React.js Tutorial: React Component Lifecycle
Introduction about React component lifecycle.
1 Lifecycle
A React component in browser can be any of the following three statuses: mounted, update and unmounted.
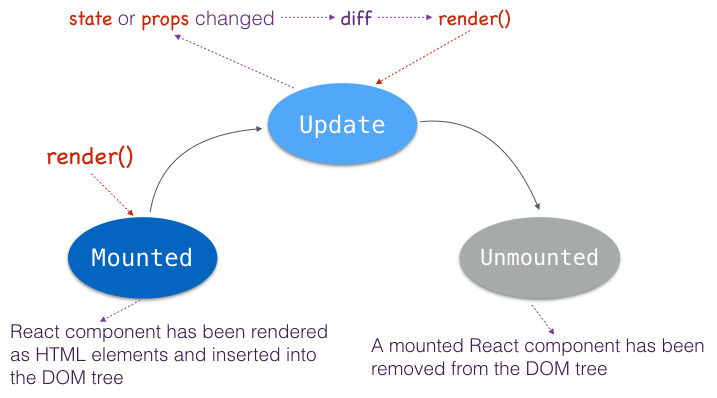
So React component lifecycle can be divided into three phases according to these statuses: mounting, updating and unmounting.
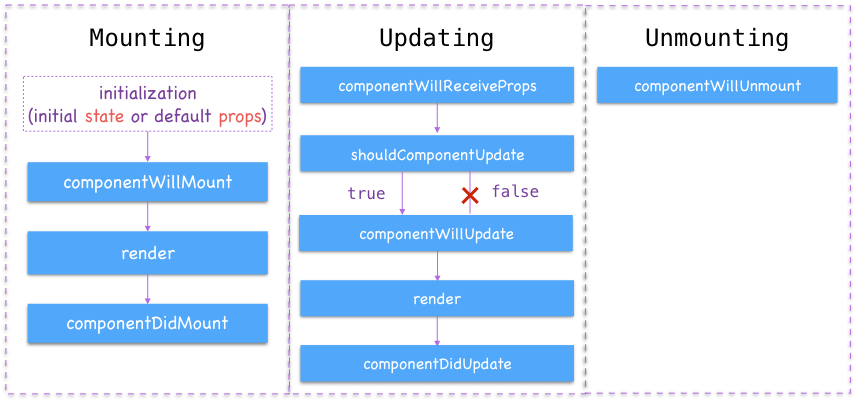
2 Mounting
React.js exposed interfaces or hook methods in each phase of component lifecycle.
2.1 Initializing state
You can optionally set initial state value in constructor() method of the component if you are using ES6 syntax.
const tom_and_jerry = [
{
name: 'Tom',
score: 55
},
{
name: 'Jerry',
score: 80
}
];
class ScoreBoard extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { players: tom_and_jerry }
}
// ...
}If you are using ES5 syntax, getInitialState() in the right place to initialize component state.
var ScoreBoard = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
return {
players: tom_and_jerry
}
},
// ...
});The getInitialState() method is called only one time before the component is mounted.
Initialization of state should typically only be done in a top level component, which acts as a role of controller view in your page.
2.2 Default props
You can also define default values of component props (properties) if the parent component does not declare their values.
Return default props using ES7+ static property initializer.
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
static defaultProps = {
name: 'Nobody',
score: 0
}
// ...
}Default props in ES6:
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
// ...
}
SinglePlayer.defaultProps = {
name: 'Nobody',
score: 0
}You can define getDefaultProps() method in ES5.
var SinglePlayer = React.createClass({
getDefaultProps: function() {
return {
name: 'Nobody',
score: 0
}
}
});The getDefaultProps() method is called only once before any instance of the component is created. So you should avoid using this.props inside getDefaultProps() method.
2.3 componentWillMount()
The componentWillMount() method is invoked only once before initial rendering.
It is also a good place to set initial state value inside componentWillMount().
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
componentWillMount() {
this.setState({
isPassed: this.props.score >= 60
});
alert('componentWillMount => ' + this.props.name);
console.log('componentWillMount => ' + this.props.name);
}
// ...
}2.4 componentDidMount()
This lifecycle method will be invoked after rendering.
It is the right place to access DOM of the component.
class ScoreBoard extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this._handleScroll = this.handleScroll.bind(this);
}
handleScroll() {}
componentDidMount() {
alert('componentDidMount in NoticeBoard');
window.addEventListener('scroll', this._handleScroll);
}
// ...
}3 Updating
3.1 componentWillReceiveProps()
void componentWillReceiveProps(object nextProps)This method will be invoked when a component is receiving new props. componentWillReceiveProps() won't be called for the initial rendering.
