HTTP Server to Client Communication
1. Client browser short polling
The most simple solution, client use Ajax to sends a request to the server in a short period circle, the server returns the latest data, then client according to the received data to update the UI.
The advantage is simple, but another side, network and CPU pressure on the server is large and the bandwidth flow is wasted (usually the data is not changed).
Client side JS:
function createXHR(){
if(typeof XMLHttpRequest !='undefined'){
return new XMLHttpRequest();
}else if(typeof ActiveXObject !='undefined' ){
if(typeof arguments.callee.activeXString!="string"){
var versions=["MSXML2.XMLHttp.6.0","MSXML2.XMLHttp.3.0",
"MSXML2.XMLHttp"],
i,len;
for(i=0,len=versions.length;i<len;i++){
try{
new ActiveXObject(versions[i]);
arguments.callee.activeXString=versions[i];
break;
}catch(ex) {
}
}
}
return new ActiveXObject(arguments.callee.activeXString);
}else{
throw new Error("no xhr object available");
}
}
function polling(url,method,data){
method=method ||'get';
data=data || null;
var xhr=createXHR();
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
if(xhr.readyState==4){
if(xhr.status>=200&&xhr.status<300||xhr.status==304){
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}else{
console.log("fail");
}
}
};
xhr.open(method,url,true);
xhr.send(data);
}
setInterval(function(){
polling('http://localhost:8088/time','get');
},2000);
Server side, NodeJS:
var http=require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(req.url=='/time'){
//res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain','Access-Control-Allow-Origin':'http://localhost'});
res.end(new Date().toLocaleString());
};
if(req.url=='/'){
fs.readFile("./pollingClient.html", "binary", function(err, file) {
if (!err) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write(file, "binary");
res.end();
}
});
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
server.on('connection',function(socket){
console.log("connection ok");
});
server.on('close',function(){
console.log('server closed');
});
2.Long Polling
Long polling is itself not a true push; long polling is a variation of the traditional polling technique, but it allows emulating a push mechanism under circumstances where a real push is not possible, such as sites with security policies that require rejection of incoming HTTP/S Requests.
With long polling, the client requests information from the server exactly as in normal polling, but with the expectation the server may not respond immediately. If the server has no new information for the client when the poll is received, instead of sending an empty response, the server holds the request open and waits for response information to become available. Once it does have new information, the server immediately sends an HTTP/S response to the client, completing the open HTTP/S Request. Upon receipt of the server response, the client often immediately issues another server request. In this way the usual response latency (the time between when the information first becomes available and the next client request) otherwise associated with polling clients is eliminated.
Client Side JS:
function createXHR(){
if(typeof XMLHttpRequest !='undefined'){
return new XMLHttpRequest();
}else if(typeof ActiveXObject !='undefined' ){
if(typeof arguments.callee.activeXString!="string"){
var versions=["MSXML2.XMLHttp.6.0","MSXML2.XMLHttp.3.0",
"MSXML2.XMLHttp"],
i,len;
for(i=0,len=versions.length;i<len;i++){
try{
new ActiveXObject(versions[i]);
arguments.callee.activeXString=versions[i];
break;
}catch(ex) {
}
}
}
return new ActiveXObject(arguments.callee.activeXString);
}else{
throw new Error("no xhr object available");
}
}
function longPolling(url,method,data){
method=method ||'get';
data=data || null;
var xhr=createXHR();
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
if(xhr.readyState==4){
if(xhr.status>=200&&xhr.status<300||xhr.status==304){
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}else{
console.log("fail");
}
longPolling(url,method,data);
}
};
xhr.open(method,url,true);
xhr.send(data);
}
longPolling('http://localhost:8088/time','get');
When XHR object's readySate equal 4, that means the server side have been response the data, connection closed, next time will re-request the server to establish connection.
