OpenCV 之 平面单应性
上篇 OpenCV 之 图象几何变换 介绍了等距、相似和仿射变换,本篇侧重投影变换的平面单应性、OpenCV相关函数、应用实例等。
1 投影变换
1.1 平面单应性
投影变换 (Projective Transformation),是仿射变换的泛化 (或普遍化),二者区别如下:
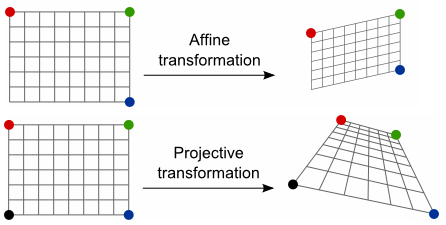
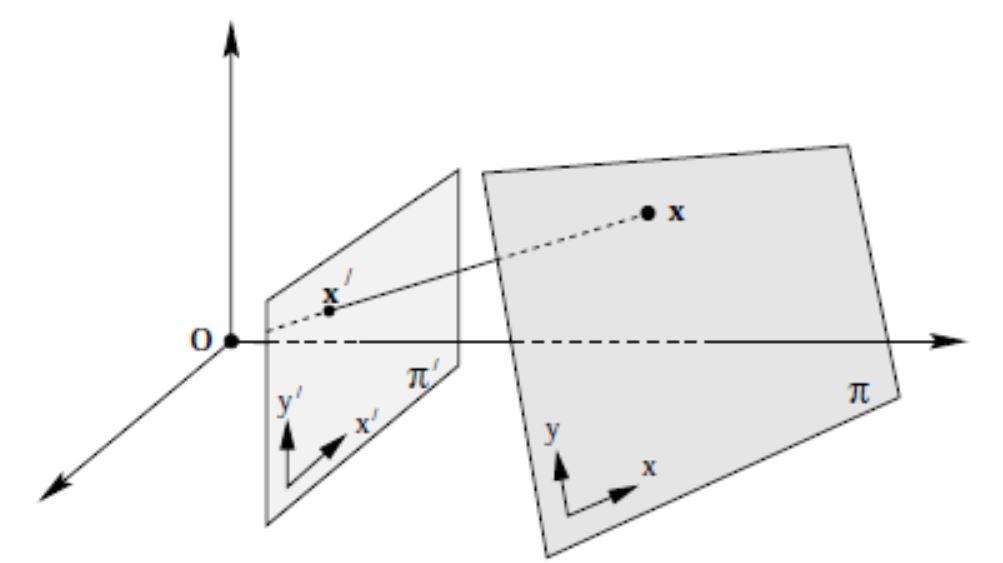
假定平面 $P^{2}$ 与 $Q^{2}$ 之间,存在映射 $H_{3 \times 3}$,使得 $P^{2}$ 内任意点 $(x_p, y_q, 1)$,满足下式:
$\quad \begin{bmatrix} x_q \\ y_q \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} h_{11} & h_{12} & h_{13} \\ h_{21} & h_{22} & h_{23} \\ h_{31} & h_{32} & h_{33} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x_p \\ y_p \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = H_{3 \times 3} \begin{bmatrix} x_p\\ y_p \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}$
当 $H$ 非奇异时,$P^{2}$ 与 $Q^{2}$ 之间的映射即为 2D 投影变换,也称 平面单应性, $H_{3 \times 3}$ 则为 单应性矩阵
例如:在相机标定中,如果选取了 二维平面标定板,则 物平面 和 像平面 之间的映射,就是一种典型的 平面单应性
1.2 单应性矩阵
$H$ 有 9 个未知数,但实际只有 8 个自由度 (DoF),其归一化通常有两种方法:
第一种方法,令 $h_{33}=1$;第二种方法,加单位向量限制 $h_{11}^2+h_{12}^2+h_{13}^2+h_{21}^2+h_{22}^2+h_{23}^2+h_{31}^2+h_{32}^2+h_{33}^2=1$
下面接着第一种方法,继续推导公式如下:
$\quad x' = \dfrac{h_{11}x + h_{12}y + h_{13}}{h_{31}x + h_{32}y + 1} $
$\quad y' = \dfrac{h_{21}x + h_{22}y + h_{23}}{h_{31}x + h_{32}y + 1} $
整理得:
$\quad x \cdot h_{11} + y \cdot h_{12} + h_{13} - xx' \cdot h_{31} - yx' \cdot h_{32} = x' $
$\quad x \cdot h_{21} + y \cdot h_{22} + h_{23} - xy' \cdot h_{31} - yy' \cdot h_{32} = y' $
一组对应特征点 $(x, y) $ -> $ (x', y')$ 可构造 2 个方程,要求解 8 个未知数 (归一化后的),则需要 8 个方程,4 组对应特征点
