python--第三天总结
【collection系列】
1、计数器(counter)
Counter是对字典类型的补充,用于追踪值的出现次数。
ps:具备字典的所有功能 + 自己的功能
- c = Counter('abcdeabcdabcaba')
- print c
- 输出:Counter({'a': 5, 'b': 4, 'c': 3, 'd': 2, 'e': 1})
import collections 或from collections import Counter
2、有序字典(orderedDict )
from collections import OrderedDict
orderdDict是对字典类型的补充,他记住了字典元素添加的顺序
3、默认字典(defaultdict)
学前需求:
- 有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。
- 即: {'k1': 大于66 , 'k2': 小于66}
values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
my_dict = {}
for value in values:
if value>66:
if my_dict.has_key('k1'):
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k1'] = [value]
else:
if my_dict.has_key('k2'):
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'] = [value]
原生字典解决方法
from collections import defaultdict values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] my_dict = defaultdict(list) for value in values:
if value>66:
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
defaultdict字典解决方法
defaultdict是对字典的类型的补充,他默认给字典的值设置了一个类型。
class defaultdict(dict):
"""
defaultdict(default_factory[, ...]) --> dict with default factory The default factory is called without arguments to produce
a new value when a key is not present, in __getitem__ only.
A defaultdict compares equal to a dict with the same items.
All remaining arguments are treated the same as if they were
passed to the dict constructor, including keyword arguments.
"""
def copy(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D. """
pass def __copy__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" D.copy() -> a shallow copy of D. """
pass def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass def __init__(self, default_factory=None, **kwargs): # known case of _collections.defaultdict.__init__
"""
defaultdict(default_factory[, ...]) --> dict with default factory The default factory is called without arguments to produce
a new value when a key is not present, in __getitem__ only.
A defaultdict compares equal to a dict with the same items.
All remaining arguments are treated the same as if they were
passed to the dict constructor, including keyword arguments. # (copied from class doc)
"""
pass def __missing__(self, key): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
__missing__(key) # Called by __getitem__ for missing key; pseudo-code:
if self.default_factory is None: raise KeyError((key,))
self[key] = value = self.default_factory()
return value
"""
pass def __reduce__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return state information for pickling. """
pass def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass default_factory = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""Factory for default value called by __missing__().""" defaultdict
defaultdict
冒泡算法
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*- values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] my_dict = {} for value in values:
if value > 66:
if my_dict.has_key('k1'):
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k1'] = [value] else:
