OpenCV 之 特征检测
特征,也称 兴趣点 或 关键点,如下:蓝框内区域平坦,无特征;黑框内有“边缘”,红框内有“角点”,后二者都可视为“特征”

角点作为一种特征,它具有旋转不变性,如下:当图像旋转时,代表角点响应函数 R 的特征椭圆,其形状保持不变
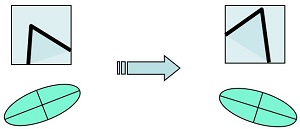
但是,角点不具有尺度不变性,如下:左图中被检测为角点的特征,当放大到右图的尺度空间时,则会被检测为 边缘 或 曲线
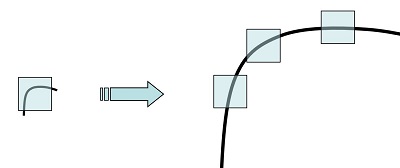
下面介绍几种具有尺度不变性的特征检测算法,如 SIFT、SURF、ORB、BRISK、KAZE 和 AKAZE 等
1 特征检测
1.1 SIFT
SIFT 全称 Scale Invariant Feature Transform,是特征检测中里程碑式的算法,也是目前最有效的特征检测,该算法申请了专利,直到 2020年3月才过专利保护期
OpenCV 从 4.4.0 起,已经将 SIFT 移到了主模块 feature2d 中,SIFT 继承自 Feature2D 类,而 Feature2D 继承自 Algorithm 类,SIFT 的创建函数 create() 定义如下:
class SIFT : public Feature2D
{
public:
static Ptr<SIFT> create(
int nfeatures = 0, // The number of best features to retain
int nOctaveLayers = 3, // The number of layers in each octave. 3 is the value used in D.Lowe paper
double contrastThreshold = 0.04, // The contrast threshold used to filter out weak features in low-contrast regions
double edgeThreshold = 10, // The threshold used to filter out edge-like features
double sigma = 1.6 ); // The sigma of the Gaussian applied to the input image at the octave 0
Algorithm 类中有两个虚函数:detect() 检测特征,compute() 计算描述符
class Feature2D : public virtual Algorithm
{
public:
/* Detects keypoints in an image (first variant) or image set(second variant). */
virtual void detect(InputArray image, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, InputArray mask=noArray() );
/* Computes the descriptors for a set of keypoints detected in an image (first variant) or image set (second variant). */
virtual void compute(InputArray image, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, OutputArray descriptors );
1.2 SURF
SIFT 算法虽好,但计算速度不够快,于是 SIFT 的近似版 SURF (Speeded Up Robust Features) 应运而生, SURF 的运行时间约为 SIFT 的 1/3
SURF 属于 xfeature2d 模块,也继承自 Feature2D 类,其 create() 函数定义如下:
namespace xfeatures2d
{
class SURF : public Feature2D
{
public:
static Ptr<SURF> create(
double hessianThreshold = 100, // Threshold for hessian keypoint detector used in SURF
int nOctaves = 4, // Number of pyramid octaves the keypoint detector will use
int nOctaveLayers = 3, // Number of octave layers within each octave
bool extended = false, // Extended descriptor flag (true, 128-element descriptors; false, 64-element descriptors)
bool upright = false); // Up-right or rotated features flag (true,do not compute orientation of features; false, compute orientation)
其中,hessianThreshold 为海森阈值,只有大于该阈值的特征才会被保留;海森阈值越大,对应检测到的特征越少;海森阈值取决于图像对比度,一般 300~500 之间的检测效果较好
1.3 CenSurE
CenSurE (Center Surround Extremas),是在 SURF 基础上做的一种改进,基于 CenSurE 特征检测 和 M-SURF 特征描述符,号称比 SURF 更快,可用于实时处理领域
OpenCV 并没有完全实现 CenSurE 算法,而是借鉴衍生出了 StarDetector,其 create() 函数定义如下:
static Ptr<StarDetector> create(
int maxSize = 45, //
int responseThreshold = 30, //
int lineThresholdProjected = 10, //
int lineThresholdBinarized = 8, //
int suppressNonmaxSize = 5 //
);
2 实时特征检测
SURF 的运行速度比 SIFT 快 3 倍,但在一些实时处理系统 (视觉里程计) 或低功耗设备中,SURF 还是不够快,于是,便有了下面的两种算法
2.1 ORB
OpenCV Labs 实现了一种更快的算法 ORB - Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF,它是在 FAST 角点检测 和 BRIEF 特征描述符的基础上修改实现的
视觉 SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping 同步定位与建图) 领域中,著名的开源项目 ORB-SLAM,其中的特征提取就是基于 ORB 算法
OpenCV 中 ORB 的 create() 函数定义如下:
static Ptr<ORB> create (
int nfeatures = 500, // The maximum number of features to retain
float scaleFactor = 1.2f, // Pyramid decimation ratio, greater than 1
int nlevels = 8, // The number of pyramid levels
int edgeThreshold = 31, // This is size of the border where the features are not detected
int firstLevel = 0, // The level of pyramid to put source image to