Server Side NodeJS:
var http=require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(req.url=='/time'){
setInterval(function(){
sendData(res);
},20000);
};
if(req.url=='/'){
fs.readFile("./lpc.html", "binary", function(err, file) {
if (!err) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write(file, "binary");
res.end();
}
});
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
function sendData(res){
var randomNum=Math.floor(10*Math.random());
console.log(randomNum);
if(randomNum>=0&&randomNum<=5){
res.end(new Date().toLocaleString());
}
}
3. HTTP Stream Communication
Long-polling technique, to keep long time connection between client and server: the server side will block the response, and the client to polling.
There's another way named http-stream communication, principle is: keep the connection with serer during one request, then server push the data to client continuously.It's not one time response but instead, like byte by byte. The difference between polling is: only one time request, keep connection, response data in this connection.
Below the solusion of this:
3.1 XHR Object Streaming
The idea is to construct a XHR object, monitoring its onreadystatechange event, when readyState is 3,get responseText and then processed, readyState 3 means data transmission, the whole communication is not over, so it will continues get the data send from server, until readyState become 4,then a communication end. During the process, the data transmitted by the server to the client is sent via several times by stream, and the client is also get the data via stream, so it is called the http-streaming data flow.
Client JS:
function createStreamClient(url,progress,done){
//received为接收到数据的计数器
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest(),received=0;
xhr.open("get",url,true);
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
var result;
if(xhr.readyState==3){
//console.log(xhr.responseText);
result=xhr.responseText.substring(received);
received+=result.length;
progress(result);
}else if(xhr.readyState==4){
done(xhr.responseText);
}
};
xhr.send(null);
return xhr;
}
var client=createStreamClient("http://localhost:8088/stream",function(data){
console.log("Received:"+data);
},function(data){
console.log("Done,the last data is:"+data);
})
Server Code:
var http=require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
var count=0;
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(req.url=='/stream'){
res.setHeader('content-type', 'multipart/octet-stream');
var timer=setInterval(function(){
sendRandomData(timer,res);
},2000);
};
if(req.url=='/'){
fs.readFile("./xhr-stream.html", "binary", function(err, file) {
if (!err) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write(file, "binary");
res.end();
}
});
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
function sendRandomData(timer,res){
var randomNum=Math.floor(10000*Math.random());
console.log(randomNum);
if(count++==10){
clearInterval(timer);
res.end(randomNum.toString());
}
res.write(randomNum.toString());
}
3.2 IFrame data flow
To resolve the low version of IE does not allow get responseText property when XHR's readyState is 3. In order to achieve on IE, iframe based data stream communication mode come out.
Specifically, load iframe dynamicly in the browser, make SRC attribute to the server URL, it's actually send a HTTP request to server, then create a function to process data in browser.Via iframe between server and client to push data to client side.
But the returned data similar to the <script type=\ "text/javascript\" >parent.process ("+randomNum.toString") (+ "') </script> , once browser receives the data, it will parsed into JS code and find the function on the page then execute,to achieve real-time updates to the client.
Client JS:
function process(data){
console.log(data);
}
var dataStream = function (url) {
var ifr = document.createElement("iframe"),timer;
ifr.src = url;
document.body.appendChild(ifr);
};
dataStream('http://localhost:8088/htmlfile');
Server:
var http=require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
var count=0;
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(req.url=='/htmlfile'){
res.setHeader('content-type', 'text/html');
var timer=setInterval(function(){
sendRandomData(timer,res);
},2000);
};
if(req.url=='/'){
fs.readFile("./htmlfile-stream.html", "binary", function(err, file) {
if (!err) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write(file, "binary");
res.end();
}
});
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
function sendRandomData(timer,res){
var randomNum=Math.floor(10000*Math.random());
console.log(randomNum.toString());
if(count++==10){
clearInterval(timer);
res.end("<script type=\"text/javascript\">parent.process('"+randomNum.toString()+"')</script>");
}
res.write("<script type=\"text/javascript\">parent.process('"+randomNum.toString()+"')</script>");
}
3.3 Htmlfile dataflow
For IE, new problem there when use iframe solution above. Before the server send back all the communication, the browser title will in loading status, and the bottom is also showning loading. This is not a good experience for a product, so Google's genius has come up with a hack mode. In IE, dynamic create a htmlfile object, it's ActiveX object COM component, which actually a HTML document in memory, by adding the generated iframe to the memory HTMLfile, and use iframe data stream communication to achieve the above effect. Meanwhile, as the HTMLfile object is not directly added to the page, so will not cause the browser display loading status.
