MQTT研究之EMQ:【wireshark抓包分析】
基于上篇博文【SSL双向验证】的环境基础,进行消息的具体梳理.
环境基础信息:
. 单台Linux CentOS7.2系统,安装一个EMQTTD的实例broker。
. emq的版本2.3.11。
. 客户端分为mosquitto_pub,以及MQTT.fx 1.7.1的subscriber。
. 证书是通过openssl(version:1.0.2k-fips)生成的,rootCA是自签名的,subscriber和publisher的证书是通过rootCA签署的。
. 抓包工具wireshark(version: 2.6.,下载地址https://www.wireshark.org/download/win64/),分析SSL/TLS通信的消息流.
第一步:通过wireshark抓取SSL双向验证的消息
下面是我测试过程中,得到的消息流程,我的测试环境,在TLS的两层消息结构(record layer,handshake layer)中的握手协议环节,得到的cipher suite的值是:TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384。
先简单介绍下,这个cipher suite的含义,这个应该是SSL/TLS协议中比较难以理解的一个概念。这个说简单点,就是秘钥协商(Key agreement)的顶层设计,后续的消息流程都是密切的基于这个cipher suite的值而有较大的不同,准确的说,秘钥交换(Key exchange)和上诉红色部分关系最为密切.
1、秘钥协商和秘钥交换这两个概念,看到很多地方的讨论和描述中,似乎没有区分的很明确,依据我的理解,秘钥协商和秘钥交换,确实有很大的关联性,不可能完全割裂或者分离关系,只是两个概念描述的侧重点不同,秘钥协商更多表述怎么做这个逻辑,而秘钥交换,更多侧重怎么做的实际动作或者流程。