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
// Calculate state according to props changes
this.setState({
isPassed: nextProps.score >= 60
});
}
}The old props can be accessed via this.props inside componentWillReceiveProps(). Typically, you can set state according to changes of props in this method.
3.2 shouldComponentUpdate()
boolean shouldComponentUpdate(object nextProps,
object nextState)shouldComponentUpdate() will be invoked before rendering when new props or state are being received. This method won't be called on initial rendering.
shouldComponentUpdate() returns true by default.
This method is usually an opportunity to prevent the unnecessary rerendering considering performance. Just let shouldComponentUpdate() return false, then the render() method of the component will be completely skipped until the next props or state change.
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// Don't rerender if score doesn't change,
if ( nextProps.score == this.props.score ) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}3.3 componentWillUpdate()
void componentWillUpdate(object nextProps,
object nextState)Invoked just before render(), but after shouldComponentUpdate() (of course, return a true). This method is not called for the initial rendering.
Use this as an opportunity to prepare for an update.
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
alert('componentWillUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
console.log('componentWillUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
}
}3.4 componentDidUpdate()
void componentDidUpdate(object prevProps,
object prevState)Invoked immediately after the component's updates are flushed to the DOM. This method is not called for the initial rendering.
You can perform DOM operations after an update inside this function.
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
alert('componentDidUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
console.log('componentDidUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
}
}4 Unmounting
void componentWillUnmount()This is invoked immediately before a component is unmounted or removed from the DOM.
Use this as an opportunity to perform cleanup operations. For example, unbind event listeners here to avoid memory leaking.
class ScoreBoard extends React.Component {
componentWillUnmount() {
window.removeEventListener('scroll', this._handleScroll);
}
}5 Sample codes
Complete sample codes to log each lifecycle method call in browser's console.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>React Component Lifecycle Demo</title>
<!-- react includes two parts: react.js and react-dom.js -->
<script src="//fb.me/react-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="//fb.me/react-dom-15.2.1.js"></script>
<!-- babel standalone -->
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/babel-standalone/6.10.3/babel.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
const tom_and_jerry = [
{
name: 'Tom',
score: 55
},
{
name: 'Jerry',
score: 80
}
];
class SinglePlayer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { isPassed: false }
}
componentWillMount() {
// Mark it as 'Pass' if score >= 60
this.setState({
isPassed: this.props.score >= 60
});
console.log('componentWillMount => ' + this.props.name);
alert('componentWillMount => ' + this.props.name);
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount => ' + this.props.name);
alert('componentDidMount => ' + this.props.name);
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
// Calculate state according to props changes
this.setState({
isPassed: nextProps.score >= 60
});
console.log('componentWillReceiveProps => ' + this.props.name + ': ' + nextProps.score);
alert('componentWillReceiveProps => ' + this.props.name + ': ' + nextProps.score);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// Don't rerender if score doesn't change,
if ( nextProps.score == this.props.score ) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate => ' + this.props.name + '? false');
alert('shouldComponentUpdate => ' + this.props.name + '? false');
return false;
}
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate => ' + this.props.name + '? true');
alert('shouldComponentUpdate => ' + this.props.name + '? true');
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('componentWillUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
alert('componentWillUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('componentDidUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
alert('componentDidUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
alert('componentDidUpdate => ' + this.props.name);
}
render() {
console.log("render => " + this.props.name);
return (
<div>
<h5><span>Name: </span>{this.props.name}</h5>
<p><span>Score: </span><em>{this.props.score}</em></p>
<p><span>Pass: </span><input type="checkbox" defaultChecked={this.state.isPassed} disabled={true} /></p>
</div>
);
}
}
class ScoreBoard extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
players: tom_and_jerry
};
}
changeScore(amount) {
if ( typeof(amount) != "number" ) {
return;
}
let players = this.state.players;
let tom = players[0];
tom.score = tom.score + amount;
tom.score = (tom.score > 100) ? 100 : tom.score;
tom.score = (tom.score < 0) ? 0 : tom.score;
players[0] = tom;
this.setState({ players: players });
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>Score Board</h4>
<div>
<button onClick={ (amount) => this.changeScore(5) }>Score of Tom: +5</button>
<button onClick={ (amount) => this.changeScore(-5) }>Score of Tom: -5</button>
</div>
{
this.state.players.map((v, idx) => {
return <SinglePlayer key={idx} name={v.name} score={v.score} />
})
}
</div>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>React Component Lifecycle Demo</h1>
<ScoreBoard />
</div>
)
}
}
// Mount root App component
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'));
</script>
</body>
</html>
https://www.codevoila.com/post/57/reactjs-tutorial-react-component-lifecycleReact.js Tutorial: React Component Lifecycle的更多相关文章
- WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN REACT.JS AND REACT NATIVE?
