dsp6657的helloworld例程测试-第一篇
环境搭建可以参考http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_ed2e19900102xi2j.html
1. 先从mcsdk导入工程,helloworld例程
2. 提示有错误,估计是库找不到的原因。
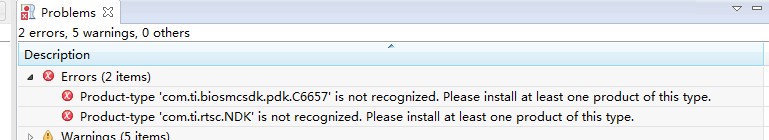
3. 打开CCS的配置页面,add加入需要的库,分别是NDK,PDK,其中NDK就是网络Network Developer's Kit开发包,如果CCS添加NDK失败的话,可能是NDK的版本太旧了,去下载个新的,下载地址:http://software-dl.ti.com/dsps/dsps_public_sw/sdo_sb/targetcontent/ndk/index.html,自己选个版本即可

4. 看下工程源码,其实想找个简单的入门例程研究,可惜找了个网络TCP/IP协议栈的,研究研究吧
- /*
- * helloWorld_bios6.c
- * TCP/IP Stack 'Hello World!' Example ported to use BIOS6 OS.
- */
- //--------------------------------------------------------------------------
- // IP Stack 'Hello World!' Example
- // To test it as is, use with helloWorld.exe from \winapps directory
- //
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <ti/ndk/inc/netmain.h>
- /* BIOS6 include */
- #include <ti/sysbios/BIOS.h>
- /* Platform utilities include */
- #include "ti/platform/platform.h"
- #include "ti/platform/resource_mgr.h"
- /* Platform Information - we will read it form the Platform Library */
- platform_info gPlatformInfo;
- //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- // Title String
- //
- char *VerStr = "\nTCP/IP Stack 'Hello World!' Application\n\n";
- // Our NETCTRL callback functions
- static void NetworkOpen();
- static void NetworkClose();
- static void NetworkIPAddr( IPN IPAddr, uint IfIdx, uint fAdd );
- // Fun reporting function
- static void ServiceReport( uint Item, uint Status, uint Report, HANDLE hCfgEntry );
- // External references
- extern int dtask_udp_hello();
- //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- // Configuration
- //
- char *HostName = "tidsp";
- char *LocalIPAddr = "192.168.2.100";
- char *LocalIPMask = "255.255.255.0"; // Not used when using DHCP
- char *GatewayIP = "192.168.2.101"; // Not used when using DHCP
- char *DomainName = "demo.net"; // Not used when using DHCP
- char *DNSServer = "0.0.0.0"; // Used when set to anything but zero
- /*************************************************************************
- * @b EVM_init()
- *
- * @n
- *
- * Initializes the platform hardware. This routine is configured to start in
- * the evm.cfg configuration file. It is the first routine that BIOS
- * calls and is executed before Main is called. If you are debugging within
- * CCS the default option in your target configuration file may be to execute
- * all code up until Main as the image loads. To debug this you should disable
- * that option.
- *
- * @param[in] None
- *
- * @retval
- * None
- ************************************************************************/
- void EVM_init()
- {
- int i;
- platform_init_flags sFlags;
- platform_init_config sConfig;
- /* Status of the call to initialize the platform */
- Int32 pform_status;
- /* Platform Information - we will read it form the Platform Library */
- platform_info sPlatformInfo;
- /*
- * You can choose what to initialize on the platform by setting the following
- * flags. We will initialize everything.
