从flink-example分析flink组件(1)WordCount batch实战及源码分析
上一章<windows下flink示例程序的执行> 简单介绍了一下flink在windows下如何通过flink-webui运行已经打包完成的示例程序(jar),那么我们为什么要使用flink呢?
flink的特征
官网给出的特征如下:
1、一切皆为流(All streaming use cases )
- 事件驱动应用(Event-driven Applications)
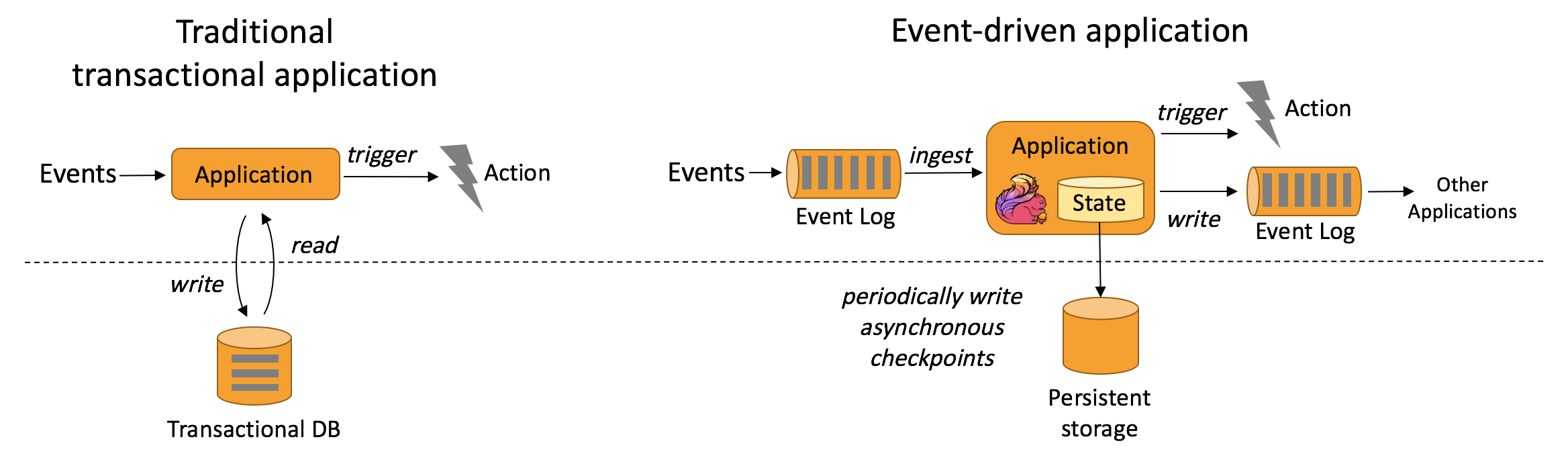
- 流式 & 批量分析(Stream & Batch Analytics)

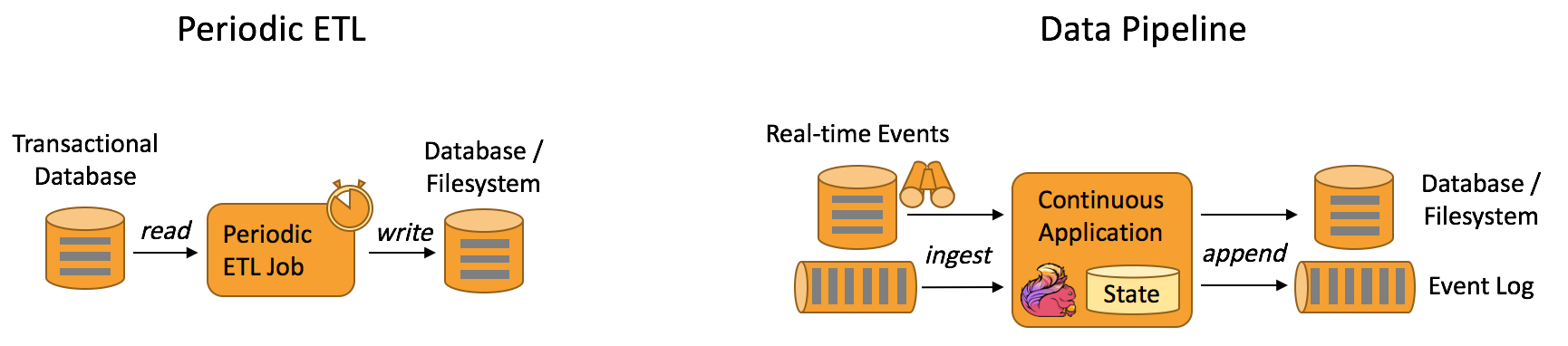
- 数据管道&ETL(Data Pipelines & ETL)
2、正确性保证(Guaranteed correctness)
- 唯一状态一致性(Exactly-once state consistency)
- 事件-事件处理(Event-time processing)
- 高超的最近数据处理(Sophisticated late data handling)
3、多层api(Layered APIs)
- 基于流式和批量数据处理的SQL(SQL on Stream & Batch Data)
- 流水数据API & 数据集API(DataStream API & DataSet API)
- 处理函数 (时间 & 状态)(ProcessFunction (Time & State))

4、易用性
- 部署灵活(Flexible deployment)
- 高可用安装(High-availability setup)
- 保存点(Savepoints)
5、可扩展性
- 可扩展架构(Scale-out architecture)
- 大量状态的支持(Support for very large state)
- 增量检查点(Incremental checkpointing)
6、高性能
- 低延迟(Low latency)
- 高吞吐量(High throughput)
- 内存计算(In-Memory computing)
flink架构
1、层级结构
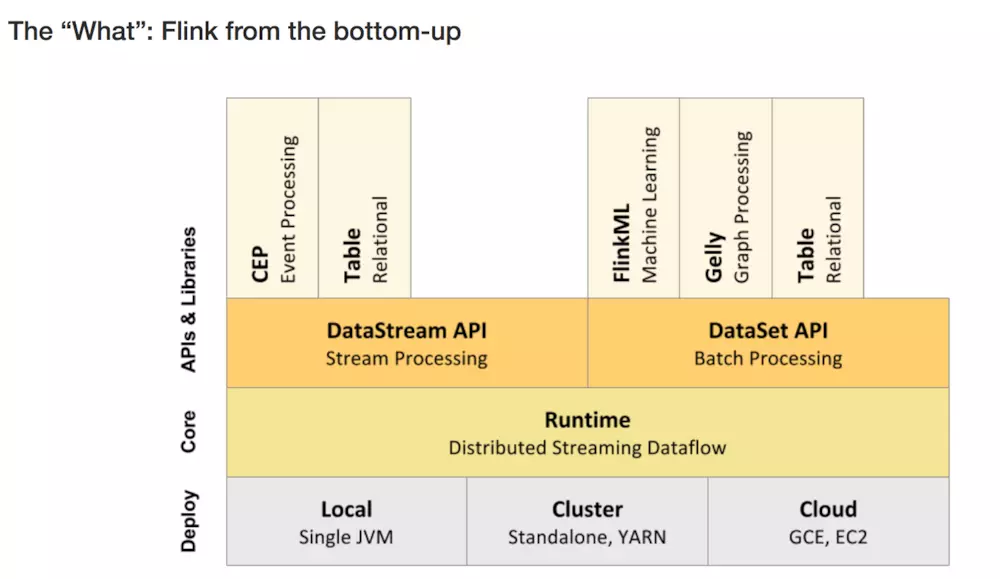
2.工作架构图
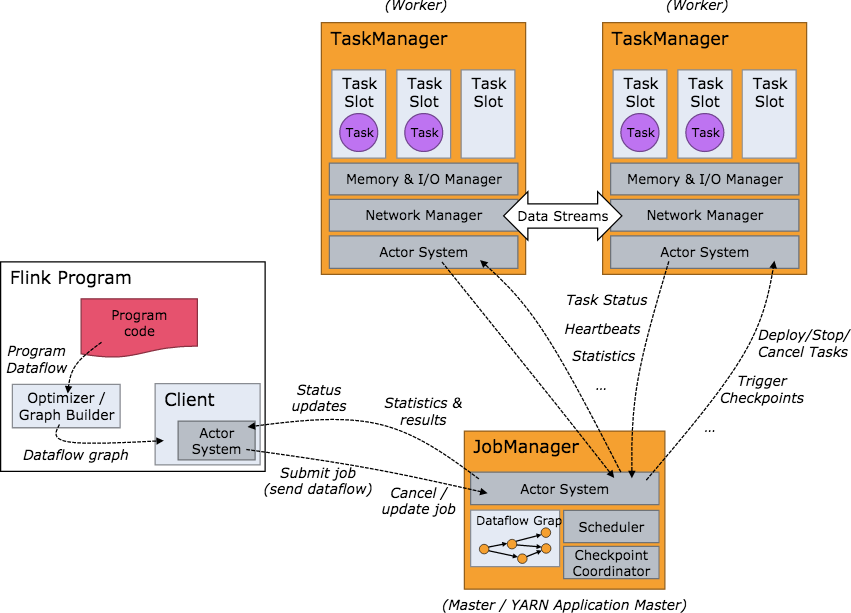
flink实战
1、依赖文件pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>flinkDemo</groupId>
<artifactId>flinkDemo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-java</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
<!--<scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-streaming-java_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
<!--<scope>provided</scope>-->
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-connector-kafka-0.10 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka-0.10_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.flink/flink-hbase -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-hbase_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
