posix多线程--三种基本线程编程模型
本文介绍了三种构建线程解决方案的方式。
一、流水线:每个线程执行同一种操作,并把操作结果传递给下一步骤的线程。

代码示例如下:
终端输入一个int值,每个线程将该值加1,并将结果传给下一个线程。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
typedef struct stage_tag
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int data;
int ready;
pthread_t tid;
struct stage_tag *next;
}stage_t;
typedef struct pipe_tag
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
stage_t *head;
stage_t *tail;
int stages;
}pipe_t;
void pipe_send(stage_t *stage,int data)
{
stage->data =data;
stage->ready = ;
pthread_cond_signal(&stage->cond);
}
void *thread_route(void *arg)
{
stage_t *stage = (stage_t *)arg;
while(!stage->ready)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&stage->cond,&stage->mutex);
}
int data = stage->data+;
stage_t *next = stage->next;
if(next!=NULL)
{
pipe_send(next,data);
}
return NULL;
}
void create_pipe(pipe_t *pipe,int stages)
{
// pipe = (pipe_t *)malloc(sizeof(pipe_t));
pipe->stages = stages;
int i;
stage_t *stage;
stage_t *last;
for(i=;i<=stages;i++)
{
stage = (stage_t *)malloc(sizeof(stage_t));
stage->data = i;
if(i==)
{
pipe->head = stage;
}
if(last!=NULL)
{
last->next = stage;
}
last = stage;
}
last->next=NULL;
pipe->tail = last;
for(stage=pipe->head;stage->next!=NULL;stage=stage->next)
{
pthread_create(&stage->tid,NULL,thread_route,(void *)stage);
printf("stage %d\n",stage->data);
}
/* free(pipe);
for(stage=pipe->head;stage!=NULL;stage=stage->next)
{
free(stage);
}
*/
}
int main(void)
{
pipe_t my_pipe;
long value,result;
char line[];
create_pipe(&my_pipe,);
pipe_send(my_pipe.head,);
sleep();
printf("result is %d\n",my_pipe.tail->data);
return ;
}
二、工作组:数据由一组线程分别独立地处理。
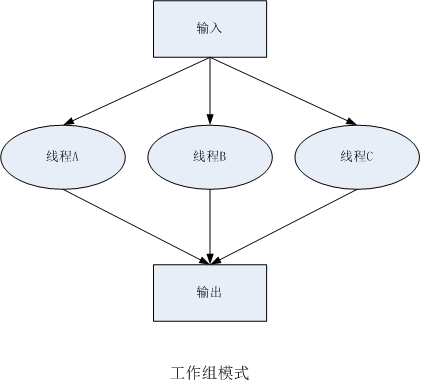
代码示例如下:
程序有两个参数:filepath:文件或目录路径;search:待查找字符串
程序将文件路径排队给工作组,工作组线程判断该路径是文件还是目录,如果是文件,它将在文件中搜索字符串;如果是目录,它将使用readdir_r查找该目录中的所有子目录和文件,并将每一项添加到工作队列。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
typedef struct work_tag
{
struct work_tag *next;
char *path;
char *search;
}work_t,*work_p;
typedef struct worker_tag
{
int index;
pthread_t tid;
struct crew_tag *crew; }worker_t,*worker_p;
typedef struct crew_tag
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_cond_t done;
long work_count;
work_t *first,*last;
worker_t workers[];
}crew_t,*crew_p;
void *thread_route(void *arg)
{
worker_p worker = (worker_t *)arg;
crew_p crew = worker->crew;
struct dirent *entry;
entry = (struct dirent*)malloc(sizeof(struct dirent)+sizeof(size_t));
pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex);
while(crew->work_count ==)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&crew->cond,&crew->mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex);
printf("worker is running: %d\n",worker->index);
while()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex);
while(crew->first==NULL)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&crew->cond,&crew->mutex);
}
printf("worker %d woke %#lx %d\n",worker->index,crew->first,crew->work_count);
work_p work = crew->first;
crew->first = work->next;
if(crew->first==NULL)
crew->last = NULL;
printf("worker %d took %#lx,leave first %#lx,last %#lx\n",worker->index,work,crew->first,crew->last);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex);
struct stat filestat;
lstat(work->path,&filestat);
if(S_ISLNK(filestat.st_mode))
printf("worker %d:%s is a link,skipping.\n",worker->index,work->path);
else if(S_ISDIR(filestat.st_mode)){