Client Code:
function connect_htmlfile(url, callback) {
var transferDoc = new ActiveXObject("htmlfile");
transferDoc.open();
transferDoc.write(
"<!DOCTYPE html><html><body><script type=\"text/javascript\">" +
"document.domain='" + document.domain + "';" +
"<\/script><\/body><\/html>");
transferDoc.close();
var ifrDiv = transferDoc.createElement("div");
transferDoc.body.appendChild(ifrDiv);
ifrDiv.innerHTML = "<iframe src='" + url + "'><\/iframe>";
transferDoc.callback=callback;
setInterval( function () {}, 10000);
}
function prograss(data) {
alert(data);
}
connect_htmlfile('http://localhost:8088/htmlfile',prograss);
4.SSE(Server Sent Event)
Server-Sent Events enables efficient server-to-client streaming of text-based event data—e.g., real-time notifications or updates generated on the server. To meet this goal, SSE introduces two components: a new EventSource interface in the browser, which allows the client to receive push notifications from the server as DOM events, and the "event stream" data format, which is used to deliver the individual updates.
The combination of the EventSource API in the browser and the well-defined event stream data format is what makes SSE both an efficient and an indispensable tool for handling real-time data in the browser:
- Low latency delivery via a single, long-lived connection
- Efficient browser message parsing with no unbounded buffers
- Automatic tracking of last seen message and auto reconnect
- Client message notifications as DOM events
Under the hood, SSE provides an efficient, cross-browser implementation of XHR streaming; the actual delivery of the messages is done over a single, long-lived HTTP connection. However, unlike dealing XHR streaming on our own, the browser handles all the connection management and message parsing, allowing our applications to focus on the business logic! In short, SSE makes working with real-time data simple and efficient. Let’s take a look under the hood.
Server Code:
var source=new EventSource('http://localhost:8088/evt');
source.addEventListener('message', function(e) {
console.log(e.data);
}, false);
source.onopen=function(){
console.log('connected');
}
source.onerror=function(err){
console.log(err);
}
Client Code:
var http=require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
var count=0;