2、cipher suite的简单介绍
就拿我这个测试的cipher suite值说明吧。
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
键值交换签名协议 数据加密算法 信息认证码算法
更详细的介绍,可以对照下面这个图:

秘钥协商/交换,是为了在握手的过程中,基于给定的cipher suite完成shared secret的生成过程,这个秘钥就是用来为后续数据传输的时候对称加密用的密码。信息验证码协议,是为了保证数据传输的时候的数据一致性或者完整性的。
在我们这个测试中,基于上述cipher suite得到的消息流如下:
C->S: Client Hello
S->C: Server Hello
S->C: Certificate,Server Key Exchange, Certificate Request, Server Hello Done
C->S: Certificate, Client Key Exchange
C->S: Certificate Verify,Change Cipher Spec,Encrypted Handshake Message
S->C: Change Cipher Spec,Encrypted Handshake Message
C->S: Application Data
S->C: Application Data
a. C->S: Client Hello
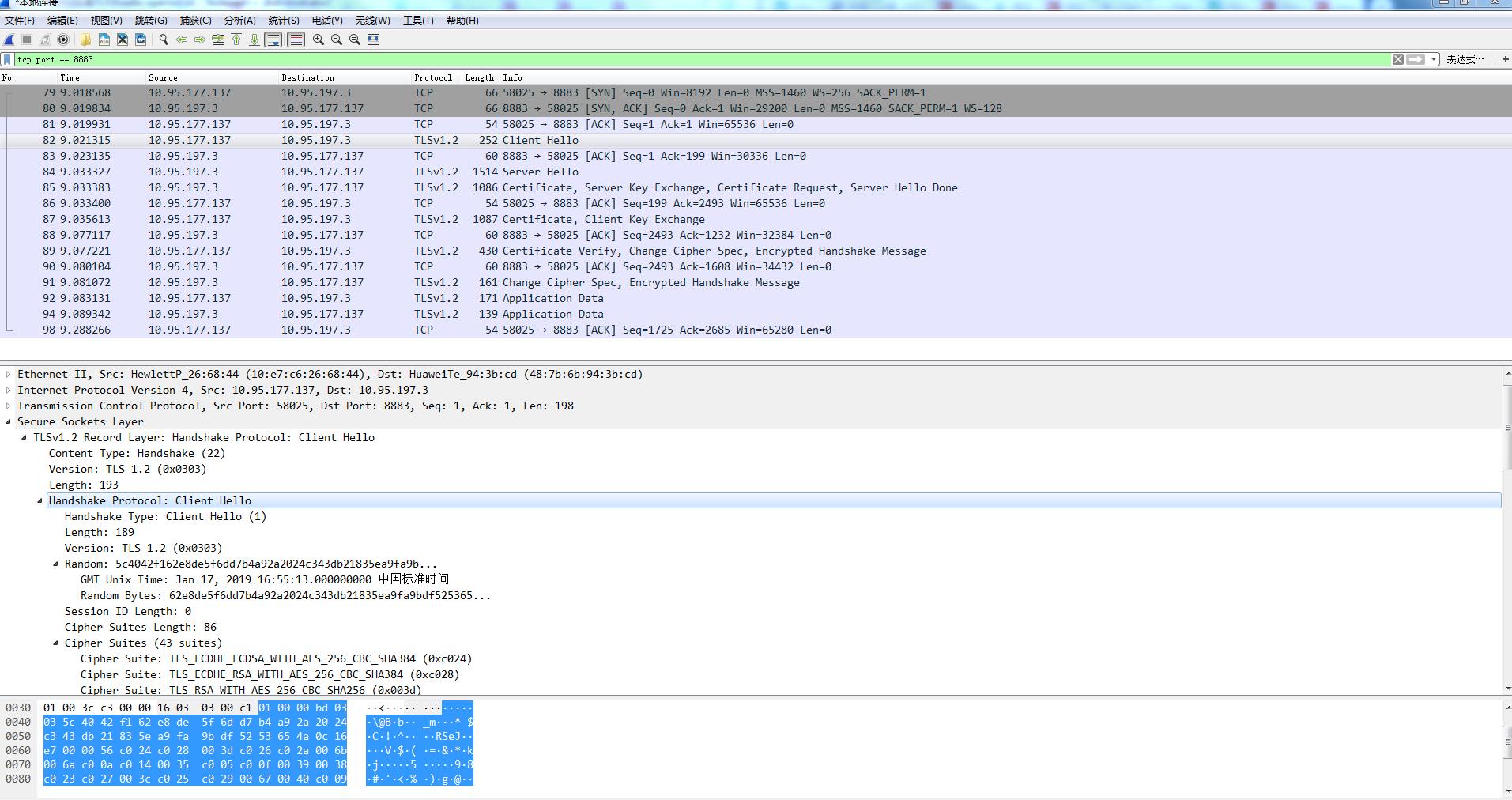
b. S->C: Server Hello

c. S->C: Certificate,Server Key Exchange, Certificate Request, Server Hello Done (这里的Certificate Request,就是服务端要求客户端上报证书)
