hdfs源码分析第一弹
1. hdfs定义
HDFS is the primary distributed storage used by Hadoop applications. A HDFS cluster primarily consists of a NameNode that manages the file system metadata and DataNodes that store the actual data.
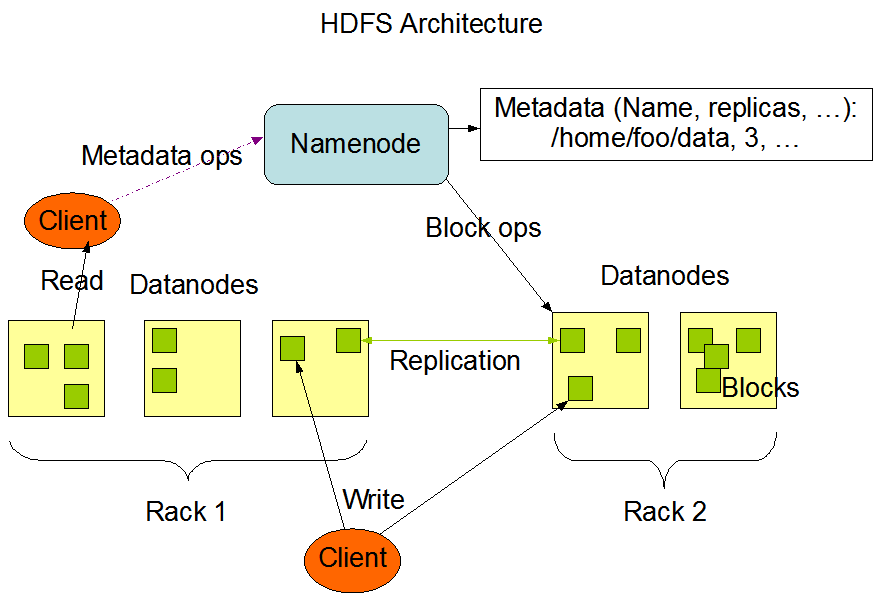
2. hdfs架构
3. hdfs实例
作为文件系统,文件的读写才是核心:
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; public class HadoopDFSFileReadWrite { static void usage () {
System.out.println("Usage : HadoopDFSFileReadWrite <inputfile> <output file>");
System.exit(1);
} static void printAndExit(String str) {
System.err.println(str);
System.exit(1);
} public static void main (String[] argv) throws IOException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); if (argv.length != 2)
usage(); // Hadoop DFS deals with Path
Path inFile = new Path(argv[0]);
Path outFile = new Path(argv[1]); // Check if input/output are valid
if (!fs.exists(inFile))
printAndExit("Input file not found");
if (!fs.isFile(inFile))
printAndExit("Input should be a file");
if (fs.exists(outFile))
printAndExit("Output already exists"); // Read from and write to new file
FSDataInputStream in = fs.open(inFile);
FSDataOutputStream out = fs.create(outFile);
byte buffer[] = new byte[256];
try {
int bytesRead = 0;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error while copying file");
} finally {
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
}
上述示例,将一个文件的内容复制到另一个文件中,具体步骤如下:
第一步:创建一个文件系统实例,给该实例传递新的配置。
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
第二步:获取文件路径
// Hadoop DFS deals with Path
Path inFile = new Path(argv[0]);
Path outFile = new Path(argv[1]); // Check if input/output are valid
if (!fs.exists(inFile))
printAndExit("Input file not found");
if (!fs.isFile(inFile))
printAndExit("Input should be a file");
if (fs.exists(outFile))
printAndExit("Output already exists");
第三步:打开文件输入输出流,将输入流写到输出流中:
// Read from and write to new file
FSDataInputStream in = fs.open(inFile);
FSDataOutputStream out = fs.create(outFile);
