; /**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //pair类引入了一个类型变量T
{
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }//无参构造器
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
package pair1; /**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };
Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//类名调用,minmax是static静态方法
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg
{
/**
* Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings.//获得数组的最大值与最小值
* @param a an array of strings
* @return a pair with the min and max values, or null if a is null or empty
*/
public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a)
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;//空引用和空数组
String min = a[0];
String max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);//返回新队
}
}
实验截图如下:
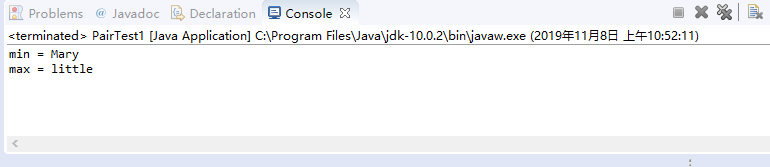
泛型类的定义与使用:
测试程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材315页 PairTest2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型程序设计代码处添加相关注释;
l 了解泛型方法、泛型变量限定的定义及用途。
程序代码如下:
package pair2; /**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //pair类引入了一个类型变量T
{
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
package pair2; import java.time.*; /**
* @version 1.02 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDate[] birthdays =
{
LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper
LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace
LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann
LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22),
};//初始化一个localDate对象,名为birthdays
Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays);//静态方法可以通过类名调用
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg
{
/**
Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T.//获取T类型对象数组的最小值和最大值
@param a an array of objects of type T
@return a pair with the min and max values, or null if a is null or empty
*/
public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a)
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
T min = a[0];
T max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);
}
}
运行截图如下:

总结:
1、泛型类定义的泛型,在整个类中有效。如果被方法使用,那么泛型类的对象明确要操作的具体类型后,所有要操作的类型就已经固定了。
2、为了让不同方法可以操作不同类型,而且类型还不确定。那么可以将泛型定义在方法上。
3、特殊之处:
静态方法不可以访问类上定义的泛型。
如果静态方法操作的应用数据类型不确定,可以将泛型定义在方法上。
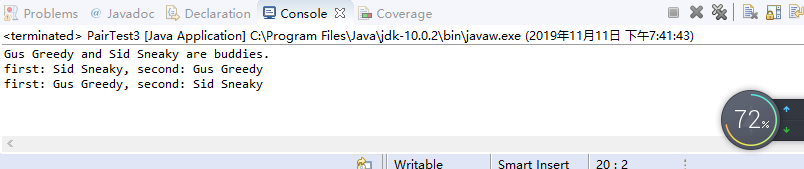
测试程序3:
l 用调试运行教材335页 PairTest3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解通配符类型的定义及用途。
实验代码如下:
package pair3; /**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15);//创建了一个Manager类对象
var cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15);
var buddies = new Pair<Manager>(ceo, cfo);
printBuddies(buddies); ceo.setBonus(1000000);
cfo.setBonus(500000);
Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo }; var result = new Pair<Employee>();
minmaxBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
maxminBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
} public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p)
{
Employee first = p.getFirst();
Employee second = p.getSecond();
System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies.");
} public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)
{
if (a.length == 0) return;
Manager min = a[0];
Manager max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i];
if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i];
}
result.setFirst(min);
result.setSecond(max);
} public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)
{
minmaxBonus(a, result);
PairAlg.swapHelper(result); // OK--swapHelper captures wildcard type//swapHelper捕获通配符类型
}
// can't write public static <T super manager> . . .// 不能写公共静态 <T super manager> ...