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(req.url=='/evt'){
//res.setHeader('content-type', 'multipart/octet-stream');
res.writeHead(200, {"Content-Type":"tex" +
"t/event-stream", "Cache-Control":"no-cache",
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*',
"Connection":"keep-alive"});
var timer=setInterval(function(){
if(++count==10){
clearInterval(timer);
res.end();
}else{
res.write('id: ' + count + '\n');
res.write("data: " + new Date().toLocaleString() + '\n\n');
}
},2000);
};
if(req.url=='/'){
fs.readFile("./sse.html", "binary", function(err, file) {
if (!err) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.write(file, "binary");
res.end();
}
});
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
Browser Support for SSE:
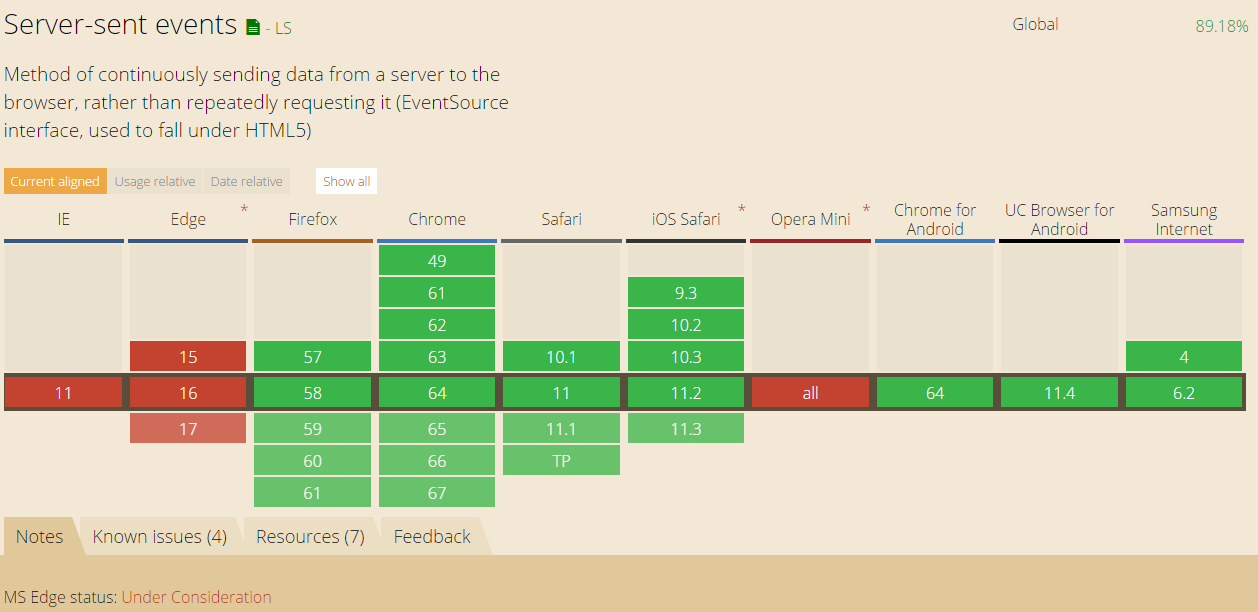
5. WebSocket
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011, and the WebSocket API in Web IDL is being standardized by the W3C.
WebSocket is a different TCP protocol from HTTP. Both protocols are located at layer 7 in the OSI model and, as such, depend on TCP at layer 4. Although they are different, RFC 6455 states that WebSocket "is designed to work over HTTP ports 80 and 443 as well as to support HTTP proxies and intermediaries" thus making it compatible with the HTTP protocol. To achieve compatibility, the WebSocket handshake uses the HTTP Upgrade header[1] to change from the HTTP protocol to the WebSocket protocol.
The WebSocket protocol enables interaction between a web client (e.g. a browser) and a web server with lower overheads, facilitating real-time data transfer from and to the server. This is made possible by providing a standardized way for the server to send content to the client without being first requested by the client, and allowing for messages to be passed back and forth while keeping the connection open. In this way, a two-way (bi-directional) ongoing conversation can take place between the client and the server. The communications are done over TCP port number 80 (or 443 in the case of TLS-encrypted connections), which is of benefit for those environments which block non-web Internet connections using a firewall. Similar two-way browser-server communications have been achieved in non-standardized ways using stopgap technologies such as Comet.
After the hand shake, will use WS/WSS protocol instead of HTTP.