- */
- memset( (void *) &sFlags, , sizeof(platform_init_flags));
- memset( (void *) &sConfig, , sizeof(platform_init_config));
- sFlags.pll = ;
- sFlags.ddr = ;
- sFlags.tcsl = ; /* Time stamp counter */
- sFlags.phy = ; /* Ethernet */
- sFlags.ecc = ;
- sConfig.pllm = ;
- pform_status = platform_init(&sFlags, &sConfig);
- /* If we initialized the platform okay */
- if (pform_status == Platform_EOK) {
- /* Get information about the platform so we can use it in various places */
- memset( (void *) &sPlatformInfo, , sizeof(platform_info));
- (void) platform_get_info(&sPlatformInfo);
- }
- else {
- /* Intiialization of the platform failed... die */
- printf("Platform failed to initialize. Error code %d \n", pform_status);
- printf("We will die in an infinite loop... \n");
- while () {
- (void) platform_led(, PLATFORM_LED_ON, (LED_CLASS_E) PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
- (void) platform_delay();
- (void) platform_led(, PLATFORM_LED_OFF, (LED_CLASS_E) PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
- (void) platform_delay();
- };
- }
- platform_write_configure(PLATFORM_WRITE_PRINTF);
- platform_uart_init();
- platform_uart_set_baudrate();
- /* Check to see that we are running on the Master Core */
- if (platform_get_coreid() != ) {
- /* We are not on the Master Core... die */
- printf("You must run this application on Core 0. \n");
- printf("We will die in an infinite loop... \n");
- while () {
- (void) platform_led(, PLATFORM_LED_ON, (LED_CLASS_E) PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
- (void) platform_delay();
- (void) platform_led(, PLATFORM_LED_OFF, (LED_CLASS_E) PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
- (void) platform_delay();
- };
- }
- /* Clear the state of the LEDs to OFF */
- for (i=; i < sPlatformInfo.led[].count; i++) {
- platform_led(i, PLATFORM_LED_OFF, (LED_CLASS_E) PLATFORM_USER_LED_CLASS);
- }
- return;
- }
- //---------------------------------------------------------------------
- // Main Entry Point
- //---------------------------------------------------------------------
- int main()
- {
- /* Start the BIOS 6 Scheduler */
- BIOS_start ();
- }
- //
- // Main Thread
- //
- int StackTest()
- {
- int rc;
- int i;
- HANDLE hCfg;
- //
- // THIS MUST BE THE ABSOLUTE FIRST THING DONE IN AN APPLICATION before
- // using the stack!!
- //
- rc = NC_SystemOpen( NC_PRIORITY_LOW, NC_OPMODE_INTERRUPT );
- if( rc )
- {
- platform_write("NC_SystemOpen Failed (%d)\n",rc);
- for(;;);
- }
- // Print out our banner
- platform_write(VerStr);
- //
- // Create and build the system configuration from scratch.
- //
- // Create a new configuration
- hCfg = CfgNew();
- if( !hCfg )
- {
- platform_write("Unable to create configuration\n");
- goto main_exit;
- }
- // We better validate the length of the supplied names
- if( strlen( DomainName ) >= CFG_DOMAIN_MAX ||
- strlen( HostName ) >= CFG_HOSTNAME_MAX )
- {
- printf("Names too long\n");
- goto main_exit;
- }
- // Add our global hostname to hCfg (to be claimed in all connected domains)
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_SYSINFO, CFGITEM_DHCP_HOSTNAME, ,
- strlen(HostName), (UINT8 *)HostName, );
- // If the IP address is specified, manually configure IP and Gateway
- if (!platform_get_switch_state())
- {
- CI_IPNET NA;
- CI_ROUTE RT;
- IPN IPTmp;
- // Setup manual IP address
- bzero( &NA, sizeof(NA) );
- NA.IPAddr = inet_addr(LocalIPAddr);
- NA.IPMask = inet_addr(LocalIPMask);
- strcpy( NA.Domain, DomainName );
- NA.NetType = ;
- // Add the address to interface 1
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_IPNET, , ,
- sizeof(CI_IPNET), (UINT8 *)&NA, );
- // Add the default gateway. Since it is the default, the
- // destination address and mask are both zero (we go ahead
- // and show the assignment for clarity).
