2018CCPC 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 网络赛
链接
1.括号序列贪心/CF&51nod原题
【分析】:
贪心,每次到i的时候,假如你要在i里面要卖掉股票,获益是a[i], 肯定要在前面要么:1)把已经卖了的变成不买不卖,需要-a[j], 2)把已经不买不卖的变成买,需要-a[j]
【原题链接】:CF&E
CF&D
51nod高卖低买
3.构造/封闭运算/费马小定理下模意义/重新定义+和 *
【题意】:
输入:素数p
要求构造规则a[p*p],使其满足:(m+n)p=mp+n^p
a的含义:
a[i][j] = (i-1) + (j-1),a[p+i][j] = (i-1) * (j-1)
【 + 意义】加法全0
【 * 意义】
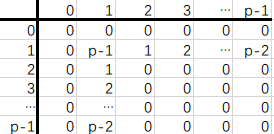
【分析】:(转载自 http://www.cnblogs.com/xiuwenli/p/9534918.html)
给定的p是素数,要求给定一个加法运算表和乘法运算表,使(m+n)p=mp+np(0≤m,n<p)。
因为给定的p是素数,根据费马小定理得 (m+n)p−1≡1(mod p)
因此,(m+n)p≡m+n (mod p),
同时,mp+np≡m+n (mod p)。
所以在模p意义下,(m+n)p=mp+np(0≤m,n<p) 恒成立,且加法运算与乘法运算封闭。
等式两边%p,发现左右都是n+m。等式成立,所以所需的加法群和乘法群就很明显
就是%p意义下的加法群和乘法群。
4.费马大定理/勾股数定理/15浙工大校赛原题
【原题链接】n==2的情况
Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2)C. Pythagorean Triples
给出一个整数问是否能找出另外两个数使得构成一组勾股数。如不能则输出-1,反之,则输出任意符合的两个数。
7.分组后单调队列/倍增/线段树
9.子树/树形dp与阶乘/dfs/结论题
10.树状数组/线段树优化dp
【1001】
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
multiset<pair<int,bool> > st;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 4;
int t, n, a;
int main()
{
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
st.clear();
ll ans = 0;
int cnt = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ll a;
scanf("%lld", &a);
if(!st.empty()&&(*st.begin()).first<a)
{
ans += (a - (*st.begin()).first);
if((*st.begin()).second==true)
cnt++;
st.erase(st.begin());
st.insert(make_pair(a, true));
st.insert(make_pair(a, false));
}
else
{
st.insert(make_pair(a, true));
}
}
printf("%lld %d\n", ans, cnt * 2);
}
return 0;
}
【1003】
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int ti=0;ti<T;ti++)
{
int p;
scanf("%d", &p);
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < p; j++)
{
if (j)printf(" ");
printf("%d", (i + j) % p);
}
printf("\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < p; j++)
{
if (j)printf(" ");
printf("%d", (i*j) % p);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
【1004】
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
ll a, n;
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &a);
if (n > 2)printf("-1 -1\n");
else
{
if (n == 0)printf("-1 -1\n");
else if (n == 1)printf("%lld %lld\n", 1, a + 1);
else if (n == 2)
{
if (a & 1)
{
ll x = (a - 1) / 2;
ll c = x*x + (x + 1)*(x + 1);
printf("%lld %lld\n", c - 1, c);
}
else
{
ll x = a / 2;
printf("%lld %lld\n", x*x - 1, x*x + 1);
}
}
}
}
}
【1007-单调队列】
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[10010];
int n,m,k;
long long s;
long long ans;
bool vis[10010];
long long sum[30010];
int b[30010];
void gao(vector<int> vec) {
int sz = vec.size();
sum[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 3*sz; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i-1] + a[vec[(i-1)%sz]];
}
long long s1 = 0;
long long tt = m/sz-1;
if (tt < 0) tt = 0;
s1 = tt*sum[sz];
if (s1 < 0) s1 = 0;
int lm = m - tt*sz;
long long ms = 0;
int st, ed;
st = 0; ed = 0;
b[ed++] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 3*sz; i++) {
while (st < ed && b[st] < i - lm)st++;
ms = max(ms, sum[i] - sum[b[st]]);
while (st < ed && sum[b[ed-1]] >= sum[i])ed--;
b[ed++] = i;
}
ans = min(ans, max(0LL, s - s1 - ms));
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
int iCase = 0;
while (T--) {
iCase++;
cin>>n>>s>>m>>k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
ans = s;