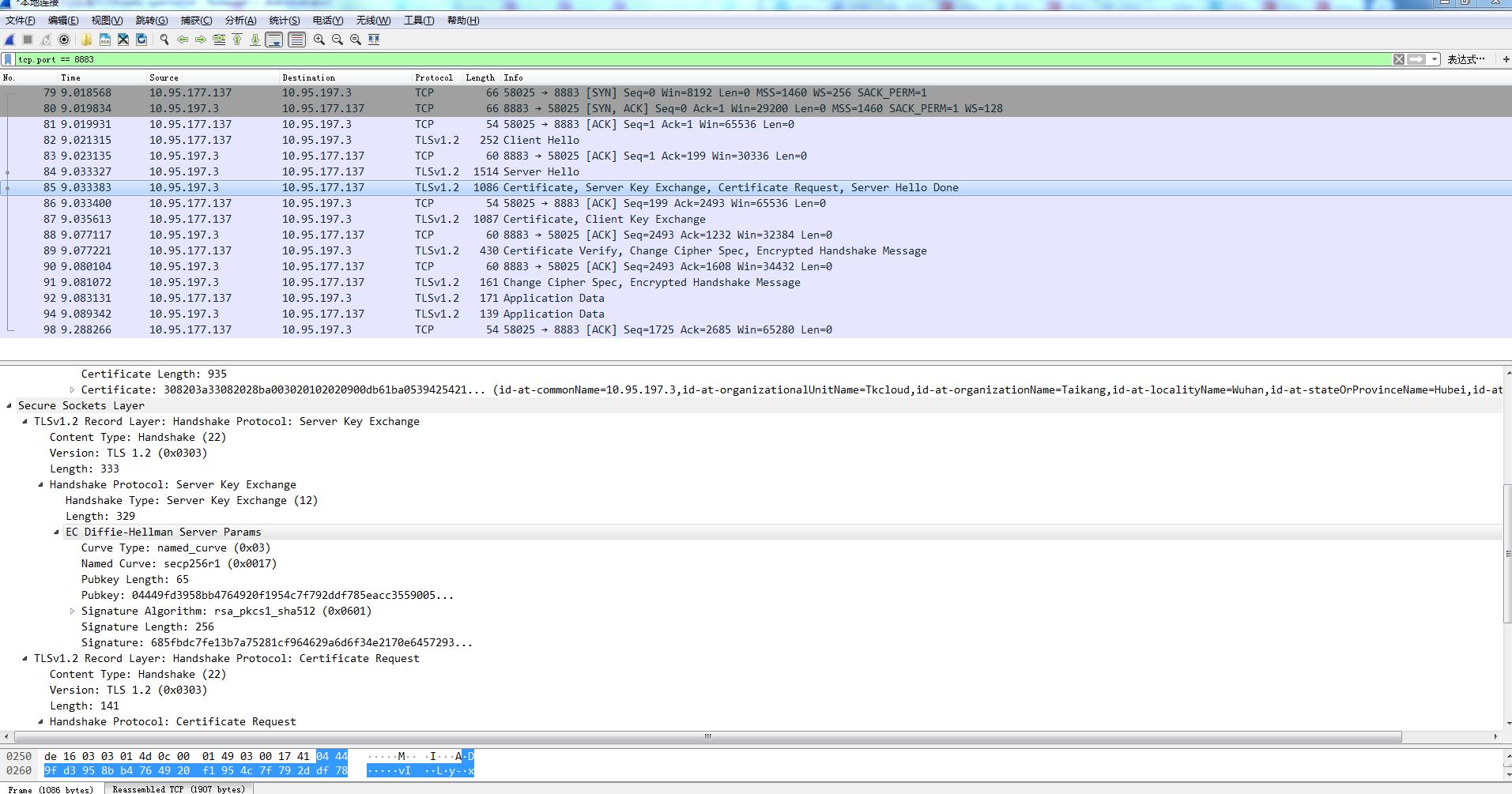
d. C->S: Certificate, Client Key Exchange (这个环节很重要,体现了双向SSL验证的特征了,服务端要求的身份验证,即希望校验客户端的证书的过程)

e. C->S: Certificate Verify,Change Cipher Spec,Encrypted Handshake Message
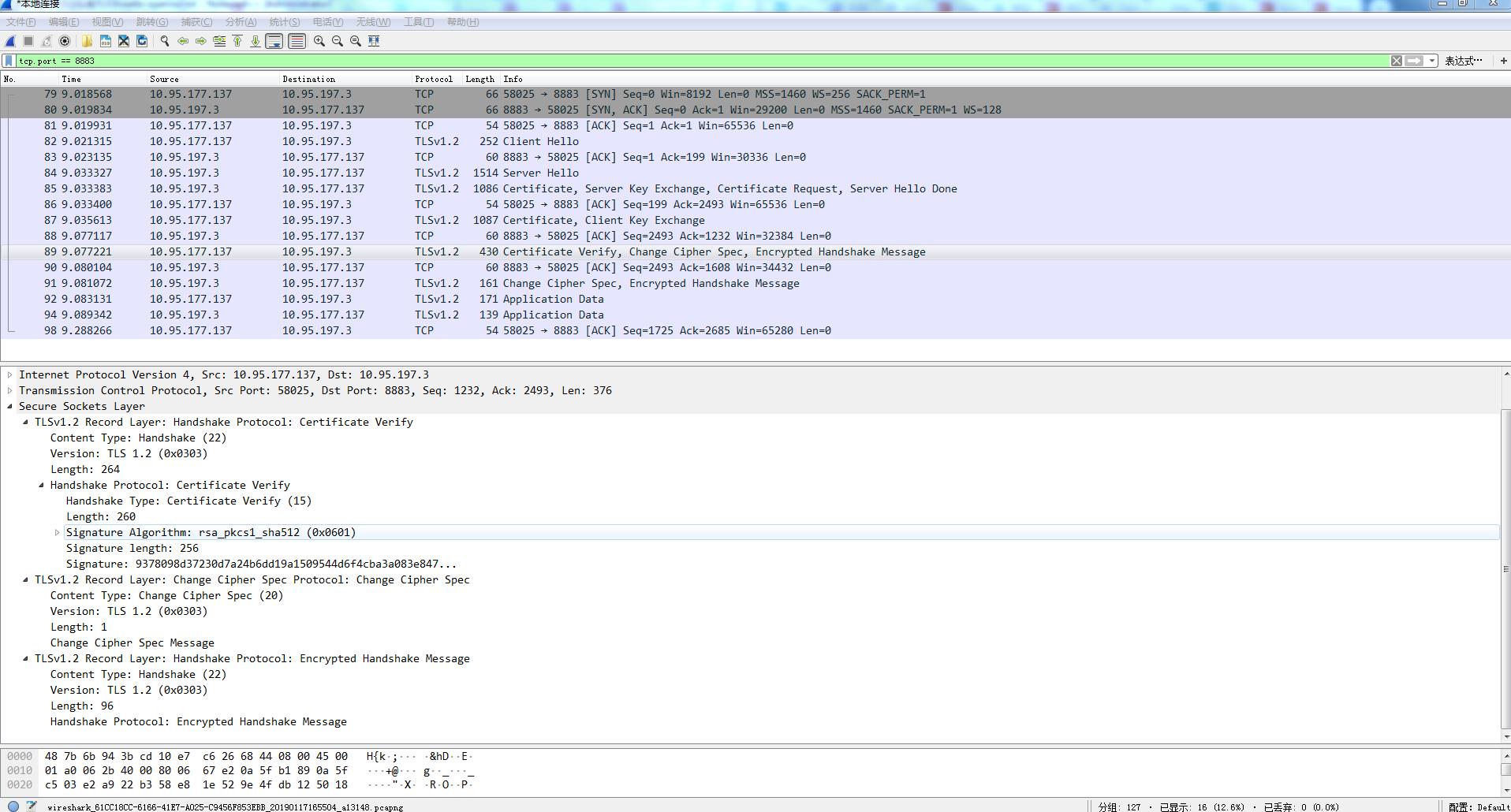
这个消息,其实理解起来似乎有点不好理解。为何客户端要上报Certificate Verify呢?
). certificate Verify消息必须在client key exchange后面由客户端发出去给服务器端。
). 这个消息,是客户端构建的,内容是客户端收发的所有的handshake消息(不含当前这个Verify的消息)拼接后的内容进行hash,然后用证书对应的私钥进行签名后所得的内容S1。
). 这个消息,服务端会进行验证。验证的逻辑,通过对服务端缓存的客户端消息,以及服务端发送的所有handshake消息,同样进行拼接然后计算hash值h2,用客户端的证书中的公钥解析Verify中的签名S1得到对应的hash值h1,对比h1和和
,若相同,则验证通过,否则失败。
可以参考这个链接中的内容,其实,他的解释或者介绍,也是基于RFC文档中的内容进行的,只是比较白话了,相对好懂些。
f. S->C: Change Cipher Spec,Encrypted Handshake Message

g.C->S: Application Data

第二步:单向SSL验证(客户端验证服务端的合法性)
1. 配合broker
## Path to the file containing the user's private PEM-encoded key.
##
## See: http://erlang.org/doc/man/ssl.html
##
## Value: File
#listener.ssl.external.keyfile = /etc/emqttd/certs/key.pem
listener.ssl.external.keyfile = /opt/certs/server.key ## Path to a file containing the user certificate.
##
## See: http://erlang.org/doc/man/ssl.html
##
## Value: File
#listener.ssl.external.certfile = /etc/emqttd/certs/cert.pem
listener.ssl.external.certfile = /opt/certs/server.crt ## Path to the file containing PEM-encoded CA certificates. The CA certificates
## are used during server authentication and when building the client certificate chain.
##
## Value: File
## listener.ssl.external.cacertfile = /etc/emqttd/certs/cacert.pem
listener.ssl.external.cacertfile = /opt/certs/rootCA.crt ## The Ephemeral Diffie-Helman key exchange is a very effective way of