$\quad \begin{bmatrix} x_{1} & y_{1} & 1 &0 &0&0 & -x_{1}x'_{1} & -y_{1}x'_{1} \\ 0&0&0& x_{1} & y_{1} &1& -x_{1}y'_{1} & -y_{1}y'_{1} \\ x_{2} & y_{2} & 1 &0 &0&0 & -x_{2}x'_{2} & -y_{2}x'_{2} \\ 0&0&0& x_{2} & y_{2} &1& -x_{2}y'_{2} & -y_{2}y'_{2} \\ x_{3} & y_{3} & 1 &0 &0&0 & -x_{3}x'_{3} & -y_{3}x'_{3} \\ 0&0&0& x_{3} & y_{3} &1& -x_{3}y'_{3} & -y_{3}y'_{3} \\ x_{4} & y_{4} & 1 &0 &0&0 & -x_{4}x'_{4} & -y_{4}x'_{4} \\ 0&0&0& x_{4} & y_{4} &1& -x_{4}y'_{4} & -y_{4}y'_{4} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} h_{11} \\ h_{12}\\h_{13}\\h_{21}\\h_{22}\\h_{23}\\h_{31}\\h_{32} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x'_{1}\\y'_{1}\\x'_{2}\\y'_{2}\\x'_{3}\\y'_{3}\\x'_{4}\\y'_{4} \end{bmatrix} $
因此,求 $H$ 可转化为 $Ax=b$ 的通用解,参见 OpenCV 中 getPerspectiveTransform() 函数的源码实现
2 OpenCV 函数
2.1 投影变换矩阵
a) 四组对应特征点:已知四组对应特征点坐标,带入 getPerspectiveTransform() 函数中,可求解 src 投影到 dst 的单应性矩阵 $H_{3 \times 3}$
Mat getPerspectiveTransform (
const Point2f src[], // 原图像的四角顶点坐标
const Point2f dst[], // 目标图像的四角顶点坐标
int solveMethod = DECOMP_LU // solve() 的解法
)
该函数的源代码实现如下:先构造8组方程,转化为 $Ax=b$ 的问题,调用 solve() 函数来求解
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[], int solveMethod)
{
Mat M(3, 3, CV_64F), X(8, 1, CV_64F, M.ptr());
double a[8][8], b[8];
Mat A(8, 8, CV_64F, a), B(8, 1, CV_64F, b); for( int i = 0; i < 4; ++i )
{
a[i][0] = a[i+4][3] = src[i].x;
a[i][1] = a[i+4][4] = src[i].y;
a[i][2] = a[i+4][5] = 1;
a[i][3] = a[i][4] = a[i][5] =
a[i+4][0] = a[i+4][1] = a[i+4][2] = 0;
a[i][6] = -src[i].x*dst[i].x;
a[i][7] = -src[i].y*dst[i].x;
