learning ext2 filesystem notes
reference: http://e2fsprogs.sourceforge.net/ext2intro.html
reference: http://www.nongnu.org/ext2-doc/index.html
reference: http://www.science.unitn.it/~fiorella/guidelinux/tlk/
Each file is represented by a structure, called an inode. Each inode contains the description of the file: file type, access rights, owners, timestamps, size, pointers to data blocks. The addresses of data blocks allocated to a file are stored in its inode. When a user requests an I/O operation on the file, the kernel code converts the current offset to a block number, uses this number as an index in the block addresses table and reads or writes the physical block.
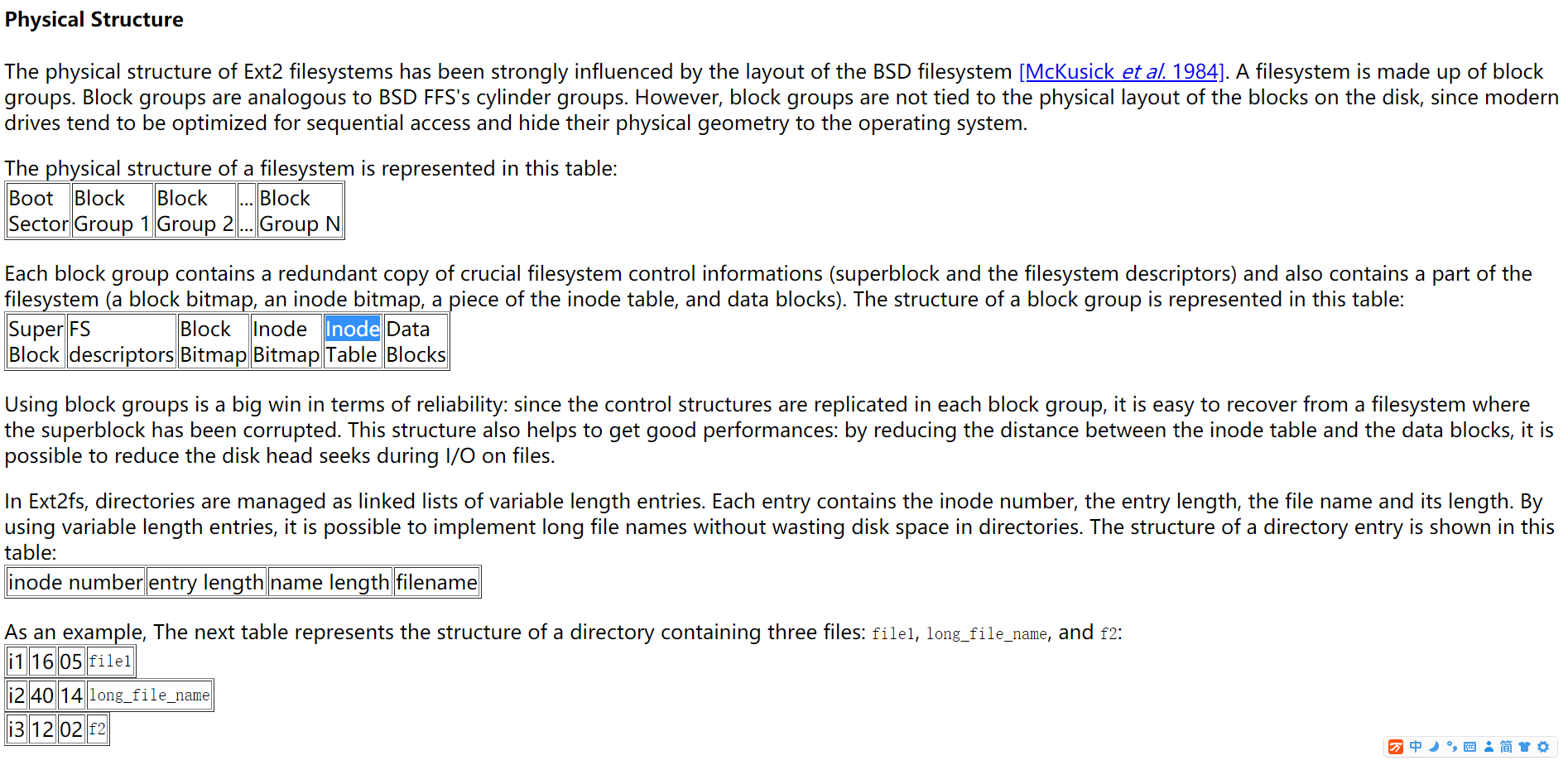
Directories:
Directories are implemented as a special type of files. Actually, a directory is a file containing a list of entries. Each entry contains an inode number and a file name. When a process uses a pathname, the kernel code searchs in the directories to find the corresponding inode number. After the name has been converted to an inode number, the inode is loaded into memory and is used by subsequent requests.
