springboot:异步调用@Async
在后端开发中经常遇到一些耗时或者第三方系统调用的情况,我们知道Java程序一般的执行流程是顺序执行(不考虑多线程并发的情况),但是顺序执行的效率肯定是无法达到我们的预期的,这时就期望可以并行执行,常规的做法是使用多线程或线程池,需要额外编写代码实现。在spring3.0后引入了@Async注解,使用该注解可以达到线程池的执行效果,而且在开发上非常简单。
一、概述
springboot是基于spring框架的,在springboot环境下演示@Async注解的使用方式。先看下该注解的定义,
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Async {
/**
* A qualifier value for the specified asynchronous operation(s).
* <p>May be used to determine the target executor to be used when executing this
* method, matching the qualifier value (or the bean name) of a specific
* {@link java.util.concurrent.Executor Executor} or
* {@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor TaskExecutor}
* bean definition.
* <p>When specified on a class level {@code @Async} annotation, indicates that the
* given executor should be used for all methods within the class. Method level use
* of {@code Async#value} always overrides any value set at the class level.
* @since 3.1.2
*/
String value() default "";
}
可以看到该注解只有一个属性,那就是value,从注释上知道value指定的是执行该任务的线程池,也就是说我们可以使用子定义的线程池执行我们的任务,而不是系统默认的。在看该注解上的注解,
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
也就是说该注解可以用在方法和类上。标记在类上表示类中的所有方法都以异步方式执行,也就是提交到线程池执行。
二、详述
上面简单对@Async注解进行了解释,下面看用法。
1、@EnableAsync注解
在springboot中要使用@Async注解必须在springboot启动类上使用@EnableAsync注解,开启@Async注解的自动配置,如下,
package com.example.demo; import com.example.demo.properties.ApplicationPro;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ApplicationPro.class})
//开启@Async注解的自动配置
@EnableAsync
public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
} }
只有在启动类上使用@EnableAsync注解,@Async注解才会生效。
2、@Async注解
上面使用@EnableAsync注解已经开启了对@Async注解的配置,下面看具体的异步调用类,
package com.example.demo.service; import com.example.demo.Student;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.concurrent.Future; @Service
@Async
public class AsyncService {
public Future<Student> get(){
Student stu=new Student("1","3");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return AsyncResult.forValue(stu);
} public void executeRemote(){
try {
Thread.sleep(10000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
首先,要使该类让spring管理必须使用@Service注解(或其他注解也可以),然后在类上标记@Async注解,前面说过@Async注解可以在方法或类上使用,在类上使用则表示类中的所有方法均使用异步执行的方式。异步执行类中有两个方法,每个方法为了演示执行的耗时操作均睡眠10s。这两个方法一个是有返回值的,另一个是无返回值的,重点看有返回值的,
public Future<Student> get(){
Student stu=new Student("1","3");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000l);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return AsyncResult.forValue(stu);
}
为什么方法的返回值是Future,在@Async注释上有下面这句话,
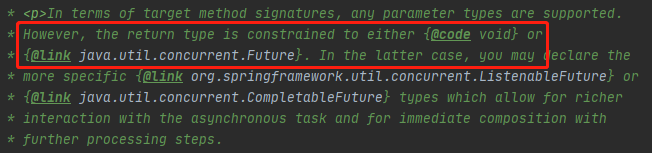
从上面的注解正好可以说明返回Future是没问题,但是我们的方法就是一个普通的方法,要怎么才能返回Future类那,不慌,spring针对@Async注解提供了AsyncResult类,从类名就知道该类就是为了@Async注解准备的,
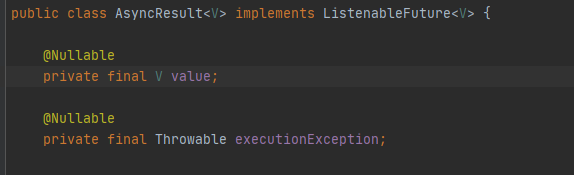
使用其中的forValue方法,便可以返回一个带有泛型的Future类了。
看下测试类,
package com.example.demo.controller; import com.example.demo.Student;
import com.example.demo.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("async")
public class ControllerAsyncTest {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody
public Student get(){
try {
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
//调用带有返回值的get方法
Future<Student> result=asyncService.get();
//调用无返回值的executeRemote方法
asyncService.executeRemote(); Student student=result.get();
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时间:"+(end-start));
return student;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
测试类就是一个简单的controller,调用了get和executeRemote方法,这两个方法分别会睡眠10s,而且get会有返回值,下面看是否可以拿到get的返回值,并看下调用这两个方法的时间,
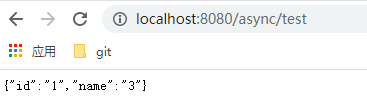
可以成功拿到返回值,看执行时间,
2020-12-12 21:37:43.556 INFO 11780 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 5 ms
执行时间:10006
执行时间是10006ms,也就是10s多,按照上面的分析两个方法分别睡眠了10s,如果同步执行那肯定是20s,把@Async注解去掉看执行时间,
2020-12-12 21:41:07.840 INFO 11584 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed initialization in 5 ms
执行时间:20001
执行时间是20001ms,算上两个方法睡眠的时间,和测试类本身的时间,20001ms是没错的。从这里可以看出@Async注解的作用,把每个方法当作任务提交给了线程池,提高了任务执行的时间。
另外,在获取异步的执行结果使用了下面的方法,
Future<Student> result=asyncService.get();
asyncService.executeRemote();
//获得执行结果
Student student=result.get();
由于在主线程要获得任务的执行结果,使用Future类的get方法获得结果,该结果需要等到任务执行完以后才可以获得。
三、总结
本文讲解了异步调用@Async注解的使用,
1、使用@EnableAsync注解开启对@Async注解的支持;
2、在类或方法上使用@Async注解;
有不当之处,欢迎指正,谢谢!
springboot:异步调用@Async的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot学习笔记(七):SpringBoot使用AOP统一处理请求日志、SpringBoot定时任务@Scheduled、SpringBoot异步调用Async、自定义参数
SpringBoot使用AOP统一处理请求日志 这里就提到了我们Spring当中的AOP,也就是面向切面编程,今天我们使用AOP去对我们的所有请求进行一个统一处理.首先在pom.xml中引入我们需要的 ...