a[i+4][6] = -src[i].x*dst[i].y;
a[i+4][7] = -src[i].y*dst[i].y;
b[i] = dst[i].x;
b[i+4] = dst[i].y;
} solve(A, B, X, solveMethod);
M.ptr<double>()[8] = 1.; return M;
}
b) 多组对应特征点:对于两个平面之间的投影变换,只要求得对应的两组特征点,带入 findHomography() 函数,便可得到 srcPoints 投影到 dstPoints 的 $H_{3 \times 3}$
Mat findHomography (
InputArray srcPoints, // 原始平面特征点坐标,类型是 CV_32FC2 或 vector<Point2f>
InputArray dstPoints, // 目标平面特征点坐标,类型是 CV_32FC2 或 vector<Point2f>
int method = 0, // 0--最小二乘法; RANSAC--基于ransac的方法
double ransacReprojThreshold = 3, // 最大允许反投影误差
OutputArray mask = noArray(), //
const int maxIters = 2000, // 最多迭代次数
const double confidence = 0.995 // 置信水平
)
2.2 投影变换图像
已知单应性矩阵$H_{3 \times 3}$,将任意图像代入 warpPerspective() 中,便可得到经过 2D投影变换 的目标图像
void warpPerspective (
InputArray src, // 输入图像
OutputArray dst, // 输出图象(大小 dsize,类型同 src)
InputArray M, // 3x3 单应性矩阵
Size dsize, // 输出图像的大小
int flags = INTER_LINEAR, // 插值方法
int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, //
const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar() //
)
3 单应性的应用
3.1 图像校正
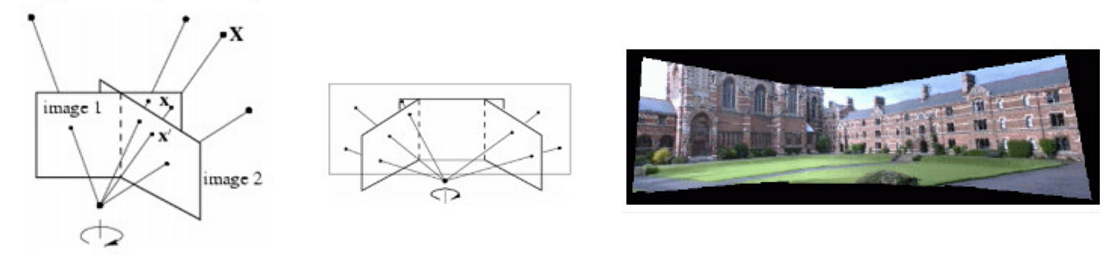
像平面 image1 和 image2 是相机在不同位置对同一物平面所成的像,分别对应右下图的 PP1、PP2 和 PP3,这三个平面任选两个都互有 平面单应性
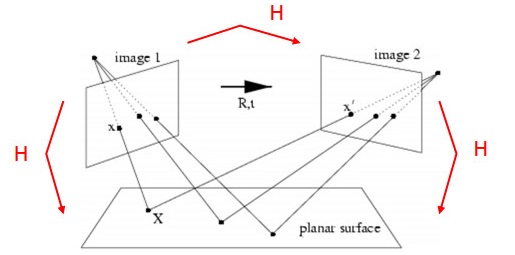
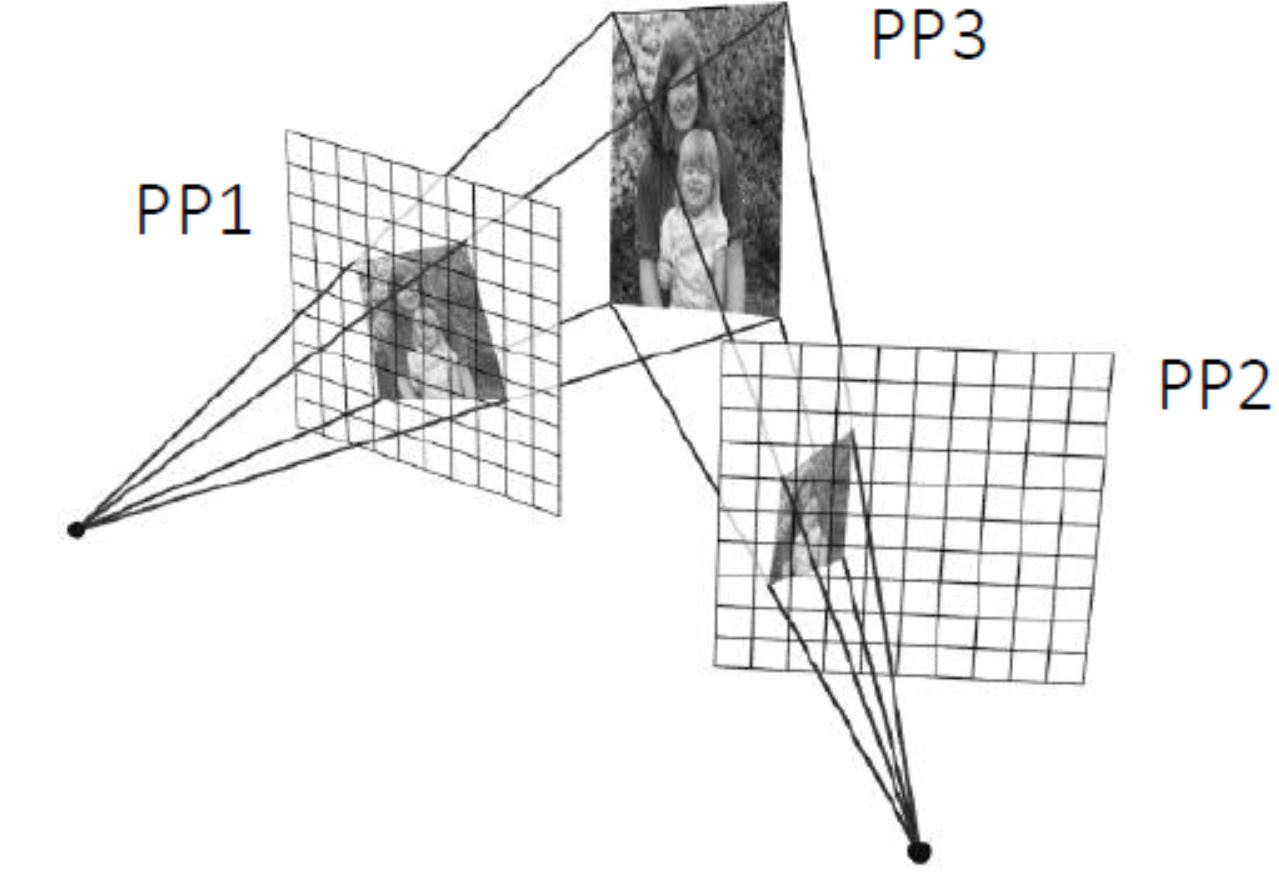
以相机标定过程为例,当相机从不同角度对标定板进行拍摄时,利用任意两个像平面之间的单应性,可将各角度拍摄的图像,转换为某一特定视角的图像

3.2 图像拼接
当相机围绕其投影轴,只做旋转运动时,所有的像素点可等效视为在一个无穷远的平面上,则单应性矩阵可由旋转变换 $R$ 和 相机标定矩阵 $K$ 来表示
$\quad \large s \begin{bmatrix} x' \\ y' \\1 \end{bmatrix} = \large K \cdot \large R \cdot \large K^{-1} \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{bmatrix}$