what happend when a extern stroage was mounted:
When a filesystem is to be mounted, the appropriate mount function is called. This function is responsible for reading the superblock from the disk, initializing its internal variables, and returning a mounted filesystem descriptor to the VFS. After the filesystem is mounted, the VFS functions can use this descriptor to access the physical filesystem routines.
A mounted filesystem descriptor contains several kinds of data: informations that are common to every filesystem types, pointers to functions provided by the physical filesystem kernel code, and private data maintained by the physical filesystem code. The function pointers contained in the filesystem descriptors allow the VFS to access the filesystem internal routines.
Two other types of descriptors are used by the VFS: an inode descriptor and an open file descriptor. Each descriptor contains informations related to files in use and a set of operations provided by the physical filesystem code. While the inode descriptor contains pointers to functions that can be used to act on any file (e.g. create, unlink), the file descriptors contains pointer to functions which can only act on open files (e.g. read, write).
Note: When such a file is deleted, random data is written in the disk blocks previously allocated to the file. This prevents malicious people from gaining access to the previous content of the file by using a disk editor.
root@IoTP:~# dumpe2fs /dev/mmcblk1p2
dumpe2fs 1.42.13 (17-May-2015)
Filesystem volume name: rootfs
Last mounted on: /
Filesystem UUID: 69277f59-15ba-4705-95eb-b6200ad095dc
Filesystem magic number: 0xEF53
Filesystem revision #: 1 (dynamic)
Filesystem features: has_journal ext_attr resize_inode dir_index filetype needs_recovery sparse_super large_file
Filesystem flags: unsigned_directory_hash
Default mount options: user_xattr acl
Filesystem state: clean
Errors behavior: Continue
Filesystem OS type: Linux
Inode count: 236176
Block count: 944384
Reserved block count: 47219
Free blocks: 753105
Free inodes: 204057
First block: 0
Block size: 4096
Fragment size: 4096
Reserved GDT blocks: 230
Blocks per group: 32768
Fragments per group: 32768
Inodes per group: 8144
Inode blocks per group: 509
Filesystem created: Wed Jan 16 05:11:41 2019
Last mount time: Wed Jan 16 06:05:42 2019
Last write time: Wed Jan 16 06:05:42 2019
Mount count: 6
Maximum mount count: -1
Last checked: Wed Jan 16 05:11:41 2019
Check interval: 0 (<none>)
Lifetime writes: 666 MB
Reserved blocks uid: 0 (user root)
Reserved blocks gid: 0 (group root)
First inode: 11
Inode size: 256
Required extra isize: 28
Desired extra isize: 28
Journal inode: 8
First orphan inode: 173330
Default directory hash: half_md4
Directory Hash Seed: 32104d28-8e90-4157-9c6a-3a5950fc100a
Journal backup: inode blocks
Journal features: journal_incompat_revoke
Journal size: 64M
Journal length: 16384
Journal sequence: 0x000000a8
Journal start: 9
Group 0: (Blocks 0-32767)
Primary superblock at 0, Group descriptors at 1-1
Reserved GDT blocks at 2-231
Block bitmap at 232 (+232), Inode bitmap at 233 (+233)
Inode table at 234-742 (+234)
8123 free blocks, 8134 free inodes, 1 directories