byte buffer[] = new byte[256];
try {
int bytesRead = 0;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) > 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error while copying file");
} finally {
in.close();
out.close();
}
上面文件读写功能涉及到了文件系统FileSystem、配置文件Configuration、输入流/输出流FSDataInputStream/FSDataOutputStream
4. 基本概念分析
4.1 文件系统
文件系统的层次结构如下所示:
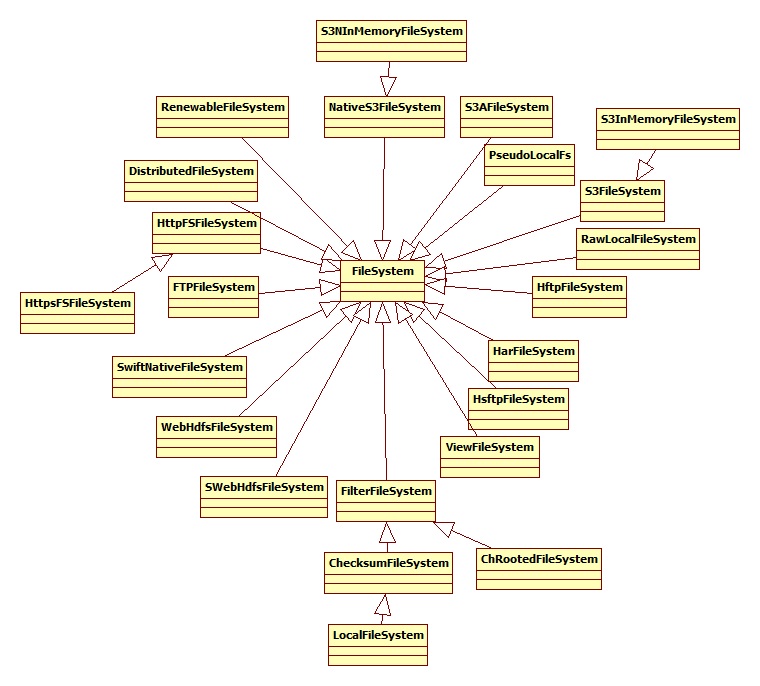
文件系统有两个重要的分支,一个是分布式文件系统,另一个是“本地”(映射到本地连接的磁盘)文件系统,本地磁盘适用于比较少的hadoop实例和测试。绝大部分情况下使用分布式文件系统,hadoop 分布式文件系统使用多个机器的系统,但对用户来说只有一个磁盘。它的容错性和大容量性使它非常有用。
4.2 配置文件
配置文件的层次结构如下:
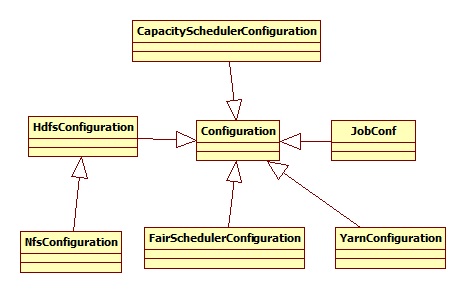
我们关注的是HdfsConfiguration,其涉及到的配置文件有hdfs-default.xml和hdfs-site.xml:
static {
addDeprecatedKeys();
// adds the default resources
Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-default.xml");
Configuration.addDefaultResource("hdfs-site.xml");
}
4.3 输入/输出流
输入/输出流和文件系统相对应,先看一下输入流:
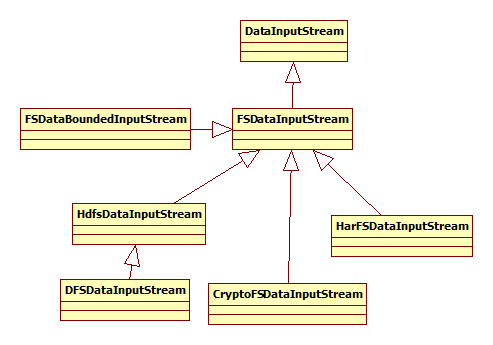
其中,HdfsDataInputStream是FSDataInputStream的实现,其构造函数为:
public HdfsDataInputStream(DFSInputStream in) throws IOException {
super(in);
}
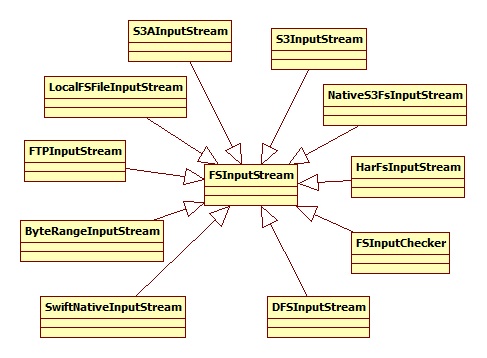
DFSInputStream层次结构如下图所示:
在了解一下输出流:
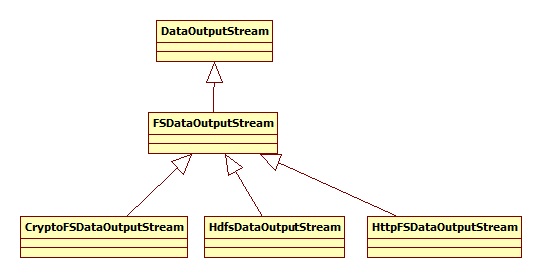
其中,重点是HdfsDataOutputStream,其构造函数为:
public HdfsDataOutputStream(DFSOutputStream out, FileSystem.Statistics stats,
long startPosition) throws IOException {
super(out, stats, startPosition);
}
DFSOutputStream 的层次结构为:
参考文献:
【1】http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.6.0/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsUserGuide.html
【2】http://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.6.0/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsDesign.html
【3】http://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/HadoopDfsReadWriteExample
【4】http://blog.csdn.net/gaoxingnengjisuan/article/details/11177049
hdfs源码分析第一弹的更多相关文章
- hdfs源码分析第二弹
以写文件为例,串联整个流程的源码: FSDataOutputStream out = fs.create(outFile); 1. DistributedFileSystem 继承并实现了FileSy ...