因此,如果已知相机的标定矩阵,以及旋转变换前后的位姿,可利用平面单应性,将旋转变换前后的两幅图像拼接起来
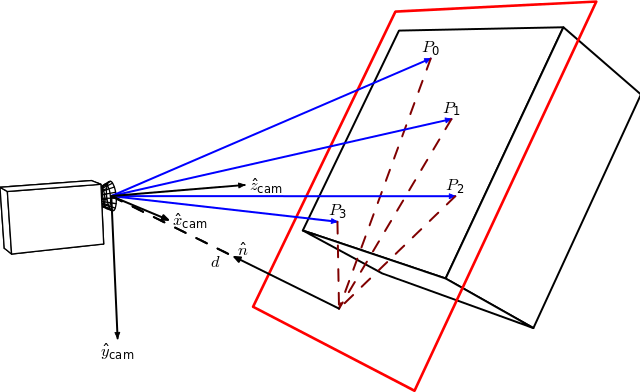
3.3 位姿估计
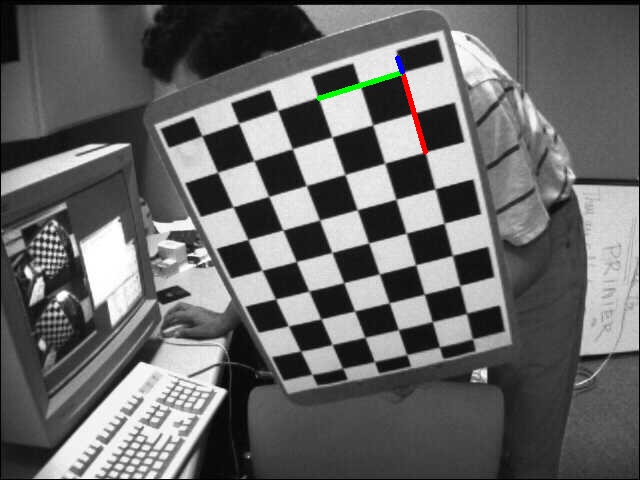
如下所示,当相机对着一个带多个特征点的平面拍摄时,物、像平面之间便有了单应性映射 $H_1$:定义 $\widehat{n}$ 为平面的法向量,$d$ 为物平面到相机的距离 (沿着$\widehat{n}$的方向)
如果相机变换位姿,从不同角度对该平面进行成像,则可建立起相机所有位姿和该平面的单应性映射 $H_2,H_3,H_4 ... $ ,从而计算得出相机的位姿 (也称 PnP 问题)
4 代码示例
4.1 图像校正
#include <iostream> #include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp" using namespace std;
using namespace cv; Size kPatternSize = Size(9, 6); int main()
{
// 1) read image
Mat src = imread("chessboard1.jpg");
Mat dst = imread("chessboard2.jpg");
if (src.empty() || dst.empty())
return -1; // 2) find chessboard corners
vector<Point2f> corners1, corners2;
bool found1 = findChessboardCorners(src, kPatternSize, corners1);
bool found2 = findChessboardCorners(dst, kPatternSize, corners2);
if (!found1 || !found2)
return -1; // 3) get subpixel accuracy of corners
Mat src_gray, dst_gray;
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(dst, dst_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
cornerSubPix(src_gray, corners1, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS | cv::TermCriteria::COUNT, 30, 0.1));
cornerSubPix(dst_gray, corners2, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS | cv::TermCriteria::COUNT, 30, 0.1)); // 4)
Mat H = findHomography(corners1, corners2, RANSAC);
// 5)
Mat src_warp;
warpPerspective(src, src_warp, H, src.size()); // 6)
