About the iOS File System
两个维度:
1)是否给用户使用;
2)是否持久存储。
During installation of a new app, the installer creates a number of container directories for the app inside the sandbox directory. Each container directory has a specific role. The bundle container directory holds the app’s bundle, whereas the data container directory holds data for both the app and the user. The data container directory is further divided into a number of subdirectories that the app can use to sort and organize its data.
https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/FileManagement/Conceptual/FileSystemProgrammingGuide/FileSystemOverview/FileSystemOverview.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40010672-CH2-SW12
About the iOS File System
The iOS file system is geared toward apps running on their own. To keep the system simple, users of iOS devices do not have direct access to the file system and apps are expected to follow this convention.
iOS Standard Directories: Where Files Reside
For security purposes, an iOS app’s interactions with the file system are limited to the directories inside the app’s sandbox directory. During installation of a new app, the installer creates a number of container directories for the app inside the sandbox directory. Each container directory has a specific role. The bundle container directory holds the app’s bundle, whereas the data container directory holds data for both the app and the user. The data container directory is further divided into a number of subdirectories that the app can use to sort and organize its data. The app may also request access to additional container directories—for example, the iCloud container—at runtime.
These container directories constitute the app’s primary view of the file system. Figure 1-1 shows a representation of the sandbox directory for an app.
Figure 1-1 An iOS app operating within its own sandbox directory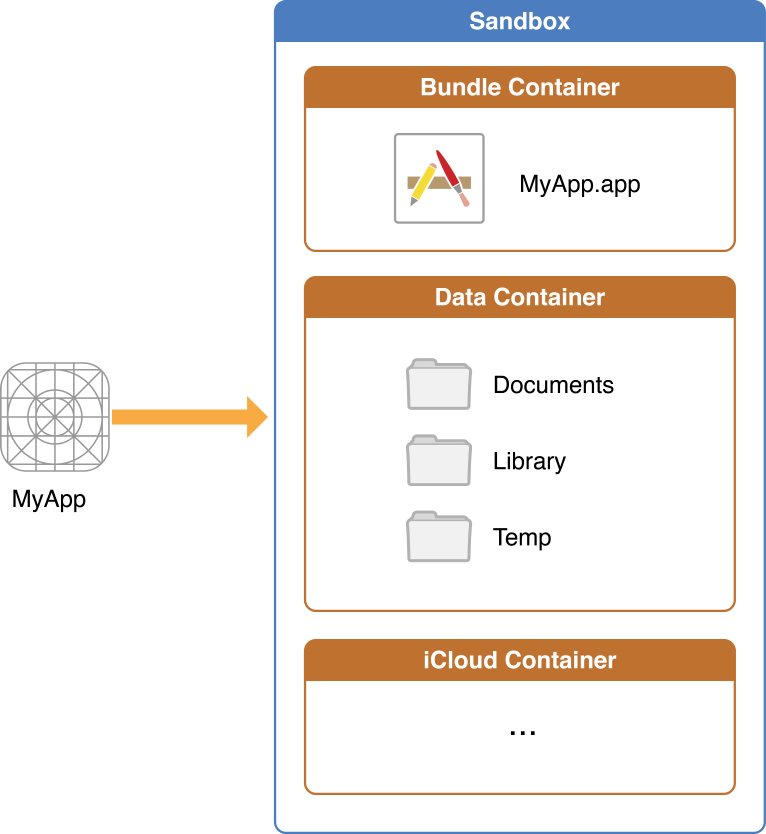
An app is generally prohibited from accessing or creating files outside its container directories. One exception to this rule is when an app uses public system interfaces to access things such as the user’s contacts or music. In those cases, the system frameworks use helper apps to handle any file-related operations needed to read from or modify the appropriate data stores.
Table 1-1 lists some of the more important subdirectories inside the sandbox directory and describes their intended usage. This table also describes any additional access restrictions for each subdirectory and points out whether the directory’s contents are backed up by iTunes and iCloud.
|
Directory |
Description |
|---|---|
|
AppName |
This is the app’s bundle. This directory contains the app and all of its resources. You cannot write to this directory. To prevent tampering, the bundle directory is signed at installation time. Writing to this directory changes the signature and prevents your app from launching. You can, however, gain read-only access to any resources stored in the apps bundle. For more information, see the Resource Programming Guide The contents of this directory are not backed up by iTunes or iCloud. However, iTunes does perform an initial sync of any apps purchased from the App Store. |
|
|
Use this directory to store user-generated content. The contents of this directory can be made available to the user through file sharing; therefore, his directory should only contain files that you may wish to expose to the user. The contents of this directory are backed up by iTunes and iCloud. |
|
|
Use this directory to access files that your app was asked to open by outside entities. Specifically, the Mail program places email attachments associated with your app in this directory. Document interaction controllers may also place files in it. Your app can read and delete files in this directory but cannot create new files or write to existing files. If the user tries to edit a file in this directory, your app must silently move it out of the directory before making any changes. The contents of this directory are backed up by iTunes and iCloud. |
|
|
This is the top-level directory for any files that are not user data files. You typically put files in one of several standard subdirectories. iOS apps commonly use the Use the The contents of the For additional information about the Library directory and its commonly used subdirectories, see The Library Directory Stores App-Specific Files. |
|
|
Use this directory to write temporary files that do not need to persist between launches of your app. Your app should remove files from this directory when they are no longer needed; however, the system may purge this directory when your app is not running. The contents of this directory are not backed up by iTunes or iCloud. |
An iOS app may create additional directories in the Documents, Library, and tmp directories. You might do this to better organize the files in those locations.
For information about how to get references to the preceding directories from your iOS app, see Locating Items in the Standard Directories. For tips on where to put files, see Where You Should Put Your App’s Files.