- HDFS源码分析数据块校验之DataBlockScanner
DataBlockScanner是运行在数据节点DataNode上的一个后台线程.它为所有的块池管理块扫描.针对每个块池,一个BlockPoolSliceScanner对象将会被创建,其运行在一个单独 ...
- HDFS源码分析之UnderReplicatedBlocks(二)
UnderReplicatedBlocks还提供了一个数据块迭代器BlockIterator,用于遍历其中的数据块.它是UnderReplicatedBlocks的内部类,有三个成员变量,如下: // ...
- HDFS源码分析EditLog之获取编辑日志输入流
在<HDFS源码分析之EditLogTailer>一文中,我们详细了解了编辑日志跟踪器EditLogTailer的实现,介绍了其内部编辑日志追踪线程EditLogTailerThread的 ...
- HDFS源码分析心跳汇报之BPServiceActor工作线程运行流程
在<HDFS源码分析心跳汇报之数据结构初始化>一文中,我们了解到HDFS心跳相关的BlockPoolManager.BPOfferService.BPServiceActor三者之间的关系 ...
- HDFS源码分析心跳汇报之数据块增量汇报
在<HDFS源码分析心跳汇报之BPServiceActor工作线程运行流程>一文中,我们详细了解了数据节点DataNode周期性发送心跳给名字节点NameNode的BPServiceAct ...
- HDFS源码分析心跳汇报之数据结构初始化
在<HDFS源码分析心跳汇报之整体结构>一文中,我们详细了解了HDFS中关于心跳的整体结构,知道了BlockPoolManager.BPOfferService和BPServiceActo ...
- HDFS源码分析DataXceiver之整体流程
在<HDFS源码分析之DataXceiverServer>一文中,我们了解到在DataNode中,有一个后台工作的线程DataXceiverServer.它被用于接收来自客户端或其他数据节 ...
- HDFS源码分析之UnderReplicatedBlocks(一)
http://blog.csdn.net/lipeng_bigdata/article/details/51160359 UnderReplicatedBlocks是HDFS中关于块复制的一个重要数据 ...
随机推荐
- 20155336 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第四周学习总结
20155336 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第四周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第六章 继承:面向对象中,为避免多个类间重复定义共同行为.(简单说就是将相同的程序代码提升为 ...
- SupperSocket深入浅出
这篇文章出要是SuperSocket底层如何接收数据 Process(ArraySegment<byte> segment) 获取加载数据(直到数据全部接收后返回) namespace S ...
- MySQL入门篇(一)之MySQL部署
MySQL 二进制免编译安装 (1)下载二进制免编译版本mysql 5.6.35 [root@localhost tools]# wget http://mirrors.sohu.com/mysql/ ...
- golang 单元测试
单元测试是质量保证十分重要的一环,好的单元测试不仅能及时地发现问题,更能够方便地调试,提高生产效率.所以很多人认为写单元测试是需要额外的时间,会降低生产效率,是对单元测试最大的偏见和误解. go 语言 ...
- javaweb(二十四)——jsp传统标签开发
一.标签技术的API 1.1.标签技术的API类继承关系 二.标签API简单介绍 2.1.JspTag接口 JspTag接口是所有自定义标签的父接口,它是JSP2.0中新定义的一个标记接口,没有任何属 ...
- Codeforces Round #503 (by SIS, Div. 2) D. The hat
有图可以直观发现,如果一开始的pair(1,1+n/2)和pair(x, x+n/2)大小关系不同 那么中间必然存在一个答案 简单总结就是大小关系不同,中间就有答案 所以就可以使用二分 #includ ...
- elasticsearch备份与恢复
备注:以下代码在kibana插件下运行: # 创建一个备份用的仓库# type:fs文件系统# 支持Shared filesystem, Amazon S3, HDFS和Azure #Cloud# l ...
- Atom 插件 Sync Settings 备份与恢复
当使用 Atom IDEA.随着使用的越来越多,安装的插件也越来越多,一旦电脑重装后需要复原开发环境,这将是一件比较头疼的事.「Sync Settings」插件可以帮助我们解决这个问题. 操作流程 安 ...
- NUMA 体系架构
NUMA 体系架构 SMP 体系架构 NUMA 体系架构 NUMA 结构基本概念 Openstack flavor NUMA 策略 Nova 实现 NUMA 流程 1. SMP 体系架构 CPU 计算 ...
- #Ubuntu 18.04 安装tensorflow-gpu 1.9
参考 https://tensorflow.google.cn/install/install_linux http://nvidia.com/cuda http://developer.nvidia ...