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (vis[i])continue;
vector<int>vec;
int now = i;
vec.push_back(i);
vis[now] = true;
now = (now+k)%n;
while (now != i) {
vec.push_back(now);
vis[now] = true;
now = (now+k)%n;
}
gao(vec);
}
printf("Case #%d: ", iCase);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
【线段树】
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn = 4e4+7;
struct Segment_tree
{
struct Node
{
ll Max;
ll Size,son[2];
void init()
{
son[0]=son[1]=Size=Max=0;
}
} T[maxn*4];
ll cnt,root;
void init(ll l,ll r,ll *a)
{
cnt=0;
root=build(l,r,a);
}
inline void update(ll pos)
{
if(T[pos].Size==1)return ;
T[pos].Max=max(T[T[pos].son[0]].Max,T[T[pos].son[1]].Max);
}
inline ll build(ll l,ll r,ll *a)
{
ll pos=++cnt;
T[pos].init();
T[pos].Size=r-l+1;
if(l==r)
{
T[pos].Max=a[l];
return pos;
}
ll mid=(l+r)>>1;
T[pos].son[0]=build(l,mid,a);
T[pos].son[1]=build(mid+1,r,a);
update(pos);
return pos;
}
void cov(ll L,ll R,ll i,ll v,ll pos=1)
{
if(L==R)
{
T[pos].Max=max(T[pos].Max,v);
return ;
}
ll mid=(L+R)>>1;
if(i<=mid)
cov(L,mid,i,v,T[pos].son[0]);
else
cov(mid+1,R,i,v,T[pos].son[1]);
update(pos);
}
ll query_Max(ll L,ll R,ll l,ll r,ll pos=1)
{
if(l>r)return 0;
if(L==l&&R==r)
{
return T[pos].Max;
}
ll mid=(L+R)>>1;
if(r<=mid)
return query_Max(L,mid,l,r,T[pos].son[0]);
else if(l>mid)
return query_Max(mid+1,R,l,r,T[pos].son[1]);
else
return max(query_Max(L,mid,l,mid,T[pos].son[0]),query_Max(mid+1,R,mid+1,r,T[pos].son[1]));
}
}tree;
ll a[maxn],ans;
ll n,s,m,k;
bool vis[maxn];
ll p[maxn],sum[maxn];
ll solve(ll start){
ll sz=0;
for(ll i=start;!vis[i];i=(i+k)%n){
vis[i]=1;
p[++sz]=i;
}
for(ll i=sz+1;i<=sz*4;i++){
p[i]=p[i-sz];
}
for(ll i=1;i<=sz*4;i++)
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+a[p[i]];
tree.init(1,sz*4,sum);
for(ll i=1;i<=sz;i++){
if(m<=sz){
ll sm=tree.query_Max(1,sz*4,i,i+m-1)-sum[i-1];
ans=max(ans,sm);
}
else {
if(sum[sz]<=0){
ll sm=tree.query_Max(1,sz*4,i,i+(m%sz)+sz-1)-sum[i-1];
ans=max(ans,sm);
}
else {
ll sm=sum[sz]*((m/sz)-1)+tree.query_Max(1,sz*4,i,i+(m%sz)+sz-1)-sum[i-1];
ans=max(ans,sm);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ll t;
scanf("%I64d",&t);
for(ll cas=1;cas<=t;cas++){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
ans=0;
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&s,&m,&k);
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%I64d",a+i);
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
if(!vis[i]){
solve(i);
}
}
printf("Case #%I64d: %I64d\n",cas,max(0ll,s-ans));
}
return 0;
}
【倍增】
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define debug(x) cerr<<#x<<" = "<<(x)<<endl
#define eps 1e-8
#define pi acos(-1.0)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pll;
const int MAXN=(int)1e4+5;
const int MOD=(int)1e9+7;
struct node{
ll a,b;
node(){}
node(ll x){
b=x;
a=max(x,0ll);
}
node operator + (const node &p)const{
node re;
re.b=b+p.b;
re.a=max(a,b+p.a);
return re;
}
};
node a[MAXN][33];
int nxt[MAXN][33];
node cal(int x,int y){
int k=0;
node re=node(0);
while(y){
if(y&1){
re=re+a[x][k];
x=nxt[x][k];
}
k++;
y>>=1;
}
return re;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
for(int ca=1;ca<=t;ca++){
int n,m,k;ll s;
scanf("%d%lld%d%d",&n,&s,&m,&k);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
a[i][0]=node(x);
nxt[i][0]=(i+k)%n;
}
for(int j=1;(1<<j)<=m;j++){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i][j]=a[i][j-1]+a[nxt[i][j-1]][j-1];