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
imshow("src_warp", src_warp); waitKey(0);
}
结果如下:
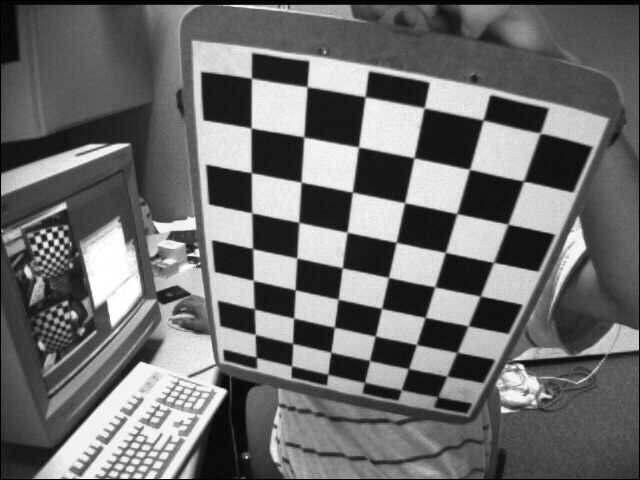
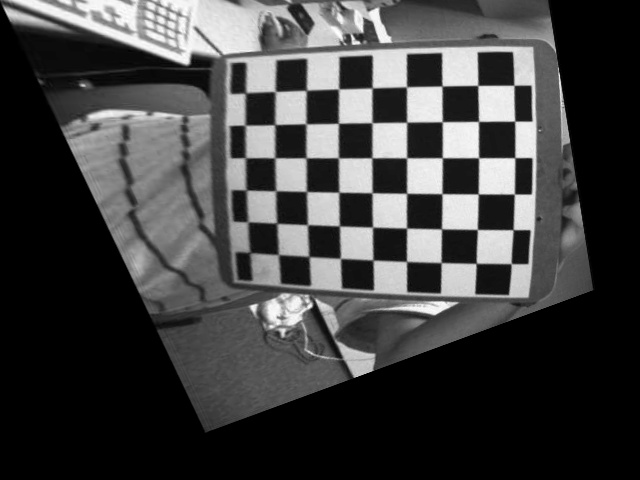



视角1的图像 视角2的图像 视角1的图像校正为视角2
4.2 图像拼接
用 Blender 软件,获取相机只做旋转变换时的视图1和视图2,在已知相机标定矩阵和旋转矩阵的情况下,可计算出两个视图之间的单应性矩阵,从而完成拼接。
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp" using namespace cv; int main()
{
// 1) read image
Mat img1 = imread("view1.jpg");
Mat img2 = imread("view2.jpg");
if (img1.empty() || img2.empty())
return -1; // 2) camera pose from Blender at location 1
Mat c1Mo = (Mat_<double>(4, 4) << 0.9659258723258972, 0.2588190734386444, 0.0, 1.5529145002365112,
0.08852133899927139, -0.3303661346435547, -0.9396926164627075, -0.10281121730804443,
-0.24321036040782928, 0.9076734185218811, -0.342020183801651, 6.130080699920654,
0, 0, 0, 1); // camera pose from Blender at location 2
Mat c2Mo = (Mat_<double>(4, 4) << 0.9659258723258972, -0.2588190734386444, 0.0, -1.5529145002365112,
-0.08852133899927139, -0.3303661346435547, -0.9396926164627075, -0.10281121730804443,
0.24321036040782928, 0.9076734185218811, -0.342020183801651, 6.130080699920654,
0, 0, 0, 1); // 3) camera intrinsic parameters
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 700.0, 0.0, 320.0,
0.0, 700.0, 240.0,
0, 0, 1);
// 4) extract rotation
Mat R1 = c1Mo(Range(0, 3), Range(0, 3));
Mat R2 = c2Mo(Range(0, 3), Range(0, 3)); // 5) compute rotation displacement: c1Mo * oMc2
Mat R_2to1 = R1 * R2.t(); // 6) homography