Free blocks: 752-783, 792-815, 824-847, 856-879, 887-911, 943-975, 1024-1039, 1044-1055, 1057-1073, 1216-1231, 1281-1311, 1327-1359, 1369-1391, 1440-1455, 1497-1503, 1521-1551, 1570-1615, 1618-1647, 1696-1711, 1736-1759, 1780-1807, 1856-1871, 1886-1887, 1898-1935, 1954-1999, 2030-2063, 2094-2127, 2135-2159, 2194-2223, 2228-2255, 2259-2287, 2336-2351, 2356-2367, 2388-2415, 2427-2447, 2484-2511, 2516-2543, 2592-2607, 2725-2751, 2766-2799, 2831-2863, 2870-2895, 2900-2927, 2970-2991, 3022-3055, 3104-3119, 3181-3199, 3214-3247, 3252-3277, 3296-3311, 3328-3347, 3387-3391, 3417-3439, 3455-3514, 3536-3599, 3626-3663, 3712-3791, 3840-3903, 3968-3983, 4124-4223, 4326-4528, 4608-4623, 4813-4847, 5088-5103, 5105-5167, 5200-5215, 5760-5775, 5887, 5910-5935, 5952-5967, 5969-5999, 6291-6303, 6335, 6366-6383, 6385-6418, 6675-6703, 6720-6735, 6757-6799, 6836-6863, 6900-6927, 6962-6991, 7040-7055, 7100-7103, 7136-7151, 7731-7762, 7791-7823, 7872-7887, 7916-7935, 7966-7983, 7988-8015, 8020-8047, 8062-8079, 8159-8175, 8839-8863, 8894-8911, 8933-8964, 9029-9071, 9141-9151, 9183-9199, 9215-9231, 9278-9295, 9344-9359, 9401-9407, 9440-9455, 9536-9551, 9622-9631, 9664-9679, 9744-9759, 9780-9807, 9856-9871, 9936-9951, 9970-9999, 10043-10063, 10098-10127, 10171-10191, 10235-10255, 10296-10319, 10363-10383, 10427-10447, 10496-10511, 10632-10663, 10690-10735, 10784-10799, 10885-10911, 10944-10959, 11002-11007, 11040-11055, 11146-11167, 11200-11215, 11315-11327, 11352-11375, 11404-11439, 11488-11503, 11574-11583, 11616-11631, 11739-11759, 11784-11807, 11840-11855, 12000-12015, 12049-12080, 12145-12159, 12177-12207, 12282-12313, 12368-12399, 12436-12463, 12512-12527, 12603-12623, 12672-12687, 12738-12767, 12800-12815, 12866-12895, 12920-12943, 12978-13007, 13046-13071, 13106-13135, 13179-13199, 13236-13263, 13305-13327, 13376-13391, 13445-13471, 13504-13519, 13647-13679, 13713-13744, 13809-13823, 13829-13871, 13920-13935, 14040-14063, 14088-14111, 14144-14159, 14304-14319, 14341-14372, 14405-14447, 14491-14495, 14528-14543, 14590-14607, 14656-14671, 14726-14751, 14775-14799, 14848-14863, 14900-14911, 14934-14959, 15008-15023, 15123-15135, 15168-15183, 15192-15199, 15235-15279, 15328-15343, 15403-15423, 15442-15471, 15520-15535, 15629-15647, 15672-15695, 15697-15727, 15758-15791, 15822-15855, 15899-15919, 15959-15983, 15993-16015, 16045-16079, 16128-16143, 16170-16191, 16224-16239, 16243-16255, 16320-16335, 16375-16383, 16507-16527, 16534-16559, 16561-16591, 16632-16655, 16660-16687, 16736-16767, 16817-17051, 17132-17151, 17163-17407, 25600-26623, 27329-28671
Free inodes: 11-8144
learning ext2 filesystem notes的更多相关文章
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(3)--Learning Theory
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 本系列文章是Andrew Ng 在斯坦福的机器学习课程 CS 22 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(2)--Supervised Learning
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 本系列文章是Andrew Ng 在斯坦福的机器学习课程 CS 22 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(1)--Introduction
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 目 录 1 Introduction 1 1.1 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(6)—遗忘的数学知识
机器学习中遗忘的数学知识 最大似然估计( Maximum likelihood ) 最大似然估计,也称为最大概似估计,是一种统计方法,它用来求一个样本集的相关概率密度函数的参数.这个方法最早是遗传学家 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(5)—Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning 对于控制决策问题的解决思路:设计一个回报函数(reward function),如果learning agent(如上面的四足机器人.象棋AI程序)在决定 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(4)—无监督学习(unsupervised learning)