WS frame format as below:
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-------+-+-------------+-------------------------------+
|F|R|R|R| opcode|M| Payload len | Extended payload length |
|I|S|S|S| (4) |A| (7) | (16/64) |
|N|V|V|V| |S| | (if payload len==126/127) |
| |1|2|3| |K| | |
+-+-+-+-+-------+-+-------------+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +
| Extended payload length continued, if payload len == 127 |
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +-------------------------------+
| |Masking-key, if MASK set to 1 |
+-------------------------------+-------------------------------+
| Masking-key (continued) | Payload Data |
+-------------------------------- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +
: Payload Data continued ... :
+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +
| Payload Data continued ... |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+ Details refer to : RFC6455
Client Code:
window.onload=function(){
var ws=new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8088");
var oText=document.getElementById('message');
var oSend=document.getElementById('send');
var oClose=document.getElementById('close');
var oUl=document.getElementsByTagName('ul')[0];
ws.onopen=function(){
oSend.onclick=function(){
if(!/^\s*$/.test(oText.value)){
ws.send(oText.value);
}
};
};
ws.onmessage=function(msg){
var str="<li>"+msg.data+"</li>";
oUl.innerHTML+=str;
};
ws.onclose=function(e){
console.log("connection closed");
ws.close();
}
}
Server Code:
var crypto = require('crypto');
var WS = '258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11';
var server=require('net').createServer(function (socket) {
var key;
socket.on('data', function (msg) {
if (!key) {
//Get the response Sec-WebSocket-key header
key = msg.toString().match(/Sec-WebSocket-Key: (.+)/)[1];
key = crypto.createHash('sha1').update(key + WS).digest('base64');
socket.write('HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols\r\n');
socket.write('Upgrade: WebSocket\r\n');
socket.write('Connection: Upgrade\r\n');
//send the confirmed key back
socket.write('Sec-WebSocket-Accept: ' + key + '\r\n');
//end Http head
socket.write('\r\n');
} else {
var msg=decodeData(msg);
console.log(msg);
//if the code send by client is 8,means close the connection,terminate TCP and exit.
if(msg.Opcode==8){
socket.end();
server.unref();
}else{
socket.write(encodeData({FIN:1,
Opcode:1,
PayloadData:"Received Data is "+msg.PayloadData}));
}
}
});
});
server.listen(8000,'localhost');
//as websocket data frame formate
function decodeData(e){
var i=0,j,s,frame={
//get two byte data at the front
FIN:e[i]>>7,Opcode:e[i++]&15,Mask:e[i]>>7,
PayloadLength:e[i++]&0x7F
};
//deal special length 126 & 127
if(frame.PayloadLength==126)
frame.length=(e[i++]<<8)+e[i++];
if(frame.PayloadLength==127)
i+=4,
//Length use 4 byte int
frame.length=(e[i++]<<24)+(e[i++]<<16)+(e[i++]<<8)+e[i++];
//if use mask code
if(frame.Mask){
//get mask key
frame.MaskingKey=[e[i++],e[i++],e[i++],e[i++]];
//
for(j=0,s=[];j<frame.PayloadLength;j++)
s.push(e[i+j]^frame.MaskingKey[j%4]);
}else s=e.slice(i,frame.PayloadLength); //else get data directly
//byte array to buffer
s=new Buffer(s);
//in case buffer to string
if(frame.Opcode==1)s=s.toString();
//
frame.PayloadData=s;
//return frame
return frame;
}
//encode send data
function encodeData(e){
var s=[],o=new Buffer(e.PayloadData),l=o.length;
//first byte
s.push((e.FIN<<7)+e.Opcode);