int WTA_K = 2, // The number of points that produce each element of the oriented BRIEF descriptor
ORB::ScoreType scoreType = ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, // The default HARRIS_SCORE means that Harris algorithm is used to rank features
int patchSize = 31, // size of the patch used by the oriented BRIEF descriptor
int fastThreshold = 20 // the fast threshold
);
2.2 BRISK
BRISK 号称比 SURF 的运行速度快一个数量级,它基于 AGAST 角点检测 和 BRIEF 特征描述符,其中 AGAST 是比 FAST 更快的一种角点检测算法
BRISK 的 create() 函数如下:
/* The BRISK constructor */
static Ptr<BRISK> create(
int thresh = 30, // AGAST detection threshold score
int octaves = 3, // octaves detection octaves. Use 0 to do single scale
float patternScale = 1.0f // apply this scale to the pattern used for sampling the neighbourhood of a keypoint
); /* The BRISK constructor for a custom pattern, detection thresholdand octaves */
static Ptr<BRISK> create(
int thresh, // AGAST detection threshold score
int octaves, // detection octaves. Use 0 to do single scale.
const std::vector<float> &radiusList, // defines the radii(in pixels) where the samples around a keypoint are taken (for keypoint scale 1).
const std::vector<int> &numberList, // defines the number of sampling points on the sampling circle.Must be the same size as radiusList..
float dMax = 5.85f, // threshold for the short pairings used for descriptor formation (in pixels for keypoint scale 1)
float dMin = 8.2f, // threshold for the long pairings used for orientation determination (in pixels for keypoint scale 1)
const std::vector<int>&indexChange = std::vector<int>() // index remapping of the bits
);
2.3 BRIEF 描述符
上述 ORB 和 BRISK 中,都提到了 BRIEF 特征描述符,BRIEF 全称 Binary Robust Independent Elementary Feature),是用二进制串向量来描述特征的一种方式
SIFT 中的一个特征,对应着一个由128个浮点数组成的向量,占 512 个字节;而 SURF 的一个特征,对应着一个由 64个浮点数组成的向量,占 256 个字节
当有成千上万个特征时, 特征描述符会占用大量的内存,并且会增加匹配的时间,在一些资源受限的场合,尤其是嵌入式系统中,SIFT 和 SURF 并非最优选择
而 BRIEF 特征描述符,采用的是二进制串,可将所占字节缩减为 64 或 32 甚至 16,相比 SIFT 和 SURF,大大减少了对内存的占用,非常适合于实时处理系统
OpenCV 中 BRIEF 描述符的定义如下:
// Class for computing BRIEF descriptors described in @cite calon2010 .
class BriefDescriptorExtractor : public Feature2D
{
public:
static Ptr<BriefDescriptorExtractor> create(
int bytes = 32, // legth of the descriptor in bytes, valid values are: 16, 32 (default) or 64 .
bool use_orientation = false); // sample patterns using keypoints orientation, disabled by default.
};
3 非线性尺度空间
SIFT 和 SURF 是在线性尺度空间内的分析,在构建高斯尺度空间的过程中,高斯滤波会将图像中的边界和细节信息等,连同噪声一起模糊化掉,因此,会造成一定程度上特征定位精度的损失
为了克服高斯滤波的缺点,2012年,西班牙人 Pablo F. Alcantarilla 利用非线性扩散滤波代替高斯滤波,通过加性粒子分裂法 (Additive Operator Splitting) 构建了非线性尺度空间,提出了 KAZE 算法
KAZE 是为了纪念“尺度空间分析之父” Iijima 而取得名字,在日语中是 “风” 的意思;AKAZE 是 Accelerated KAZE,顾名思义是 KAZE 的加速版本


3.1 KAZE
KAZE 的 create() 函数如下:
/* The KAZE constructor */
static Ptr<KAZE> create (
bool extended = false, // Set to enable extraction of extended (128-byte) descriptor
bool upright = false, // Set to enable use of upright descriptors (non rotation-invariant)
float threshold = 0.001f, // Detector response threshold to accept point
int nOctaves = 4, // Maximum octave evolution of the image
int nOctaveLayers = 4, // Default number of sublevels per scale level
KAZE::DiffusivityType diffusivity = KAZE::DIFF_PM_G2 // Diffusivity type. DIFF_PM_G1, DIFF_PM_G2, DIFF_WEICKERT or DIFF_CHARBONNIER
);
3.2 AKAZE
AKAZE 的 create() 函数如下:
/* The AKAZE constructor */
static Ptr<AKAZE> create(
AKAZE::DescriptorType descriptor_type = AKAZE::DESCRIPTOR_MLDB, // Type of the extracted descriptor: DESCRIPTOR_KAZE, DESCRIPTOR_KAZE_UPRIGHT, DESCRIPTOR_MLDB or DESCRIPTOR_MLDB_UPRIGHT.