<version>0.10.1.1</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.10</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.rholder</groupId>
<artifactId>guava-retrying</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2、java程序
public class WordCountDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
// create execution environment
final ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params);
// get input data
DataSet<String> text;
if (params.has("input")) {
// read the text file from given input path
text = env.readTextFile(params.get("input"));
} else {
// get default test text data
System.out.println("Executing WordCount example with default input data set.");
System.out.println("Use --input to specify file input.");
text = WordCountData.getDefaultTextLineDataSet(env);
}
DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts =
// split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1)
text.flatMap(new Tokenizer())
// group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1"
.groupBy(0)
.sum(1);
// emit result
if (params.has("output")) {
counts.writeAsCsv(params.get("output"), "\n", " ");
// execute program
env.execute("WordCount Example");
} else {
System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path.");
counts.print();
}
}
// *************************************************************************
// USER FUNCTIONS
// *************************************************************************
/**
* Implements the string tokenizer that splits sentences into words as a user-defined
* FlatMapFunction. The function takes a line (String) and splits it into
* multiple pairs in the form of "(word,1)" ({@code Tuple2<String, Integer>}).
*/
public static final class Tokenizer implements FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>> {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) {
// normalize and split the line
String[] tokens = value.toLowerCase().split("\\W+");
// emit the pairs
for (String token : tokens) {
if (token.length() > 0) {
out.collect(new Tuple2<>(token, 1));
}
}
}
}
}
3、单步调试分析
第一步:获取环境信息ExecutionEnvironment.java
/**
* The ExecutionEnvironment is the context in which a program is executed. A
* {@link LocalEnvironment} will cause execution in the current JVM, a
* {@link RemoteEnvironment} will cause execution on a remote setup.
*
* <p>The environment provides methods to control the job execution (such as setting the parallelism)
* and to interact with the outside world (data access).
*
* <p>Please note that the execution environment needs strong type information for the input and return types
* of all operations that are executed. This means that the environments needs to know that the return
* value of an operation is for example a Tuple of String and Integer.
* Because the Java compiler throws much of the generic type information away, most methods attempt to re-
* obtain that information using reflection. In certain cases, it may be necessary to manually supply that
* information to some of the methods.
*
* @see LocalEnvironment
* @see RemoteEnvironment
*/
创建本地环境
/**
* Creates a {@link LocalEnvironment} which is used for executing Flink jobs.