- springboot 异步调用Async使用方法
引言: 在Java应用中,绝大多数情况下都是通过同步的方式来实现交互处理的:但是在处理与第三方系统交互的时候,容易造成响应迟缓的情况,之前大部分都是使用多线程来完成此类任务,其实,在spring 3. ...
- SpringBoot异步调用--@Async详解
1. 概述 在日常开发中,为了提高主线程的效率,往往需要采用异步调用处理,例如系统日志等.在实际业务场景中,可以使用消息中间件如RabbitMQ.RocketMQ.Kafka等来解决.假如对高可用 ...
- springboot之异步调用@Async
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuwenjin/p/8858050.html 引言: 在Java应用中,绝大多数情况下都是通过同步的方式来实现交互处理的:但是在处理与第三方系统交 ...
- SpringBoot系列:Spring Boot异步调用@Async
在实际开发中,有时候为了及时处理请求和进行响应,我们可能会多任务同时执行,或者先处理主任务,也就是异步调用,异步调用的实现有很多,例如多线程.定时任务.消息队列等, 这一章节,我们就来讲讲@Async ...
- SpringBoot集成篇(二) 异步调用Async
什么是异步调用? 异步调用是相对于同步调用而言的,同步调用是指程序按预定顺序一步步执行,每一步必须等到上一步执行完后才能执行,异步调用则无需等待上一步程序执行完即可执行. 如何实现异步调用? 多线程, ...
- 170719、springboot编程之异步调用@Async
1.在pom.xml中增加依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artif ...
- nodejs异步调用async
犹豫nodejs是异步编程模型,有一些在同步编程中很容易做到的事情,现在却变得很麻烦,async的流程控制就是为了简化这些操作var async = require('async'); 1.serie ...
- SpringBoot异步使用@Async原理及线程池配置
前言 在实际项目开发中很多业务场景需要使用异步去完成,比如消息通知,日志记录,等非常常用的都可以通过异步去执行,提高效率,那么在Spring框架中应该如何去使用异步呢 使用步骤 完成异步操作一般有两种 ...
随机推荐
- Java中常见内存溢出模拟及错误分析
在JVM虚拟机规范中,Java虚拟机运行时数据区域除了程序计数器(Program Counter Register)外都有可能出现OutOfMemoryError的情况,使用Hotspot虚拟机简单的 ...
- linux 用户组操作
1. 添加用户到...目录中useradd -M -s /目录 username 2. 添加用户属于多个组 usermod -G 本组(用户名),组1,组2... 用户名 3. mysql添加禁止登录 ...
- java开发两年,这些线程知识你都不知道,你怎么涨薪?
前言 什么是线程:程序中负责执行的哪个东东就叫做线程(执行路线,进程内部的执行序列),或者说是进程的子任务. Java中实现多线程有几种方法 继承Thread类: 实现Runnable接口: 实现Ca ...
- 2020阿里,字节跳动,JAVA岗(一线企业校招、社招)面试题合集
前言 以下面试题全属于一线大厂社招以及校招的面试真题,各位在做这些题目对照自己的时候请平凡心对待,不要信心受挫.其实 做为致力于一线企业校招或者社招的你来说,能把每个知识模块的一小部分问题去深入学习和 ...
- 常见的名片尺寸如何在CorelDRAW预设
说到名片想必大家肯定不陌生,是我们生活中随处可见的物品,也是商家宣传必不可少的印刷物料.那么名片的尺寸是多少?我们做名片的时候该如何把握好名片的尺寸呢?在CDR中有专门的名片尺寸,下面小编就为大家简单 ...
- guitar pro系列教程(十九):Guitar Pro添加音符之前我们要做什么?
前面的章节我们已经讲了不少关于{cms_selflink page='index' text='Guitar Pro'}的功能之类的讲解,那一般我们在打谱之前要做的是什么呢,很多新手玩家,对这方面也是 ...
- Vim注释行的方法
目录 一.Visual block 加注释 去注释 二.正则表达式 加注释 去注释 一.Visual block 加注释 1.首先按键盘上的ESC进入命令行模式 2.再按Ctrl+V进入VISUAL ...
- 对数组进行排序成最小的,相当于自己实现了一次String的compareTo函数,不过是另类的。
题目描述 输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个.例如输入数组{3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为321323. //一气呵成 ...
- Redis 基础设计结构之三 hash(哈希)
Redis 有 5 种基础数据结构,分别为:string (字符串).list (列表).set (集合).hash (哈希) 和 zset (有序集合). 今天来说一下hash(哈希),hash的数 ...
- Forethought Future Cup - Final Round (Onsite Finalists Only) C. Thanos Nim 题解(博弈+思维)
题目链接 题目大意 给你n堆石子(n为偶数),两个人玩游戏,每次选取n/2堆不为0的石子,然后从这n/2堆石子中丢掉一些石子(每一堆丢弃的石子数量可以不一样,但不能为0),若这次操作中没有n/2堆不为 ...
