Java中ArrayList源码分析
一、简介
ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组。每个ArrayList实例都有自己的容量,该容量至少和所存储数据的个数一样大小,在每次添加数据时,它会使用ensureCapacity()保证容量能容纳所有数据。
1.1、ArrayList 的继承与实现接口
ArrayList继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- ArrayList 继承了AbstractList,实现了List。它是一个数组队列,提供了相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
- ArrayList 实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在ArrayList中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访问。
- ArrayList 实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能被克隆。不过它实现的是对ArrayList 实例的浅拷贝。
- ArrayList 实现java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着ArrayList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
1.2、ArrayList 与Collection集合的关系
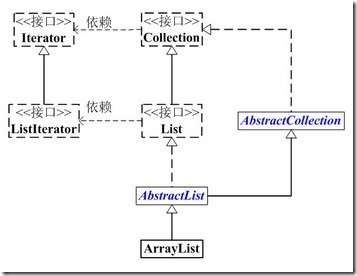
1.3、ArrayList 与Vector的区别
ArrayList 与Vector大致等同,唯一的区别就是ArrayList的操作是线程不安全的,然而Vector是线程安全的。所以,建议在单线程中才使用ArrayList,而在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
二、源码分析
对于ArrayList而言,它实现List接口、底层使用数组保存所有元素。其操作基本上是对数组的操作。
2.1、成员变量
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; // 使用serialVersionUID验证版本一致性
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 容量的初始大小
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances.
// ArrayList数据的存储之地
transient Object[] elementData; // 存储ArrayList中元素的数组
// ArrayList存储数据的个数
private int size;
2.2、构造方法
ArrayList提供了三种方式的构造器方法:
1)通过传入的initialCapacity大小构造ArrayList
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
{
if (initialCapacity > 0)
{
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
else if (initialCapacity == 0)
{
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
else
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity);
}
}
2)使用初始容量值构造ArrayList
public ArrayList()
{
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
3)通过传入的指定类集构造ArrayList
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
{
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0)
{
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else
{
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
2.3、增加元素操作
1)往数组尾部添加元素
public boolean add(E e)
{
// 1、确保容量大小
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// 2、尾部添加元素
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
2)在指定位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element)
{
// 1、检验索引
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
// 2、确保容量
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
// 3、将数据后移
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
// 4、添加元素
elementData[index] = element;
// 5、数组元素个数加1
size++;
}
==>System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
3)往数组尾部添加某类集合中所有元素,针对泛型
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
{
// 1、暂存集合c中数据
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
// 2、确保容量
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
// 3、尾部添加数据
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
// 4、数组元素个数更新
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
4)在指定位置添加某类集合中所有元素,针对泛型
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
{
// 1、检验索引
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
// 2、暂存数据
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
// 3、确保容量
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
// 4、数据后移
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
// 5、添加元素
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
// 6、数组元素个数更新
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
2.4、删除元素操作
1)删除ArrayList中第一个符合条件的元素
public boolean remove(Object o)
{
// 移除值为null的元素
if (o == null)
{
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null)
{
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
else // 移除元素
{
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index]))
{
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
// 值不存在时,移除失败
return false;
}
==>
private void fastRemove(int index)
{
// 1、修改的次数更新
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
// 2、数据前移
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
2)删除ArrayList中指定位置上的元素
public E remove(int index)
{
// 1、检验索引
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
// 2、数据前移
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
3)删除ArrayList中所包含传入集合类中的所有元素,针对泛型
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
{
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
4)删除某个范围的数据
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
{
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, numMoved);
// clear to let GC do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex - fromIndex);
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++)
{
elementData[i] = null;
}
size = newSize;
}
5)删除ArrayList中不是所传入集合类中的所有元素,针对泛型
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c)
{
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
2.5、修改操作
1)修改指定位置上的元素
public E set(int index, E element)
{
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
2.6、查找操作
1)获取指定位置上的元素
public E get(int index)
{
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
2)获取指定元素在列表中的第一个位置索引
public int indexOf(Object o)
{
if (o == null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i] == null)
return i;
} else
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
3)获取指定元素在列表中的最后一个位置索引
public int lastIndexOf(Object o)
{
if (o == null)
{
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i] == null)
return i;
} else
{
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
4)返回某个范围的视图
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
{
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
5)迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator()
{
return new Itr();
}
b>
public ListIterator<E> listIterator()
{
return new ListItr(0);
}
扩展:JAVA中ListIterator和Iterator详解与辨析
c>
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index)
{
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
2.7、状态操作
1)是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return size == 0;
}
2.8、其它常用操作
1)清空列表所有元素
public void clear()
{
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
2)克隆ArrayList实例的副本,浅拷贝
public Object clone()
{
try
{
ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e)
{
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
3)判断是否包含某个指定元素
public boolean contains(Object o)
{
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
4)获取元素的个数
public int size()
{
return size;
}
2.9、辅助操作
1)确保容量大小
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)
{
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand)
{
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
2)裁剪容量
public void trimToSize()
{
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length)
{
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
3)转换成数组
a> 该操作没有涉及到引用,属于安全操作
public Object[] toArray()
{
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
{
if (a.length < size)
// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
三、扩展区
2、Java提高篇(三四)-----fail-fast机制(转载)
5、Java集合源码剖析(转载)
参考:
http://www.jb51.net/article/42764.htm
http://zhangshixi.iteye.com/blog/674856
Java中ArrayList源码分析的更多相关文章
- Java基础 ArrayList源码分析 JDK1.8
一.概述 本篇文章记录通过阅读JDK1.8 ArrayList源码,结合自身理解分析其实现原理. ArrayList容器类的使用频率十分频繁,它具有以下特性: 其本质是一个数组,因此它是有序集合 通过 ...