Where You Should Put Your App’s Files
To prevent the syncing and backup processes on iOS devices from taking a long time, be selective about where you place files. Apps that store large files can slow down the process of backing up to iTunes or iCloud. These apps can also consume a large amount of a user's available storage, which may encourage the user to delete the app or disable backup of that app's data to iCloud. With this in mind, you should store app data according to the following guidelines:
Put user data in
Documents/. User data generally includes any files you might want to expose to the user—anything you might want the user to create, import, delete or edit. For a drawing app, user data includes any graphic files the user might create. For a text editor, it includes the text files. Video and audio apps may even include files that the user has downloaded to watch or listen to later.Put app-created support files in the
Library/Application support/directory. In general, this directory includes files that the app uses to run but that should remain hidden from the user. This directory can also include data files, configuration files, templates and modified versions of resources loaded from the app bundle.Remember that files in
Documents/andApplication Support/are backed up by default. You can exclude files from the backup by calling-[NSURL setResourceValue:forKey:error:]using theNSURLIsExcludedFromBackupKeykey. Any file that can be re-created or downloaded must be excluded from the backup. This is particularly important for large media files. If your application downloads video or audio files, make sure they are not included in the backup.Put temporary data in the
tmp/directory. Temporary data comprises any data that you do not need to persist for an extended period of time. Remember to delete those files when you are done with them so that they do not continue to consume space on the user’s device. The system will periodically purge these files when your app is not running; therefore, you cannot rely on these files persisting after your app terminates.Put data cache files in the
Library/Caches/directory. Cache data can be used for any data that needs to persist longer than temporary data, but not as long as a support file. Generally speaking, the application does not require cache data to operate properly, but it can use cache data to improve performance. Examples of cache data include (but are not limited to) database cache files and transient, downloadable content. Note that the system may delete theCaches/directory to free up disk space, so your app must be able to re-create or download these files as needed.
About the iOS File System的更多相关文章
- File System Programming --- (二)
File System Basics The file systems in OS X and iOS handle the persistent storage of data files, app ...
- File System Programming---(三)
Accessing Files and Directories Before you can open a file, you first have to locate it in the file ...
- File System Programming --- (一)
About Files and Directories The file system is an important part of any operating system. After all, ...
- File System Design Case Studies
SRC=http://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~pxk/416/notes/13-fs-studies.html Paul Krzyzanowski April 24, 2014 Int ...
- Design and Implementation of the Sun Network File System
Introduction The network file system(NFS) is a client/service application that provides shared file ...
- 乌版图 read-only file system
今天在启动虚拟机的时候,运行命令svn up的时候,提示lock,并且read-only file system,这个....我是小白啊,怎么办?前辈在专心写代码,不好打扰,果断找度娘啊 于是乎,折腾 ...
- File system needs to be upgraded. You have version null and I want version 7
安装hbase时候报错: File system needs to be upgraded. You have version null and I want version 7 注: 我安装的hba ...
- Linux系统启动错误 contains a file system with errors, check forced解决方法
/dev/sda1 contains a file system with errors, check forced./dev/sda1: Inodes that were part of a cor ...
- Linux 执行partprobe命令时遇到Unable to open /dev/sr0 read-write (Read-only file system)
在使用fdisk创建分区时,我们会使用partprobe命令可以使kernel重新读取分区信息,从而避免重启系统,但是有时候会遇到下面错误信息"Warning: Unable to open ...
随机推荐
- 「LuoguP2170」 选学霸(01背包
Description 老师想从N名学生中选M人当学霸,但有K对人实力相当,如果实力相当的人中,一部分被选上,另一部分没有,同学们就会抗议.所以老师想请你帮他求出他该选多少学霸,才能既不让同学们抗议, ...
- 状态保存机制之ViewState概述及应用
状态保存机制之ViewState概述及应用 作者: 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 无状态的根本原因是:浏览器和服务器使用Socket通信,服务器将请求结果返回给浏览器后,会关闭当前Socket ...
- python之路,day6-面向对象
一.面向过程编程 简单的说就是:如果你只是写一些简单的脚本,去做一些一次性任务,用面向过程的方式是极好的,但是如果你要处理的任务比较复杂,且需要不断迭代和维护的,那还是用面向对象最方便了. 二.面向对 ...
- centos7搭建rsync
两台主机(centos7): 172.16.0.109 server 172.16.0.106 client 一.在172.16.0.109上 yum -y install rsync #安装 mkd ...
- Ubuntu16.04安装Python3.6 和pip
root账户,不是root账户,命令前加sudo 安装: 1.add-apt-repository ppa:jonathonf/python-3.6 2.apt-get update 3.apt-ge ...
- 用ffmpeg命令将264裸码流封装成mp4(转载)
转自:http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/370256130 ffmpeg -f h264 -i source.264 -vcodec copy out.mp4
- C++笔试题库之编程、问答题 100~150道
101. winsock建立连接的主要实现步骤? 答: 服务器端:socket()建立套接字,绑定(bind)并监听(listen),用accept()等待客户端连接, accept()发现有客户端连 ...
- POJ2367【拓扑排序】
很裸的拓扑排序~ //#include <bits/stdc++.h> #include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include ...
- 洛谷CF1030F Putting Boxes Together(树状数组)
题意: 现在有n个物品,第i个物品他的位置在a[i],他的重量为w[i].每一个物品移动一步的代价为他的w[i].目前有2种操作: 1. x y 将第x的物品的重量改为y 2.l r 将编号在 [ l ...
- c#删除指定文件夹中今天之前的文件
1.说明 使用Directory类对指定文件夹下的今天或者更早日期之前的文件进行删除.原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/lengzhan/p/6423943.html 2.代码 ...
