codeforces_D. Treasure Hunting_[DP+Binary Search]
http://codeforces.com/contest/1201/problem/D
题意:n行m列的矩阵中,有k个targets,从[1, 1]出发,每次只能向上下左右四个方向移动一步,且只有在q个safecolumns上进行向上移动,最少需要多少次移动才能获得所有的targets。(2≤n,m,k,q≤2*10^5,q≤m)。
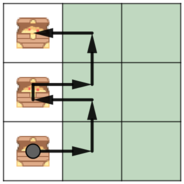


思路:
Make two arrays: left and right. left[i] is the treasure in the leftmost position in row i (0 if there are no treasures in row ii). right[i] is the treasure in the rightmost cell in row ii (0 if there are no treasures in row ii).
We can simply take out rows where there is no treasure (and add 1 to the result if there are treasure above that line, because we have to move up there).
For every row, except the last, we have to leave that row at one of the safe columns. Let's notice that the last treasure we collect in the row will be either left[i] or right[i]. Let's take a look at both possibilities: If we collect the left[i] treasure last, we have to leave the row either going left or going right to the closest safe column, because going further wouldn't worth it (consider moving up earlier and keep doing the same thing at row i+1). The same is true for right[i]. For the first row, we start at the first column, we can calculate the moves required to go up the second row at the for cells. For all the other rows, we have 4 possibilities, and we have to calculate how many moves it takes to reach the row i+1 at the 4 possible columns. For the last row, we don't have to reach a safe column, we just have to collect all the treasures there. We can count the answer for the problem from the calculated results from the previous row. Time complexity: O(16∗n)
1. 对于存在宝藏的行,最后得到的宝藏要么是最左边的要么是最右边的;
2. 假设最后拿到的是最左边的,那么可以通过这个宝藏左右最近的safecolumns离开;最后拿到的是最右边的情况也同理;
3. 对于第一行来说,若有宝藏,则获得最右边的宝藏后离开;所无宝藏,则通过离[1, 1]最近的safecolumn离开;
4. 对于其他行来说,最多可以有四种方式离开此行,最后一行不需要到达safecolumn,获得所有宝藏即可;
宝藏左右最近的safecolumn,可以通过binary search求得。
注意,若最左边的宝藏就在safecolumn上,则其左右最近的safecolumn都是此列。
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std; typedef long long LL; int findSafe(vector<int>& safes, int x){
int l = , r = safes.size()-, ret;
while(l <= r){
int m = (l+r)>>;
if(safes[m] == x)
return m;
if(safes[m] > x)
r = m - ;
else{
ret = m;
l = m + ;
}
}
return ret;
} int dist(int layer, int p1, int p2, vector<int>& leftmost, vector<int>& rightmost, vector<int>& safecol){
if(safecol[p1] > safecol[p2])
swap(p1, p2);
int d = safecol[p2] - safecol[p1];
if(rightmost[layer] > safecol[p2])
d += * (rightmost[layer]-safecol[p2]);
if(leftmost[layer] < safecol[p1])
d += * (safecol[p1]-leftmost[layer]);
return d;
} int main(){
int n, k, m, q;
cin>>n>>m>>k>>q;
vector<int> leftmost(n+, m+), rightmost(n+, ), safecol{};
for(int i=; i<k; i++){
int row, col;
cin>>row>>col;
leftmost[row] = min(leftmost[row], col);
rightmost[row] = max(rightmost[row], col);
}
for(int i=; i<q; i++){
int safe;
cin>>safe;
safecol.push_back(safe);
} sort(safecol.begin(), safecol.end()); while(leftmost[n] == m+) n--; if(n==){
cout<<rightmost[]-<<endl;
return ;
}
vector<LL> now_step{, , ,}, lst_step{, , , };
vector<int> lst_gate{-, -, -, -};
if(rightmost[] == ){
int rsafe = findSafe(safecol, );
if(safecol[rsafe] < )
rsafe++;
lst_gate[] = rsafe;
lst_step[] = safecol[rsafe]-;
}else{
int lsafe = findSafe(safecol, rightmost[]);
//cout<<rightmost[1]<<"*"<<lsafe<<endl;
lst_gate[] = lsafe;
lst_step[] = *rightmost[]-safecol[lsafe]-;
//cout<<"l10:"<<lst_step[0]<<endl;