*
* @param configuration to start the {@link LocalEnvironment} with
* @param defaultParallelism to initialize the {@link LocalEnvironment} with
* @return {@link LocalEnvironment}
*/
private static LocalEnvironment createLocalEnvironment(Configuration configuration, int defaultParallelism) {
final LocalEnvironment localEnvironment = new LocalEnvironment(configuration); if (defaultParallelism > 0) {
localEnvironment.setParallelism(defaultParallelism);
} return localEnvironment;
}
第二步:获取外部数据,创建数据集 ExecutionEnvironment.java
/**
* Creates a DataSet from the given non-empty collection. Note that this operation will result
* in a non-parallel data source, i.e. a data source with a parallelism of one.
*
* <p>The returned DataSet is typed to the given TypeInformation.
*
* @param data The collection of elements to create the data set from.
* @param type The TypeInformation for the produced data set.
* @return A DataSet representing the given collection.
*
* @see #fromCollection(Collection)
*/
public <X> DataSource<X> fromCollection(Collection<X> data, TypeInformation<X> type) {
return fromCollection(data, type, Utils.getCallLocationName());
} private <X> DataSource<X> fromCollection(Collection<X> data, TypeInformation<X> type, String callLocationName) {
CollectionInputFormat.checkCollection(data, type.getTypeClass());
return new DataSource<>(this, new CollectionInputFormat<>(data, type.createSerializer(config)), type, callLocationName);
}
数据集的继承关系
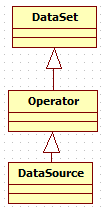
其中,DataSet是一组相同类型数据的集合,抽象类,它提供了数据的转换功能,如map,reduce,join和coGroup
/**
* A DataSet represents a collection of elements of the same type.
*
* <p>A DataSet can be transformed into another DataSet by applying a transformation as for example
* <ul>
* <li>{@link DataSet#map(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction)},</li>
* <li>{@link DataSet#reduce(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction)},</li>
* <li>{@link DataSet#join(DataSet)}, or</li>
* <li>{@link DataSet#coGroup(DataSet)}.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @param <T> The type of the DataSet, i.e., the type of the elements of the DataSet.
*/
Operator是java api的操作基类,抽象类
/**
* Base class of all operators in the Java API.
*
* @param <OUT> The type of the data set produced by this operator.
* @param <O> The type of the operator, so that we can return it.
*/
@Public
public abstract class Operator<OUT, O extends Operator<OUT, O>> extends DataSet<OUT> {
DataSource具体实现类。
/**
* An operation that creates a new data set (data source). The operation acts as the
* data set on which to apply further transformations. It encapsulates additional
* configuration parameters, to customize the execution.
*
* @param <OUT> The type of the elements produced by this data source.
*/
@Public
public class DataSource<OUT> extends Operator<OUT, DataSource<OUT>> {
第三步:对输入数据集进行转换
DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> counts =
// split up the lines in pairs (2-tuples) containing: (word,1)
text.flatMap(new Tokenizer())
// group by the tuple field "0" and sum up tuple field "1"
.groupBy(0)
.sum(1);
>>调用map DataSet.java
/**
* Applies a FlatMap transformation on a {@link DataSet}.
*
* <p>The transformation calls a {@link org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFlatMapFunction} for each element of the DataSet.
* Each FlatMapFunction call can return any number of elements including none.
*
* @param flatMapper The FlatMapFunction that is called for each element of the DataSet.
* @return A FlatMapOperator that represents the transformed DataSet.
*
* @see org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFlatMapFunction
* @see FlatMapOperator
* @see DataSet
*/
public <R> FlatMapOperator<T, R> flatMap(FlatMapFunction<T, R> flatMapper) {
if (flatMapper == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("FlatMap function must not be null.");
} String callLocation = Utils.getCallLocationName();
TypeInformation<R> resultType = TypeExtractor.getFlatMapReturnTypes(flatMapper, getType(), callLocation, true);
return new FlatMapOperator<>(this, resultType, clean(flatMapper), callLocation);
}
>>调用groupby DataSet.java
/**
* Groups a {@link Tuple} {@link DataSet} using field position keys.
*
* <p><b>Note: Field position keys only be specified for Tuple DataSets.</b>
*
* <p>The field position keys specify the fields of Tuples on which the DataSet is grouped.