- Java中HashMap源码分析
一.HashMap概述 HashMap基于哈希表的Map接口的实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用null值和null键.(除了不同步和允许使用null之外,HashMap类与Hashtab ...
- 【thinking in java】ArrayList源码分析
简介 ArrayList底层是数组实现的,可以自增扩容的数组,此外它是非线程安全的,一般多用于单线程环境下(Vector是线程安全的,所以ArrayList 性能相对Vector 会好些) Array ...
- java中LinkedList源码分析
ArrayList是动态数组,其实本质就是对数组的操作.那么LinkedList实现原理和ArrayList是完全不一样的.现在就来分析一下ArrayList和LinkeList的优劣吧LinkedL ...
- Java集合-ArrayList源码分析
目录 1.结构特性 2.构造函数 3.成员变量 4.常用的成员方法 5.底层数组扩容原理 6.序列化原理 7.集合元素排序 8.迭代器的实现 9.总结 1.结构特性 Java ArrayList类使用 ...
- java.util.ArrayList源码分析
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess ...
- java中AQS源码分析
AQS内部采用CLH队列.CLH队列是由节点组成.内部的Node节点包含的状态有 static final int CANCELLED = 1; static final int SIGNAL ...
- Java集合干货——ArrayList源码分析
ArrayList源码分析 前言 在之前的文章中我们提到过ArrayList,ArrayList可以说是每一个学java的人使用最多最熟练的集合了,但是知其然不知其所以然.关于ArrayList的具体 ...
- Java - ArrayList源码分析
java提高篇(二一)-----ArrayList 一.ArrayList概述 ArrayList是实现List接口的动态数组,所谓动态就是它的大小是可变的.实现了所有可选列表操作,并允许包括 nul ...
随机推荐
- [转]强大的vim配置文件,让编程更随意
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ma6174/archive/2011/12/10/2283393.html 花了很长时间整理的,感觉用起来很方便,共享一下. 我的vim配置主要有 ...
- sql中用逗号拼接字符串
MSSQL中可以用STUFF函数拼接成字符串. 如: SELECT FieldSomeElse, ( SELECT STUFF(( SELECT ',' + LinkField FROM Detail ...
- 安装Go语言开发环境
安装Go语言开发环境实例代码 - 详述Go语言安装所在需要的工作:安装C语言工具,安装Mercurial,更新go到新版本等操作实例. 安装go环境 1.简介 Go是一个开源项目,采用BSD授权协议. ...
- nyoj 282 You are my brother
You are my brother 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 Little A gets to know a new friend, Litt ...
- Java异常处理的误区和经验总结
本文着重介绍了 Java 异常选择和使用中的一些误区,希望各位读者能够熟练掌握异常处理的一些注意点和原则,注意总结和归纳.只有处理好了异常,才能提升开发人员的基本素养,提高系统的健壮性,提升用户体验, ...
- JAVA中List转换String,String转换List,Map转换String,String转换Map之间的转换类
<pre name="code" class="java"></pre><pre name="code" cl ...
- @RenderBody()和@RenderSection()
强大的Razor引擎 一.Razor基础简介 Razor采用了cshtml后缀的文件名,截图如下: A. 版面布局 从图上看到,新的视图引擎已经没有了Site.Master这种MasterPage了, ...
- Python邮箱客户端编写之接收邮件操作
Python的POP3类有很多方法来管理邮箱. 首先需要导入poplib库,import poplib POP3(server) 连接到邮箱服务器 user(username)将用户名发送至服务器,等 ...
- 机器学习算法-K-means聚类
引文: k均值算法是一种聚类算法.所谓聚类.他是一种无监督学习,将类似的对象归到同一个蔟中.蔟内的对象越类似,聚类的效果越好. 聚类和分类最大的不同在于.分类的目标事先已知.而聚类则不一样. 由于其产 ...
- C++ ORM ODB 入门介绍(二)
目录[-] 1. ODB中的继承类型 2. abstract和polymorphic的区别 3.polymorphic表格 4.早期版本如何实现polymorphic 5.实例 本节主要介绍ODB中的 ...