nxt[i][j]=nxt[nxt[i][j-1]][j-1];
}
}
ll ans=s;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
node tmp=cal(i,m);
ans=min(ans,max(0ll,s-tmp.a));
}
printf("Case #%d: %lld\n",ca,ans);
}
return 0;
}
【1009】
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+5;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
struct node
{
int x,y,v,nxt;
}edge[maxn<<1];
ll head[maxn],cnt,n;
ll sz[maxn];
ll an;
int add(int x,int y,int v)
{
edge[cnt].x=x;
edge[cnt].y=y;
edge[cnt].v=v;
edge[cnt].nxt=head[x];
head[x]=cnt++;
}
int dfs(int root,int fa)
{
sz[root]=1;
for(int i=head[root]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].nxt)
{
int a=edge[i].y;
int b=edge[i].v;
if(a==fa) continue;
dfs(a,root);
sz[root] += sz[a];
an = ( an + (n-sz[a])%mod * sz[a]%mod * b%mod )%mod;
}
}
ll fac[maxn];
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
fac[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=maxn;i++)
fac[i]=(fac[i-1]*i)%mod;//阶乘取余打表
an=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(sz,0,sizeof(sz));
cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++)
{
int x,y,z;
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z);
add(x,y,z);
add(y,x,z);
}
dfs(1,-1);
printf("%lld\n",(ll)(2*an%mod*fac[n-1]%mod)%mod);
}
}
【1010】
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-6;
const int INF = 1000000000;
const int maxn = 123456;
int T, n, m;
int tot, ans;
int maxs[maxn * 4];
struct Node
{
int x, y;
int val;
int idd;
}nod[maxn];
int cmp1(Node a, Node b)
{
if (a.y != b.y)
return a.y<b.y;
else
return a.x<b.x;
}
int cmp2(Node a, Node b)
{
if (a.x != b.x)
return a.x<b.x;
else
return a.y>b.y;
}
void Pushup(int rt)
{
maxs[rt] = max(maxs[rt * 2], maxs[rt * 2 + 1]);
}
void Build(int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
maxs[rt] = 0;
return;
}
int m = (l + r) / 2;
Build(l, m, rt * 2);
Build(m + 1, r, rt * 2 + 1);
Pushup(rt);
}
void Update(int pos, int l, int r, int k, int rt)
{
if (l == r)
{
maxs[rt] = k;
return;
}
int m = (l + r) / 2;
if (pos <= m)
Update(pos, l, m, k, rt * 2);
else
Update(pos, m + 1, r, k, rt * 2 + 1);
Pushup(rt);
}
int QueryMax(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt)
{
if (R == 0)
return 0;
if (l >= L&&r <= R)
return maxs[rt];
int m = (l + r) / 2;
int ret = -INF;
if (L <= m)
ret = max(ret, QueryMax(L, R, l, m, rt * 2));
if (R>m)
ret = max(ret, QueryMax(L, R, m + 1, r, rt * 2 + 1));
return ret;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
ans = -INF;
tot = 1;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d%d%d", &nod[i].x, &nod[i].y, &nod[i].val);
sort(nod + 1, nod + n + 1, cmp1);
nod[1].idd = tot++;//离散化
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (nod[i].y == nod[i - 1].y)
nod[i].idd = nod[i - 1].idd;
else
nod[i].idd = tot++;
}
sort(nod + 1, nod + n + 1, cmp2);
Build(1, n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = QueryMax(1, nod[i].idd - 1, 1, n, 1);
ans = max(x + nod[i].val, ans);
Update(nod[i].idd, 1, n, x + nod[i].val, 1);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
2018CCPC 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 网络赛的更多相关文章
- 2016中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 C. Magic boy Bi Luo with his excited tree
Magic boy Bi Luo with his excited tree Problem Description Bi Luo is a magic boy, he also has a migi ...