## ensuring Forward Secrecy by exchanging a set of keys that never hit
## the wire. Since the DH key is effectively signed by the private key,
## it needs to be at least as strong as the private key. In addition,
## the default DH groups that most of the OpenSSL installations have
## are only a handful (since they are distributed with the OpenSSL
## package that has been built for the operating system it’s running on)
## and hence predictable (not to mention, bits only).
## In order to escape this situation, first we need to generate a fresh,
## strong DH group, store it in a file and then use the option above,
## to force our SSL application to use the new DH group. Fortunately,
## OpenSSL provides us with a tool to do that. Simply run:
## openssl dhparam -out dh-params.pem
##
## Value: File
## listener.ssl.external.dhfile = /etc/emqttd/certs/dh-params.pem ## A server only does x509-path validation in mode verify_peer,
## as it then sends a certificate request to the client (this
## message is not sent if the verify option is verify_none).
## You can then also want to specify option fail_if_no_peer_cert.
## More information at: http://erlang.org/doc/man/ssl.html
##
## Value: verify_peer | verify_none
listener.ssl.external.verify = verify_none #主要是在双向验证的基础上将此配置改为verify_none ## Used together with {verify, verify_peer} by an SSL server. If set to true,
## the server fails if the client does not have a certificate to send, that is,
## sends an empty certificate.
##
## Value: true | false
## listener.ssl.external.fail_if_no_peer_cert = true
2. 通过wireshark抓取SSL消息流
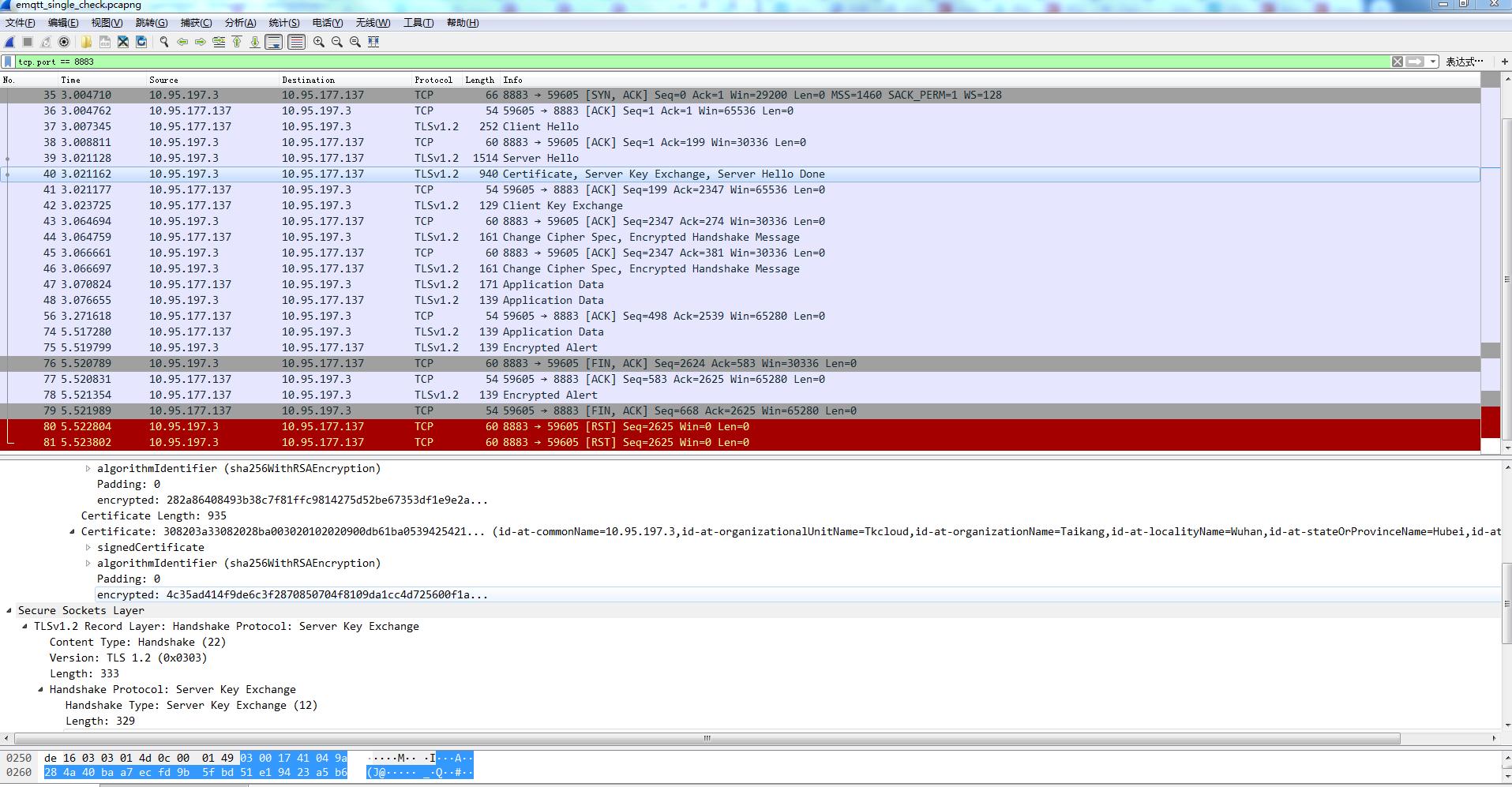