Amit Ashwini - 09 SEPTEMBER 2017 React.js was developed by Facebook to address its need for a dynami ...
- [React] 10 - Tutorial: router
Ref: REACT JS TUTORIAL #6 - React Router & Intro to Single Page Apps with React JS Ref: REACT JS ...
- React.js入门笔记
# React.js入门笔记 核心提示 这是本人学习react.js的第一篇入门笔记,估计也会是该系列涵盖内容最多的笔记,主要内容来自英文官方文档的快速上手部分和阮一峰博客教程.当然,还有我自己尝试的 ...
- Facebook React.js库 入门实例教程
作者: 阮一峰 日期: 2015年3月31日 现在最热门的前端框架,毫无疑问是 React . 上周,基于 React 的 React Native 发布,结果一天之内,就获得了 5000 颗星,受瞩 ...
- React.js入门
React 入门实例教程 现在最热门的前端框架,毫无疑问是 React . 上周,基于 React 的 React Native 发布,结果一天之内,就获得了 5000 颗星,受瞩目程度可见一斑. ...
- 13个精选的React JS框架
如果你正在使用 React.js 或 React Native 创建用户界面,可以试一试本文推荐的这些框架. React.js 和 React Native 是流行的用户界面(UI)开发平台,且都是开 ...
- React JS 基础知识17条
1. 基础实例 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script src="../build/react.js" ...
- react.js 从零开始(一)
React 是什么? 网络上的解释很多...我这里把他定义为 通过javascript 的形式组件化 html的框架... React 仅仅是 VIEW 层. React 提供了模板语法以及一些函数钩 ...
- 【每天半小时学框架】——React.js的模板语法与组件概念
[重点提前说:组件化与虚拟DOM是React.js的核心理念!] 先抛出一个论题:在React.js中,JSX语法提倡将 HTML 和 CSS 全都写入到JavaScrip ...
随机推荐
- Python3+syslog使用及相关说明
一.说明 1.1 背景说明 syslog这个东西,最早接触是在Z公司做基线安全加固的时候有启用远程日志服务器一项,然后当时还写整理了一篇“rsyslog+loganalyzer远程日志系统搭建教程(C ...
- [终极巨坑]golang+vue开发日记【一】,环境搭建篇
写在前面 这个golang+vue大部分的内容是基于bydmm(橙卡)大佬的视频学来的,我在这里只是做一下个人开发的笔记,就是图一个乐,毕竟我只是个应届毕业生,如果真的要学请:bydmm的b站空间. ...
- docker入门实例(转载)
1.Docker 是什么?Docker 是一个开源的应用容器引擎,让开发者可以打包他们的应用以及依赖包到一个可移植的镜像中,然后发布到任何流行的 Linux 或 Windows 机器上( 摘自百度 ) ...
- Django 模板语言 变量名称
Django 模板语言 变量名称 模板语言中已变量形式显示 # view 文件内 def func(request): return render(request,"index.html&q ...
- 微信小程序之使用函数防抖与函数节流
函数防抖和函数节流都是老生常谈的问题了.这两种方式都能优化 js 的性能.有些人可能会搞混两个的概念.所以,我以自己的理解,来解释这两个概念的含义.并且列举在小程序中这两个方法的使用. 函数防抖: 英 ...
- 可落地的DDD(3)-如何利用DDD进行微服务的划分
摘要 前面两篇介绍了DDD的目标管理.DDD的工程结构调整.这篇讨论微服务的划分.微服务是目前后端比较流行的架构体系了,那么如何做好一个微服务的划分?一个微服务的粒度应该是多大呢?这篇主要介绍如何结合 ...
- docker 安装tomcat容器和mysql容器
1. docker pull mysql:5.6 2.docker run -p 3306:3306 --name mysql -v /data/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql/conf. ...
- /etc/skel目录
/etc/skel目录 Linux中的/etc/skel目录(skel是skeleton的缩写,意为骨骼.框架.)是用来存放新用户配置文件的目录,当我们添加新用户时,这个目录下的所有文件会自动被复制到 ...
- EasyUI datagrid-export 将datagrid的数据导出至Excel-解决科学计数法
通过EasyUI datagrid-export.js 将datagrid的数据导出至Excel的时候,如果有类似身份证一样很长的数字,需要在后台返回数据的时候在数字前增加一个 “ ”,将数字转为字符 ...
- Python进阶----索引原理,mysql常见的索引,索引的使用,索引的优化,不能命中索引的情况,explain执行计划,慢查询和慢日志, 多表联查优化
Python进阶----索引原理,mysql常见的索引,索引的使用,索引的优化,不能命中索引的情况,explain执行计划,慢查询和慢日志, 多表联查优化 一丶索引原理 什么是索引: 索引 ...