* This method returns an {@link UnsortedGrouping} on which one of the following grouping transformation
* can be applied.
* <ul>
* <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#sortGroup(int, org.apache.flink.api.common.operators.Order)} to get a {@link SortedGrouping}.
* <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#aggregate(Aggregations, int)} to apply an Aggregate transformation.
* <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#reduce(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.ReduceFunction)} to apply a Reduce transformation.
* <li>{@link UnsortedGrouping#reduceGroup(org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.GroupReduceFunction)} to apply a GroupReduce transformation.
* </ul>
*
* @param fields One or more field positions on which the DataSet will be grouped.
* @return A Grouping on which a transformation needs to be applied to obtain a transformed DataSet.
*
* @see Tuple
* @see UnsortedGrouping
* @see AggregateOperator
* @see ReduceOperator
* @see org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.GroupReduceOperator
* @see DataSet
*/
public UnsortedGrouping<T> groupBy(int... fields) {
return new UnsortedGrouping<>(this, new Keys.ExpressionKeys<>(fields, getType()));
}
>>调用sum UnsortedGrouping.java
/**
* Syntactic sugar for aggregate (SUM, field).
* @param field The index of the Tuple field on which the aggregation function is applied.
* @return An AggregateOperator that represents the summed DataSet.
*
* @see org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.AggregateOperator
*/
public AggregateOperator<T> sum (int field) {
return this.aggregate (Aggregations.SUM, field, Utils.getCallLocationName());
}
// private helper that allows to set a different call location name
private AggregateOperator<T> aggregate(Aggregations agg, int field, String callLocationName) {
return new AggregateOperator<T>(this, agg, field, callLocationName);
}
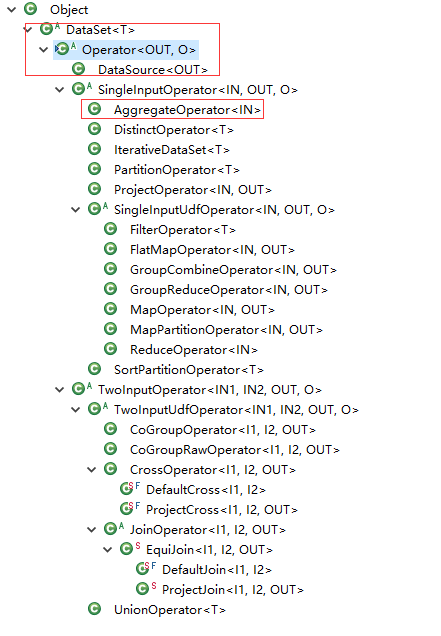
UnsortedGrouping和DataSet的关系
UnsortedGrouping使用AggregateOperator做聚合
第四步:对转换的输入值进行处理
// emit result
if (params.has("output")) {
counts.writeAsCsv(params.get("output"), "\n", " ");
// execute program
env.execute("WordCount Example");
} else {
System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path.");
counts.print();
}
如果不指定output参数,则打印到控制台
/**
* Prints the elements in a DataSet to the standard output stream {@link System#out} of the JVM that calls
* the print() method. For programs that are executed in a cluster, this method needs
* to gather the contents of the DataSet back to the client, to print it there.
*
* <p>The string written for each element is defined by the {@link Object#toString()} method.
*
* <p>This method immediately triggers the program execution, similar to the
* {@link #collect()} and {@link #count()} methods.
*
* @see #printToErr()
* @see #printOnTaskManager(String)
*/
public void print() throws Exception {
List<T> elements = collect();
for (T e: elements) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
若指定输出,则先进行输入转换为csv文件的DataSink,它是用来存储数据结果的
/**
* An operation that allows storing data results.
* @param <T>
*/
过程如下:
/**
* Writes a {@link Tuple} DataSet as CSV file(s) to the specified location with the specified field and line delimiters.
*
* <p><b>Note: Only a Tuple DataSet can written as a CSV file.</b>
* For each Tuple field the result of {@link Object#toString()} is written.