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *result;
dir = opendir(work->path);
while(){
readdir_r(dir,entry,&result);
if(result==NULL)
break;
if(strcmp(entry->d_name,".")==)
continue;
if(strcmp(entry->d_name,"..")==) continue;
work_p new_work = (work_p)malloc(sizeof(work_t));
printf("test\n");
path_max = pathconf (work->path, _PC_PATH_MAX);
new_work->path = (char*)malloc (path_max);
strcpy (new_work->path, work->path);
strcat (new_work->path, "/");
strcat (new_work->path, entry->d_name);
// char *new_dir = strcat(work->path,entry->d_name);
//new_work->path = new_dir;
new_work->search = work->search;
new_work->next = NULL;
pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex);
if(crew->first==NULL)
{
crew->first = new_work;
crew->last = new_work;
}
else{
crew->last->next = new_work;
crew->last = new_work;
}
crew->work_count++;
printf("worker %d add work %#lx,first %#lx,last %#lx,%d\n",worker->index,new_work,crew->first,crew->last,crew->work_count);
pthread_cond_signal(&crew->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex);
}
closedir(dir);
}
else if(S_ISREG(filestat.st_mode)){
FILE *file;
char buffer[];
file = fopen(work->path,"r");
fgets(buffer,sizeof(buffer),file);
char *search_ptr;
search_ptr = strstr(buffer,work->search);
if(search_ptr!=NULL){
printf("worker %d found \"%s\" in %s\n ",worker->index,work->search,work->path);
}
fclose(file); }
else{
printf("worker %d:%s format is error.\n",worker->index,work->path);
}
free(work->path);
free(work); pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex);
crew->work_count--;
printf("worker %d decremented work to %d\n",worker->index,crew->work_count);
if(crew->work_count<=){
pthread_cond_broadcast(&crew->done);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex);
}
free(entry);
return NULL;
}
void crew_create(crew_t *crew)
{
int worker_index;
crew->work_count = ;
crew->first = NULL;
crew->last = NULL;
pthread_mutex_init(&crew->mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&crew->cond,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&crew->done,NULL);
for(worker_index=;worker_index<;worker_index++){
crew->workers[worker_index].index = worker_index;
crew->workers[worker_index].crew = crew;
pthread_create(&crew->workers[worker_index].tid,
NULL,thread_route,(void *)&crew->workers[worker_index]);
}
}
void crew_start(crew_t *crew,char *filepath,char *search)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&crew->mutex);
work_p work = (work_p)malloc(sizeof(work_t));
work->path = filepath;
work->search = search;
work->next = NULL;
crew->first = work;
crew->last = work;
crew->work_count++;
pthread_cond_signal(&crew->cond);
while(crew->work_count>)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&crew->done,&crew->mutex);
}
printf("crew is done!\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&crew->mutex);
}
int main(void)
{
crew_t crew;
crew_create(&crew);
char *filepath = "/home/ubuntu/programs";
char *search = "errno";
crew_start(&crew,filepath,search);
return ;
}
三、客户端/服务器:客户端线程将工作排队,交给一个服务器线程去处理。客户端或者以同步方式等待服务器执行,或异步执行并在后面需要时查找结果。
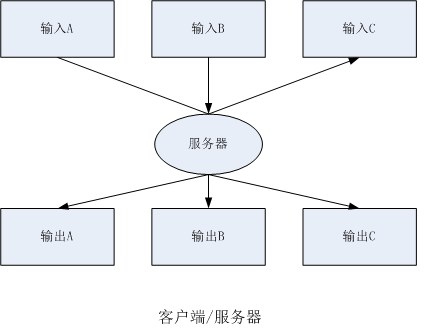
代码示例如下:
一组线程都需要从stdin中读取输入,这将导致提示-读(prompt-and-read)操作可能有些混乱。一个方法是使用flockfile和funlockfile函数来锁住stdin和stdout。,另一个方式是,使用服务器线程,将客户端读写操作排队,由服务器线程依次处理读写操作队列。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#define REQ_READ 1
#define REQ_WRITE 2
#define REQ_QUIT 3
typedef struct client_tag
{