具体的通过wireshark抓取SSL消息流
C->S: Client Hello
S->C: Server Hello
S->C: Certificate, Server Key Exchange, Server Hello Done
C->S: Client Key Exchange
C->S: Change Cipher Spec, Encrypted Handshake Message
S->C: Change Cipher Spec, Encrypted Handshake Message
C->S: Application Data
S->C: Application Data
......
S->C: Encrypted Alert
C->S: Encrypted Alert
最后,补充一下,关于DH秘钥交换的流程图,ECDH交换和DH交换流程逻辑相同,只是算法中交换的参数计算逻辑不同而已,从DH升级到ECDH是可以平滑做到的。
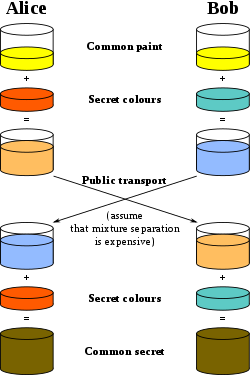
ECDH秘钥交换说明:
假设密钥交换双方为Alice、Bob,其有共享曲线参数(椭圆曲线E、阶N、基点G),对于于上图中的common paint黄色信息,是大家共有的,只是每次协商时,值不同,但是双方都是知道的。
1.Alice生成随机整数a (对应上图中的orange),计算A=a*G(这个A,对应上图中orange-tan)。Bob生成随机整数b(对应上图中的blue-green),计算B=b*G(这个B,对应上图中的light-blue)。
2.Alice将A传递给Bob。A的传递可以公开,即攻击者可以获取A。由于椭圆曲线的离散对数问题是难题,所以攻击者不可以通过A、G计算出a。Bob将B传递给Alice。同理,B的传递可以公开。
3.Bob收到Alice传递的A,计算Q=b*A (这里的Q,对应上图中yellow-brown)
4.Alice收到Bob传递的B,计算Q‘=a*B(这里的Q‘,对应上图中yellow-brown)
Alice、Bob双方即得Q=b*A=b*(a*G)=(b*a)*G=(a*b)*G=a*(b*G)=a*B=Q' (交换律和结合律),即双方得到一致的密钥Q。
到此,整个秘钥交换为核心的SSL消息流,大体就算是弄清楚了。
MQTT研究之EMQ:【wireshark抓包分析】的更多相关文章
- Wireshark抓包分析/TCP/Http/Https及代理IP的识别
前言 坦白讲,没想好怎样的开头.辗转三年过去了.一切已经变化了许多,一切似乎从没有改变. 前段时间调研了一次代理相关的知识,简单整理一下分享之.如有错误,欢迎指正. 涉及 Proxy IP应用 原理/ ...
- 用Wireshark抓包分析超过70秒的请求
超过70秒的请求是通过分析IIS日志发现的: 10.159.63.104是SLB的内网IP. 通过Wireshark抓包分析请求是9:22:21收到的(tcp.stream eq 23080): 09 ...
- Wireshark抓包分析HTTPS与HTTP报文的差异
一.什么是HTTPS: HTTPS(Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol)安全超文本传输协议 它是一个安全通信通道,它基于HTTP开发,用于在客户计算机和服务器之间交换 ...
- wireshark 抓包分析 TCPIP协议的握手
wireshark 抓包分析 TCPIP协议的握手 原网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/TankXiao/archive/2012/10/10/2711777.html 之前写过一篇 ...
