PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree[难]
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
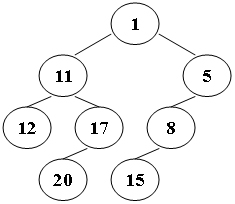
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15题目大意:给出二叉树的中根遍历和后根遍历序列,给出zigzag遍历序列,就是隔层从左到右,从右到左这样转换遍历。
//这个我当然是不会了,好久没做二叉树的题目了。
转自:https://www.liuchuo.net/archives/3758
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
vector<int> in, post, result[];
int n, tree[][], root;
struct node {
int index, depth;//保存index和深度。
};
//将二叉树的结构存储在了tree中。
void dfs(int &index, int inLeft, int inRight, int postLeft, int postRight) {
if (inLeft > inRight) return;
index = postRight;//进来之后再赋值,真的厉害。
int i = ;
while (in[i] != post[postRight]) i++;
dfs(tree[index][], inLeft, i - , postLeft, postLeft + (i - inLeft) - );
dfs(tree[index][], i + , inRight, postLeft + (i - inLeft), postRight - );
}
//dfs函数得到的root实际上是post遍历中的下标。
void bfs() {
queue<node> q;
q.push(node{root, });
while (!q.empty()) {
node temp = q.front();
q.pop();
result[temp.depth].push_back(post[temp.index]);
if (tree[temp.index][] != )//左子树不为空。
q.push(node{tree[temp.index][], temp.depth + });
//那么此时push进的是左子树,并且深度+1.
if (tree[temp.index][] != )//右子树不为空。
q.push(node{tree[temp.index][], temp.depth + });
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
in.resize(n + ), post.resize(n + );
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) cin >> in[i];//输入中序遍历
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++) cin >> post[i];//输入后序遍历
dfs(root, , n, , n);//将根存在了root中。
bfs();
printf("%d", result[][]);
for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
if (i % == ) {
for (int j = ; j < result[i].size(); j++)
printf(" %d", result[i][j]);
} else {
for (int j = result[i].size() - ; j >= ; j--)
printf(" %d", result[i][j]);
}
}
return ;
}
//柳神真厉害。
1.使用dfs在遍历的过程中传进去index引用参数,直接赋值,并且使用tree二维数组存储二叉树的结构
2.使用结构体node,存储下标和层数,下标是在post序列中可以寻到节点的。
3.对奇数层和偶数层,分别用不同的方式打印。
代码来自:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenxiwenruo/p/6506517.html
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#define LEFT 0
#define RIGHT 1
using namespace std;
const int maxn=;
int inorder[maxn];
int postorder[maxn];
int level[maxn][maxn]; //每层的节点id
int levelcnt[maxn]; //每层的节点个数
int maxlayer=;
int cnt=; //节点id
struct Node{
int left=-,right=-;
int val;
}node[maxn]; //根据中序遍历和后序遍历建立树
void build(int inL,int inR,int postL,int postR,int fa,int LorR){
if(inL>inR)
return;
int val=postorder[postR];
int idx;
//在中序遍历中找出父亲节点的索引,其左边是左子树,右边是右子树
for(int i=inL;i<=inR;i++){
if(inorder[i]==val){
idx=i;
break;
}
}
int lnum=idx-inL;//左子树的节点个数
cnt++;
node[cnt].val=val;
if(LorR==LEFT)
node[fa].left=cnt;
else if(LorR==RIGHT)
node[fa].right=cnt;
int tmp=cnt;
build(inL,idx-,postL,postL+lnum-,tmp,LEFT);
//这里的left标志是当前深度遍历中是左子树还是右子树。
build(idx+,inR,postL+lnum,postR-,tmp,RIGHT);
}
void dfs(int root,int layer){
if(root==-)
return;
maxlayer=max(layer,maxlayer);
level[layer][levelcnt[layer]]=root;
levelcnt[layer]++;
dfs(node[root].left,layer+);
dfs(node[root].right,layer+);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
cin>>inorder[i];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
cin>>postorder[i];
build(,n,,n,-,-);
dfs(,);
bool flag=true;
printf("%d",node[].val);
for(int i=;i<=maxlayer;i++){
if(flag){
for(int j=;j<levelcnt[i];j++)
printf(" %d",node[level[i][j]].val);
}
else{
for(int j=levelcnt[i]-;j>=;j--)
printf(" %d",node[level[i][j]].val);
}
flag=!flag;
}
return ;
}
1.这个是使用函数建树,具体的代码理解在代码里。
PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree[难]的更多相关文章
- PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can ...