struct client_tag *next;
int oper;
int sync;
int done_flag;
char prompt[];
char text[];
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t mutex;
}client_t;
typedef struct server_tag
{
client_t *first,*last;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}server_t;
server_t server={NULL,NULL,PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER};
pthread_mutex_t main_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t main_cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
int thread_count = ;
void client_request(int oper,int sync,const char *prompt,char *string)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&server.mutex);
client_t *client;
client = (client_t *)malloc(sizeof(client_t));
client->next = NULL;
client->oper = oper;
client->sync = sync;
if(prompt!=NULL)
strncpy(client->prompt,prompt,);
if(oper==REQ_WRITE&&string!=NULL)
strncpy(client->text,string,);
if(server.first==NULL)
{
server.first = client;
server.last = client;
}else{
server.last->next = client;
server.last = client;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&server.cond);
if(sync)
{
while(!client->done_flag)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&client->cond,&server.mutex);
}
if(oper==REQ_READ)
{
if(strlen(client->text)>)
strcpy(string,client->text);
}
}
pthread_cond_destroy(&client->cond);
free(request);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&server.mutex);
}
void *client_route(void *arg)
{
int index = (int)arg;
int loops;
char prompt[];
char string[],formatted[];
sprintf(prompt,"Client %d>",index);
while()
{
client_request(REQ_READ,,prompt,string);
if(strlen(string)==)
break;
for(loops=;loops<;loops++)
{
sprintf(formatted,"(%d#%d) %s",index,loops,string);
client_request(REQ_WRITE,,NULL,formatted);
sleep();
}
}
}
void *server_route(void *arg)
{
client_t *client;
int oper;
while()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&server.mutex);
while(server.first==NULL)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&server.cond,&server.mutex);
}
client = server.first;
server.first = client.next;
if(server.first==NULL)
server.last = NULL;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&server.mutex);
oper = client->oper;
switch(oper){
case REQ_QUIT:
break;
case REQ_READ:
if(strlen(client->prompt)>)
printf(client->prompt);
fgets(client->text,,stdin);
break;
case REQ_WRITE:
puts(client->text);
break;
default:
break;
}
free(client);
if(oper==REQ_QUIT)
break;
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t sid;
pthread_create(&sid,NULL,server_route,NULL); pthread_t cid;
int i;
for(i=;i<thread_count;i++)
{
pthread_create(&cid,NULL,client_route,(void *)count);
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&main_mutex);
while(thread_count>)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&main_cond,&main_mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&main_mutex);
printf("Done!\n");
client_request(REQ_QUIT,,NULL,NULL);
return ;
}
参考资料:《POSIX多线程程序设计》 pp.81-110
posix多线程--三种基本线程编程模型的更多相关文章
- 多线程(三) java中线程的简单使用
java中,启动线程通常是通过Thread或其子类通过调用start()方法启动. 常见使用线程有两种:实现Runnable接口和继承Thread.而继承Thread亦或使用TimerTask其底层依 ...
- 【Java 线程的深入研究1】Java 提供了三种创建线程的方法
Java 提供了三种创建线程的方法: 通过实现 Runnable 接口: 通过继承 Thread 类本身: 通过 Callable 和 Future 创建线程. 1.通过实现 Runnable 接口来 ...
- JAVA基础知识之多线程——三种实现多线程的方法及区别
所有JAVA线程都必须是Thread或其子类的实例. 继承Thread类创建线程 步骤如下, 定义Thead子类并实现run()方法,run()是线程执行体 创建此子类实例对象,即创建了线程对象 调用 ...