if my_dict.has_key('k2'):
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'] = [value]
print my_dict
4、可命名元组(namedtuple)
根据nametuple可以创建一个包含tuple所有功能以及其他功能的类型。
- import collections
- Mytuple = collections.namedtuple('Mytuple',['x', 'y', 'z'])
#创建一个扩展tuple的类,Mytuple
tuple
Mytuple = collections.namedtuple('Mytuple',['x', 'y'])
old = tuple(1,2) <==> old = (1,2)
(1,2)
new = Mytuple(1,2)
{'x':1,'y':2 }
5、双向队列(deque)
一个线程安全的双向队列
注:既然有双向队列,也有单项队列(先进先出 FIFO )
【Queue.Queue】
队列,FIFO
栈 ,弹夹
【迭代器和生成器】
一、迭代器
对于Python 列表的 for 循环,他的内部原理:查看下一个元素是否存在,如果存在,则取出,如果不存在,则报异常 StopIteration。(python内部对异常已处理)
erable 迭代
迭代器 只有循环才能取出值
二、生成器
range不是生成器 和 xrange 是生成器
readlines不是生成器 和 xreadlines 是生成器
- >>> print range(10)
- [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
- >>> print xrange(10)
- xrange(10)
-------[函数]
- 内置函数
- 自定义函数
- 导入函数
【 内置函数如下:】
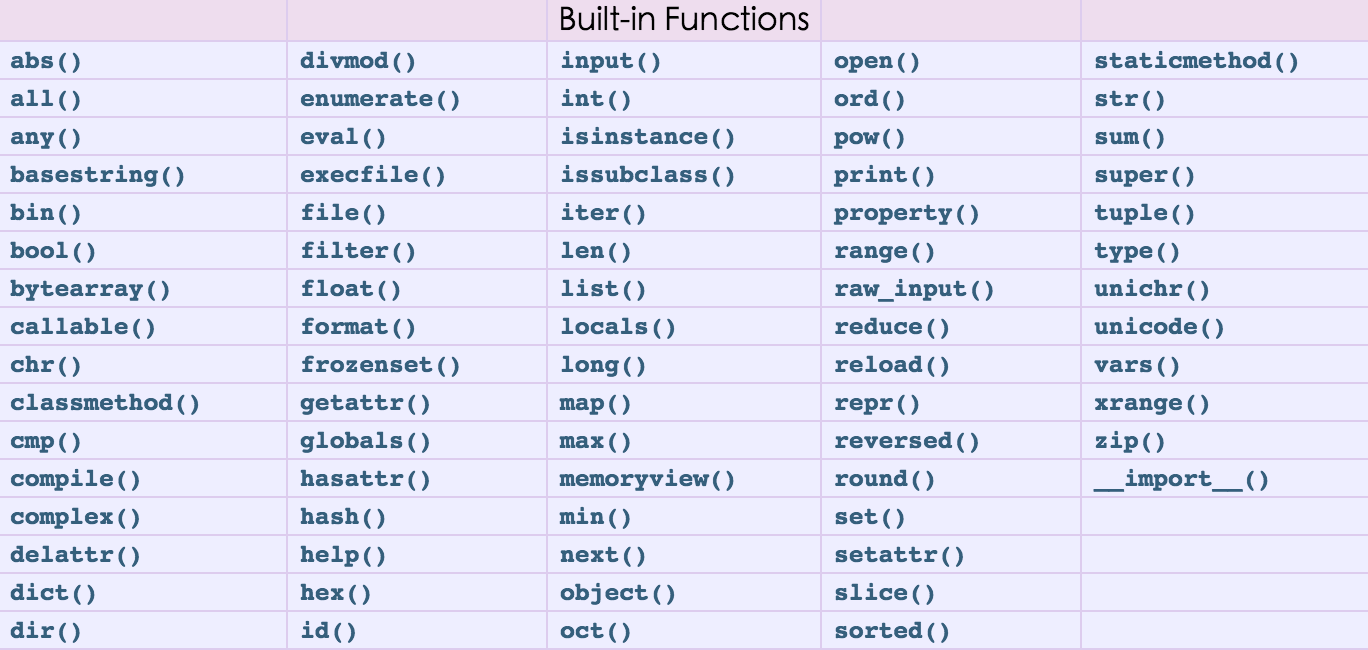
help()
dir()
vars()
type()
reload(temp)
id([12])
is
------------------
cmp(2,3)
abs()
bool()
divmod(10,3),分页
max()
min()
sum()
pow(2, 11)
------------------
len()
all() #接受一个序列,判断,序列中所有值都是真,返回真,否则假(空 为False)
any() #有一个为真,返回真
------------------
chr()
ord()
hex()
oct()
bin()
ASCII码转换
ord('A') --> 65
chr(65)
------------------
print range(10)
print xrange(10)
for i in xrange(10):
print i
for k,v in enumerate([1,2,3,4],执行数字起始值):
print k,v
------------------
print apply(Function,('aaaa')) #执行函数
print map(lambda x:x+1,[1,2,3]) #all
print filter(lambda x: x==1,[1,23,4]) #True序列
print reduce(lambda x,y:x+y,[1,2,3]) #累加
print zip(x, y,z)
【自定义函数】
函数的定义主要有如下要点:
1、def 定义函数的关键字
2、函数名,日后通过函数名调用该函数
3、函数声明,不自动执行;调用后才执行
4、函数的参数
5、函数的返回值
返回值:
1、未明确制定返回值,返回 None
2、返回值可以赋值给某个变量
函数的有三中不同的参数:
普通参数
默认参数
动态参数
# 形式参数,形参
# 实际参数,实参
参数可以有n个,传入制定个数的参数
默认参数,
1、不传,则使用默认
2、默认参数必须放在参数列表的最后
# 形式参数,形参
# 实际参数,实参
format
动态参数一
def func(*args):
pass
1、接受多个参数
2、内部自动构造元组
3、序列,*,避免内部构造元组
def func(*args):
print args[0]
func(11,22,33,44,55)
动态参数二
def func(**kwargs):
print kwargs
1、func(k1=123,k2='sss')
2、
dic = {"k1":123}
func(**dic)
func(11,22,33,44,55)
def func(*args,**kwargs):
s = "i am {0},age{1}"
s.format('alex','18')
s = 'i am {name,age{age}}'
s.format(name='alex',age=19)
[模块导入]
Python只所有应用越来越广泛,在一定程度上也依赖于其为程序员提供了大量的模块以供使用,如果想要使用模块,则需要导入。导入模块有一下几种方法:
importmodulefrommodule.xx.xximportxxfrommodule.xx.xximportxx as renamefrommodule.xx.xximport*
那么问题来了,导入模块时是根据那个路径作为基准来进行的呢?即:sys.path
【文件操作】
操作文件时,一般需要经历如下步骤:
- 打开文件
- 操作文件
一、打开文件
- 文件句柄 = file('文件路径', '模式')
注:python中打开文件有两种方式,即:open(...) 和 file(...) ,本质上前者在内部会调用后者来进行文件操作,推荐使用 open。
打开文件时,需要指定文件路径和以何等方式打开文件,打开后,即可获取该文件句柄,日后通过此文件句柄对该文件操作。
打开文件的模式有:
- r,只读模式(默认)。
- w,只写模式。【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则删除内容;】
- a,追加模式。【可读; 不存在则创建;存在则只追加内容;】
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
- r+,可读写文件。【可读;可写;可追加】
- w+,无意义
- a+,同a
"U"表示在读取时,可以将 \r \n \r\n自动转换成 \n (与 r 或 r+ 模式同使用)
- rU
- r+U
"b"表示处理二进制文件(如:FTP发送上传ISO镜像文件,linux可忽略,windows处理二进制文件时需标注)
- rb
- wb
- ab
二、操作操作
class file(object):
def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
关闭文件
"""
close() -> None or (perhaps) an integer. Close the file.