- PAT甲级1127. ZigZagging on a Tree
PAT甲级1127. ZigZagging on a Tree 题意: 假设二叉树中的所有键都是不同的正整数.一个唯一的二叉树可以通过给定的一对后序和顺序遍历序列来确定.这是一个简单的标准程序,可以按 ...
- PAT甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- pat 甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive in ...
- PAT 甲级 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805349394006016 Suppose that all the k ...
- PAT Advanced 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30) [中序后序建树,层序遍历]
题目 Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree c ...
- PAT甲题题解-1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)-中序、后序建树
根据中序遍历和前序遍历确定一棵二叉树,然后按“层次遍历”序列输出.输出规则:除根节点外,接下来每层的节点输出顺序是:先从左到右,再从右到左,交替输出 #include <iostream> ...
- PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)——二叉树,建树,层序遍历
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can ...
随机推荐
- Spring Framework 官方文档学习(四)之Validation、Data Binding、Type Conversion(一)
题外话:本篇是对之前那篇的重排版.并拆分成两篇,免得没了看的兴趣. 前言 在Spring Framework官方文档中,这三者是放到一起讲的,但没有解释为什么放到一起.大概是默认了读者都是有相关经验的 ...
- MySQL<表单&集合查询>
表单查询 简单查询 SELECT语句 查询所有字段 指定所有字段:select 字段名1,字段名2,...from 表名; select * from 表名; 查询指定字段 select 字段名1,字 ...
- nagios监控mysql
在nagios上部署check_mysql_health 监控mysql 博客分类: 架构 本监控为基于nagios服务器主动监控方法,利用check_mysql_health实现多种监控模式: ...
- Unity 的OCulus VR开发遇到的坑---OC版本差异
我作为Unity新人,没有用过Unity5之前的任何版本,不熟悉任何操作.所以,就根据官方推荐,使用了5.1.1版本,然后根据官方版本对应推荐,果断选择下载了PC端的OC的0.6.0.1版本,对应的U ...
- stm32入门(从51过渡到32)
单片机对于我来说,就是一个超级大机器,上面有一排一排数不尽的开关,我需要做的,就是根据我的设计,拿着一张超级大的表(Datasheet),把需要的开关(reg)都开关(config)到对应功能的位置( ...
- 如何使用微信小程序制作banner轮播图?
在前端工程师的工作中,banner是必不可少的,那缺少了DOM的小程序是如何实现banner图的呢?如同其他的框架封装了不同的banner图的方法,小程序也封装了banner的方法,来让我一一道来: ...
- eclipse导入maven项目时报Could not calculate build plan: Plugin org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-resources
在用Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers进行maven项目的开发时,报错Could not calculate build plan: Plugin org.apach ...
- ExtJS 6.2 基础使用
一. 安装: 下载两个压缩包:分别是 ext-6.2.0-gpl(这个是ExtJS 的SDK文件,创建新项目的时候需要用). SenchaCmd-6.5.2-windows-64bit (这个下载下来 ...
- poj_3662 最小化第k大的值
题目大意 有N个节点以及连接的P个无向边,现在要通过这P条边从1号节点连接到N号节点.若无法连接成功,则返回-1:若能够连接成功,那么其中用到了L条边,这L条边中有K条边可以免费,L-K条边不能免费, ...
- HTTP/2探索第二篇——工具及应用
版权声明:本文由张浩然原创文章,转载请注明出处: 文章原文链接:https://www.qcloud.com/community/article/88 来源:腾云阁 https://www.qclou ...