int descriptor_size = 0, // Size of the descriptor in bits. 0 -> Full size
int descriptor_channels = 3, // Number of channels in the descriptor (1, 2, 3)
float threshold = 0.001f, // Detector response threshold to accept point
int nOctaves = 4, // Maximum octave evolution of the image
int nOctaveLayers = 4, // Default number of sublevels per scale level
KAZE::DiffusivityType diffusivity = KAZE::DIFF_PM_G2 // Diffusivity type. DIFF_PM_G1, DIFF_PM_G2, DIFF_WEICKERT or DIFF_CHARBONNIER
);
3.3 AKAZE vs ORB
OpenCV Tutorials中,有 ORB 和 AKAZE 的对比实验,从所选取的图像数据集来看,AKAZE 的检测效果优于 ORB

4 代码例程
2004年 D. Lowe 提出 SIFT 算法后,在提高运算速度的方向上,先是诞生了比 SIFT 快3倍的 SURF,而后又在 SURF 的基础上改进出了 CenSurE,宣称可用于实时处理领域
BRIEF 特征描述符,利用二进制串描述符,减少了对内存的占用,提高了匹配的速度,特别适合资源受限的场合,如嵌入式系统
在 BRIEF 的基础上,ORB 结合 FAST 角点检测 和 BRIEF 描述符,BRISK 结合 AGAST 角点检测 和 BRIEF 描述符,真正实现了实时特征检测
KAZE 和 AKAZE 针对高斯滤波的缺点,另辟蹊径,直接从 线性尺度空间 跳转到 非线性尺度空间,变换尺度空间后,重新定义了特征检测
以上七种特征检测的算法,代码例程如下:
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp" using namespace cv; int main()
{
// read
Mat img = imread("messi.jpg");
if (img.empty())
return -1; // create and detect
Ptr<SIFT> detector = SIFT::create();
// Ptr<xfeatures2d::SURF> detector = xfeatures2d::SURF::create(400);
// Ptr<xfeatures2d::StarDetector> detector = xfeatures2d::StarDetector::create(20, 20);
// Ptr<ORB> detector = ORB::create(2000);
// Ptr<BRISK> detector = BRISK::create();
// Ptr<KAZE> detector = KAZE::create();
// Ptr<AKAZE> detector = AKAZE::create();
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints;
detector->detect(img, keypoints); // draw and show
Mat img_keypoints;
drawKeypoints(img, keypoints, img_keypoints);
imshow("SIFT", img_keypoints); waitKey();
}
各算法的检测效果对比如下:







后记
一开始酝酿本篇博客时,目标是将 OpenCV 中所有的特征检测算法,都阅读一遍原始论文,并弄懂 OpenCV 的代码实现,但随着阅读的深入,发现这几乎是不可能完成的任务。
第一,自己非学术科研人员,没这么多时间和精力投入;第二,数学知识的薄弱,尤其是读到 KAZE 算法,涉及到非线性尺度空间,深感数学的博大精深和自身能力的瓶颈。
“吾生也有涯,而知也无涯”,想到牛人如 David Lowe,一生最有名的也只是发明了 SIFT 算法,我等凡夫俗子更难以遑论,莫名间竟生出一些悲凉,继续写下去的动力消失殆尽 ...
好在这几天想通了,重新认清自己的水平和定位,调整当初太过宏大的目标,改目标为 “介绍 OpenCV 中的特征检测算法和使用例程”,于是,便有了本篇文章 ^_^
参考资料
OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Feature Detection and Description / Introduction to SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform)
OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Feature Detection and Description / Introduction to SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features)
Censure: Center surround extremas for realtime feature detection and matching. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2008
OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Feature Detection and Description / BRIEF (Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features)
OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Feature Detection and Description / ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)
OpenCV Tutorials / 2D Features framework (feature2d module) / AKAZE and ORB planar tracking
KAZE 和 AKAZE 作者 Pablo F. Alcantarilla 的个人主页
OpenCV 之 特征检测的更多相关文章
- OpenCV4.1.0实践(2) - Dlib+OpenCV人脸特征检测
待更! 参考: python dlib opencv 人脸68点特征检测
- OpenCV——SIFT特征检测与匹配
SIFT特征和SURF特征比较 比较项目 SIFT SURF 尺度空间极值检测 使用高斯滤波器,根据不同尺度的高斯差(DOG)图像寻找局部极值 使用方形滤波器,利用海森矩阵的行列式值检测极值,并利用积 ...