- 2018中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 1001 - Buy and Resell 【优先队列维护最小堆+贪心】
题目传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6438 Buy and Resell Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/O ...
- 2018中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 1010 YJJ's Salesman 【离散化+树状数组维护区间最大值】
题目传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6447 YJJ's Salesman Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/O ...
- 2018中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 1009 - Tree and Permutation 【dfs+树上两点距离和】
Tree and Permutation Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Oth ...
- HDU 6154 - CaoHaha's staff | 2017 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛
/* HDU 6154 - CaoHaha's staff [ 构造,贪心 ] | 2017 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 题意: 整点图,每条线只能连每个方格的边或者对角线 问面积大于n的 ...
- HDU 6150 - Vertex Cover | 2017 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛
思路来自 ICPCCamp /* HDU 6150 - Vertex Cover [ 构造 ] | 2017 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 题意: 给了你一个贪心法找最小覆盖的算法,构造一组 ...
- HDU 6156 - Palindrome Function [ 数位DP ] | 2017 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛
普通的数位DP计算回文串个数 /* HDU 6156 - Palindrome Function [ 数位DP ] | 2017 中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 2-36进制下回文串个数 */ ...
- HDU 6154 CaoHaha's staff(2017中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛)
题目代号:HDU 6154 题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6154 CaoHaha's staff Time Limit: 2000/1 ...
- 2016中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 J. Alice and Bob
Alice and Bob Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others) ...
随机推荐
- http中有关缓存相关的几个字段
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/lifeibo/article/details/5979572 Expires.Cache-Control.Last-Modified. ETag是R ...
- JS设计模式之装饰者模式
装饰者模式概述 在不改变原对象的基础上,通过对其进行包装拓展(添加属性或者方法)使原有对象可以满足用户更复杂的需求 实际需求 在已有的代码基础上,为每个表单中的input默认输入框上边显示一行提示文案 ...
- MongoDB入门(6)- 我们自己封装的MongoDB-C#版本
Wisdombud.Mongo 包含内容 MongoDB.Bson.dll MongoDB.Bson.xml MongoDB.Driver.dll MongoDB.Driver.xml Wisdomb ...
- js中style,currentStyle和getComputedStyle的区别以及获取css操作方法
在js中,之前我们获取属性大多用的都是ele.style.border这种形式的方法,但是这种方法是有局限性的,该方法只能获取到行内样式,获取不了外部的样式.所以呢下面我就教大家获取外部样式的方法,因 ...
- vijos 1002 简单压缩+DP
描述 在河上有一座独木桥,一只青蛙想沿着独木桥从河的一侧跳到另一侧.在桥上有一些石子,青蛙很讨厌踩在这些石子上.由于桥的长度和青蛙一次跳过的距离都是正整数,我们可以把独木桥上青蛙可能到达的点看成数轴上 ...
- Asp.Net Web Forms/MVC/Console App中使用Autofac
本来简单介绍了Autofac在Asp.Net Web Forms中的应用,后来又添加了mvc.控制台应用程序中使用Autofac,详情请看源码. ASP.NET Web Forms使用Autofac, ...
- 基于FPGA的HDTV视频图像灰度直方图统计算法设计
随着HDTV的普及,以LCD-TV为主的高清数字电视逐渐进入蓬勃发展时期.与传统CRT电视不同的是,这些高清数字电视需要较复杂的视频处理电路来驱动,比如:模数转换(A/D Converter).去隔行 ...
- jQuery mobile 滑动打开面板
一.首先在<head></head>里面引入jQuery库.jQuery mobile库以及jQuery mobile样式 <link rel="stylesh ...
- Centos修改镜像为国内的阿里云源或者163源等国内源
阿里安装软件镜像源 阿里云Linux安装镜像源地址:http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ 第一步:备份你的原镜像文件,以免出错后可以恢复. mv /etc/yum.repos.d/Ce ...
- mysql not null default / default
not null default 说明不能是NULL, 并设置默认值 default 设置默认值 , 但值也可能是NULL mysql> create table test (id int, n ...