Mat H = cameraMatrix * R_2to1 * cameraMatrix.inv();
H /= H.at<double>(2, 2); // 7) warp
Mat img_stitch;
warpPerspective(img2, img_stitch, H, Size(img2.cols * 2, img2.rows)); // 8) stitch
Mat half = img_stitch(Rect(0, 0, img1.cols, img1.rows));
img1.copyTo(half);
imshow("Panorama stitching", img_stitch); waitKey(0);
}
输出结果如下:


相机视图1 相机视图1 拼接后的视图
4.3 相机位姿估计
一组从不同视角拍摄的标定板,预先知道其拍摄相机的内参,则调用 solvePnPRansac() 函数,可估计出该相机拍摄时的位姿
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp" using namespace std;
using namespace cv; Size kPatternSize = Size(9, 6);
float kSquareSize = 0.025; int main()
{
// 1) read image
Mat src = imread("images/left01.jpg");
if (src.empty())
return -1;
// prepare for subpixel corner
Mat src_gray;
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); // 2) find chessboard corners
vector<Point2f> corners;
bool patternfound = findChessboardCorners(src, kPatternSize, corners); // 3) get subpixel accuracy
if (patternfound) {
cornerSubPix(src_gray, corners, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS + TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 30, 0.1));
} else {
return -1;
} // 4) define object coordinates
vector<Point3f> objectPoints;
for (int i = 0; i < kPatternSize.height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < kPatternSize.width; j++)
{
objectPoints.push_back(Point3f(float(j*kSquareSize), float(i*kSquareSize), 0));
}
} // 5) input camera intrinsic parameters
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 5.3591573396163199e+02, 0.0, 3.4228315473308373e+02,