//input second byte,check it's length and then input follow lenght data
//not use mask code
if(l<126)s.push(l);
else if(l<0x10000)s.push(126,(l&0xFF00)>>2,l&0xFF);
else s.push(
127, 0,0,0,0, //8byte data
(l&0xFF000000)>>6,(l&0xFF0000)>>4,(l&0xFF00)>>2,l&0xFF
);
//return head and data part buffer
return Buffer.concat([new Buffer(s),o]);
}
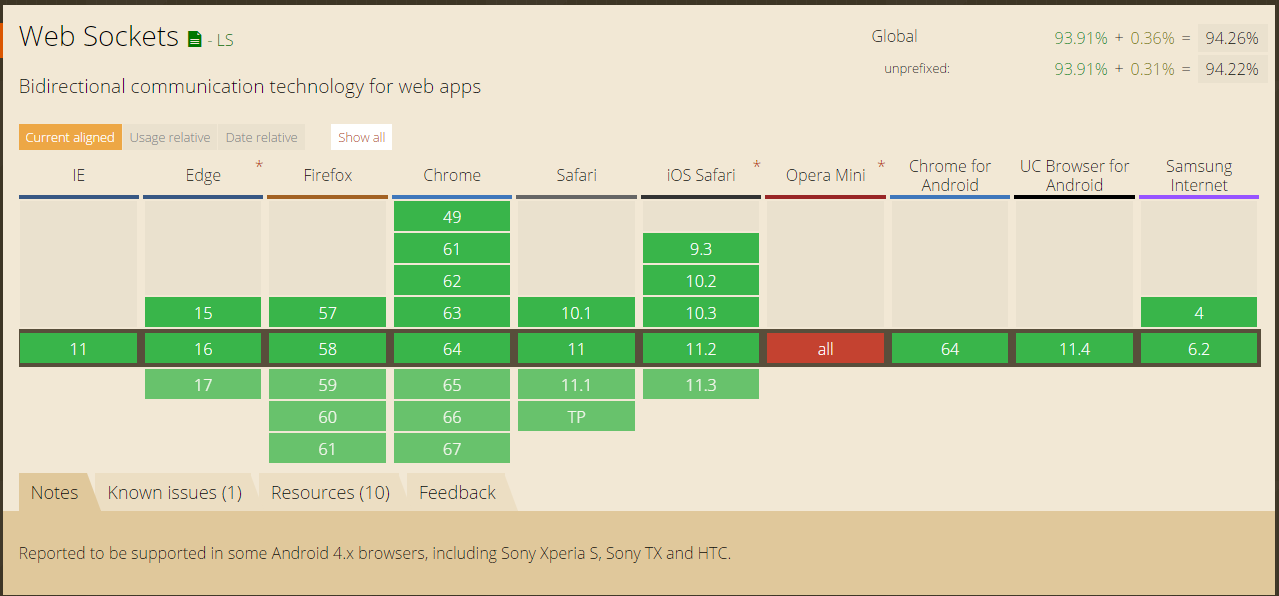
6. Solution for cross domain communication
6.1 Same-Origin Policy
We are seeing this error because we are violating something called the Same-Origin Policy (SOP). This is a security measure implemented in browsers to restrict interaction between documents (or scripts) that have different origins.
The origin of a page is defined by its protocol, host and port number. For example, the origin of this page is (‘http’,’jvaneyck.wordpress.com’, 80). Resources with the same origin have full access to each other. If pages A and B share the same origin, Javascript code included on A can perform HTTP requests to B’s server, manipulate the DOM of B or even read cookies set by B. Note that the origin is defined by the source location of the webpage. To clarify: a javascript source file loaded from another domain (e.g. a jQuery referenced from a remote CDN) will run in the origin of the HTML that includes the script, not in the domain where the javascript file originated from.
For Cross-Origin HTTP requests in specific, the SOP prescribes the following general rule: Cross-Origin writes are allowed, Cross-Origin reads are not. This means that if A and C have a different origin, HTTP requests made by A will be received correctly by C (as these are “writes”), but the script residing in A will not be able to read any data -not even the response code- returned from C. This would be a Cross-Origin “read” and is blocked by the browser resulting in the error above. In other words, the SOP does not prevent attackers to write data to their origin, it only disallows them to read data from your domain (cookie, localStorage or other) or to do anything with a response received from their domain.
The SOP is a Very Good Thing. It prevents malicious script from reading data of your domain and sending it to their servers. This means that some script kiddie will not be able to steal your cookies that easily.
6.2 Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
CORS is a mechanism that uses additional HTTP headers to let a user agent gain permission to access selected resources from a server on a different origin (domain) than the site currently in use. A user agent makes a cross-origin HTTP request when it requests a resource from a different domain, protocol, or port than the one from which the current document originated.
For security reasons, browsers restrict cross-origin HTTP requests initiated from within scripts. For example, XMLHttpRequest and the Fetch API follow the same-origin policy. This means that a web application using those APIs can only request HTTP resources from the same domain the application was loaded from unless CORS headers are used.
6.3 XHR CORS
It's basic on original XHR request, when XHR calls the open method,destination point to a cross domain address, by setting response header on the server 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin':' * ',server will tells the browser, the data from cross domain and the server allows. Browser receives this header will bypass the usual cross domain restrictions, which no difference than normal XHR communication.