- bzero( &RT, sizeof(RT) );
- RT.IPDestAddr = ;
- RT.IPDestMask = ;
- RT.IPGateAddr = inet_addr(GatewayIP);
- // Add the route
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_ROUTE, , ,
- sizeof(CI_ROUTE), (UINT8 *)&RT, );
- // Manually add the DNS server when specified
- IPTmp = inet_addr(DNSServer);
- if( IPTmp )
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_SYSINFO, CFGITEM_DHCP_DOMAINNAMESERVER,
- , sizeof(IPTmp), (UINT8 *)&IPTmp, );
- }
- // Else we specify DHCP
- else
- {
- CI_SERVICE_DHCPC dhcpc;
- // Specify DHCP Service on IF-1
- bzero( &dhcpc, sizeof(dhcpc) );
- dhcpc.cisargs.Mode = CIS_FLG_IFIDXVALID;
- dhcpc.cisargs.IfIdx = ;
- dhcpc.cisargs.pCbSrv = &ServiceReport;
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_SERVICE, CFGITEM_SERVICE_DHCPCLIENT, ,
- sizeof(dhcpc), (UINT8 *)&dhcpc, );
- }
- //
- // Configure IPStack/OS Options
- //
- // We don't want to see debug messages less than WARNINGS
- rc = DBG_WARN;
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_OS, CFGITEM_OS_DBGPRINTLEVEL,
- CFG_ADDMODE_UNIQUE, sizeof(uint), (UINT8 *)&rc, );
- //
- // This code sets up the TCP and UDP buffer sizes
- // (Note 8192 is actually the default. This code is here to
- // illustrate how the buffer and limit sizes are configured.)
- //
- // UDP Receive limit
- rc = ;
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_IP, CFGITEM_IP_SOCKUDPRXLIMIT,
- CFG_ADDMODE_UNIQUE, sizeof(uint), (UINT8 *)&rc, );
- //
- // Boot the system using this configuration
- //
- // We keep booting until the function returns 0. This allows
- // us to have a "reboot" command.
- //
- do
- {
- rc = NC_NetStart( hCfg, NetworkOpen, NetworkClose, NetworkIPAddr );
- } while( rc > );
- // Delete Configuration
- CfgFree( hCfg );
- // Close the OS
- main_exit:
- NC_SystemClose();
- return();
- }
- //
- // System Task Code [ Server Daemon Servers ]
- //
- static HANDLE hHello=;
- //
- // NetworkOpen
- //
- // This function is called after the configuration has booted
- //
- static void NetworkOpen()
- {
- // Create our local server
- hHello = DaemonNew( SOCK_DGRAM, , , dtask_udp_hello,
- OS_TASKPRINORM, OS_TASKSTKNORM, , );
- }
- //
- // NetworkClose
- //
- // This function is called when the network is shutting down,
- // or when it no longer has any IP addresses assigned to it.
- //
- static void NetworkClose()
- {
- DaemonFree( hHello );
- }
- //
- // NetworkIPAddr
- //
- // This function is called whenever an IP address binding is
- // added or removed from the system.
- //
- static void NetworkIPAddr( IPN IPAddr, uint IfIdx, uint fAdd )
- {
- IPN IPTmp;
- if( fAdd )
- printf("Network Added: ");
- else
- printf("Network Removed: ");
- // Print a message
- IPTmp = ntohl( IPAddr );
- printf("If-%d:%d.%d.%d.%d\n", IfIdx,
- (UINT8)(IPTmp>>)&0xFF, (UINT8)(IPTmp>>)&0xFF,
- (UINT8)(IPTmp>>)&0xFF, (UINT8)IPTmp&0xFF );
- }
- //
- // Service Status Reports
- //
- // Here's a quick example of using service status updates
- //
- static char *TaskName[] = { "Telnet","HTTP","NAT","DHCPS","DHCPC","DNS" };
- static char *ReportStr[] = { "","Running","Updated","Complete","Fault" };
- static char *StatusStr[] = { "Disabled","Waiting","IPTerm","Failed","Enabled" };
- static void ServiceReport( uint Item, uint Status, uint Report, HANDLE h )
- {
- printf( "Service Status: %-9s: %-9s: %-9s: %03d\n",
- TaskName[Item-], StatusStr[Status],
- ReportStr[Report/], Report&0xFF );
- //
- // Example of adding to the DHCP configuration space
- //
- // When using the DHCP client, the client has full control over access
- // to the first 256 entries in the CFGTAG_SYSINFO space.