} class PairAlg
{
public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)//?表示:类型变量通配符
{
return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null;
} public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); } public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p)
{
T t = p.getFirst();
p.setFirst(p.getSecond());
p.setSecond(t);
}
}
package pair3; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; /**
@param name the employee's name
@param salary the salary
@param year the hire year
@param month the hire month
@param day the hire day
*/
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);//调用父类的姓名。工资。年。月。日
bonus = 0;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double b)
{
bonus = b;
} public double getBonus()
{
return bonus;
}
}
package pair3; import java.time.*; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
package pair1; /**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //pair类引入了一个类型变量T
{
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }//无参构造器
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
运行截图如下:
总结:
实验2:结对编程练习,将程序提交到PTA(2019面向对象程序设计基础知识测试题(2))
(1) 编写一个泛型接口GeneralStack,要求类中方法对任何引用类型数据都适用。GeneralStack接口中方法如下:
push(item); //如item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。
pop(); //出栈,如为栈为空,则返回null。
peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty();//如为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素数量
(2)定义GeneralStack的子类ArrayListGeneralStack,要求:
ü 类内使用ArrayList对象存储堆栈数据,名为list;
ü 方法: public String toString()//代码为return list.toString();
ü 代码中不要出现类型不安全的强制转换。
(3)定义Car类,类的属性有:
private int id;
private String name;
方法:Eclipse自动生成setter/getter,toString方法。
(4)main方法要求
ü 输入选项,有quit, Integer, Double, Car 4个选项。如果输入quit,程序直接退出。否则,输入整数m与n。m代表入栈个数,n代表出栈个数。然后声明栈变量stack。
ü 输入Integer,打印Integer Test。建立可以存放Integer类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。入栈m次,出栈n次。打印栈的toString方法。最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
ü 输入Double ,打印Double Test。剩下的与输入Integer一样。
ü 输入Car,打印Car Test。其他操作与Integer、Double基本一样。只不过最后将栈中元素出栈,并将其name依次输出。
特别注意:如果栈为空,继续出栈,返回null
输入样例
Integer
5
2
1 2 3 4 5
Double
5
3
1.1 2.0 4.9 5.7 7.2
Car
3
2
1 Ford
2 Cherry
3 BYD
quit
输出样
Integer Test
push:1
push:2
push:3
push:4
push:5
pop:5
pop:4
[1, 2, 3]
sum=6
interface GeneralStack
Double Test
push:1.1
push:2.0
push:4.9
push:5.7
push:7.2
pop:7.2
pop:5.7
pop:4.9
[1.1, 2.0]
sum=3.1
interface GeneralStack
Car Test
push:Car [id=1, name=Ford]
push:Car [id=2, name=Cherry]
push:Car [id=3, name=BYD]
pop:Car [id=3, name=BYD]
pop:Car [id=2, name=Cherry]
[Car [id=1, name=Ford]]
Ford
interface GeneralStack
结对编程代码如下:
package wyt;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner; interface GeneralStack<T>{
public T push(T item); //如果item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。
public T pop(); //出栈,如为栈为空,则返回null。
public T peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty(); //如为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素数量
}
class ArrayListGeneralStack implements GeneralStack{ //创建一个实现GeneralStack接口的类
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
@Override //重写toString方法
public String toString() {
return list.toString();
} @Override //重写压栈方法
public Object push(Object item) {
if (list.add(item)){
return item;
}else {
return false;
}
} @Override //重写出栈方法
public Object pop() {
if (list.size()==0){ //判断栈为空时,返回null
return null;
}
return list.remove(list.size()-1);
} @Override //重写获取栈顶元素的函数
public Object peek() {
return list.get(list.size()-1);
} @Override
public boolean empty() { //栈为空时,直接返回boolean值
if (list.size()==0){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
} @Override //重写得到栈中元素个数的函数
public int size() {
return list.size();
}
} class Car{ //定义一个Car类
private int id; //两个私有属性
private String name; @Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [" +
"id=" + id +
", name=" + name +
']';
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Car(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
String s=sc.nextLine();
//输入选项,有quit, Integer, Double, Car 4个选项。
if (s.equals("Double")){ //输入Double ,打印Double Test。