0.0, 5.3591573396163199e+02, 2.3557082909788173e+02,
0.0, 0.0, 1.);
Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -2.6637260909660682e-01, -3.8588898922304653e-02, 1.7831947042852964e-03,
-2.8122100441115472e-04, 2.3839153080878486e-01); // 6) compute rotation and translation vectors
Mat rvec, tvec;
solvePnPRansac(objectPoints, corners, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec); // 7) project estimated pose on the image
drawFrameAxes(src, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec, 2*kSquareSize);
imshow("Pose from coplanar points", src); waitKey(0);
}
从不同角度拍摄的标定板,其估计的相机位姿如下:
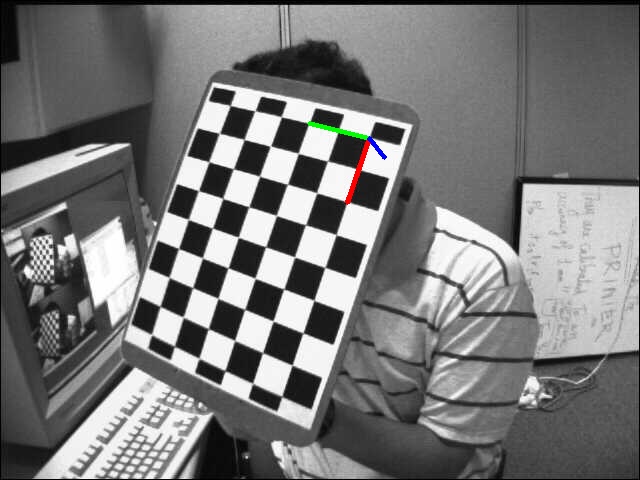


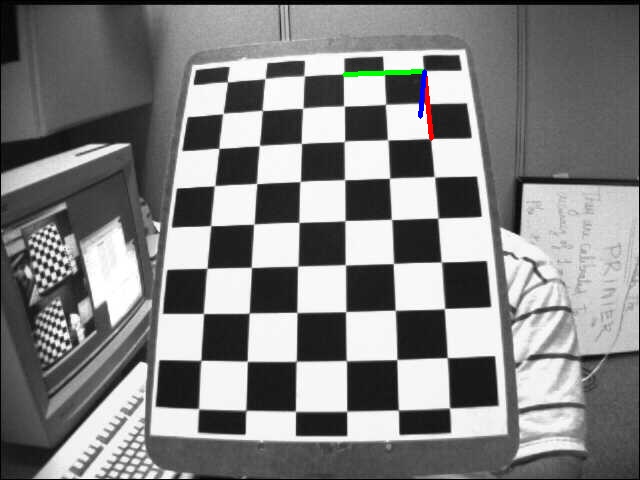
位姿1 位姿2 位姿3 位姿4
参考资料:
OpenCV Tutorials / feature2d module / Basic concepts of the homography explained with code
OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction / Pose Estimation
Affine and Projective Transformations
OpenCV 之 平面单应性的更多相关文章
- OpenCV仿射变换+投射变换+单应性矩阵
本来想用单应性求解小规模运动的物体的位移,但是后来发现即使是很微小的位移也会带来超级大的误差甚至错误求解,看起来这个方法各种行不通,还是要匹配知道深度了以后才能从三维仿射变换来入手了,纠结~ esti ...
- 相机标定 和 单应性矩阵H
求解相机参数的过程就称之为相机标定. 1.相机模型中的四个平面坐标系: 1.1图像像素坐标系(u,v) 以像素为单位,是以图像的左上方为原点的图像坐标系: 1.2图像物理坐标系(也叫像平面坐标系)(x ...
- 【Computer Vision】图像单应性变换/投影/仿射/透视
一.基础概念 1. projective transformation = homography = collineation. 2. 齐次坐标:使用N+1维坐标来表示N维坐标,例如在2D笛卡尔坐标 ...
- 单应性(homography)变换的推导
矩阵的一个重要作用是将空间中的点变换到另一个空间中.这个作用在国内的<线性代数>教学中基本没有介绍.要能形像地理解这一作用,比较直观的方法就是图像变换,图像变换的方法很多,单应性变换是其中 ...