- //
- // Note that the DHCP client will erase all CFGTAG_SYSINFO tags except
- // CFGITEM_DHCP_HOSTNAME. If the application needs to keep manual
- // entries in the DHCP tag range, then the code to maintain them should
- // be placed here.
- //
- // Here, we want to manually add a DNS server to the configuration, but
- // we can only do it once DHCP has finished its programming.
- //
- if( Item == CFGITEM_SERVICE_DHCPCLIENT &&
- Status == CIS_SRV_STATUS_ENABLED &&
- (Report == (NETTOOLS_STAT_RUNNING|DHCPCODE_IPADD) ||
- Report == (NETTOOLS_STAT_RUNNING|DHCPCODE_IPRENEW)) )
- {
- IPN IPTmp;
- // Manually add the DNS server when specified
- IPTmp = inet_addr(DNSServer);
- if( IPTmp )
- CfgAddEntry( , CFGTAG_SYSINFO, CFGITEM_DHCP_DOMAINNAMESERVER,
- , sizeof(IPTmp), (UINT8 *)&IPTmp, );
- }
- }
5. 刚开始这些代码看的不是很明白。main函数里面为啥只有一个BIOS_start();函数?不是应该创建任务之类的?
- int main()
- {
- /* Start the BIOS 6 Scheduler */
- BIOS_start ();
- }
6. 下面函数怎么运行的?
- int StackTest()