if(safecol[lsafe]<rightmost[] && lsafe+ < safecol.size()){
lst_gate[] = lsafe+;
lst_step[] = safecol[lsafe+]-;
}
} for(int i=; i<n; i++){
if(leftmost[i] == m+){
for(int j=; j<; j++)
lst_step[j]++;
continue;
}else{
vector<int> now_gate{-, -, -, -};
int g1 = findSafe(safecol, leftmost[i]);
int g2 = findSafe(safecol, rightmost[i]);
//cout<<g1<<" "<<g2<<endl;
now_gate[] = g1;
if(safecol[g1] < leftmost[i] && g1+ < safecol.size())
now_gate[] = g1+;
now_gate[] = g2;
if(safecol[g2] < rightmost[i] && g2+ < safecol.size())
now_gate[] = g2+;
for(int j=; j<; j++){
now_step[j] = (*1e5+) * (*1e5);
for(int u=; u<; u++)
if(lst_gate[u]> && now_gate[j]>){
int d = +dist(i,now_gate[j], lst_gate[u], leftmost, rightmost, safecol);
//cout<<now_gate[j]<<" "<<lst_gate[u]<<endl;
//cout<<"d:"<<i<<" "<<d<<endl;
//cout<<"ld:"<<" "<<lst_step[u]<<endl;
now_step[j] = min(now_step[j], lst_step[u]+d);
}
}
lst_step = now_step;
lst_gate = now_gate;
}
}
LL ret = (*1e5+) * (*1e5);
for(int u=; u<; u++)
if(lst_gate[u] > ){
int d = +rightmost[n]-leftmost[n]+min(abs(rightmost[n]-safecol[lst_gate[u]]), abs(leftmost[n]-safecol[lst_gate[u]]));
//cout<<"d:"<<" "<<d<<endl;
//cout<<"lst_step:"<<lst_step[u]<<endl;
ret = min(ret, lst_step[u]+d);
}
printf("%I64d\n", ret);
return ;
}
codeforces_D. Treasure Hunting_[DP+Binary Search]的更多相关文章
- 96. Unique Binary Search Trees (Tree; DP)
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- Unique Binary Search Trees(dp)
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- Unique Binary Search Trees I&II——给定n有多少种BST可能、DP
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Trees 独一无二的二叉搜索树
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Trees II 独一无二的二叉搜索树之二
Given n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n. For e ...
- Leetcode 86. Unique Binary Search Trees
本题利用BST的特性来用DP求解.由于BST的性质,所以root左子树的node全部<root.而右子树的node全部>root. 左子树 = [1, j-1], root = j, 右子 ...
- Unique Binary Search Trees
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- LeetCode-96. Unique Binary Search Trees
Description: Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1.. ...
- LeeCode - Unique Binary Search Trees
题目: Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For e ...
随机推荐
- 阶段1 语言基础+高级_1-3-Java语言高级_06-File类与IO流_08 转换流_6_练习_转换文件编码
- c#处理bin文件
1. fs.Position 写入的位置,从哪个位置开始写 fs.Write(byte1,0,byte1.Length); byte1写入的byte[], 写入内容从第几位开始取,length取多长 ...
- 树莓派3b折腾指南
最近入手了树梅派3b,搭建了宿舍共享的热点和NAS,搭建透明代理科学上网的计划还没实现. 先报个价,一套折腾下来花了500大洋,树梅派3加外壳200,电源加内存卡100,显示器淘宝二手150,有线键鼠 ...
- Shell脚本中单引号(‘)和双引号(“)的使用区别
在Linux操作系统上编写Shell脚本时候,我们是在变量的前面使用$符号来获取该变量的值,通常在脚本中使用”$param”这种带双引号的格式,但也有出现使用'$param'这种带引号的使用的场景,首 ...
- python 正则表达式 re.split
内置函数split与re库中的split,有很多相似处 #!use/bin/python #coding:utf-8 import re str= "https://i.cnb1logs.c ...
- 编程字体Source Code Pro 免费下载
对于程序员来说,好的字体应该满足的基本条件: 字母和数字易于分辨,如: 英文字母o 和 阿拉伯数字 0 ,或者 英文字母 l 和 阿拉伯数字 1 ,两个单引号 '' 和双引号 ”. 字体等宽,保持对齐 ...
- 【ABAP系列】SAP 业务界面同时显示KEY和文本
公众号:SAP Technical 本文作者:matinal 原文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/SAPmatinal/ 原文链接:[MM系列]SAP 业务界面同时显示KEY和 ...
- [LeetCode]29 两数相除和一个小坑点
给定两个整数,被除数 dividend 和除数 divisor.将两数相除,要求不使用乘法.除法和 mod 运算符. 返回被除数 dividend 除以除数 divisor 得到的商. 示例 1: 输 ...
- JavaScript之基础语法
第一章 javascript语法 一, js代码的引入 方式一:在html页写js代码 <script> alert('hello,world') </script> 方式二: ...
- Kotlin学习(3)类
声明类和接口: //类 class A{ } //接口,接口中的方法可以有默认实现 interface B{ fun show(){ print("i'm B") } } //用冒 ...