- wireshark抓包分析工具的使用
# wireshark抓包分析工具的使用 ## 常用抓包指令 - `ip.src==192.168.60.26 and ip.dst==111.7.187.220 and tcp.port == 80 ...
- Wireshark抓包分析TCP建立/释放链接的过程以及状态变迁分析
Wireshark抓包分析TCP建立/释放链接的过程以及状态变迁分析 一.介绍计算机网络体系结构 1.计算机的网络体系结构 在抓包分析TCP建立链接之前首先了解下计算机的网络通信的模型,我相信学习过计 ...
- wireshark抓包分析——TCP/IP协议
本文来自网易云社区 当我们需要跟踪网络有关的信息时,经常会说"抓包".这里抓包究竟是什么?抓到的包又能分析出什么?在本文中以TCP/IP协议为例,简单介绍TCP/IP协议以及如何通 ...
- 【计算机网络】wireshark抓包分析1
学习计算机网络很久了,但总是局限于书本知识,感觉get不到重点.经师兄建议用wireshark抓包分析看看. 我自己以前并没有做过抓包分析,所以这篇博文可能会有很多错误,只是我自己的一个记录,路过的亲 ...
- TCP/IP详解卷1 - wireshark抓包分析
TCP/IP详解卷1 - 系列文 TCP/IP详解卷1 - 思维导图(1) TCP/IP详解卷1 - wireshark抓包分析 引言 在初学TCP/IP协议时,会觉得协议是一种很抽象的东西,通过wi ...
- 使用wireshark抓包分析-抓包实用技巧
目录 使用wireshark抓包分析-抓包实用技巧 前言 自定义捕获条件 输入配置 输出配置 命令行抓包 抓取多个接口 抓包分析 批量分析 合并包 结论 参考文献 使用wireshark抓包分析-抓包 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL创建新用户以及ERROR 1396 (HY000)问题解决
登 录mysql mysql -u root -p 创建允许本地 IP访问localhost的Mysql数据库时出错 create user 'lijing'@'localhost' identif ...
- Jmeter性能结果分析
1.压测结果指标 Samples:表示一共发出的请求数 Average:平均响应时间,默认情况下是单个Request的平均响应时间(ms) Error%:测试出现的错误请求数量百分比.若出现错误就要看 ...
- 2018-CVTE中央研究院-自然语言处理算法工程师-电话初面问题
楼主NLP初学者一名,有幸参加2018年CVTE中央研究院自然语言处理电话面试,问题总结如下: 1.详细的介绍自己的学术论文(感觉他们非常重视这块),会问你网络的具体构造,注意力机制如何计算以及为何你 ...
- 【原创】Arduino入门基础知识总结
一.概述 Arduino是源自意大利的一个开放源代码的硬件项目平台,该平台包括一块具备简单I/O功能的电路板以及一套程序开发环境软件. Arduino可以用来开发交互产品,比如它可以读取大量的开 ...
- KeepAlive--高可用解决方案
原文地址https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011078937 一:keepalive简述 一;高可用的解决方案 1)vrrp协议的实现keepalive 2)ais ...
- 2018-计算机系机试-A
#include<stdio.h> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #includ ...
- 怎么在Mac中的Safari查看网页源码
一般情况下,Safari中右键是没有查看网页源文件这个选项的: 但是通过设置是可以看到的~ 1.首先找到电脑左上角的Safari然后选择偏好设置: 2.接着选择 “高级”页签,勾选最下面的 “在菜单栏 ...
- 1055 - Expression #1 of ORDER BY clause is not in GROUP BY clause and contai
之前一直使用的mysql5,突然换成8之后,有许多地方不一样,今天就碰到一个. 在使用sql语句创建表时,报错: 1055 - Expression #1 of ORDER BY clause is ...
- [转]CentOS7利用systemctl添加自定义系统服务
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/saneri/p/7778756.html CentOS7自定义系统服务 CentOS7的服务systemctl脚本存放在:/usr/lib/sy ...
- mysql 数据库导出与导入
1.数据库导出 语句:mysqldump -u用戶名 -p密码 -d 数据库名 表名 > 脚本名; 1.导出整个数据库结构和数据 mysqldump -h localhost -uroot -p ...