7. 是不是BIOS的图形配置界面搞定的?去看下图形配置界面。图形配置界面应该有个.tcf文件,但是工程没找到?
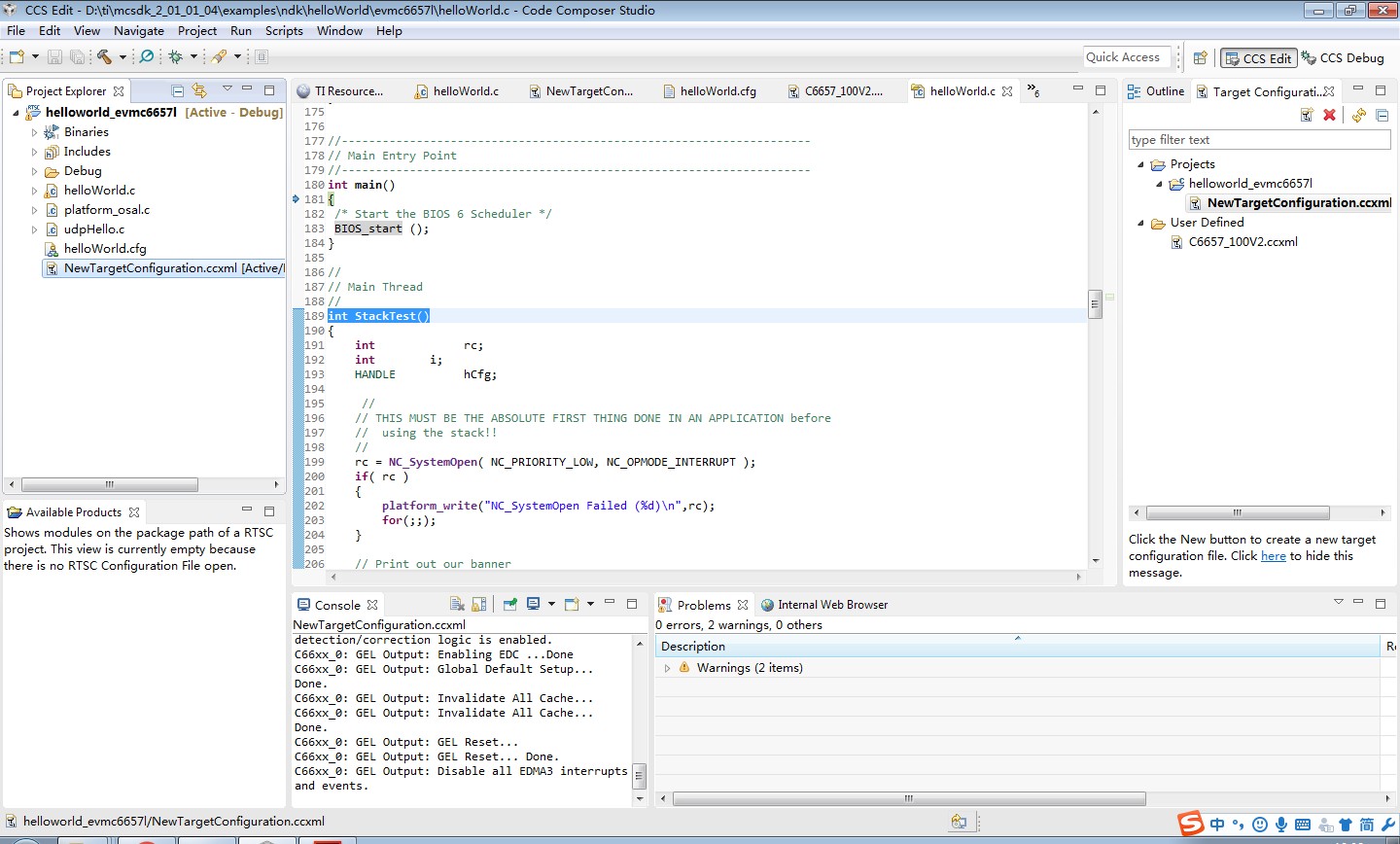
8. 下面的是使用协议栈必须首先调用的函数
- rc = NC_SystemOpen( NC_PRIORITY_LOW, NC_OPMODE_INTERRUPT );
9. 接着是配置网络参数的函数
- CfgAddEntry( hCfg, CFGTAG_SYSINFO, CFGITEM_DHCP_HOSTNAME, ,
- strlen(HostName), (UINT8 *)HostName, );
10. 这次疑问很多,RTSC是德州仪器提出的嵌入式组件,我理解就是把代码模块化,这个模块化的工作交给CCS去管理,比如需要一个ADC模块,在CCS里面配置就可以,CCS会把代码加入你的工程,XDCTools 是完成上面的工具,RTSC是一种理念。
dsp6657的helloworld例程测试-第一篇的更多相关文章
- dsp6657的helloworld例程测试-第二篇-CFG文件
1. 上一篇疑问,int StackTest()这个函数是怎么运行的,后来在.cfg文件找到了答案,.cfg包含丰富的信息,对于用惯C语言的,确实不太习惯 var Memory = xdc.useMo ...
- 创龙DSP6748开发板上电测试-第一篇
1. 创龙DSP6748开发板测试.2980元的售价很高,我估计新的1200元比较合适,当然创龙定价是按照供需关系的.仿真器XDS100V2卖598元,真是狮子大张口. 2. 上电是5V-2A的电源. ...
- 天嵌IMX6开发板测试-第一篇
1.看下开发板介绍 品牌: 天嵌 CPU型号: NXP i.MX6Q 架构: Cortex_A9 主频: *1GHz 内存: 2GB DDR3 存储: 8GB eMMC FLA(64GB可扩) 2. ...
- 使用cnblogs发布第一篇文章,HelloWorld
HelloWorld! 瞅瞅源码的样式,嗯,语法高亮还是可以的,辨识度还是挺高的. <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta c ...