Sets data attribute .closed to True. A closed file cannot be used for
further I/O operations. close() may be called more than once without
error. Some kinds of file objects (for example, opened by popen())
may return an exit status upon closing.
"""
def fileno(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
文件描述符
"""
fileno() -> integer "file descriptor".
This is needed for lower-level file interfaces, such os.read().
"""
return 0
def flush(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
刷新文件内部缓冲区
""" flush() -> None. Flush the internal I/O buffer. """
pass
def isatty(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
判断文件是否是同意tty设备
""" isatty() -> true or false. True if the file is connected to a tty device. """
return False
def next(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
获取下一行数据,不存在,则报错
""" x.next() -> the next value, or raise StopIteration """
pass
def read(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取指定字节数据
"""
read([size]) -> read at most size bytes, returned as a string.
If the size argument is negative or omitted, read until EOF is reached.
Notice that when in non-blocking mode, less data than what was requested
may be returned, even if no size parameter was given.
"""
pass
def readinto(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取到缓冲区,不要用,将被遗弃
""" readinto() -> Undocumented. Don't use this; it may go away. """
pass
def readline(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
仅读取一行数据
"""
readline([size]) -> next line from the file, as a string.
Retain newline. A non-negative size argument limits the maximum
number of bytes to return (an incomplete line may be returned then).
Return an empty string at EOF.
"""
pass
def readlines(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取所有数据,并根据换行保存值列表
"""
readlines([size]) -> list of strings, each a line from the file.
Call readline() repeatedly and return a list of the lines so read.
The optional size argument, if given, is an approximate bound on the
total number of bytes in the lines returned.
"""
return []
def seek(self, offset, whence=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
指定文件中指针位置
"""
seek(offset[, whence]) -> None. Move to new file position.
Argument offset is a byte count. Optional argument whence defaults to
0 (offset from start of file, offset should be >= 0); other values are 1
(move relative to current position, positive or negative), and 2 (move
relative to end of file, usually negative, although many platforms allow
seeking beyond the end of a file). If the file is opened in text mode,
only offsets returned by tell() are legal. Use of other offsets causes
undefined behavior.
Note that not all file objects are seekable.
"""
pass
def tell(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
获取当前指针位置
""" tell() -> current file position, an integer (may be a long integer). """
pass
def truncate(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
截断数据,仅保留指定之前数据
"""
truncate([size]) -> None. Truncate the file to at most size bytes.
Size defaults to the current file position, as returned by tell().
"""
pass
def write(self, p_str): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
写内容
"""
write(str) -> None. Write string str to file.
Note that due to buffering, flush() or close() may be needed before
the file on disk reflects the data written.
"""
pass
def writelines(self, sequence_of_strings): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
将一个字符串列表写入文件
"""
writelines(sequence_of_strings) -> None. Write the strings to the file.
Note that newlines are not added. The sequence can be any iterable object
producing strings. This is equivalent to calling write() for each string.
"""
pass
def xreadlines(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
可用于逐行读取文件,非全部
"""
xreadlines() -> returns self.
For backward compatibility. File objects now include the performance
optimizations previously implemented in the xreadlines module.
"""
pass
三、with
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下文,即:
with open('log','r') as f:
...