1 Unsupervised Learning 1.1 k-means clustering algorithm 1.1.1 算法思想 1.1.2 k-means的不足之处 1 ...
- Deep Learning Workbench Installation Notes
1. ROS Indigo (30 min) Just flow ROSWiki: http://wiki.ros.org/indigo/Installation/Ubuntu NOW simply ...
- lua: Learning Official Doc notes
dynamically typed vars: basic types: nil, boolean, number, string, function, userdata, thread & ...
- Ext FileSystem Family、Ext2、Ext3
catalog . 简介 . Ext2文件系统 . Ext3文件系统 . 小结 1. 简介 VFS虚拟文件系统接口和数据结构构成了一个框架,各个文件系统的实现都必须在框架内运转,但这并不要求每个文件系 ...
随机推荐
- 关于java中的类的学习
设计模式应该牵扯到类的分布排列了,尽管现在我只能这么表达. 下面来自段帅发来的视频课程中的整理: 类与类之间的关系 每天进步一点点 类是java程序中最小组成单位,要理解后才可以更能理解类继承,重载, ...
- 桌面共享UDP组播实现
组播(Multicast)传输:在发送者和每一接收者之间实现点对多点网络连接.如果一台发送者同时给多个的接收者传输相同的数据,也只需复制一份的相同数据包.它提高了数据传送效率.减少了骨干网络出现拥塞的 ...
- 深蓝色 --ppt
Deep Learning of Binary Hash Codes for Fast Image Retrieval [Paper] [Code-Caffe] 1. 摘要 针对图像检索问题,提出简单 ...
- 【Python】【内置函数】【bytes&bytearray&str&array】
[bytes] 英文文档: class bytes([source[, encoding[, errors]]]) Return a new “bytes” object, which is an i ...
- AtCoder square869120 Contest #3 F sushi
本文版权归ljh2000和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 本文作者:ljh2000 作者博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/ljh2000-jump/ ...
- Java中关于Arrays.asList()的操作
我们可以通过Arrays.asList() 产生一个List,但是要记住,我们通过Arrays.asList产生的list是基于一个固定大小的数组的, 仅支持那些不会改变数组大小的操作.所以我们在使用 ...
- 一个对iBatis的总结写的不错(转载)
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/panxueji/article/details/9852795 一. ibatis介绍 ibatis始于2002年,2010年更名为mybatis, ...
- 在采用vue-cli Post Get
需要依赖插件 vue-resource npm install vue-resource --save https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/cookbook/using-axios-to- ...
- Linux Shell学习笔记(一)
Shell,见名知意,就是一个作为用户与Linux OS间接口的程序,允许用户向OS输入需要执行的命令.Shell众多,这里只介绍Bash. 0)实验的Shell版本 显示shell版本: /bin/ ...
- MINA2.0用户手册中文版
MINA2.0用户手册中文版--第一章 MINA2.0入门 MINA2.0用户手册中文版--第二章 第一节 MINA应用程序架构 MINA2.0用户手册中文版--第二章 第二节 TCP服务端实例 MI ...