*
* @param filePath The path pointing to the location the CSV file is written to.
* @param rowDelimiter The row delimiter to separate Tuples.
* @param fieldDelimiter The field delimiter to separate Tuple fields.
* @param writeMode The behavior regarding existing files. Options are NO_OVERWRITE and OVERWRITE.
*
* @see Tuple
* @see CsvOutputFormat
* @see DataSet#writeAsText(String) Output files and directories
*/
public DataSink<T> writeAsCsv(String filePath, String rowDelimiter, String fieldDelimiter, WriteMode writeMode) {
return internalWriteAsCsv(new Path(filePath), rowDelimiter, fieldDelimiter, writeMode);
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <X extends Tuple> DataSink<T> internalWriteAsCsv(Path filePath, String rowDelimiter, String fieldDelimiter, WriteMode wm) {
Preconditions.checkArgument(getType().isTupleType(), "The writeAsCsv() method can only be used on data sets of tuples.");
CsvOutputFormat<X> of = new CsvOutputFormat<>(filePath, rowDelimiter, fieldDelimiter);
if (wm != null) {
of.setWriteMode(wm);
}
return output((OutputFormat<T>) of);
}
/**
* Emits a DataSet using an {@link OutputFormat}. This method adds a data sink to the program.
* Programs may have multiple data sinks. A DataSet may also have multiple consumers (data sinks
* or transformations) at the same time.
*
* @param outputFormat The OutputFormat to process the DataSet.
* @return The DataSink that processes the DataSet.
*
* @see OutputFormat
* @see DataSink
*/
public DataSink<T> output(OutputFormat<T> outputFormat) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(outputFormat); // configure the type if needed
if (outputFormat instanceof InputTypeConfigurable) {
((InputTypeConfigurable) outputFormat).setInputType(getType(), context.getConfig());
} DataSink<T> sink = new DataSink<>(this, outputFormat, getType());
this.context.registerDataSink(sink);
return sink;
}
最后执行job
@Override
public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception {
if (executor == null) {
startNewSession();
} Plan p = createProgramPlan(jobName); // Session management is disabled, revert this commit to enable
//p.setJobId(jobID);
//p.setSessionTimeout(sessionTimeout); JobExecutionResult result = executor.executePlan(p); this.lastJobExecutionResult = result;
return result;
}
这一阶段是内容比较多,放到下一篇讲解吧
总结
Apache Flink 功能强大,支持开发和运行多种不同种类的应用程序。它的主要特性包括:批流一体化、精密的状态管理、事件时间支持以及精确一次的状态一致性保障等。Flink 不仅可以运行在包括 YARN、 Mesos、Kubernetes 在内的多种资源管理框架上,还支持在裸机集群上独立部署。在启用高可用选项的情况下,它不存在单点失效问题。事实证明,Flink 已经可以扩展到数千核心,其状态可以达到 TB 级别,且仍能保持高吞吐、低延迟的特性。世界各地有很多要求严苛的流处理应用都运行在 Flink 之上。
其应用场景如下:
1、事件驱动型应用
典型的事件驱动型应用实例:
反欺诈
异常检测
基于规则的报警
业务流程监控
(社交网络)Web 应用
2、数据分析应用
典型的数据分析应用实例
电信网络质量监控
移动应用中的产品更新及实验评估分析
消费者技术中的实时数据即席分析
大规模图分析
3、数据管道应用
典型的数据管道应用实例
电子商务中的实时查询索引构建
电子商务中的持续 ETL
参考资料
【2】https://blog.csdn.net/yangyin007/article/details/82382734
【3】https://flink.apache.org/zh/usecases.html
从flink-example分析flink组件(1)WordCount batch实战及源码分析的更多相关文章
- 从flink-example分析flink组件(3)WordCount 流式实战及源码分析
前面介绍了批量处理的WorkCount是如何执行的 <从flink-example分析flink组件(1)WordCount batch实战及源码分析> <从flink-exampl ...
- Apache Beam WordCount编程实战及源码解读
概述:Apache Beam WordCount编程实战及源码解读,并通过intellij IDEA和terminal两种方式调试运行WordCount程序,Apache Beam对大数据的批处理和流 ...