Advantage is client side no need to modify code, server only need to add'Access-Control-Allow-Origin':'*' header. It supported by non IE browsers such as FF, Safari, opera, chrome and so on. Cross domain XHR has some limitations compared to non - cross domain XHR, which is for security reason, as below:
- Client can not use the setRequestHeader to customise header.
- Cookie can not be sent and received;
- Call getAllResponseHeaders() method will always return an empty string.
Above considerations to prevent common cross site scripting attacks (XSS) and Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF).
Client Code:
var polling=function(){
var xhr=new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange=function(){
if(xhr.readyState==4)
if(xhr.status==200){
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
xhr.open('get','http://localhost:8088/cors');
xhr.send(null);
};
setInterval(function(){
polling();
},1000);
Server Code:
var http=require('http');
var fs = require("fs");
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(req.url=='/cors'){
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain','Access-Control-Allow-Origin':'http://localhost'});
res.end(new Date().toString());
}
if(req.url=='/jsonp'){
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
server.on('connection',function(socket){
console.log("Client connection OK");
});
server.on('close',function(){
console.log('server closed');
});
Note on the server need to set Access-Control-Allow-Origin to allowed domain.
6.4 XDR CORS
For IE8-IE10, it's not support oringinal XHR object to raise cross domain request. It have it own XDomainRequest object which similar to XHR object, limitations below:
- Cookie will not be sent with the request and will not return with the response;
- Only the Content-Type field in the request header can be set;
- No access to the response header information;
- Only Get and Post requests are supported;
- Only support IE8-IE10.
Client Code:
var polling=function(){
var xdr=new XDomainRequest();
xdr.onload=function(){
console.log(xdr.responseText);
};
xdr.onerror=function(){
console.log('failed');
};
xdr.open('get','http://localhost:8088/cors');
xdr.send(null);
};
setInterval(function(){
polling();
},1000);
Server code as above.
6.5 JSONP CORS
This solution use the HTML page script tags have no restrictions on cross domain, make the SRC property to be the destination server address,actually send a HTTP request via the script tag. After server receives the request, the response data is their own data and the calls to the client JS function.It's principle similar to above iframe flow mode, client browser will parses and execution the receives script, to achieve the purpose of updating UI.
Client Code:
function callback(data){
console.log("Response Data:"+data);
}
function sendJsonp(url){
var oScript=document.createElement("script");
oScript.src=url;
oScript.setAttribute('type',"text/javascript");
document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(oScript);
}
setInterval(function(){
sendJsonp('http://localhost:8088/jsonp?cb=callback');
},1000);
Server Code:
var http=require('http');
var url=require('url');
var server=http.createServer(function(req,res){
if(/\/jsonp/.test(req.url)){
var urlData=url.parse(req.url,true);
var methodName=urlData.query.cb;
res.writeHead(200,{'Content-Type':'application/javascript'});
//res.end("<script type=\"text/javascript\">"+methodName+"("+new Date().getTime()+");</script>");
res.end(methodName+"("+new Date().getTime()+");");
//res.end(new Date().toString());
}
}).listen(8088,'localhost');
server.on('connection',function(socket){
console.log("Client Connection OK");
});
server.on('close',function(){
console.log('Server Closed');
});
Refers:
http://www.52im.net/thread-338-1-1.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WebSocket
https://caniuse.com/#search=websocket
HTTP Server to Client Communication的更多相关文章
- C Socket Programming for Linux with a Server and Client Example Code
Typically two processes communicate with each other on a single system through one of the following ...
- Open Source VOIP applications, both clients and servers (开源sip server & sip client 和开发库)
SIP Proxies SBO SIP Proxy Bypass All types of Internet Firewall JAIN-SIP Proxy Mini-SIP-Proxy A very ...