- 机器学习进阶-案例实战-图像全景拼接-图像全景拼接(RANSCA) 1.sift.detectAndComputer(获得sift图像关键点) 2.cv2.findHomography(计算单应性矩阵H) 3.cv2.warpPerspective(获得单应性变化后的图像) 4.cv2.line(对关键点位置进行连线画图)
1. sift.detectAndComputer(gray, None) # 计算出图像的关键点和sift特征向量 参数说明:gray表示输入的图片 2.cv2.findHomography(kp ...
- python opencv3 FLANN单应性匹配
git:https://github.com/linyi0604/Computer-Vision 匹配准确率非常高. 单应性指的是图像在投影发生了 畸变后仍然能够有较高的检测和匹配准确率 # codi ...
- opencv 仿射变换 投射变换, 单应性矩阵
仿射 estimateRigidTransform():计算多个二维点对或者图像之间的最优仿射变换矩阵 (2行x3列),H可以是部分自由度,比如各向一致的切变. getAffineTransform( ...
- OpenCV-Python 特征匹配 + 单应性查找对象 | 四十五
目标 在本章节中,我们将把calib3d模块中的特征匹配和findHomography混合在一起,以在复杂图像中找到已知对象. 基础 那么我们在上一环节上做了什么?我们使用了queryImage,找到 ...
- 相机标定:PNP基于单应面解决多点透视问题
利用二维视野内的图像,求出三维图像在场景中的位姿,这是一个三维透视投影的反向求解问题.常用方法是PNP方法,需要已知三维点集的原始模型. 本文做了大量修改,如有不适,请移步原文: ...
随机推荐
- Immutable.js 实现原理
Immutable.js 实现原理 Immutable collections for JavaScript v4.0.0-rc.12 released on Oct 31, 2018 https:/ ...
- React Hooks vs React Class vs React Function All In One
React Hooks vs React Class vs React Function All In One React Component Types React Hooks Component ...
- iPad pro & 显示器
iPad pro 显示器 iPad Pro 如何当做外接屏幕使用 XDisplay https://www.splashtop.com/wiredxdisplay https://play.googl ...
- useState & useEffect
useState & useEffect https://overreacted.io/zh-hans/a-complete-guide-to-useeffect/ https://react ...
- nodejs stream 创建读写流
const fs = require("fs"); const { Writable, Readable, Duplex, Transform } = require(" ...
- Masterboxan INC :个股出现疯涨,投资者需警惕股市泡沫
随着标普500指数自去年三月以来的暴涨,引发了很多亏损企业股价飙升,同时许多场外投资者盲目跟风,加剧了个股的疯涨.对于此现象,美国万事达资产管理有限公司不得不多次发文提醒投资者:个股出现疯涨,投资者需 ...
- Baccarat流动性挖矿的收益能否持续?该如何参与Baccarat流动性挖矿?
2020年DeFi市场火热,众多投资机构纷纷入场,分享这场资本盛宴.然而,目前市面上大多数DeFi项目手续费高昂,小资金的投资者无法入市.为了让更多的用户参与其中,NGK推出了Baccarat流动性挖 ...
- 快速读懂 HTTP/3 协议
在 深入浅出:HTTP/2 一文中详细介绍了 HTTP/2 新的特性,比如头部压缩.二进制分帧.虚拟的"流"与多路复用,性能方面比 HTTP/1 有了很大的提升.与所有性能优化过程 ...
- HTML页面顶部出现空白部分(#65279字符?)解决办法
1.在火狐下面用Firebug,选择body,点编辑html的时候,看到是多出了一个这个代表的意思,还真不知道,搜索后了解到是一种中文的编码规则, UTF-8不需要BOM来表明字节顺序. 制作 ...
- CPU使用率原理及计算方式
本文转载自CPU使用率原理及计算方式 CPU:超线程和多核 超线程(Hyper-Threading ) 超线程是Intel最早提出一项技术,最早出现在2002年的Pentium4上.单个采用超线程的C ...