- LARK BOARD开发板试用第一篇-上电测试学习
1. 先看下板子外观,做工很不错 2. 主芯片的型号是,SoC 为 Cyclone V SX 系列的 5CSXFC6D6F31,不仅在芯片中包含传统的 FPGA 架构,还集成了基于 ARM Corte ...
- go [第一篇]初识
[第一篇] 简介 Go 是一个开源的编程语言,它能让构造简单.可靠且高效的软件变得容易. Go是从2007年末由Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, Ken Thompson主持开发 ...
- 第一篇 入门必备 (Android学习笔记)
第一篇 入门必备 第1章 初识Android 第2章 搭建你的开发环境 第3章 创建第一个程序--HelloWorld 第4章 使用Android工具 ●Android之父 Android安迪·罗 ...
- 深入学习jQuery选择器系列第一篇——基础选择器和层级选择器
× 目录 [1]id选择器 [2]元素选择器 [3]类选择器[4]通配选择器[5]群组选择器[6]后代选择器[7]兄弟选择器 前面的话 选择器是jQuery的根基,在jQuery中,对事件处理.遍历D ...
- 前端工程师技能之photoshop巧用系列第一篇——准备篇
× 目录 [1]作用 [2]初始化 [3]常用工具[4]快捷键 前面的话 photoshop是前端工程师无法回避的一个软件,这个软件本身很强大,但我们仅仅需要通过这个工具来完成基本的切图工作即可.本文 ...
随机推荐
- xss实现获取内网ip
前提得浏览器支持webRTC,测试的时候google浏览器测试成功,火狐浏览器不支持webRTC, 再在xss平台直接复制如下js代码: function form_ip(ip,port){ var ...
- 解决windows7无法连接CentOS7系统中oracle问题:ORA-12514 TNS 监听程序当前无法识别
linux开启后终端按下面输入(容易忘记,记录下): [oracle@localhost ~]$ lsnrctl stop #先关闭监听服务 [oracle@localh ...
- 《metasploit渗透测试魔鬼训练营》学习笔记第三章----情报搜集
Kali渗透测试系统集成了metasploit开源的漏洞测试框架,是渗透测试必备的神器.下面是我在学习metasploit的笔记,有什么错误的地方请指出来,我会立即纠正的~ 一.情报搜集 1. ...
- jquery Mobile入门—多页面切换示例学习
1.在JQuery Mobile中,多个页面的切换是通过<a>元素.并将<href>属性设置为#+对应的id号的方式进行的. 2.多页面切换示例代码: 复制代码代码如下: &l ...
- translate动画实例
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta name="viewport&quo ...
- 卢卡斯定理Lucas
卢卡斯定理Lucas 在数论中,\(Lucas\)定理用于快速计算\(C^m_n ~ \% ~p\),即证明\(C^m_n = \prod_{i = 0} ^kC^{m_i}_{n_i}\)其中\(m ...
- 错误的另一个常见原因是默认的安全组规则。default security group默认情况下不允许ICMP(ping命令使用的协议)
可以在openstack horizon界面中添加ICMP和ssh(TCP)规则,也可以通过命令行.命令行方式给默认安全组添加规则的方法如下: $ nova secgroup-add-rule def ...
- 如何在localStorage中存取数组
默认localStorage只能存取字符串 那么如何存取数组呢 let newlist = [] localStorage.setItem('recent', JSON.stringify(newli ...
- JDK的跳表源码分析
JDK源码中的跳表实现类: ConcurrentSkipListMap和ConcurrentSkipListSet. 其中ConcurrentSkipListSet的实现是基于ConcurrentSk ...
- 【腾讯敏捷转型No.7】QQ邮箱如何通过敏捷成为行业第一
前几篇文章讲到2006年的腾讯是如何开始敏捷转型的,接下来这篇文章,我将向大家讲述,腾讯开始敏捷转型之后,QQ邮箱是如何通过敏捷成为行业第一. 众所周知,张小龙是“微信之父”,对他熟悉的人,应该也知道 ...