- TCP连接的状态与关闭方式及其对Server与Client的影响
TCP连接的状态与关闭方式及其对Server与Client的影响 1. TCP连接的状态 首先介绍一下TCP连接建立与关闭过程中的状态.TCP连接过程是状态的转换,促使状态发生转换的因素包括用户调用. ...
- navicat 连接sqlserver提示要安装 sql server native client
navicat 连接sqlserver提示要安装 sql server native client 解决方法:其实navicat自带sqlncli_x64.msi,就在安装目录下,安装后问题解决!
- Netty4.0学习笔记系列之一:Server与Client的通讯
http://blog.csdn.net/u013252773/article/details/21046697 本文是学习Netty的第一篇文章,主要对Netty的Server和Client间的通讯 ...
- 浅谈Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server和Client获得Service Manager接口之路
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6627260 在前面一篇文章浅谈Service ...
- 基于winsocket的框体Server和Client
前面学了一点Winsock的知识,会编写简单的Server和Client,现在就想通过VS2008编写框体的Server和Client,而不是在控制台上的操作了,毕竟学编程就是要多加练习,在实践中发现 ...
- Winsock网络编程笔记(3)----基于UDP的server和client
在上一篇随笔中,对Winsock中基于tcp面向连接的Server和Client通信进行了说明,但是,Winsock中,Server和Client间还可以通过无连接通信,也就是采用UDP协议.. 因此 ...
- Winsock网络编程笔记(2)----基于TCP的server和client
今天抽空看了一些简单的东西,主要是对服务器server和客户端client的简单实现. 面向连接的server和client,其工作流程如下图所示: 服务器和客户端将按照这个流程就行开发..(个人觉得 ...
随机推荐
- 泊爷带你学go -- 经典的继承与接口 简直吊炸天 !
package main import ( "fmt" ) type TeamBase struct { m_TeamId uint64 m_Rid uint32 m_RoomRu ...
- JVM逃逸分析
开启逃逸分析: -server -XX:+DoEscapeAnalysis -XX:+PrintGCDetail -Xmx10m -Xms10m 关闭逃逸分析: -server -XX:-DoEsca ...
- 在eclipse上集成安装阿里巴巴代码规约P3C插件
在eclipse上集成安装阿里巴巴代码规约P3C插件 参照网址: https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/2d5afd6923e78b85a3e28e5e.html 首先进 ...
- MSP430中断的一个细节问题
关于中断标志: 从SPI发送一字节数据: void SPI_Set_SD_Byte(unsigned char txData) { UCB0TXBUF = txData; // 写入发送缓冲区 whi ...
- shell 统计字符串 字符个数
统计“abbc”中“b”的个数 1:awknum=`echo abbc | awk -F"b" '{print NF-1}'` 2:trnum=`echo abbc | tr -c ...
- python学习第三次记录
python学习第三次记录 python中常用的数据类型: 整数(int) ,字符串(str),布尔值(bool),列表(list),元组(tuple),字典(dict),集合(set). int.数 ...
- 微信小程序实际开发中学习
三个概念 微信:就是一个聊天工具 微信公众号:企业或个人用于管理其粉丝/用户的应用(类似于APP) 微信小程序:不需要下载安装直接可以使用的软件/应用/APP 小程序与公众号的区别: 定位不同(小程序 ...
- servlet之servlet(二)
·servlet用于创建返回基于客服请求的动态页面(整个).部分页面.与数据库交互 ·servlet接口: 继承servlet接口后,要在web.xml中配置和映射servlet.配置servlet初 ...
- VBO最佳实践
VBO的大小 一个VBO应该多大? 你可以创建一个很小的VBO,但最佳方案是把很多对象放到一个VBO里面,这样的话可以减少调用gl函数的数量,比如glBindBuffer.glVertexPointe ...
- 复习string和数组
两种实例化方式的区别 1)直接赋值(String str = "hello"):只开辟一块堆内存空间,并且会自动入池,不会产生垃圾. 2)构造方法(String str= new ...