- Android 中三种启用线程的方法
在多线程编程这块,我们经常要使用Handler(处理),Thread(线程)和Runnable这三个类,那么他们之间的关系你是否弄清楚了呢? 首先说明Android的CPU分配的最小单元是线程,Han ...
- Java 多线程 三种实现方式
Java多线程实现方式主要有三种:继承Thread类.实现Runnable接口.使用ExecutorService.Callable.Future实现有返回结果的多线程.其中前两种方式线程执行完后都没 ...
- JAVA多线程三种实现方式
JAVA多线程实现方式主要有三种:继承Thread类.实现Runnable接口.使用ExecutorService.Callable.Future实现有返回结果的多线程.其中前两种方式线程执行完后都没 ...
- java线程(1)——三种创建线程的方式
前言 线程,英文Thread.在java中,创建线程的方式有三种: 1.Thread 2.Runnable 3.Callable 在详细介绍下这几种方式之前,我们先来看下Thread类和Runnabl ...
- java线程——三种创建线程的方式
前言 线程,英文Thread.在java中,创建线程的方式有三种: 1.Thread 2.Runnable 3.Callable 在详细介绍下这几种方式之前,我们先来看下Thread类和Runnabl ...
- 三种Shell脚本编程中避免SFTP输入密码的方法
最近编程中用到sftp上传文件,且需要用crontab预设定时上传事件.而sftp不同于ftp,没有提供选项如 -i 可以将密码直接编码进程序.使用sftp指令,会自动请求用户输入密码. 总结一下可以 ...
随机推荐
- PyQt5——安装Eric6
Eric6是PyQt编程最理想的IDE.windows版的安装很简单.下面的安装也是在windows上进行的.linux版的我安装有点问题,有时间再折腾. 下载: Eric6官网:http://eri ...
- Class.forName和registerDriver的区别
我们都知道JDBC的代码怎么写,比如以MySQL JDBC为例 //注册JDBC驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //然后就可以 ...
- python easy_install 发生Unable to find vcvarsall.bat错误的处理方法
用python安装mmseg分词包时发生了 Unable to find vcvarsall.bat 错误 Searching for mmseg Reading http://pypi.python ...
- 2、classpath、path、JAVA_HOME的作用
windows xp下配置JDK环境变量: 1.安装JDK,安装过程中可以自定义安装目录等信息,例如我们选择安装目录为D:\java\jdk1.5.0_08: 2.安装完成后,右击“我的电脑”,点击“ ...
- springMVC + hadoop + httpclient 文件上传请求直接写入hdfs
1.首先是一个基于httpclient的java 应用程序,代码在这篇文章的开头:点击打开链接 2.我们首先写一个基于springMVC框架的简单接收请求上传的文件保存本地文件系统的demo,程序代码 ...
- smack 4.1.2+openfire 3.10.2i
openfire 和以往版本号配置没有多大差别就不具体介绍了,网上搜会有一大堆的图解 以下主要说一下smack 4.1.2 的开发使用,在网上看了好多文章包含stackoverflow的都没有4.1以 ...
- Xshell和Xftp5配置连接阿里云服务器
配置Xftp5 配置成功后 配置Xshell 记住用户名和密码 连接成功
- Java获取资源的路径
在Java中,有两种路径: 类路径 文件夹路径 使用类路径有两种方式: object.getClass().getResource()返回资源的URL MyClass.class.getResourc ...
- 浅谈 JavaScriptCore
来源:XcodeMen(王瑞华) 链接:http://t.cn/RVqQI5p 本文由我们团队的王瑞华童鞋撰写. OS X Mavericks 和 iOS 7 引入了 JavaScriptCore 库 ...
- iOS开发之多媒体播放
iOS开发之多媒体播放 iOS sdk中提供了很多方便的方法来播放多媒体.本文将利用这些SDK做一个demo,来讲述一下如何使用它们来播放音频文件. AudioToolbox framework 使用 ...