如此方式,当with代码块执行完毕时,内部会自动关闭并释放文件资源。
在Python 2.7 后,with又支持同时对多个文件的上下文进行管理,即:
- with open('log1') as obj1, open('log2') as obj2:
- pass
==其它
入口文件常用的 vars
__file__
__doc__
__name__
python--第三天总结的更多相关文章
- 学习Python的三种境界
前言 王国维在<人间词话>中将读书分为了三种境界:"古今之成大事业.大学问者,必经过三种之境界:'昨夜西风凋碧树,独上高楼,望尽天涯路'.此第一境也.'衣带渐宽终不悔,为伊消得人 ...
- selenium webdriver (python) 第三版
感谢 感谢购买第二版的同学,谢谢你们对本人劳动成果的支持!也正是你们时常问我还出不出第三版了,也是你们的鼓励,让我继续学习整理本文档. 感谢乙醇前辈,第二版的文档是放在他的淘宝网站上卖的,感谢他的帮忙 ...
- Python第三天 序列 数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典
Python第三天 序列 数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典 数据类型数值字符串列表元组字典 序列序列:字符串.列表.元组序列的两个主要特点是索引操作符和切片操作符- 索引操作符让我 ...
- 简学Python第三章__函数式编程、递归、内置函数
#cnblogs_post_body h2 { background: linear-gradient(to bottom, #18c0ff 0%,#0c7eff 100%); color: #fff ...
- 初学Python(三)——字典
初学Python(三)——字典 初学Python,主要整理一些学习到的知识点,这次是字典. #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- d = {1:"name",2:" ...
- Python第三天 序列 5种数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典 各种数据类型的的xx重写xx表达式
Python第三天 序列 5种数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典 各种数据类型的的xx重写xx表达式 目录 Pycharm使用技巧(转载) Python第一天 安装 shell ...
- python selenium 三种等待方式详解[转]
python selenium 三种等待方式详解 引言: 当你觉得你的定位没有问题,但是却直接报了元素不可见,那你就可以考虑是不是因为程序运行太快或者页面加载太慢造成了元素不可见,那就必须要加等待 ...
- python第三十一课--递归(2.遍历某个路径下面的所有内容)
需求:遍历某个路径下面的所有内容(文件和目录,多层级的) import os #自定义函数(递归函数):遍历目录层级(多级) def printDirs(path): dirs=os.listdir( ...
- Python的三种格式化输出
今天刚学了python的三种格式化输出,以前没接触过这么有趣的输出方式,现在来分享一下. #!/user/bin/env python#coding:utf-8#三种格式化输出 #第一种格式化输出na ...
- Python进阶(三十五)-Fiddler命令行和HTTP断点调试
Python进阶(三十五)-Fiddler命令行和HTTP断点调试 一. Fiddler内置命令 上一节(使用Fiddler进行抓包分析)中,介绍到,在web session(与我们通常所说的se ...
随机推荐
- Maven项目jar包的依懒范围
- maven 插件深入了解
http://www.infoq.com/cn/news/2011/04/xxb-maven-7-plugin http://www.infoq.com/cn/news/2011/05/xxb-mav ...
- centos7 更新yum报错initscripts conflicts with centos-release-7-3.1611.el7.centos.x86_64
1.centos7的系统的yum 更新系统报错: --> 解决依赖关系完成错误:initscripts conflicts with centos-release-7-3.1611.el7.ce ...
- Hive高级聚合GROUPING SETS,ROLLUP以及CUBE
scala> import org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveContextimport org.apache.spark.sql.hive.HiveContext s ...
- EditText获取焦点
这三个属性必须同时设置: private EditText passwde = null; passwde.setFocusable(true); passwde.setFocusableInTouc ...
- 使用MagicAJax的AjaxPanel时有时会弹出"Using the AjaxCallHelper write methods outside of an AjaxCall is not allowed."
------解决方案--------------------------------------------------------1.看下你的输出是不是包含在<ajax:AjaxPanel I ...
- Ajax 要点
Ajax 全称为“Asynchronous JavaScript and XML”(异步JavaScript和XML) Ajax的实现是基于 xmlHttp对象 异步发送请求 XMLHttpReque ...
- [bcc32 Error] ws2def.h(231): E2238 Multiple declaration for 'sockaddr'
[bcc32 Error] ws2def.h(231): E2238 Multiple declaration for 'sockaddr' Full parser context ksrGe ...
- es6 初级之展开运算符
1.1 先看一个求最大值的例子 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset ...
- Java读写hdfs上的avro文件
1.通过Java往hdfs写avro文件 import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; i ...