- SpringCloudGateway微服务网关实战与源码分析 - 中
实战 路由过滤器工厂 路由过滤器允许以某种方式修改传入的HTTP请求或传出的HTTP响应.路由过滤器的作用域是特定的路由.SpringCloud Gateway包括许多内置的GatewayFilter ...
- Django drf:认证及组件、token、局部钩子源码分析
一.drf认证功能 二.token讲解 三.局部钩子源码分析 一.drf认证功能 1.认证简介: 只有认证通过的用户才能访问指定的url地址,比如:查询课程信息,需要登录之后才能查看,没有登录则不能查 ...
- [源码分析]Java1.8中StringJoiner的使用以及源码分析
[源码分析]StringJoiner的使用以及源码分析 StringJoiner是Java里1.8新增的类, 或许有一部分人没有接触过. 所以本文将从使用例子入手, 分析StringJoiner的源码 ...
- Spring事务源码分析专题(一)JdbcTemplate使用及源码分析
Spring中的数据访问,JdbcTemplate使用及源码分析 前言 本系列文章为事务专栏分析文章,整个事务分析专题将按下面这张图完成 对源码分析前,我希望先介绍一下Spring中数据访问的相关内容 ...
- Java源码分析:Guava之不可变集合ImmutableMap的源码分析
一.案例场景 遇到过这样的场景,在定义一个static修饰的Map时,使用了大量的put()方法赋值,就类似这样-- public static final Map<String,String& ...
- SpringCloudAlibaba注册中心与配置中心之利器Nacos实战与源码分析(上)
不断踩坑并解决问题是每个程序员进阶到资深的必要经历并以此获得满足感,而不断阅读开源项目源码和总结思想是每个架构师成长最佳途径.本篇拉开SpringCloud Alibaba最新版本实战和原理序幕,以工 ...
- SpringCloudAlibaba分布式流量控制组件Sentinel实战与源码分析(上)
概述 定义 Sentinel官网地址 https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/index.html 最新版本v1.8.4 Sentinel官网文档地址 https://senti ...
随机推荐
- js的replace, 高亮
";console.log(str.replace(/\,/g, "")); //输出 123 ";console.log(str);//输出123 " ...
- ubuntu14.04禁用USB外存储设备
ubuntu 14.04中禁用usb外存储设备: 在网上找了很多方法,大概都是下面的命令,而实际测试的时候没有什么作用. gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.media-h ...
- python str操作
1. str.format():使用“{}”占位符格式化字符串(占位符中的索引号形式和键值对形式可以混合使用). 1 >>> string = 'python{}, django{} ...
- do{}while(0)
有时会在源码中或在写代码时在宏定义中用到do...while(0). 采用这种方式进行宏定义, 主要是为了防止出现以下错误 : do{}while(0) 空的宏定义避免出现warnning. #def ...
- flask之配置文件的加载和动态url的使用
七行代码实现一个flask app from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/') def helloworld(): re ...
- pandas - 案例(股票分析)
需求: 使用tushare包获取某股票的历史行情数据. 输出该股票所有收盘比开盘上涨3%以上的日期. 输出该股票所有开盘比前日收盘跌幅超过2%的日期. 假如我从2010年1月1日开始,每月第一个交易日 ...
- 第三节:numpy之数组数学运算
- vue 中全局filter过滤器的配置及使用
在项目中使用到的经常用到过滤器,比如时间,数据截取等过滤器,如果在每个.vue中都可以复制同一个过滤器,这可以达到目的,但是遇到方法有bug时就需要诸葛修改进入不同的页面修改,这样既费时又费力,优先可 ...
- ansible common modules
##Some common modules[cloud modules] [clustering modules] [command modules]command - executes a comm ...
- noip模拟赛 PA
分析:很显然这是一道搜索题,可能是由于我的搜索打的太不美观了,这道题又WA又T......如果对每一个询问都做一次bfs是肯定会T的,注意到前70%的数据范围,N的值都相等,我们可以把给定N的所有情况 ...