- opencv图像特征检测之斑点检测
前面说过,图像特征点检测包括角点和斑点,今天来说说斑点,斑点是指二维图像中和周围颜色有颜色差异和灰度差异的区域,因为斑点代表的是一个区域,所以其相对于单纯的角点,具有更好的稳定性和更好的抗干扰能力. ...
- OpenCV——Brisk特征检测、匹配与对象查找
检测并绘制特征点: #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp> #include < ...
- OpenCV——HOG特征检测
API: HOGDescriptor(Size _winSize, ---:窗口大小,即检测的范围大小,前面的64*128 Size _blockSize,--- 前面的2*2的cell,即cell的 ...
- OpenCV——ORB特征检测与匹配
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/S4b1OGjRWX1kktefyHAo8A #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include ...
- OpenCV——SURF特征检测、匹配与对象查找
SURF原理详解:https://wenku.baidu.com/view/2f1e4d8ef705cc1754270945.html SURF算法工作原理 选择图像中的POI(Points of i ...
- Opencv HOG特征检测
HOGDescriptor hogDescriptor = HOGDescriptor(); hogDescriptor.setSVMDetector(hogDescriptor.getDefault ...
- OpenCV入门指南----人脸检测
本篇介绍图像处理与模式识别中最热门的一个领域——人脸检测(人脸识别).人脸检测可以说是学术界的宠儿,在不少EI,SCI高级别论文都能看到它的身影.甚至很多高校学生的毕业设计都会涉及到人脸检测.当然人脸 ...
随机推荐
- 日志挖掘针对DML语句
作用: 针对用户的误操作,比如更改数据错误,误删除表等,可以用日志挖掘的方式,跟踪哪个用户什么时候做的操作,并进行数据还原. 一.前期准备: 1.添加最小补充日志,能够记录到更详细的信息,为日志挖掘分 ...
- .NET Core/.NET5/.NET6 开源项目汇总5:权限管理系统项目
系列目录 [已更新最新开发文章,点击查看详细] 企业管理系统一般包含后台管理UI.组织机构管理.权限管理.日志.数据访问.表单.工作流等常用必备功能.下面收集的几款优秀开源的管理系统,值得大家 ...
- redis不完整的事务实现Transaction
使用场景 redis一个命令执行是单线程的,不用担心并发冲突,如果你想有几个命令想像一个命令一样,在这几个命令执行过程中不会执行别的客户端发来的命令 ,也就是原子性,就可以用 redis Transa ...
- 一文带你走遍Git世界,教会你Git的使用
@ 目录 这篇文章教会Git 1. Git是什么? 1.1 发展历程 1.2 Git是什么? 1.3 Git和SVN 2.Git有什么用? 2.1 代码合并 2.2 代码备份 2.3 代码还原 2.4 ...
- 在vue中下拉框切换事件中改新建表单中的一个值,页面不显示
事件中改新建表单中的一个值,页面不显示,当另一个对象值发生改变时,这个页面上的值才会显示 由于新建表单是弹窗,在弹出时会重新给每个字段重新赋值,在赋值时没给这个字段赋值(常见新加功能时,加了一个字段, ...
- 堆&&优先队列&&TreeMap
题目描述 5710. 积压订单中的订单总数 题解 题目不难,主要是要读懂题意,一步步模拟,代码较长,需要细心检查. 坑较多,比如我犯了很多傻逼问题:想都不想就拿1<<9+7当作100000 ...
- ClouderaManager安装kafka报错
是因为默认的java heap size是50M,将broker_max_heap_size参数设置为512M后,重启kafka服务即可
- [心得]redis集群环境搭建的错误
安装redis集群需要版本号在3.0以上 redis-cluster安装前需要安装ruby环境 搭建集群需要使用到官方提供的ruby脚本. 需要安装ruby的环境. yum -y install ru ...
- Leetcode No.121 Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock(c++实现)
1. 题目 1.1 英文题目 You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the it ...
- Java | Map集合
Map集合 在现实生活中,有非常多的东西,是和另外一种东西对应的,并且还是唯一的,比如:身份证号与个人,个人与手机,一夫一妻...等,这种关系就是对应关系,又叫做映射.Java为这种数据类型提供了专门 ...