System.out.println("Double Test");
int count=sc.nextInt();
int pop_time=sc.nextInt();
ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack();//建立可以存放Double类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ //入栈次数
System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(sc.nextDouble()));
}
for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ //出栈次数
System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); //打印栈的toString方法
double sum=0;
int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
sum+=(double)arrayListGeneralStack.pop(); //最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
System.out.println("interface GeneralStack");
}else if (s.equals("Integer")){ //输入Integer,打印Integer Test。
System.out.println("Integer Test");
int count=sc.nextInt();
int pop_time=sc.nextInt();
ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack();//建立可以存放Integer类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ //入栈次数
System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(sc.nextInt()));
}
for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ //出栈次数
System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); //打印栈的toString方法。
int sum=0;
int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
sum+=(int)arrayListGeneralStack.pop(); //最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
System.out.println("interface GeneralStack");
}else if (s.equals("Car")){ //输入Car,打印Car Test。
System.out.println("Car Test");
int count=sc.nextInt();
int pop_time=sc.nextInt();
ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack(); //创建可以存放Car类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ //入栈次数
int id=sc.nextInt();
String name=sc.next();
Car car = new Car(id,name);
System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(car));
}
for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ //出栈次数
System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); //定义toString方法
if (arrayListGeneralStack.size()>0){ //栈不为空
int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
Car car=(Car) arrayListGeneralStack.pop();//将栈中元素出栈,并将其name依次输出。
System.out.println(car.getName());
}
}
System.out.println("interface GeneralStack");
}else if (s.equals("quit")){ //如果输入quit,程序直接退出。
break;
}
} }
}
运行截图如下:

实验总结:
1):这周我们学习了第八章泛型程序设计中的相关知识点,定义了简单的泛型类,通过上课时老师的讲解和课下学长的讲解,对不会的知识点有了进一步的掌握,对Java这门学科有了更深入的了解。
2):这周的实验有对上周实验的反思,我发现了很多不足。首先接手问题之后的思路不清晰,其次代码编写不够,这周泛型设计的学习,了解到泛型类具备可重用性、类型安全和效率等性质,是程序性能得到提升。课下我还需继续努力。
201871010126 王亚涛 《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十一周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 20172325 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》第十一周学习总结
20172325 2017-2018-2 <Java程序设计>第十一周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 Android简介 Android操作系统是一种多用户的Linux系统,每个应用程序作为单 ...
随机推荐
- leetcode 贪心算法
贪心算法中,是以自顶向下的方式使用最优子结构,贪心算法会先做选择,在当时看起来是最优的选择,然后再求解一个结果的子问题. 贪心算法是使所做的选择看起来都是当前最佳的,期望通过所做的局部最优选择来产生一 ...
- 【Eureka篇三】Eureka如何管理服务调用(6)
在Eureka Client启动时,将自身的服务的信息发送到Eureka Server.然后进行2调用当前服务器节点中的其他服务信息,保存到Eureka Client中.当服务间相互调用其它服务时,在 ...
- 微信小程序云开发-从0打造云音乐全栈小程序
第1章 首门小程序“云开发”课程,你值得学习本章主要介绍什么是小程序云开发以及学习云开发的重要性,并介绍项目的整体架构,真机演示项目功能,详细介绍整体课程安排.课程适用人群以及需要掌握的前置知识.通过 ...
- Vue中MVVM模式的双向绑定原理 和 代码的实现
今天带大家简单的实现MVVM模式,Object.defineProperty代理(proxy)数据 MVVM的实现方式: 模板编译(Compile) 数据劫持(Observer) Object ...
- flask 第一章
1.安装flask 首先安装python的虚拟环境,每个环境之间的包并不会产生冲突 ,相当于一个单独的 小空间. 由于自己使用的是windows开发环境 所以安装虚拟包的命令如下 pip inst ...
- 【Oracle】Oracle自动内存管理AMM
Oracle自动内存管理AMM AMM(Automatic Memory Management)自动内存管理,分配一整块内存区域,Oracle数据库自动分配管理SGA和PGA的内存.具体通过设置两个参 ...
- [LeetCode#178]Rank Scores
Write a SQL query to rank scores. If there is a tie between two scores, both should have the same ra ...
- sudo: ulimit: command not found
在这看到的:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17483723/command-not-found-when-using-sudo-ulimit 修改系统文件打开数 ...
- javascript的数据类型检测
JavaScript有两种数据类型,分别是基本数据类型和引用数据类型.其中基本数据类型包括Undefined.Null.Boolean.Number.String和Symbol(ES6新增,表示独一无 ...
- EntityFrameworkCore 学习笔记之示例一
直接贴代码了: 1. Program.cs using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System; using System.Threading.Task ...
